Deck 21: RNA Synthesis, Processing, and Gene Silencing
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/100
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: RNA Synthesis, Processing, and Gene Silencing
1
Which protein-synthesizing RNA molecule carries an amino acid to the ribosome active site?
A) rRNA
B) tRNA
C) mRNA
D) siRNA
A) rRNA
B) tRNA
C) mRNA
D) siRNA
rRNA
2
RNA is a dynamic biomolecule because it can
A) be a component in protein synthesis, regulate protein synthesis, and be synthesized and function in cell nucleus.
B) catalyze its own synthesis.
C) contain a ribose sugar backbone.
D) be stable to hydrolysis.
A) be a component in protein synthesis, regulate protein synthesis, and be synthesized and function in cell nucleus.
B) catalyze its own synthesis.
C) contain a ribose sugar backbone.
D) be stable to hydrolysis.
be a component in protein synthesis, regulate protein synthesis, and be synthesized and function in cell nucleus.
3
Which class of RNA molecules is unique to eukaryotic organisms?
A) transfer RNA
B) ribosomal RNA
C) small nuclear RNA
D) messenger RNA
A) transfer RNA
B) ribosomal RNA
C) small nuclear RNA
D) messenger RNA
small nuclear RNA
4
A 7-methylguanylate cap and poly(A) tail is added to mRNA to
A) differentiate the mRNA from the tRNA.
B) facilitate binding and translation by the ribosome.
C) increase mRNA splicing efficiency.
D) signify the start and end of the gene sequence.
A) differentiate the mRNA from the tRNA.
B) facilitate binding and translation by the ribosome.
C) increase mRNA splicing efficiency.
D) signify the start and end of the gene sequence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Of the following protein synthesizing RNA molecules, which codes for a protein?
A) tRNA
B) siRNA
C) mRNA
D) rRNA
A) tRNA
B) siRNA
C) mRNA
D) rRNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
RNA is typically more susceptible to backbone hydrolysis than DNA because of the
A) presence of simpler nucleotides.
B) presence of a 2 ' OH group.
C) presence of a 3 ' OH group.
D) lack of thymine nucleotides.
A) presence of simpler nucleotides.
B) presence of a 2 ' OH group.
C) presence of a 3 ' OH group.
D) lack of thymine nucleotides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which enzyme is important in the processing of tRNA and mRNA from prokaryotes?
A) RNaseP
B) snRNA
C) reverse transcriptase
D) ribozyme
A) RNaseP
B) snRNA
C) reverse transcriptase
D) ribozyme

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
How are RNA structures different from protein structures?
A) RNA is single stranded, whereas proteins are not.
B) RNA can H-bond with itself, whereas proteins cannot.
C) RNA mutations can lead to nonfunctioning proteins, whereas protein mutations do not.
D) RNA adopts less defined tertiary structures than proteins.
A) RNA is single stranded, whereas proteins are not.
B) RNA can H-bond with itself, whereas proteins cannot.
C) RNA mutations can lead to nonfunctioning proteins, whereas protein mutations do not.
D) RNA adopts less defined tertiary structures than proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
RNA is a highly dynamic biomolecule in that it
A) can fold and hydrogen bond with itself, DNA, proteins, or small molecules to adopt largely modified tertiary structures.
B) is less capable of forming stable H-bonds than DNA.
C) is often shorter than DNA.
D) is largely composed of a phosphate backbone.
A) can fold and hydrogen bond with itself, DNA, proteins, or small molecules to adopt largely modified tertiary structures.
B) is less capable of forming stable H-bonds than DNA.
C) is often shorter than DNA.
D) is largely composed of a phosphate backbone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The most significant influence on why mRNA is processed differently in prokaryotes than eukaryotes is the fact that
A) eukaryotes separate transcription and translation with a nucleus.
B) prokaryotes are often polycistronic.
C) eukaryotes are multicellular organisms.
D) prokaryotes do not add a poly(A) tail.
A) eukaryotes separate transcription and translation with a nucleus.
B) prokaryotes are often polycistronic.
C) eukaryotes are multicellular organisms.
D) prokaryotes do not add a poly(A) tail.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
It has been estimated that as much as % of the human genome is transcribed into noncoding RNA, whereas % of the E. coli genome is noncoding RNA.
A) 10; 90
B) 90; 10
C) 50; 10
D) 25; 2
A) 10; 90
B) 90; 10
C) 50; 10
D) 25; 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which is often removed from eukaryotic mRNA before translation?
A) poly(A) tails
B) exons
C) polycistrons
D) introns
A) poly(A) tails
B) exons
C) polycistrons
D) introns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Prokaryotic mRNA is commonly processed through
A) splicing by RNaseP enzymes.
B) immediate translation during transcription.
C) addition of 7-methylguanylate cap.
D) removal of exons.
A) splicing by RNaseP enzymes.
B) immediate translation during transcription.
C) addition of 7-methylguanylate cap.
D) removal of exons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) is generated from
A) the tips of chromosomes.
B) the transcription of genomic DNA.
C) the splicing of used mRNA.
D) an infection of viral RNA.
A) the tips of chromosomes.
B) the transcription of genomic DNA.
C) the splicing of used mRNA.
D) an infection of viral RNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is a coding RNA molecule?
A) short interfering RNA.
B) TERC RNA.
C) small nucleolar RNA.
D) messenger RNA.
A) short interfering RNA.
B) TERC RNA.
C) small nucleolar RNA.
D) messenger RNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following RNA molecules has the LEAST number of different sequences in a given organism?
A) tRNA
B) rRNA
C) mRNA
D) snRNA
A) tRNA
B) rRNA
C) mRNA
D) snRNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which class of RNA molecule is typically the shortest in length?
A) transfer RNA
B) messenger RNA
C) small nuclear RNA
D) micro RNA
A) transfer RNA
B) messenger RNA
C) small nuclear RNA
D) micro RNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The RNA type directly involved in protein synthesis is
A) small nuclear RNA.
B) short interfering RNA.
C) ribosomal RNA.
D) long nc RNA.
A) small nuclear RNA.
B) short interfering RNA.
C) ribosomal RNA.
D) long nc RNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A knockout mutation in the X-inactive specific transcript (XIST) lncRNA of mice would result in
A) one inactivated X chromosome in female mice.
B) the inhibited transcription and translation of X-linked proteins.
C) two inactive X chromosomes in female mice.
D) two active X chromosomes in female mice.
A) one inactivated X chromosome in female mice.
B) the inhibited transcription and translation of X-linked proteins.
C) two inactive X chromosomes in female mice.
D) two active X chromosomes in female mice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which RNA molecule does NOT bind to the ribosome?
A) tRNA
B) rRNA
C) mRNA
D) snRNA
A) tRNA
B) rRNA
C) mRNA
D) snRNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are found on
A) exons of protein-coding genes.
B) introns of protein-coding genes.
C) non-functional rRNA.
D) protein-coding mRNA.
A) exons of protein-coding genes.
B) introns of protein-coding genes.
C) non-functional rRNA.
D) protein-coding mRNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In which direction is mRNA synthesized by RNA polymerase?
A) in the 3 ' to 5 ' direction
B) with 5 ' to 3 ' phosphodiester linkages
C) in the 5 ' to 3 ' direction
D) It depends on whether the sense or antisense strand is transcribed.
A) in the 3 ' to 5 ' direction
B) with 5 ' to 3 ' phosphodiester linkages
C) in the 5 ' to 3 ' direction
D) It depends on whether the sense or antisense strand is transcribed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What are factors in RNA synthesis?
A) DNA promoter regions
B) RNA polymerases
C) transcription factors
D) receptor proteins
A) DNA promoter regions
B) RNA polymerases
C) transcription factors
D) receptor proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Eukaryotic promoters, but NOT prokaryotic promoters,
A) are located before the transcription start site.
B) bind transcription factors.
C) are located after the transcription start site.
D) assist in activating transcription.
A) are located before the transcription start site.
B) bind transcription factors.
C) are located after the transcription start site.
D) assist in activating transcription.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which biochemical lab technique is used in the DNA footprinting technique?
A) gel electrophoresis
B) polymerase chain reaction
C) plasmid ligation
D) cloning
A) gel electrophoresis
B) polymerase chain reaction
C) plasmid ligation
D) cloning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Weak prokaryotic promoters
A) can bind to different transcription factors.
B) have a DNA sequence that is significantly different from that of other common promotors.
C) can be easily bound to factors.
D) give weak DNA footprinting signals.
A) can bind to different transcription factors.
B) have a DNA sequence that is significantly different from that of other common promotors.
C) can be easily bound to factors.
D) give weak DNA footprinting signals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which is true of RNA polymerases in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms?
A) They are composed of an analogous 2 ' core.
B) There is a single enzyme type per organism.
C) They make copies of RNA from either DNA or RNA templates.
D) They have the same number of cofactors in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
A) They are composed of an analogous 2 ' core.
B) There is a single enzyme type per organism.
C) They make copies of RNA from either DNA or RNA templates.
D) They have the same number of cofactors in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Approximately how many different types of RNA promotors are needed in eukaryotic systems?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which is NOT required in the prokaryotic transcription initiation complex?
A) a primer
B) RNA polymerase
C) initiation factor
D) a ribonucleotide triphosphate (NTP)
A) a primer
B) RNA polymerase
C) initiation factor
D) a ribonucleotide triphosphate (NTP)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Eukaryotic transcription promoters
A) are typically found after the transcription start site.
B) have a single sequence and bind one RNA polymerase type.
C) may bind to both transcription factors and RNA polymerases.
D) are all controlled by a ubiquitous factor.
A) are typically found after the transcription start site.
B) have a single sequence and bind one RNA polymerase type.
C) may bind to both transcription factors and RNA polymerases.
D) are all controlled by a ubiquitous factor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What do factors bind to in RNA synthesis?
A) DNA promoters and RNA polymerase
B) RNA promoters and DNA
C) DNA and RNA
D) transcription factors
A) DNA promoters and RNA polymerase
B) RNA promoters and DNA
C) DNA and RNA
D) transcription factors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Using the DNA footprinting technique, which of the following were/was identified as binding site(s) for factors?
A) -35 box
B) -5 and -35 box
C) -10 and -35 box
D) -10 box
A) -35 box
B) -5 and -35 box
C) -10 and -35 box
D) -10 box

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Strong prokaryotic promoters
A) bind tightly to the transcription factors.
B) have factors that are larger, more stable proteins.
C) generally result in a higher rate of transcription.
D) are less common in prokaryotes.
A) bind tightly to the transcription factors.
B) have factors that are larger, more stable proteins.
C) generally result in a higher rate of transcription.
D) are less common in prokaryotes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The information gained from the DNA footprinting technique is the
A) DNA sequence.
B) promotor region of a gene.
C) location of a gene in DNA.
D) location of a DNA binding protein on DNA.
A) DNA sequence.
B) promotor region of a gene.
C) location of a gene in DNA.
D) location of a DNA binding protein on DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The strand of DNA is transcribed into mRNA.
A) leading
B) coding
C) lagging
D) template
A) leading
B) coding
C) lagging
D) template

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Eukaryotic transcription promoters
A) require multiple DNA binding regions.
B) are largely conserved across the genome.
C) can stimulate DNA polymerases by direct binding.
D) control translational as well as transcriptional events.
A) require multiple DNA binding regions.
B) are largely conserved across the genome.
C) can stimulate DNA polymerases by direct binding.
D) control translational as well as transcriptional events.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The function of DNase I is that it
A) cuts DNA whenever DNA binding proteins are present.
B) cuts double-stranded DNA by cutting phosphodiester bonds.
C) cuts DNA binding proteins.
D) makes an RNA copy of DNA.
A) cuts DNA whenever DNA binding proteins are present.
B) cuts double-stranded DNA by cutting phosphodiester bonds.
C) cuts DNA binding proteins.
D) makes an RNA copy of DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Eukaryotic RNA polymerase
A) is a ribozyme.
B) contains as many as five protein subunits in the final functional enzyme.
C) synthesizes all RNA types.
D) has a common core structure resembling that of prokaryotic RNA polymerase.
A) is a ribozyme.
B) contains as many as five protein subunits in the final functional enzyme.
C) synthesizes all RNA types.
D) has a common core structure resembling that of prokaryotic RNA polymerase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What prokaryotic promoter would most likely control a housekeeping gene?
A) weak promoter
B) -10 and -35 box
C) TATA box
D) strong promoter
A) weak promoter
B) -10 and -35 box
C) TATA box
D) strong promoter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The DNA sequence of prokaryotic gene promotors were found to be
A) largely conserved.
B) distinct for each gene.
C) capable of binding different promoters.
D) strong binders of DNA polymerase.
A) largely conserved.
B) distinct for each gene.
C) capable of binding different promoters.
D) strong binders of DNA polymerase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Group I and group II introns are similar in their
A) requirement for metal ion cofactors.
B) requirement for exogenous nucleoside binding.
C) DNA composition.
D) intron lariat structure.
A) requirement for metal ion cofactors.
B) requirement for exogenous nucleoside binding.
C) DNA composition.
D) intron lariat structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Prokaryotic transcription could terminate by
A) association of a factor with the DNA.
B) RNA with GC stem loop structures.
C) a G-rich region on the DNA.
D) RNA polymerase without the elongation factor.
A) association of a factor with the DNA.
B) RNA with GC stem loop structures.
C) a G-rich region on the DNA.
D) RNA polymerase without the elongation factor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Most post-transcriptional RNA processing reactions are catalyzed by
A) DNAzymes.
B) ribozymes.
C) ligases.
D) transferases.
A) DNAzymes.
B) ribozymes.
C) ligases.
D) transferases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What best describes the composition of the spliceosome?
A) small nuclear ribonucleoprotein
B) RNA only
C) protein
D) mRNA
A) small nuclear ribonucleoprotein
B) RNA only
C) protein
D) mRNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
At what point during transcription does the F factor dissociate from the RNA polymerase?
A) in the initiation phase
B) in the termination phase
C) before the elongation phase
D) during the elongation phase
A) in the initiation phase
B) in the termination phase
C) before the elongation phase
D) during the elongation phase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which is true of ribozymes?
A) They have conserved primary sequences.
B) They are not true catalysts.
C) They are transcription factors.
D) They have conserved secondary and tertiary structures.
A) They have conserved primary sequences.
B) They are not true catalysts.
C) They are transcription factors.
D) They have conserved secondary and tertiary structures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The following is referred to as the ribozyme. 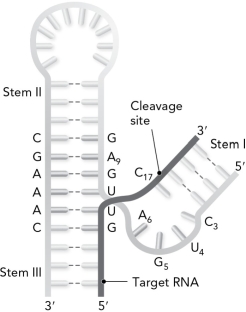
A) stem-loop
B) hairpin
C) hammerhead
D) cloverleaf

A) stem-loop
B) hairpin
C) hammerhead
D) cloverleaf

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The spliceosome
A) is a cis-acting ribozyme.
B) resembles group II introns in its mechanism and product.
C) performs the same function in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
D) is a protein enzyme.
A) is a cis-acting ribozyme.
B) resembles group II introns in its mechanism and product.
C) performs the same function in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
D) is a protein enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Eukaryotic RNA polymerase II facilitates the
A) removal of exons.
B) addition of 7-methylguanylate cap.
C) addition of a poly(A) tail.
D) translation of the RNA transcript.
A) removal of exons.
B) addition of 7-methylguanylate cap.
C) addition of a poly(A) tail.
D) translation of the RNA transcript.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The C-terminal domain (CTD) of the eukaryotic RNA polymerase II is involved in the transcriptional process of
A) addition of a poly(A) tail.
B) removal of exons.
C) directing RNA to the cytoplasm.
D) product phosphorylation.
A) addition of a poly(A) tail.
B) removal of exons.
C) directing RNA to the cytoplasm.
D) product phosphorylation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Trans activity refers to the __________ for a ribozyme.
A) cleavage of another identical RNA molecule
B) intermolecular cleavage of substrate
C) intramolecular cleavage
D) conserved activity of all enzymes
A) cleavage of another identical RNA molecule
B) intermolecular cleavage of substrate
C) intramolecular cleavage
D) conserved activity of all enzymes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What is a difference between group I and group II introns?
A) intron cleaving versus exon ligating abilities
B) cis versus trans cleaving capabilities
C) linear versus lariat intron products
D) nucleophilic versus electrophilic hydroxyl attacks
A) intron cleaving versus exon ligating abilities
B) cis versus trans cleaving capabilities
C) linear versus lariat intron products
D) nucleophilic versus electrophilic hydroxyl attacks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A difference between transcription in prokaryotes and eukaryotes is the
A) lack of need for a primer.
B) presence of a transcription bubble.
C) addition of a poly(A) tail.
D) direction of transcription on the DNA template.
A) lack of need for a primer.
B) presence of a transcription bubble.
C) addition of a poly(A) tail.
D) direction of transcription on the DNA template.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In E. coli, RNA-DNA base pairs are maintained and about base pairs of single-stranded DNA are maintained in the transcription bubble.
A) 20; 80
B) 8; 17
C) 17; 20
D) 200; 1000
A) 20; 80
B) 8; 17
C) 17; 20
D) 200; 1000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Cis-acting enzymes are
A) self-operating enzymes.
B) enzymes that operate on a target molecule.
C) intermolecular-operating enzymes.
D) enzymes that operate on other enzymes.
A) self-operating enzymes.
B) enzymes that operate on a target molecule.
C) intermolecular-operating enzymes.
D) enzymes that operate on other enzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Identify the location of action of the spliceosome.
A) nuclear pore
B) nucleus
C) rough endoplasmic reticulum
D) cytoplasm
A) nuclear pore
B) nucleus
C) rough endoplasmic reticulum
D) cytoplasm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The group I and group II introns catalyze which class of reaction?
A) transferase
B) cleavage
C) hydrolysis
D) transesterification
A) transferase
B) cleavage
C) hydrolysis
D) transesterification

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The initiation, elongation, and termination of eukaryotic transcription is controlled by the
A) extent of phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of the RNA polymerase.
B) presence of initiation, elongation, and termination factors binding to RNA polymerase.
C) unwinding the double-stranded DNA.
D) length of the RNA transcript.
A) extent of phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of the RNA polymerase.
B) presence of initiation, elongation, and termination factors binding to RNA polymerase.
C) unwinding the double-stranded DNA.
D) length of the RNA transcript.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What do group I introns require that group II introns do not?
A) ATP hydrolysis
B) metal ion cofactors
C) guanosine cofactor binding
D) external RNA substrate
A) ATP hydrolysis
B) metal ion cofactors
C) guanosine cofactor binding
D) external RNA substrate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The initiation of transcription in eukaryotes
A) occurs in the same manner as prokaryotic transcription.
B) requires the complete unfolding of the gene into single-stranded DNA.
C) requires many more transcription factors than prokaryotic transcription.
D) uses RNA polymerase as well as helicase and primase.
A) occurs in the same manner as prokaryotic transcription.
B) requires the complete unfolding of the gene into single-stranded DNA.
C) requires many more transcription factors than prokaryotic transcription.
D) uses RNA polymerase as well as helicase and primase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
List the classes and types of noncoding RNAs that are found typically in eukaryotic organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What is the biggest difference between miRNA and siRNA?
A) One is derived from the nucleus and one is derived from double-stranded RNA.
B) One regulates gene expression, whereas the other regulates protein synthesis.
C) One binds to mRNA and suppresses its translation and one binds to mRNA and signals degradation.
D) One binds to the DNA gene and inhibits transcription and one binds to the mRNA and signals degradation.
A) One is derived from the nucleus and one is derived from double-stranded RNA.
B) One regulates gene expression, whereas the other regulates protein synthesis.
C) One binds to mRNA and suppresses its translation and one binds to mRNA and signals degradation.
D) One binds to the DNA gene and inhibits transcription and one binds to the mRNA and signals degradation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which enzyme degrades the poly(A) tail in the degradation of mRNA?
A) poly(A) binding protein
B) exosome
C) CCR4
D) DCP1 and DCP2
A) poly(A) binding protein
B) exosome
C) CCR4
D) DCP1 and DCP2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which is central to the addition of the 7-methylguanosine cap to mRNA?
A) RNA polymerase 1
B) guanine-N7 methyltransferase
C) GMP
D) snoRNA
A) RNA polymerase 1
B) guanine-N7 methyltransferase
C) GMP
D) snoRNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The enzyme responsible for making siRNA is
A) RISC.
B) snoRNA.
C) exosome.
D) dicer.
A) RISC.
B) snoRNA.
C) exosome.
D) dicer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which RNA molecule is expressed in the genome to regulate gene expression?
A) RNAi
B) snoRNA
C) miRNA
D) siRNA
A) RNAi
B) snoRNA
C) miRNA
D) siRNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The roles of U1, U2, U4, U5, and U6 in the spliceosome complex are to
A) bind mRNA and facilitate the splicing reaction.
B) bind the small nuclear RNA.
C) carry the products from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
D) bind proteins and hold the complex together.
A) bind mRNA and facilitate the splicing reaction.
B) bind the small nuclear RNA.
C) carry the products from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
D) bind proteins and hold the complex together.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Antisense RNA binds to and sense RNA binds to .
A) template DNA; coding DNA
B) tRNA; mRNA
C) coding DNA; template DNA
D) mRNA; coding DNA
A) template DNA; coding DNA
B) tRNA; mRNA
C) coding DNA; template DNA
D) mRNA; coding DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
More than 100 different RNA base modifications have been identified, and most of those are found in
A) mRNA.
B) rRNA.
C) snRNA.
D) tRNA.
A) mRNA.
B) rRNA.
C) snRNA.
D) tRNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
miRNA is
A) involved in stimulating gene expression.
B) derived from degraded mRNA.
C) expressed in the nucleus and is involved in regulating gene expression.
D) derived from degraded virus RNA strands.
A) involved in stimulating gene expression.
B) derived from degraded mRNA.
C) expressed in the nucleus and is involved in regulating gene expression.
D) derived from degraded virus RNA strands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Many noncoding RNAs are involved in gene silencing. Gene silencing refers to
A) the splicing of mRNA into alternative transcripts.
B) defense mechanisms against RNA viruses.
C) mechanisms inhibiting gene expression.
D) the modification of genes through RNA-mediated mutation.
A) the splicing of mRNA into alternative transcripts.
B) defense mechanisms against RNA viruses.
C) mechanisms inhibiting gene expression.
D) the modification of genes through RNA-mediated mutation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which type of RNA facilitates RNA interference by resulting in degraded mRNA?
A) snoRNA
B) siRNA
C) miRNA
D) rRNA
A) snoRNA
B) siRNA
C) miRNA
D) rRNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which is the correct order of mRNA degradation?
A) (1) poly(A) tail removal; (2) 7-methylguanosine cap removal; (3) RNA hydrolysis
B) (1) 7-methylguanosine cap removal; (2) RNA hydrolysis; (3) poly(A) tail removal
C) (1) 7-methylguanosine cap removal; (2) poly(A) tail removal; (3) RNA hydrolysis
D) (1) RNA hydrolysis; (2) Poly(A) tail removal; (3) 7-methylguanosine cap removal
A) (1) poly(A) tail removal; (2) 7-methylguanosine cap removal; (3) RNA hydrolysis
B) (1) 7-methylguanosine cap removal; (2) RNA hydrolysis; (3) poly(A) tail removal
C) (1) 7-methylguanosine cap removal; (2) poly(A) tail removal; (3) RNA hydrolysis
D) (1) RNA hydrolysis; (2) Poly(A) tail removal; (3) 7-methylguanosine cap removal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Using the picture below, describe the three ways that RNA is a highly dynamic biomolecule.
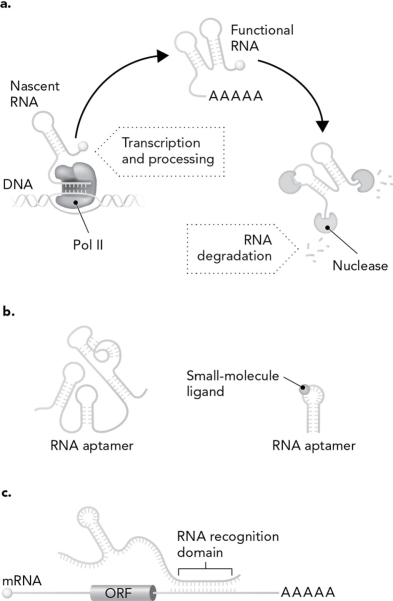


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A common RNA base modification is
A) methylation.
B) amination.
C) carboxylation.
D) hydroxylation.
A) methylation.
B) amination.
C) carboxylation.
D) hydroxylation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Different mRNAs can be obtained from the same gene by
A) terminating transcription at different stop codons.
B) splicing the mRNA with different exons.
C) adding the 7-methylguanosine cap at different sites.
D) alternate folding of mRNA.
A) terminating transcription at different stop codons.
B) splicing the mRNA with different exons.
C) adding the 7-methylguanosine cap at different sites.
D) alternate folding of mRNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which enzyme is responsible for adding the poly(A) tail to mRNA?
A) cleavage stimulatory factor (CStF)
B) poly(A) polymerase
C) cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor (CPSF)
D) poly(A) binding protein
A) cleavage stimulatory factor (CStF)
B) poly(A) polymerase
C) cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor (CPSF)
D) poly(A) binding protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
List the four ways that long noncoding RNAs are thought to function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
List the three main ways that eukaryotic mRNA molecules are processed before translation, which prokaryotic organisms to do not require.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Name the RNA molecules involved in protein expression and synthesis that are found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms, and name the RNA molecules involved in protein expression and synthesis only in eukaryotic organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



