Deck 50: Behavioural Ecology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/39
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 50: Behavioural Ecology
1
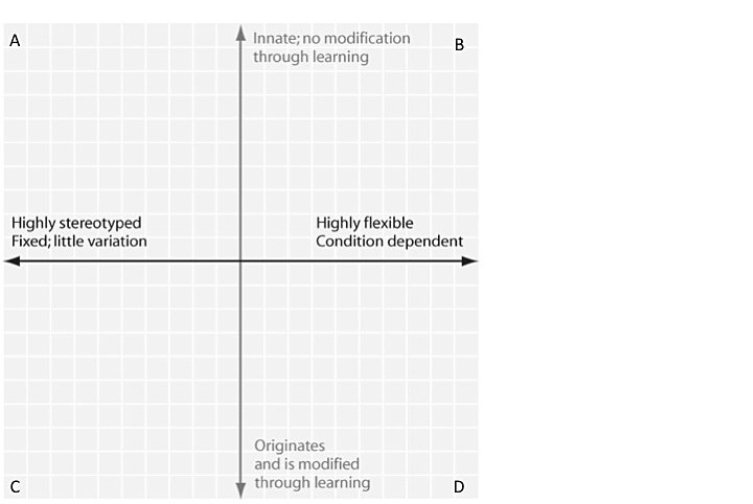 Figure 50.1
Figure 50.1In Figure 50.1, in which quadrant would the egg- rolling behaviour of a goose be plotted?
A) quadrant A
B) quadrant B
C) quadrant C
D) quadrant D
A
2
How would you classify the genetic basis for most behavioural traits in the animal kingdom?
A) Many genes typically code for one behaviour.
B) Behaviours are learned, not coded by genes.
C) One gene typically codes for one behaviour.
D) One gene typically codes for many behaviours.
A) Many genes typically code for one behaviour.
B) Behaviours are learned, not coded by genes.
C) One gene typically codes for one behaviour.
D) One gene typically codes for many behaviours.
A
3
You observe scrub jays hiding food and notice that one particular individual only pretends to hide food. What kind of experiment could you perform to test whether this was random or in response to another signal?
A) Attempt to reproduce the behaviour in captivity by using bird models and a computer simulation.
B) Hypothesize a set of signals that could produce this behaviour and try to match the behaviours with the signals.
C) Observe more of these behaviours in the wild and try to determine if the behaviour is random.
D) All of the above would be excellent experiments.
A) Attempt to reproduce the behaviour in captivity by using bird models and a computer simulation.
B) Hypothesize a set of signals that could produce this behaviour and try to match the behaviours with the signals.
C) Observe more of these behaviours in the wild and try to determine if the behaviour is random.
D) All of the above would be excellent experiments.
B
4
The recognition and manipulation of facts about the world is termed
A) conditioning.
B) cognition.
C) learning.
D) imprinting.
A) conditioning.
B) cognition.
C) learning.
D) imprinting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Lobsters can navigate back home at night using Earth's magnetic field. Is this statement a proximate cause or an ultimate cause?
A) proximate cause
B) ultimate cause
A) proximate cause
B) ultimate cause

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which one of the following examples best illustrates classical conditioning?
A) birds hatching in isolation and singing their species- specific song
B) geese following the first thing they see upon hatching
C) cats seeing a mouse and chasing it
D) cats running into the kitchen when they hear a food can being opened
A) birds hatching in isolation and singing their species- specific song
B) geese following the first thing they see upon hatching
C) cats seeing a mouse and chasing it
D) cats running into the kitchen when they hear a food can being opened

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following statements about imprinting is FALSE?
A) Imprinting only occurs on a specific colour/shape.
B) Imprinting is a type of learning.
C) Imprinting is fast and irreversible.
D) Imprinting only occurs during a critical period.
A) Imprinting only occurs on a specific colour/shape.
B) Imprinting is a type of learning.
C) Imprinting is fast and irreversible.
D) Imprinting only occurs during a critical period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In testing a hypothesis that "territorial defence in European robins is a fixed action pattern that is released by the sight of orange feathers," researchers found that robins defended their territory by attacking anything that was of similar size and had an orange patch. How would you show that it was indeed colour that initiated the defence responses?
A) Repeat the experiment removing the orange patch.
B) Repeat the experiment using other shapes.
C) Repeat the experiment with giant specimens.
D) Repeat the experiment using live specimens.
A) Repeat the experiment removing the orange patch.
B) Repeat the experiment using other shapes.
C) Repeat the experiment with giant specimens.
D) Repeat the experiment using live specimens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Based on your knowledge of cost- benefit analysis, why would you expect some white- fronted bee- eaters to fly very far away from the nests to forage when there are food sources nearby?
A) Predation is highest closest to the nest.
B) Food near the nest is usually of lower quality.
C) Competition for food is too intense near the nest.
D) There might be some plentiful food sources further away.
A) Predation is highest closest to the nest.
B) Food near the nest is usually of lower quality.
C) Competition for food is too intense near the nest.
D) There might be some plentiful food sources further away.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In the case of the redback spider, would males be better off, in terms of fitness, looking for another female to mate with instead of provoking his mate to eat him?
A) Yes, this would increase his fitness, as it would provoke the first female to allow him to mate more, and he would get a second mating opportunity with another female.
B) No, this would decrease his fitness, as his first mate would expel his sperm once he left the area.
C) Yes, this would greatly increase his fitness, as he would be able to produce more offspring and with a variety of mates increasing the chance that some of his offspring would survive.
D) No, this would decrease his fitness as he would likely not find a second mate and would decrease his sperm transfer to the female he has found.
A) Yes, this would increase his fitness, as it would provoke the first female to allow him to mate more, and he would get a second mating opportunity with another female.
B) No, this would decrease his fitness, as his first mate would expel his sperm once he left the area.
C) Yes, this would greatly increase his fitness, as he would be able to produce more offspring and with a variety of mates increasing the chance that some of his offspring would survive.
D) No, this would decrease his fitness as he would likely not find a second mate and would decrease his sperm transfer to the female he has found.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Learning has the most influence on behaviour when
A) animals have parents or other sources to learn from, and when animals have enormous cognitive ability.
B) making mistakes does not result in death, and when animals have parents or other sources to learn from.
C) making mistakes does not result in death.
D) animals have enormous cognitive ability.
E) animals have parents or other sources to learn from.
A) animals have parents or other sources to learn from, and when animals have enormous cognitive ability.
B) making mistakes does not result in death, and when animals have parents or other sources to learn from.
C) making mistakes does not result in death.
D) animals have enormous cognitive ability.
E) animals have parents or other sources to learn from.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
You have captured a number of rats from a wild population and quickly surmise with tests that they are very good at avoiding food with poisons. What would best explain this observation?
A) Rats may learn this behaviour from their parents or siblings.
B) Rats may experience a large variety of toxins in their environment and learn to avoid them.
C) Rats are probably just intelligent enough to avoid poison.
D) Rats may be able to tolerate large amounts of poison.
A) Rats may learn this behaviour from their parents or siblings.
B) Rats may experience a large variety of toxins in their environment and learn to avoid them.
C) Rats are probably just intelligent enough to avoid poison.
D) Rats may be able to tolerate large amounts of poison.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which would be the best way to obtain evidence of a bird's cognitive abilities?
A) In captivity, have the bird solve problems like those it would face in the wild.
B) In captivity, have the bird attempt to solve novel problems.
C) Observe the bird solving problems in the wild.
D) All of the above would obtain equal evidence toward thinking ability.
A) In captivity, have the bird solve problems like those it would face in the wild.
B) In captivity, have the bird attempt to solve novel problems.
C) Observe the bird solving problems in the wild.
D) All of the above would obtain equal evidence toward thinking ability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
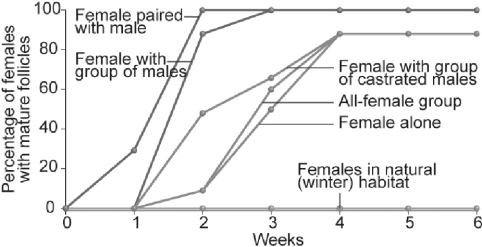 Figure 50.2
Figure 50.2-Which of the following conclusions is most logical based on the data above?
A) Females produce eggs more quickly when exposed to many males.
B) All non- isolated females do just as well as isolated females.
C) Females produce more eggs more quickly when exposed to breeding males.
D) All of the above answers apply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
You see young spiders hatch from eggs, and, within 5 hours, they are dispersing far from their parents and forming webs. What can you hypothesize about their behaviour?
A) Web- building is a random behaviour.
B) Web- building is innate since there is no parental involvement.
C) Web- building is an inflexible behaviour.
D) Web- building is learned by observation.
A) Web- building is a random behaviour.
B) Web- building is innate since there is no parental involvement.
C) Web- building is an inflexible behaviour.
D) Web- building is learned by observation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
How would self- sacrifice of male redback spiders be an adaptive behaviour?
A) Males are able to mate with one female, then mate with another female nearby, before being devoured by the first female.
B) The chance of a male meeting more than one female is quite low; self- sacrifice maximizes mating time with and sperm transfer to any female the male finds.
C) Males only use self- sacrificing behaviour once they have mated with several females and have exhausted their sperm supplies.
D) When males meet a female and self- sacrifice, it activates enzymes that make his sperm more fit and able to fertilize more eggs.
A) Males are able to mate with one female, then mate with another female nearby, before being devoured by the first female.
B) The chance of a male meeting more than one female is quite low; self- sacrifice maximizes mating time with and sperm transfer to any female the male finds.
C) Males only use self- sacrificing behaviour once they have mated with several females and have exhausted their sperm supplies.
D) When males meet a female and self- sacrifice, it activates enzymes that make his sperm more fit and able to fertilize more eggs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
You observe scrub jays hiding food and notice that one particular individual only pretends to hide food. Your experiments associate the presence of other siblings with the frequency of pretending to cache food. A colleague shows you animals of the same species that do not perform this pretend caching. How does this information affect your conclusions about this behaviour?
A) It suggests that your experimental design is flawed.
B) It prevents you from making conclusions.
C) It suggests that this behaviour might be learned.
D) It does not affect anything.
A) It suggests that your experimental design is flawed.
B) It prevents you from making conclusions.
C) It suggests that this behaviour might be learned.
D) It does not affect anything.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
You observe a species of bird that, upon hatching, has contact with its parents only while being fed. You also never hear the parents sing during the feeding process. What would you propose about song learning in this species of bird?
A) Song learning in this species is most likely innate.
B) Song learning in this species is most likely learned.
C) This species does not hear.
D) The period of imprinting is likely later in the bird's life.
A) Song learning in this species is most likely innate.
B) Song learning in this species is most likely learned.
C) This species does not hear.
D) The period of imprinting is likely later in the bird's life.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A cage containing male mosquitoes has a small earphone placed on top, through which the sound of a female mosquito is played. All the males immediately fly to the earphone and go through all the steps of copulation. What is the best explanation for this behaviour?
A) Through classical conditioning, the male mosquitoes have associated the inappropriate stimulus from the earphone with the normal response of copulation.
B) The males learn to associate the sound with females.
C) The sound from the earphone irritates the male mosquitoes, causing them to attempt to sting it.
D) The reproductive drive is so strong that when males are deprived of females, they will attempt to mate with anything that has even the slightest female characteristic.
E) Copulation is a fixed action pattern, and the female flight sound is a sign stimulus that initiates it.
A) Through classical conditioning, the male mosquitoes have associated the inappropriate stimulus from the earphone with the normal response of copulation.
B) The males learn to associate the sound with females.
C) The sound from the earphone irritates the male mosquitoes, causing them to attempt to sting it.
D) The reproductive drive is so strong that when males are deprived of females, they will attempt to mate with anything that has even the slightest female characteristic.
E) Copulation is a fixed action pattern, and the female flight sound is a sign stimulus that initiates it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
 Figure 50.1
Figure 50.1In which quadrant of the figure above would bird migration be plotted?
A) quadrant A
B) quadrant B
C) quadrant C
D) quadrant D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In red- winged blackbirds, which of the following stimuli elicited the greatest territorial defence response?
A) playing a recording of a blackbird call in the territory
B) presenting both the model of a male, and playing the recording
C) presenting a model of a male in the territory
D) All of the above elicited equal responses.
A) playing a recording of a blackbird call in the territory
B) presenting both the model of a male, and playing the recording
C) presenting a model of a male in the territory
D) All of the above elicited equal responses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
It is rather easy to understand why relatives help each other in the animal kingdom-they share some of the same genes, and some self- sacrificing behaviour will help the greater sum of their genes. What would be a reason for self- sacrificing behaviour to have evolved in animals that are unrelated?
A) This behaviour might elicit a benefit at some future point in time.
B) This behaviour might have aided groups of unrelated animals.
C) This behaviour might have arisen due to genetic drift.
D) Answers A and B both apply.
E) Answers A and C both apply.
A) This behaviour might elicit a benefit at some future point in time.
B) This behaviour might have aided groups of unrelated animals.
C) This behaviour might have arisen due to genetic drift.
D) Answers A and B both apply.
E) Answers A and C both apply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Migration in birds is guided in part by
A) olfactory cues.
B) day- length changes caused by latitude.
C) temperature changes.
D) celestial navigation.
A) olfactory cues.
B) day- length changes caused by latitude.
C) temperature changes.
D) celestial navigation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Any process in which a signal from one individual modifies the behaviour of a recipient individual is termed
A) perception.
B) reflex.
C) cognition.
D) communication.
A) perception.
B) reflex.
C) cognition.
D) communication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
With regard to understanding the evolution of cooperation, what is the principal prediction that can be made from the expression Br > C?
A) Natural selection will favour cooperation among close relatives.
B) Cooperation evolves because it benefits all members of a species.
C) Natural selection will favour cooperation among any individuals.
D) Cooperation evolves because it enhances the species' fitness.
E) Selection favours self- sacrifice in reproduction.
A) Natural selection will favour cooperation among close relatives.
B) Cooperation evolves because it benefits all members of a species.
C) Natural selection will favour cooperation among any individuals.
D) Cooperation evolves because it enhances the species' fitness.
E) Selection favours self- sacrifice in reproduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
 Figure 50.2
Figure 50.2In the figure above, do the data support the hypothesis that females need spring- like light conditions to produce mature follicles?
A) yes
B) no
C) cannot be determined

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If phototaxis is orientation toward light, what would be the proper term to describe ants following a trail of their own pheromones?
A) chemotaxis
B) hormotaxis
C) pheromotaxis
D) stereotaxis
A) chemotaxis
B) hormotaxis
C) pheromotaxis
D) stereotaxis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
How do altruistic behaviours arise through natural selection?
A) Altruistic behaviours lower stress in populations, which increases the survivability of all the members of the population.
B) The altruist is appreciated by other members of the population because its survivability has been enhanced by virtue of its risky behaviour.
C) Animals that perform altruistic acts are allowed by their population to breed more, thereby passing on their behaviour genes to future generations.
D) By his or her actions, the altruist increases the likelihood that some of its genes will be passed on to the next generation.
A) Altruistic behaviours lower stress in populations, which increases the survivability of all the members of the population.
B) The altruist is appreciated by other members of the population because its survivability has been enhanced by virtue of its risky behaviour.
C) Animals that perform altruistic acts are allowed by their population to breed more, thereby passing on their behaviour genes to future generations.
D) By his or her actions, the altruist increases the likelihood that some of its genes will be passed on to the next generation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
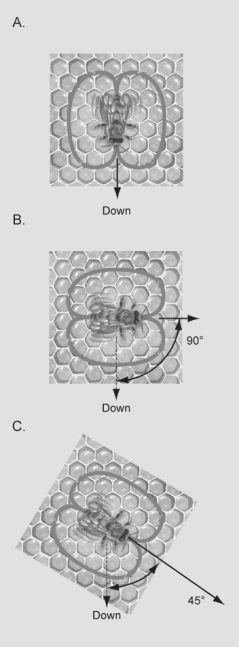 Figure 50.4
Figure 50.4In the diagrams shown in the figure above, which dance is indicating that the food is the farthest from the hive?
A) dance A
B) dance B
C) dance C
D) All of the above indicate the same distance from the hive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A pied kingfisher in its first year of life helps in the feeding of three full siblings that would not have survived without the helper's efforts. What is its indirect fitness in its first year?
A) 0.50
B) 0.75
C) 1.00
D) 0.25
E) 1.50
A) 0.50
B) 0.75
C) 1.00
D) 0.25
E) 1.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In house sparrows Passer domesticus), it is generally found that both males and females care for the eggs and young. However, some male house sparrows do not provide parental care. In addition, it is known that young that receive parental care from both the male and female are more likely to survive to fledging leaving the nest). Which of the following activities by males that do not provide parental care would represent the most beneficial trade- off for the reduced survival of their offspring?
A) mating with additional females and fathering more eggs
B) attacking the nests of neighbouring males
C) grooming to eliminate parasites from their feathers
D) eating to build up energy stores for migration
A) mating with additional females and fathering more eggs
B) attacking the nests of neighbouring males
C) grooming to eliminate parasites from their feathers
D) eating to build up energy stores for migration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
How could you test whether male dewlaps a colourful flap of skin hanging from an anole lizard's throat) were an important cue for female egg production?
A) Remove dewlaps from courting males and measure corresponding female egg production.
B) Relate size of male dewlap to female dewlap.
C) Remove dewlaps from females and measure corresponding egg production.
D) All of the above answers apply.
A) Remove dewlaps from courting males and measure corresponding female egg production.
B) Relate size of male dewlap to female dewlap.
C) Remove dewlaps from females and measure corresponding egg production.
D) All of the above answers apply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
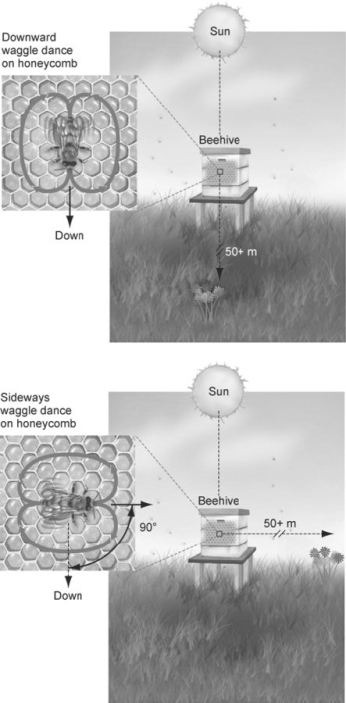 Figure 50.3
Figure 50.3What does the figure above show about the nature of the "waggle dance"?
A) The waggle dance is random in relation to the food source.
B) The direction of the waggle dance indicates the location of the hive relative to the Sun.
C) The vigor of the waggle dance indicates the location of the food relative to the Sun.
D) The vigor of the waggle dance indicates the size of the food source.
E) The direction of the waggle dance indicates the location of the food relative to the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
(a)
(b)
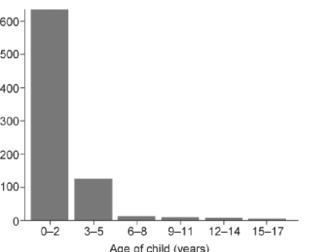
Figure 50.5
-Which of the following has greatest coefficient of relatedness?
A) black bear siblings
B) tiger siblings
C) worker honey bees
D) human fraternal twins

(b)

Figure 50.5
-Which of the following has greatest coefficient of relatedness?
A) black bear siblings
B) tiger siblings
C) worker honey bees
D) human fraternal twins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Homing pigeons' ability to always return to their home, no matter where they are released, is an excellent example of
A) compass orientation.
B) true navigation.
C) piloting.
D) all of the above.
A) compass orientation.
B) true navigation.
C) piloting.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What was the main reason the honeybees would switch from the "round dance" to the "waggle dance"?
A) The original food source was exhausted.
B) The ratio of females to males in the hive shifted.
C) The preferred food source was farther away.
D) An intruder approached the hive.
A) The original food source was exhausted.
B) The ratio of females to males in the hive shifted.
C) The preferred food source was farther away.
D) An intruder approached the hive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
You observe that by flashing a small light in a particular sequence, you can attract male fireflies of a certain species. You begin to think how this signal may be used against these males. Which of the hypotheses seems to be the most logical?
A) This particular signal will be used only by this species of firefly.
B) This particular signal will be used commonly by other firefly species as a way to lure males and prey on them.
C) This particular signal will be used rarely by other firefly species as a way to lure males and prey on them.
D) This particular signal will be used widely by males of this species in territorial disputes.
A) This particular signal will be used only by this species of firefly.
B) This particular signal will be used commonly by other firefly species as a way to lure males and prey on them.
C) This particular signal will be used rarely by other firefly species as a way to lure males and prey on them.
D) This particular signal will be used widely by males of this species in territorial disputes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
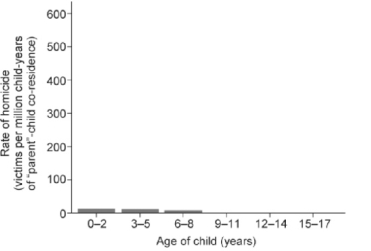
(a)

(b)

Figure 50.5
-In the figure above, which is the most logical conclusion from the data?
A) Older children are more at risk when living with a stepparent.
B) All stepparents are unfit to raise nonbiological children.
C) Older children will not die of homicide when living with biological parents.
D) Young children are more at risk when living with a stepparent.

(b)

Figure 50.5
-In the figure above, which is the most logical conclusion from the data?
A) Older children are more at risk when living with a stepparent.
B) All stepparents are unfit to raise nonbiological children.
C) Older children will not die of homicide when living with biological parents.
D) Young children are more at risk when living with a stepparent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A lizard's bobbing dewlap a colourful flap of skin hanging from an Anolis lizard's throat) is an example of a
A) signal.
B) reflex.
C) stimulus.
D) communication.
A) signal.
B) reflex.
C) stimulus.
D) communication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



