Deck 20: Antimicrobial Drugs
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/55
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: Antimicrobial Drugs
1
In what way are semisynthetic penicillins and natural penicillins alike?
A) Both are resistant to penicillinase.
B) Both are resistant to stomach acids.
C) Both are bactericidal.
D) Both are based on fi- lactam.
E) Both are broad spectrum.
A) Both are resistant to penicillinase.
B) Both are resistant to stomach acids.
C) Both are bactericidal.
D) Both are based on fi- lactam.
E) Both are broad spectrum.
D
2
Which of the following antibiotics causes misreading of mRNA?
A) chloramphenicol - inhibits peptide bonds at 50S subunit
B) oxazolidinone - prevents formation of 70S ribosome
C) aminoglycoside - changes shape of 30S units
D) streptogamin - prevents release of peptide from 70S ribosome
E) tetracyclines - bind with 30S subunit
A) chloramphenicol - inhibits peptide bonds at 50S subunit
B) oxazolidinone - prevents formation of 70S ribosome
C) aminoglycoside - changes shape of 30S units
D) streptogamin - prevents release of peptide from 70S ribosome
E) tetracyclines - bind with 30S subunit
C
3
Which of the following antibiotics are used to treat fungal infections? 1. aminoglycosides
2) cephalosporins
3) griseofulvin
4) polyenes
5) bacitracin
A) 1, 2, and 3
B) 3 and 4
C) 3, 4, and 5
D) 4 and 5
E) All of these antibiotics are used to treat fungal infections.
2) cephalosporins
3) griseofulvin
4) polyenes
5) bacitracin
A) 1, 2, and 3
B) 3 and 4
C) 3, 4, and 5
D) 4 and 5
E) All of these antibiotics are used to treat fungal infections.
B
4
In Table 20.2, the antibiotic that exhibited bactericidal action was
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.
E) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided.
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.
E) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In the presence of penicillin, a cell dies because
A) it undergoes lysis.
B) its contents leak out.
C) it plasmolyzes.
D) it lacks a cell membrane.
E) it lacks a cell wall.
A) it undergoes lysis.
B) its contents leak out.
C) it plasmolyzes.
D) it lacks a cell membrane.
E) it lacks a cell wall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Figure 20.1
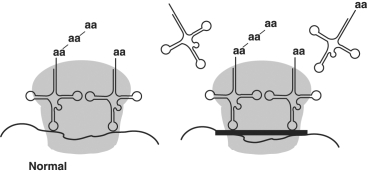
The antibiotic tetracycline binds to the 30S subunit of the ribosome, as shown in Figure 20.1. The effect is to
A) prevent attachment of DNA.
B) prevent transcription.
C) stop the ribosome from moving along the mRNA.
D) prevent peptide bond formation.
E) interfere with the attachment of the tRNA to mRNA- ribosome complex.

The antibiotic tetracycline binds to the 30S subunit of the ribosome, as shown in Figure 20.1. The effect is to
A) prevent attachment of DNA.
B) prevent transcription.
C) stop the ribosome from moving along the mRNA.
D) prevent peptide bond formation.
E) interfere with the attachment of the tRNA to mRNA- ribosome complex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Mebendazole is used to treat cestode infections. It interferes with microtubule formation; therefore, it would NOT affect
A) human cells.
B) fungi.
C) protozoa.
D) helminths.
E) bacteria.
A) human cells.
B) fungi.
C) protozoa.
D) helminths.
E) bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Lamisil is an allylamine used to treat dermatomycoses. Lamisil's method of action is similar to that of
A) griseofulvin.
B) bacitracin.
C) polymyxin B.
D) echinocandins.
E) azole antibiotics.
A) griseofulvin.
B) bacitracin.
C) polymyxin B.
D) echinocandins.
E) azole antibiotics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Penicillin was considered a "miracle drug" for all of the following reasons EXCEPT
A) it was the first antibiotic.
B) it inhibits gram- positive cell wall synthesis.
C) it does not affect eukaryotic cells.
D) it kills bacteria.
E) it has selective toxicity.
A) it was the first antibiotic.
B) it inhibits gram- positive cell wall synthesis.
C) it does not affect eukaryotic cells.
D) it kills bacteria.
E) it has selective toxicity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following does NOT constitute an advantage of using two antibiotics together?
A) It lessens the toxicity of individual drugs.
B) Two are always twice as effective as one.
C) It can prevent drug resistance.
D) It allows treatment to be provided prior to diagnosis.
E) All of these are advantages of using two antibiotics together.
A) It lessens the toxicity of individual drugs.
B) Two are always twice as effective as one.
C) It can prevent drug resistance.
D) It allows treatment to be provided prior to diagnosis.
E) All of these are advantages of using two antibiotics together.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
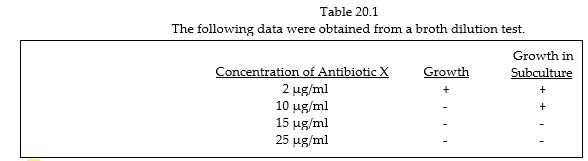
Table 20.1
The following data were obtained from a broth dilution test.
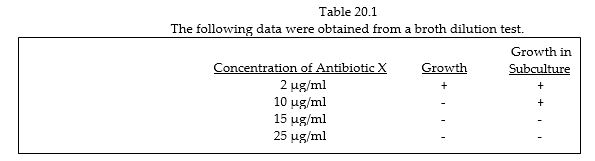
In Table 20.1, the minimal bactericidal concentration of antibiotic X is
A) 2 µg/ml.
B) 25 µg/ml.
C) 15 µg/ml.
D) 10 µg/ml.
E) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided.
The following data were obtained from a broth dilution test.

In Table 20.1, the minimal bactericidal concentration of antibiotic X is
A) 2 µg/ml.
B) 25 µg/ml.
C) 15 µg/ml.
D) 10 µg/ml.
E) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Figure 20.4
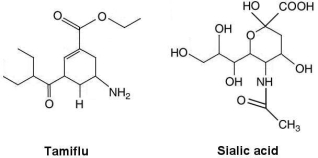
The structures of the influenza drug Tamiflu and sialic acid, the substrate for influenza virus's neuramidase, are shown in Figure 20.4. What is the method of action of Tamiflu?
A) prevents synthesis of virus spikes
B) inhibits cell wall synthesis
C) competitive inhibition
D) inhibits plasma membrane synthesis
E) inhibits synthesis of neuramidase

The structures of the influenza drug Tamiflu and sialic acid, the substrate for influenza virus's neuramidase, are shown in Figure 20.4. What is the method of action of Tamiflu?
A) prevents synthesis of virus spikes
B) inhibits cell wall synthesis
C) competitive inhibition
D) inhibits plasma membrane synthesis
E) inhibits synthesis of neuramidase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following drugs does NOT act by competitive inhibition?
A) isoniazid
B) streptomycin
C) trimethoprim
D) ethambutol
E) sulfonamide
A) isoniazid
B) streptomycin
C) trimethoprim
D) ethambutol
E) sulfonamide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following would be selective against the tubercle bacillus?
A) ethambutol - inhibits mycolic acid synthesis
B) streptomycin - inhibits protein synthesis
C) bacitracin - inhibits peptidoglycan synthesis
D) vancomycin - inhibits peptidoglycan synthesis
E) streptogramin - inhibits protein synthesis
A) ethambutol - inhibits mycolic acid synthesis
B) streptomycin - inhibits protein synthesis
C) bacitracin - inhibits peptidoglycan synthesis
D) vancomycin - inhibits peptidoglycan synthesis
E) streptogramin - inhibits protein synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following methods of action would be bacteriostatic?
A) competitive inhibition with folic acid synthesis
B) competitive inhibition with DNA gyrase
C) inhibition of protein synthesis
D) injury to plasma membrane
E) inhibition of cell wall synthesis
A) competitive inhibition with folic acid synthesis
B) competitive inhibition with DNA gyrase
C) inhibition of protein synthesis
D) injury to plasma membrane
E) inhibition of cell wall synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
To date, most of our natural antibiotics have been found to be produced by members of what genus?
A) Streptomyces
B) Cephalosporium
C) Penicillium
D) Paenibacillus
E) Bacillus
A) Streptomyces
B) Cephalosporium
C) Penicillium
D) Paenibacillus
E) Bacillus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
More than half of our antibiotics are
A) produced by Fleming.
B) produced by fungi.
C) produced by eukaryotic organisms.
D) produced by bacteria.
E) synthesized in laboratories.
A) produced by Fleming.
B) produced by fungi.
C) produced by eukaryotic organisms.
D) produced by bacteria.
E) synthesized in laboratories.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Table 20.2
The following results were obtained from a disk- diffusion test for microbial susceptibility to antibiotics. Staphylococcus aureus was the test organism.
-In Table 20.2, the most effective antibiotic tested was
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.
E) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided.
The following results were obtained from a disk- diffusion test for microbial susceptibility to antibiotics. Staphylococcus aureus was the test organism.
-In Table 20.2, the most effective antibiotic tested was
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.
E) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following antibiotics is NOT bactericidal?
A) rifampins
B) aminoglycosides
C) cephalosporins
D) penicillin
E) polyenes
A) rifampins
B) aminoglycosides
C) cephalosporins
D) penicillin
E) polyenes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Figure 20.3
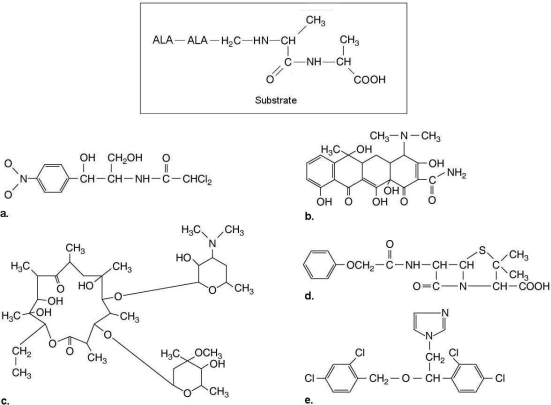
The substrate for transpeptidase used to synthesize peptidoglycan is shown in Figure 20.3. Which of the drugs shown would inhibit peptidoglycan synthesis?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) e

The substrate for transpeptidase used to synthesize peptidoglycan is shown in Figure 20.3. Which of the drugs shown would inhibit peptidoglycan synthesis?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) e

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which one of the following does NOT belong with the others?
A) monobactam
B) cephalosporin
C) streptomycin
D) bacitracin
E) penicillin
A) monobactam
B) cephalosporin
C) streptomycin
D) bacitracin
E) penicillin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Antimicrobial peptides work by
A) disrupting the plasma membrane.
B) complementary base pairing with DNA.
C) hydrolyzing peptidoglycan.
D) inhibiting cell- wall synthesis.
E) inhibiting protein synthesis.
A) disrupting the plasma membrane.
B) complementary base pairing with DNA.
C) hydrolyzing peptidoglycan.
D) inhibiting cell- wall synthesis.
E) inhibiting protein synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Figure 20.2
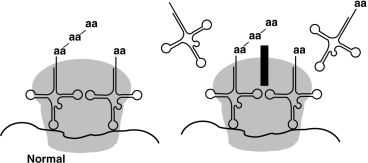
The antibiotic cycloheximide binds to the 60S subunit of the ribosome, as shown in Figure 20.2. The effect is to
A) prevent peptide bond formation in prokaryotes.
B) prevent mRNA-ribosome binding in eukaryotes.
C) prevent ribosome formation in bacteria.
D) prevent transcription in prokaryotes.
E) prevent polypeptide elongation in eukaryotes.

The antibiotic cycloheximide binds to the 60S subunit of the ribosome, as shown in Figure 20.2. The effect is to
A) prevent peptide bond formation in prokaryotes.
B) prevent mRNA-ribosome binding in eukaryotes.
C) prevent ribosome formation in bacteria.
D) prevent transcription in prokaryotes.
E) prevent polypeptide elongation in eukaryotes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is mismatched?
A) Florey and Chain - identification of Penicillium as the producer of penicillin
B) Fleming - identification of penicillin
C) Ehrlich - "magic bullet" theory
D) Kirby and Bauer - disc- diffusion method
E) None of these is mismatched.
A) Florey and Chain - identification of Penicillium as the producer of penicillin
B) Fleming - identification of penicillin
C) Ehrlich - "magic bullet" theory
D) Kirby and Bauer - disc- diffusion method
E) None of these is mismatched.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The antibiotic actinomycin D binds between adjacent G- C pairs, thus interfering with
A) peptide bond formation.
B) transcription.
C) plasma membrane function.
D) cellular respiration.
E) translation.
A) peptide bond formation.
B) transcription.
C) plasma membrane function.
D) cellular respiration.
E) translation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following organisms would MOST likely be sensitive to natural penicillin?
A) Penicillium
B) penicillinase- producing Neisseria gonorrhoeae
C) Streptococcus pyogenes
D) helminths
E) Mycoplasma
A) Penicillium
B) penicillinase- producing Neisseria gonorrhoeae
C) Streptococcus pyogenes
D) helminths
E) Mycoplasma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Most of the available antimicrobial agents are effective against
A) fungi.
B) viruses.
C) bacteria.
D) protozoa.
E) All of the answers are correct.
A) fungi.
B) viruses.
C) bacteria.
D) protozoa.
E) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The antimicrobial drugs with the broadest spectrum of activity are
A) chloramphenicol.
B) aminoglycosides.
C) penicillin G.
D) tetracyclines.
E) macrolides.
A) chloramphenicol.
B) aminoglycosides.
C) penicillin G.
D) tetracyclines.
E) macrolides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following antimicrobial agents is recommended for use against fungal infections?
A) polymyxin
B) amphotericin B
C) cephalosporin
D) penicillin
E) bacitracin
A) polymyxin
B) amphotericin B
C) cephalosporin
D) penicillin
E) bacitracin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following does NOT affect eukaryotic cells?
A) antihelminthic drugs
B) semisynthetic penicillins
C) antiprotozoan drugs
D) antifungal drugs
E) nucleotide analogs
A) antihelminthic drugs
B) semisynthetic penicillins
C) antiprotozoan drugs
D) antifungal drugs
E) nucleotide analogs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following statements about drugs that competitively inhibit DNA polymerase or RNA polymerase is FALSE?
A) They cause cellular plasmolysis.
B) They are used against viral infections.
C) They interfere with protein synthesis.
D) They cause mutations.
E) They can affect host cell DNA.
A) They cause cellular plasmolysis.
B) They are used against viral infections.
C) They interfere with protein synthesis.
D) They cause mutations.
E) They can affect host cell DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following statements about drug resistance is FALSE?
A) It may be due to enzymes that degrade some antibiotics.
B) It may be carried on a plasmid.
C) It is found only in gram- negative bacteria.
D) It may be due to increased uptake of a drug.
E) It may be transferred from one bacterium to another during conjugation.
A) It may be due to enzymes that degrade some antibiotics.
B) It may be carried on a plasmid.
C) It is found only in gram- negative bacteria.
D) It may be due to increased uptake of a drug.
E) It may be transferred from one bacterium to another during conjugation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following antibiotics is recommended for use against gram- negative bacteria?
A) polymyxin
B) cephalosporin
C) bacitracin
D) polyenes
E) penicillin
A) polymyxin
B) cephalosporin
C) bacitracin
D) polyenes
E) penicillin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which compound would be the most useful to treat candidiasis?
A) penicillin
B) guanine
C) uracil
D) thymine
E) flucytosine
A) penicillin
B) guanine
C) uracil
D) thymine
E) flucytosine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Niclosamide prevents ATP generation in mitochondria. You would expect this drug to be effective against
A) Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
B) gram- negative bacteria.
C) gram- positive bacteria.
D) viruses.
E) helminths.
A) Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
B) gram- negative bacteria.
C) gram- positive bacteria.
D) viruses.
E) helminths.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following antibiotics does NOT interfere with cell wall synthesis?
A) cephalosporins
B) vancomycin
C) macrolides
D) natural penicillins
E) semisynthetic penicillins
A) cephalosporins
B) vancomycin
C) macrolides
D) natural penicillins
E) semisynthetic penicillins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Use of antibiotics in animal feed leads to antibiotic- resistant bacteria because
A) bacteria from other animals replace those killed by the antibiotics.
B) the antibiotics persist in soil and water.
C) the few surviving bacteria that are affected by the antibiotics develop immunity to the antibiotics, which they pass on to their progeny.
D) the antibiotics cause new mutations to occur in the surviving bacteria, which results in resistance to antibiotics.
E) the antibiotics kill susceptible bacteria, but the few that are naturally resistant live and reproduce, and their progeny repopulate the host animal.
A) bacteria from other animals replace those killed by the antibiotics.
B) the antibiotics persist in soil and water.
C) the few surviving bacteria that are affected by the antibiotics develop immunity to the antibiotics, which they pass on to their progeny.
D) the antibiotics cause new mutations to occur in the surviving bacteria, which results in resistance to antibiotics.
E) the antibiotics kill susceptible bacteria, but the few that are naturally resistant live and reproduce, and their progeny repopulate the host animal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A drug that inhibits mitosis, such as griseofulvin, would be more effective against
A) fungi.
B) mycobacteria.
C) gram- positive bacteria.
D) wall- less bacteria.
E) gram- negative bacteria.
A) fungi.
B) mycobacteria.
C) gram- positive bacteria.
D) wall- less bacteria.
E) gram- negative bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Protozoan and helminthic diseases are difficult to treat because
A) their cells are structurally and functionally similar to human cells.
B) they replicate inside human cells.
C) they have more genes than bacteria.
D) they do not reproduce.
E) they do not have ribosomes.
A) their cells are structurally and functionally similar to human cells.
B) they replicate inside human cells.
C) they have more genes than bacteria.
D) they do not reproduce.
E) they do not have ribosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following antimicrobial agents has the fewest side effects?
A) penicillin
B) streptomycin
C) chloramphenicol
D) erythromycin
E) tetracycline
A) penicillin
B) streptomycin
C) chloramphenicol
D) erythromycin
E) tetracycline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) Acyclovir inhibits DNA synthesis.
B) Interferon inhibits glycolysis.
C) Amantadine inhibits the release of viral nucleic acid.
D) Azoles inhibit plasma membrane synthesis.
E) Fluoroquinolone inhibits DNA synthesis.
A) Acyclovir inhibits DNA synthesis.
B) Interferon inhibits glycolysis.
C) Amantadine inhibits the release of viral nucleic acid.
D) Azoles inhibit plasma membrane synthesis.
E) Fluoroquinolone inhibits DNA synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Due to its target, rifamycins can be effective over a broad spectrum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Only microbes produce antimicrobial peptides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Penicillin and streptomycin are commonly used in syngerism because they display the same mode of action.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Table 20.2
The following results were obtained from a disk- diffusion test for microbial susceptibility to antibiotics. Staphylococcus aureus was the test organism.
-In Table 20.2, which antibiotic would be most useful for treating a Salmonella infection?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided.
The following results were obtained from a disk- diffusion test for microbial susceptibility to antibiotics. Staphylococcus aureus was the test organism.
-In Table 20.2, which antibiotic would be most useful for treating a Salmonella infection?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
An antibiotic that attacks the LPS layer would be expected to have a narrow spectrum of activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Phage therapy has been used in the past as an antiviral treatment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Table 20.3
The following data were obtained from a broth dilution test: Bacteria from the 0.25 µg/ml tube were transferred to new growth media containing antibiotic X with the following results:
-The data in Table 20.3 show that these bacteria
A) developed resistance to antibiotics.
B) are pathogenic.
C) were killed by 0.5 µg/ml of antibiotic X.
D) were killed by 0.125 µg/ml of antibiotic X.
E) were resistant to 1.0 µg/ml at the start of the experiment.
The following data were obtained from a broth dilution test: Bacteria from the 0.25 µg/ml tube were transferred to new growth media containing antibiotic X with the following results:
-The data in Table 20.3 show that these bacteria
A) developed resistance to antibiotics.
B) are pathogenic.
C) were killed by 0.5 µg/ml of antibiotic X.
D) were killed by 0.125 µg/ml of antibiotic X.
E) were resistant to 1.0 µg/ml at the start of the experiment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
PABA serves as the competitive inhibitor in the action of sulfanilamides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Table 20.1
The following data were obtained from a broth dilution test.
In Table 20.1, the minimal inhibitory concentration of antibiotic X is
A) 10 µg/ml.
B) 15 µg/ml.
C) 25 µg/ml.
D) 2 µg/ml.
E) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided.
The following data were obtained from a broth dilution test.

In Table 20.1, the minimal inhibitory concentration of antibiotic X is
A) 10 µg/ml.
B) 15 µg/ml.
C) 25 µg/ml.
D) 2 µg/ml.
E) The answer cannot be determined based on the information provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Antiviral drugs target viral processes that occur during viral infection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Drug resistance occurs
A) when antibiotics are used indiscriminately.
B) against antibiotics and not against synthetic chemotherapeutic agents.
C) when antibiotics are taken after the symptoms disappear.
D) because bacteria are normal microbiota.
E) All of the answers are correct.
A) when antibiotics are used indiscriminately.
B) against antibiotics and not against synthetic chemotherapeutic agents.
C) when antibiotics are taken after the symptoms disappear.
D) because bacteria are normal microbiota.
E) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Both trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole inhibit reactions along the same metabolic pathway.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Undergrowth of fungi after antibiotic use is commonly referred to as a superinfection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Community- acquired MRSA is typically more virulent than health care- associated MRSA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



