Deck 36: Plant Nutrition
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/37
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 36: Plant Nutrition
1
Which elements are responsible for the greater part of plant wet weight?
A) oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen
B) carbon, nitrogen, oxygen
C) carbon, oxygen, hydrogen
D) oxygen, hydrogen, phosphorus
E) carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus
A) oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen
B) carbon, nitrogen, oxygen
C) carbon, oxygen, hydrogen
D) oxygen, hydrogen, phosphorus
E) carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus
C
2
The micronutrient iron is abundant in soil, but often unavailable to plants due to insolubility. Knowing that the reaction FeOH)3 + 3H+ -Fe3+ + 3H2O occurs, and assuming all soil samples have same total amount of iron in them, which type of soil would you predict to have the highest amount of soluble iron?
A) acidic
B) neutral
C) alkaline
D) The amount of iron in soil does not depend on pH.
A) acidic
B) neutral
C) alkaline
D) The amount of iron in soil does not depend on pH.
A
3
A scientist observed a plant where only the young leaves are deteriorating. What nutrient is likely in short supply?
A) nitrogen
B) potassium
C) a mobile nutrient
D) iron
E) phosphorous
A) nitrogen
B) potassium
C) a mobile nutrient
D) iron
E) phosphorous
D
4
What is the charge on the inside of a plant cell plasma membrane?
A) neutral
B) negative
C) positive
A) neutral
B) negative
C) positive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What type of soil contains the highest amount of oxygen?
A) gravel
B) silt
C) sand
D) clay
A) gravel
B) silt
C) sand
D) clay

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is not true about an essential nutrient?
A) It is necessary for plant growth and reproduction.
B) It cannot be synthesized by a plant.
C) It is required for a specific structure or metabolic function.
D) It is produced by symbiotic bacteria.
E) All of the above are correct.
A) It is necessary for plant growth and reproduction.
B) It cannot be synthesized by a plant.
C) It is required for a specific structure or metabolic function.
D) It is produced by symbiotic bacteria.
E) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
You want to grow a plant that prefers neutral pH in a limestone soil. What should you add to the soil to improve plant growth?
A) aluminum hydroxide [AlOH)3 + 2H+ -AlOH)2+ + 2H2O]
B) potassium nitrate KNO3 -K+ + NO3- )
C) sulfur S + H2O + 3/2 O2 -2 H+ + SO42- )
D) calcium carbonate CaCO3 + H2O -HCO3- + Ca2+ + OH- )
A) aluminum hydroxide [AlOH)3 + 2H+ -AlOH)2+ + 2H2O]
B) potassium nitrate KNO3 -K+ + NO3- )
C) sulfur S + H2O + 3/2 O2 -2 H+ + SO42- )
D) calcium carbonate CaCO3 + H2O -HCO3- + Ca2+ + OH- )

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which elements are most often the limiting nutrients for plant growth?
A) nitrogen, sodium, phosphorus
B) nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur
C) nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus
D) calcium, nitrogen, phosphorus
E) phosphorus, potassium, carbon
A) nitrogen, sodium, phosphorus
B) nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur
C) nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus
D) calcium, nitrogen, phosphorus
E) phosphorus, potassium, carbon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is the function of proton pumps localized in the plant plasma membrane?
A) to transfer metal ions across the plasma membrane
B) to transfer phosphorous groups from ATP to proteins
C) to create ATP
D) to transfer anions across the plasma membrane
E) to create a membrane potential
A) to transfer metal ions across the plasma membrane
B) to transfer phosphorous groups from ATP to proteins
C) to create ATP
D) to transfer anions across the plasma membrane
E) to create a membrane potential

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What type of soil is most difficult for roots to penetrate?
A) clay
B) gravel
C) humus
D) sand
E) silt
A) clay
B) gravel
C) humus
D) sand
E) silt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which criteria allow biologists to divide chemicals into macronutrients and micronutrients?
A) whether or not they are essential for plant growth
B) their availability in the soil
C) the way they are used by plants
D) the amounts in which plants need them
E) all of the above
A) whether or not they are essential for plant growth
B) their availability in the soil
C) the way they are used by plants
D) the amounts in which plants need them
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following experiments is able to determine if an element is essential for plant growth?
A) measuring the amount of the element in the soil before and after plant growth
B) growth of a plant by hydroponics without an element
C) measuring the weight of the plant and soil before and after plant growth
D) chemical analysis of plant ash
E) all of the above
A) measuring the amount of the element in the soil before and after plant growth
B) growth of a plant by hydroponics without an element
C) measuring the weight of the plant and soil before and after plant growth
D) chemical analysis of plant ash
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Humus is comprised of which of the following components?
A) gravel, sand, and silt
B) loams
C) clay
D) biotic and decaying organic material
E) inorganic material
A) gravel, sand, and silt
B) loams
C) clay
D) biotic and decaying organic material
E) inorganic material

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
To understand the role of zinc in plant growth and development, you are growing a tomato plant using hydroponics. Which plant organs do you expect to have defects if you provide the plant with a solution devoid of zinc?
A) above- ground organs
B) all organs
C) stems
D) roots
E) leaves
A) above- ground organs
B) all organs
C) stems
D) roots
E) leaves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Soil leaching is usually
A) beneficial for plants.
B) harmful for plants.
C) neutral for plants.
A) beneficial for plants.
B) harmful for plants.
C) neutral for plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Why do plants use cotransporters instead of ion channels to transfer anions into cells?
A) Cotransporters are able to transfer anions against the proton gradient, but ion channels cannot.
B) Cotransporters are able to transfer anions against the concentration gradient, but ion channels cannot.
C) Cotransporters are able to transfer anions against the membrane potential gradient, but ion channels cannot.
D) Anions are too bulky to be transported by ion channels.
A) Cotransporters are able to transfer anions against the proton gradient, but ion channels cannot.
B) Cotransporters are able to transfer anions against the concentration gradient, but ion channels cannot.
C) Cotransporters are able to transfer anions against the membrane potential gradient, but ion channels cannot.
D) Anions are too bulky to be transported by ion channels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
How would you expect the root system of a plant grown by hydroponics to compare to the root system of a plant grown in soil?
A) more developed
B) absent
C) less developed
D) the same
A) more developed
B) absent
C) less developed
D) the same

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
To determine the requirement of chlorine for plant growth, you decided to perform a hydroponic experiment. What solution are you going to use to grow control plants for comparison with chlorine- derived plants?
A) water with micronutrients and chlorine
B) water with essential elements
C) water with macronutrients and chlorine
D) water with chlorine
E) pure water
A) water with micronutrients and chlorine
B) water with essential elements
C) water with macronutrients and chlorine
D) water with chlorine
E) pure water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following binds to clay particles?
A) potassium and nitrate ions
B) nitrate ions
C) phosphoric acid
D) potassium ions
E) carbon dioxide
A) potassium and nitrate ions
B) nitrate ions
C) phosphoric acid
D) potassium ions
E) carbon dioxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The ability for a plant's roots to obtain nutrients and oxygen from the soil is partly determined by a soil's texture. Texture describes which of the following soil components?
A) the amount of added fertilizer
B) proportions of gravel, sand, clay, and silt
C) moisture level
D) dissolved oxygen
E) decaying organic material
A) the amount of added fertilizer
B) proportions of gravel, sand, clay, and silt
C) moisture level
D) dissolved oxygen
E) decaying organic material

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What major benefits do plants and mycorrhizal fungi receive from their symbiotic relationship?
A) Plants receive sugars, and fungi receive nitrogen.
B) Plants receive macronutrients, and fungi receive micronutrients.
C) Plants receive nitrogen and phosphorus, and fungi receive sugars.
D) Plants receive micronutrients, and fungi receive sugars.
A) Plants receive sugars, and fungi receive nitrogen.
B) Plants receive macronutrients, and fungi receive micronutrients.
C) Plants receive nitrogen and phosphorus, and fungi receive sugars.
D) Plants receive micronutrients, and fungi receive sugars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
While hiking in a forest, you notice an unusual plant growing on the branches of a tree. What will help you to determine if this plant is epiphytic or parasitic?
A) The root of an epiphytic plant will be in the soil, but a parasitic plant will grow from the trunk of a tree.
B) The roots of a parasitic plant will penetrate under the bark into the tree xylem, and the roots of an epithetic plant will not.
C) The epithetic plant will have leaves forming tanks collecting water, and the parasitic plant will not.
D) If the plant is green, it is epiphytic; if not, then it is parasitic.
A) The root of an epiphytic plant will be in the soil, but a parasitic plant will grow from the trunk of a tree.
B) The roots of a parasitic plant will penetrate under the bark into the tree xylem, and the roots of an epithetic plant will not.
C) The epithetic plant will have leaves forming tanks collecting water, and the parasitic plant will not.
D) If the plant is green, it is epiphytic; if not, then it is parasitic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is a typical habitat for carnivorous plants?
A) tundra
B) bog
C) woodlands
D) mangrove
E) desert
A) tundra
B) bog
C) woodlands
D) mangrove
E) desert

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Researchers are interested in improving crop plants to enable them to form a symbiotic relationship with nitrogen- fixing bacteria. What genes would you need to transfer to a plant that does not associate with rhizobia to enable it to do so?
A) genes responsible for the synthesis of flavonoids and receptor for Nod factors
B) receptor for Nod factors and leghemoglobin gene
C) genes responsible for the synthesis of Nod factors and receptor for flavonoids
D) genes responsible for the synthesis of Nod factors and receptor for flavonoids and leghemoglobin gene
E) None of the above is sufficient, since many more genes need to be transferred.
A) genes responsible for the synthesis of flavonoids and receptor for Nod factors
B) receptor for Nod factors and leghemoglobin gene
C) genes responsible for the synthesis of Nod factors and receptor for flavonoids
D) genes responsible for the synthesis of Nod factors and receptor for flavonoids and leghemoglobin gene
E) None of the above is sufficient, since many more genes need to be transferred.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
After mutagenesis and screening, you have found a mutant that is able to grow in soil with high salt content. Chemical analysis showed that this plant has a decreased amount of Na+ relative to normal plants. What kind of mutation do you predict this plant contains?
A) mutation in the plasma membrane sodium channel
B) mutation within the Casparian strip
C) mutation in the tonoplast sodium channel
D) mutation in the metallothioneins
E) mutation in the tonoplast antiporter
A) mutation in the plasma membrane sodium channel
B) mutation within the Casparian strip
C) mutation in the tonoplast sodium channel
D) mutation in the metallothioneins
E) mutation in the tonoplast antiporter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Give two reasons that relatively few plants thrive in bogs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What is the right sequence of steps during infection of plants by nitrogen- fixing bacteria?
A) Rhizobia release Nod factors; roots release flavonoids; rhizobia proliferate inside of root hair; infection thread grows into the root cortex; nodule forms.
B) Rhizobia release flavonoids; roots release Nod factors; rhizobia proliferate inside of root hair; infection thread grows into the root cortex; nodule forms.
C) Roots release flavonoids; rhizobia release Nod factors; rhizobia proliferate inside of root hair; nodule forms; infection thread grows into the root cortex.
D) Roots release Nod factors; rhizobia release flavonoids; rhizobia proliferate inside of root hair; nodule forms; infection thread grows into the root cortex.
E) Roots release flavonoids; rhizobia release Nod factors; rhizobia proliferate inside of root hair; infection thread grows into the root cortex; nodule forms.
A) Rhizobia release Nod factors; roots release flavonoids; rhizobia proliferate inside of root hair; infection thread grows into the root cortex; nodule forms.
B) Rhizobia release flavonoids; roots release Nod factors; rhizobia proliferate inside of root hair; infection thread grows into the root cortex; nodule forms.
C) Roots release flavonoids; rhizobia release Nod factors; rhizobia proliferate inside of root hair; nodule forms; infection thread grows into the root cortex.
D) Roots release Nod factors; rhizobia release flavonoids; rhizobia proliferate inside of root hair; nodule forms; infection thread grows into the root cortex.
E) Roots release flavonoids; rhizobia release Nod factors; rhizobia proliferate inside of root hair; infection thread grows into the root cortex; nodule forms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Both ectomycorrhizal fungi and rhizobia are able to supply plants with usable forms of nitrogen. From what sources do rhizobia and ectomycorrhizal fungi that are associated with plants obtain nitrogen?
A) They both absorb ammonia from soil, which they nitrify to NO2- .
B) They both absorb N2 from the atmosphere.
C) Fungi obtain nitrogen by decomposition of organic material, and rhizobia absorb N2 from the atmosphere.
D) They both obtain nitrogen by decomposition of organic material.
E) Fungi absorb N2 from the atmosphere, and rhizobia obtain nitrogen by decomposition of organic material.
A) They both absorb ammonia from soil, which they nitrify to NO2- .
B) They both absorb N2 from the atmosphere.
C) Fungi obtain nitrogen by decomposition of organic material, and rhizobia absorb N2 from the atmosphere.
D) They both obtain nitrogen by decomposition of organic material.
E) Fungi absorb N2 from the atmosphere, and rhizobia obtain nitrogen by decomposition of organic material.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Why is nitrogen fixation an essential process?
A) Fixed nitrogen is often the limiting factor in plant growth.
B) Nitrogen fixation can only be done by certain prokaryotes.
C) Nitrogen- fixing capacity can be genetically engineered.
D) Nitrogen fixation is very expensive in terms of metabolic energy.
E) Nitrogen fixers are sometimes symbiotic with legumes.
A) Fixed nitrogen is often the limiting factor in plant growth.
B) Nitrogen fixation can only be done by certain prokaryotes.
C) Nitrogen- fixing capacity can be genetically engineered.
D) Nitrogen fixation is very expensive in terms of metabolic energy.
E) Nitrogen fixers are sometimes symbiotic with legumes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
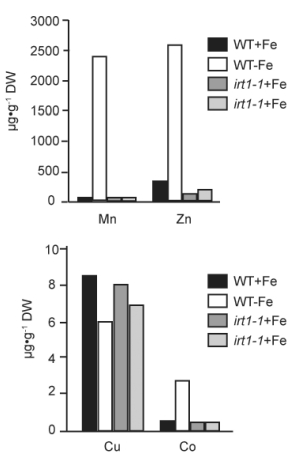 } \text { of iron for 5 days. DW = dry weight} Figure 36.2 -The IRT1 gene is responsible for most of the iron uptake activity in roots Vert et al., Plant Cell 14 [2002]:1223- 33). To determine the specificity of the IRT1 transporter in Arabidopsis plants, researchers measured the concentration of manganese, zinc, copper, and cobalt contained in wild- type and irt1- 1 mutant plants. What conclusions about IRT1 specificity can you draw from the above data? A) IRT1 participates in the transport of iron, zinc, manganese, and cobalt independent of iron concentration. B) Under iron- deficient conditions, IRT1 is important for the transport of iron and copper. C) IRT1 is important for the transport of iron and copper independent of iron concentration. D) Under iron- deficient conditions, IRT1 is highly specific for Fe. E) Under iron- deficient conditions, IRT1 is necessary for the transport of iron, zinc, manganese, and cobalt. " class="answers-bank-image d-inline" loading="lazy" >
} \text { of iron for 5 days. DW = dry weight} Figure 36.2 -The IRT1 gene is responsible for most of the iron uptake activity in roots Vert et al., Plant Cell 14 [2002]:1223- 33). To determine the specificity of the IRT1 transporter in Arabidopsis plants, researchers measured the concentration of manganese, zinc, copper, and cobalt contained in wild- type and irt1- 1 mutant plants. What conclusions about IRT1 specificity can you draw from the above data? A) IRT1 participates in the transport of iron, zinc, manganese, and cobalt independent of iron concentration. B) Under iron- deficient conditions, IRT1 is important for the transport of iron and copper. C) IRT1 is important for the transport of iron and copper independent of iron concentration. D) Under iron- deficient conditions, IRT1 is highly specific for Fe. E) Under iron- deficient conditions, IRT1 is necessary for the transport of iron, zinc, manganese, and cobalt. " class="answers-bank-image d-inline" loading="lazy" >Figure 36.2
-The IRT1 gene is responsible for most of the iron uptake activity in roots Vert et al., Plant Cell 14
[2002]:1223- 33). To determine the specificity of the IRT1 transporter in Arabidopsis plants, researchers measured the concentration of manganese, zinc, copper, and cobalt contained in wild- type and irt1- 1 mutant plants.
What conclusions about IRT1 specificity can you draw from the above data?
A) IRT1 participates in the transport of iron, zinc, manganese, and cobalt independent of iron concentration.
B) Under iron- deficient conditions, IRT1 is important for the transport of iron and copper.
C) IRT1 is important for the transport of iron and copper independent of iron concentration.
D) Under iron- deficient conditions, IRT1 is highly specific for Fe.
E) Under iron- deficient conditions, IRT1 is necessary for the transport of iron, zinc, manganese, and cobalt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Where are ion channels localized?
A) in the cytoplasm
B) on the intracellular surface of plasma membranes
C) inside the nucleus
D) spanning plasma membranes
E) on the extracellular surface of plasma membranes
A) in the cytoplasm
B) on the intracellular surface of plasma membranes
C) inside the nucleus
D) spanning plasma membranes
E) on the extracellular surface of plasma membranes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
![-Iron shortage is the most common human nutritional deficiency in the world. Plants are the major source of iron in most diets, so researchers are interested in understanding their mechanism of iron intake and in developing iron- rich crops. Recently, researchers showed Vert et al., IRT1, an Arabidopsis transporter essential for iron uptake from the soil and for plant growth. Plant Cell 14 [2002]:1223- 33) that under iron- deficient conditions, the IRT1 gene is responsible for most of the iron uptake activity in roots. To demonstrate the importance of IRT1 for iron accumulation, researchers measured leaf iron content in irt1- 1 mutants containing deactivated IRT1. Mutant plants were grown in iron- poor soil irt1- 1 in graph) and soil rich with iron irt1- 1 +Fe in graph). Wild- type WT) plants grown in iron- poor soil were used as a control. Which of the graphs represent the data researchers might have received in their experiment?](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6548/11ecf6bb_2cdf_6dce_a28d_7b4c4012e739_TB6548_00.jpg)
-Iron shortage is the most common human nutritional deficiency in the world. Plants are the major source of iron in most diets, so researchers are interested in understanding their mechanism of iron intake and in developing iron- rich crops. Recently, researchers showed Vert et al., IRT1, an Arabidopsis transporter essential for iron uptake from the soil and for plant growth. Plant Cell 14 [2002]:1223- 33) that under iron- deficient conditions, the IRT1 gene is responsible for most of the iron uptake activity in roots. To demonstrate the importance of IRT1 for iron accumulation, researchers measured leaf iron content in irt1- 1 mutants containing deactivated IRT1. Mutant plants were grown in iron- poor soil irt1- 1 in graph) and soil rich with iron irt1- 1 +Fe in graph).
Wild- type WT) plants grown in iron- poor soil were used as a control. Which of the graphs represent the data researchers might have received in their experiment?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
 } \text { of iron for 5 days. DW = dry weight} Figure 36.2 -Which of the following is being replenished when carnivorous plants trap and digest small animals? A) energy B) lipids and steroids C) carbohydrates D) nitrogen and other minerals E) water " class="answers-bank-image d-inline" loading="lazy" >
} \text { of iron for 5 days. DW = dry weight} Figure 36.2 -Which of the following is being replenished when carnivorous plants trap and digest small animals? A) energy B) lipids and steroids C) carbohydrates D) nitrogen and other minerals E) water " class="answers-bank-image d-inline" loading="lazy" >Figure 36.2
-Which of the following is being replenished when carnivorous plants trap and digest small animals?
A) energy
B) lipids and steroids
C) carbohydrates
D) nitrogen and other minerals
E) water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Spanish moss, an epiphyte, obtains nutrients from which possible source?
A) insects
B) soil
C) humus
D) the oak tree it lives on
E) dust
A) insects
B) soil
C) humus
D) the oak tree it lives on
E) dust

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In an experiment, you find that the addition of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi to the soil improves the growth rate of tomato plants. Which of the following conclusions are supported by your experiment?
A) Hyphae of fungi were able to penetrate the walls of the tomato root cells.
B) Tomato plants associate with mycorrhizal fungi.
C) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi can supply tomato plants with nutrients and water.
D) The soil used was deficient in nitrogen or phosphorus.
E) All of the above answers apply.
A) Hyphae of fungi were able to penetrate the walls of the tomato root cells.
B) Tomato plants associate with mycorrhizal fungi.
C) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi can supply tomato plants with nutrients and water.
D) The soil used was deficient in nitrogen or phosphorus.
E) All of the above answers apply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
After mutagenesis and screening take place, you have found a mutant that is able to grow in soil with high copper content. Protein analysis shows that the concentration of metallothioneins in the mutant is different from that in normal plants. How does the concentration of metallothioneins likely differ in the mutant relative to the normal plant?
A) The concentration of metallothioneins is greater in the mutant.
B) The concentration of metallothioneins is lower in the mutant.
C) Metallothioneins are absent in the mutant.
D) Metallothioneins are the most abundant proteins in the mutant.
A) The concentration of metallothioneins is greater in the mutant.
B) The concentration of metallothioneins is lower in the mutant.
C) Metallothioneins are absent in the mutant.
D) Metallothioneins are the most abundant proteins in the mutant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
After mutagenesis, the bacteria Sinorhizobium meliloti became unable to colonize Medicago truncatula plants due to the absence of recognition by the host plant. Which of the following genes is most likely the site of mutation?
A) Nod factors
B) peptidoglycans of the bacterial cell wall
C) flavonoid- synthesizing enzyme
D) leghemoglobin
E) nitrogenase
A) Nod factors
B) peptidoglycans of the bacterial cell wall
C) flavonoid- synthesizing enzyme
D) leghemoglobin
E) nitrogenase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



