Deck 9: Glycolysis: a Paradigm of Metabolic Regulation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/100
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Glycolysis: a Paradigm of Metabolic Regulation
1
Which of the following metabolic pathways is only found in plants?
A) glycolysis
B) citrate cycle
C) photosynthesis
D) urea cycle
A) glycolysis
B) citrate cycle
C) photosynthesis
D) urea cycle
photosynthesis
2
What is the main difference between energy conversion pathways and metabolite synthesis pathways?
A) Energy conversion pathways produce ATP.
B) Energy conversion pathways deplete ATP.
C) Metabolite synthesis pathway uses ATP to break down metabolites.
D) Metabolite synthesis pathway uses ATP to break down pyruvate.
A) Energy conversion pathways produce ATP.
B) Energy conversion pathways deplete ATP.
C) Metabolite synthesis pathway uses ATP to break down metabolites.
D) Metabolite synthesis pathway uses ATP to break down pyruvate.
Energy conversion pathways produce ATP.
3
Glucose and fructose are both C6H1 2O6. What is the structural difference between them?
A) Glucose is a five-membered ring and fructose is a six-membered ring.
B) Fructose is a five-membered ring and glucose is a six-membered ring.
C) Glucose is a linear molecule and fructose is a ring.
D) Glucose is found in the boat conformation and fructose is a chair conformation.
A) Glucose is a five-membered ring and fructose is a six-membered ring.
B) Fructose is a five-membered ring and glucose is a six-membered ring.
C) Glucose is a linear molecule and fructose is a ring.
D) Glucose is found in the boat conformation and fructose is a chair conformation.
Fructose is a five-membered ring and glucose is a six-membered ring.
4
For the following reaction A B, if at equilibrium DG ' > 0, what can be said about the directionality of the reaction?
A) strongly favored in the forward direction
B) strongly favored in the reverse direction
C) strongly favored in both directions
D) Not enough information is given.
A) strongly favored in the forward direction
B) strongly favored in the reverse direction
C) strongly favored in both directions
D) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Calculate the net G ' for the following series of reactions: 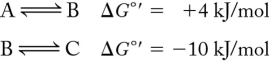
A) 14 kJ/mol
B) -6 kJ/mol
C) 6 kJ/mol
D) 0 kJ/mol
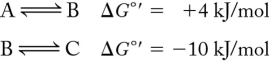
A) 14 kJ/mol
B) -6 kJ/mol
C) 6 kJ/mol
D) 0 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is an energy conversion pathway?
A) urea cycle
B) citrate cycle
C) nitrogen fixation and assimilation
D) fatty acid degradation and synthesis
A) urea cycle
B) citrate cycle
C) nitrogen fixation and assimilation
D) fatty acid degradation and synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A chiral center is an atom with
A) two different functional groups and a strong dipole.
B) four different functional groups and which lacks a plane of symmetry.
C) all the same functional groups and a plane of symmetry.
D) the ability to hydrogen bond.
A) two different functional groups and a strong dipole.
B) four different functional groups and which lacks a plane of symmetry.
C) all the same functional groups and a plane of symmetry.
D) the ability to hydrogen bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Metabolism is best defined as a collection of
A) biochemical reactions that convert chemical energy into work.
B) biochemical reactions that convert mechanical energy into work.
C) enzymes that convert glucose into carbon dioxide.
D) enzymes that convert amino acids into proteins.
A) biochemical reactions that convert chemical energy into work.
B) biochemical reactions that convert mechanical energy into work.
C) enzymes that convert glucose into carbon dioxide.
D) enzymes that convert amino acids into proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following pathways are found in both plants and animals?
A) photosynthesis and carbon fixation
B) urea cycle
C) nitrogen fixation
D) citrate cycle
A) photosynthesis and carbon fixation
B) urea cycle
C) nitrogen fixation
D) citrate cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Flux is defined as the rate at which is/are interconverted.
A) enzymes
B) metabolites
C) sugars
D) energy
A) enzymes
B) metabolites
C) sugars
D) energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Compare the structure of an aldose to a ketose.
A) Ketose has a carbon backbone with an aldehyde group at the end of the molecule, whereas aldose has a ketone group at the end of the molecule.
B) Ketose has a carbon backbone with a ketone group at the end of the molecule, whereas aldose has an aldehyde group at the end of the molecule.
C) Both have a carbon backbone where ketose has a ketone group at the end of the molecule, and aldose also has an aldehyde group at the end of the molecule.
D) Both have a carbon backbone where ketose has a ketone group on the second carbon in the molecule, and aldose also has an aldehyde group at the end of the molecule.
A) Ketose has a carbon backbone with an aldehyde group at the end of the molecule, whereas aldose has a ketone group at the end of the molecule.
B) Ketose has a carbon backbone with a ketone group at the end of the molecule, whereas aldose has an aldehyde group at the end of the molecule.
C) Both have a carbon backbone where ketose has a ketone group at the end of the molecule, and aldose also has an aldehyde group at the end of the molecule.
D) Both have a carbon backbone where ketose has a ketone group on the second carbon in the molecule, and aldose also has an aldehyde group at the end of the molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Catabolic pathways are always paired with anabolic pathways. Why?
A) Catabolic pathways build up new molecules and anabolic break down molecules.
B) Catabolic pathways break down molecules and anabolic build up new molecules.
C) Both require ATP to operate.
D) Both require redox reactions to operate.
A) Catabolic pathways build up new molecules and anabolic break down molecules.
B) Catabolic pathways break down molecules and anabolic build up new molecules.
C) Both require ATP to operate.
D) Both require redox reactions to operate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
How can an unfavorable reaction ( G ' > 0) still occur in a metabolic pathway?
A) Link it to another unfavorable reaction.
B) Link it to a favorable reaction.
C) They cannot be used in metabolic pathway reactions.
D) Increase the temperature of the reaction.
A) Link it to another unfavorable reaction.
B) Link it to a favorable reaction.
C) They cannot be used in metabolic pathway reactions.
D) Increase the temperature of the reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is the correct formula for glucose?
A)C12H22O11
B) C6H 12O6
C) C6H6O6
D) C14N2H 18O5
A)C12H22O11
B) C6H 12O6
C) C6H6O6
D) C14N2H 18O5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A shared intermediate can be defined as a molecule that is
A) a reactant in a pathway.
B) the final product of a pathway.
C) the final product of a pathway and the reactant of the next pathway.
D) favorable to produce.
A) a reactant in a pathway.
B) the final product of a pathway.
C) the final product of a pathway and the reactant of the next pathway.
D) favorable to produce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What may be the root cause of the slowing of the flux of metabolites through the glycolysis and gluconeogenesis pathways in your body?
A) elevated levels of amino acids in the body
B) elevated levels of glycogen in the body
C) lowered levels of protein synthesis
D) lowered levels of enzyme activity
A) elevated levels of amino acids in the body
B) elevated levels of glycogen in the body
C) lowered levels of protein synthesis
D) lowered levels of enzyme activity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the following series of reactions, what is the shared intermediate? 
A) glucose-6-P
B) fructose-6-P
C) ATP
D) fructose-1,6-P

A) glucose-6-P
B) fructose-6-P
C) ATP
D) fructose-1,6-P

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Review the figure below. Shared intermediates are used so effectively in coupled reactions because they 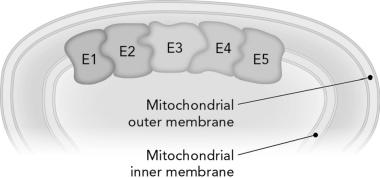
A) allow products to diffuse through membrane to increase concentration gradient.
B) increase the value of G ' .
C) decrease the value of Q.
D) limit product diffusion and allow intermediates to channel from one enzyme to the next.

A) allow products to diffuse through membrane to increase concentration gradient.
B) increase the value of G ' .
C) decrease the value of Q.
D) limit product diffusion and allow intermediates to channel from one enzyme to the next.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In the reaction A B, if at equilibrium [B] >> [A], what can be said about the directionality of the reaction?
A) strongly favored in the forward direction
B) strongly favored in the reverse direction
C) strongly favored in both directions
D) Not enough information is given.
A) strongly favored in the forward direction
B) strongly favored in the reverse direction
C) strongly favored in both directions
D) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Is the net reaction favorable for the following series of coupled reactions? 
A) Yes, G ' < 0
B) No, G ' < 0
C) Yes, G ' > 0
D) No, G ' > 0

A) Yes, G ' < 0
B) No, G ' < 0
C) Yes, G ' > 0
D) No, G ' > 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Sucrose is a nonreducing sugar. Why?
A) Sucrose does not contain an aldehyde functional group.
B) Sucrose does not react with heat.
C) Sucrose is a pyranose that cannot be reacted with copper.
D) Sucrose is a disaccharide that cannot be converted to an open chain.
A) Sucrose does not contain an aldehyde functional group.
B) Sucrose does not react with heat.
C) Sucrose is a pyranose that cannot be reacted with copper.
D) Sucrose is a disaccharide that cannot be converted to an open chain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Explain the difference between a Fisher projection and a Haworth projection.
A) Fischer projections illustrate the cyclic form, whereas Haworth projections represent the linear form.
B) The Haworth projection illustrates the six-membered rings, whereas the Fischer projection represents the five-membered rings.
C) Haworth projections illustrate the cyclic form, whereas Fischer projections represent the linear form.
D) Fischer projections show the boat conformation, whereas Haworth projections show the chair conformation.
A) Fischer projections illustrate the cyclic form, whereas Haworth projections represent the linear form.
B) The Haworth projection illustrates the six-membered rings, whereas the Fischer projection represents the five-membered rings.
C) Haworth projections illustrate the cyclic form, whereas Fischer projections represent the linear form.
D) Fischer projections show the boat conformation, whereas Haworth projections show the chair conformation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In the following figure, what is the linkage between the two monosaccharide units and is this a reducing sugar? 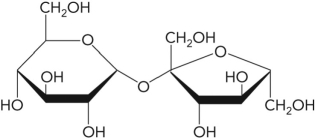
A) " 1 2, nonreducing"
B) " 1 1, nonreducing"
C) " 1 2, reducing"
D) " 1 2, reducing"

A) " 1 2, nonreducing"
B) " 1 1, nonreducing"
C) " 1 2, reducing"
D) " 1 2, reducing"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In which of the following metabolic conversions is ATP "consumed" during glycolysis?
A) 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate 3-phosphoglycerate
B) glucose glucose-6-phosphate
C) 2-Phosphoglycerate 3-phosphoglycerate
D) glucose-6-phosphate fructose-6-phosphate
A) 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate 3-phosphoglycerate
B) glucose glucose-6-phosphate
C) 2-Phosphoglycerate 3-phosphoglycerate
D) glucose-6-phosphate fructose-6-phosphate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of following is an anomeric pair?
A) "D-glucose and D-fructose"
B) "D-glucose and L-fructose"
C) "D-glucose and L-glucose"
D) " -D-glucose and -D-glucose"
A) "D-glucose and D-fructose"
B) "D-glucose and L-fructose"
C) "D-glucose and L-glucose"
D) " -D-glucose and -D-glucose"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
During the cyclization of D-glucose, where is a new chiral center formed?
A) C-1
B) C-3
C) C-4
D) C-5
A) C-1
B) C-3
C) C-4
D) C-5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is NOT a reason why glycolysis is considered one of the core metabolic pathways in nature?
A) Glycolytic enzymes are hugely conserved among all living organisms.
B) It is a primary pathway for ATP generation under anaerobic conditions.
C) Metabolites of glycolysis are precursors for a large number of interdependent pathways.
D) It is a primary pathway for nitrogen generation.
A) Glycolytic enzymes are hugely conserved among all living organisms.
B) It is a primary pathway for ATP generation under anaerobic conditions.
C) Metabolites of glycolysis are precursors for a large number of interdependent pathways.
D) It is a primary pathway for nitrogen generation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Define ketose.
A) Only ketose molecules have CH2OH.
B) Ketose molecules have ketone functional groups.
C) Ketose molecules have aldehyde functional groups.
D) Ketose molecules are all five-membered rings.
A) Only ketose molecules have CH2OH.
B) Ketose molecules have ketone functional groups.
C) Ketose molecules have aldehyde functional groups.
D) Ketose molecules are all five-membered rings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The glycolytic pathway is responsible for passing molecules to which other pathways?
A) citrate cycle and nitrogen fixation
B) photosynthesis and oxidative phosphorylation
C) citrate cycle and oxidative phosphorylation
D) urea cycle and fatty acid synthesis
A) citrate cycle and nitrogen fixation
B) photosynthesis and oxidative phosphorylation
C) citrate cycle and oxidative phosphorylation
D) urea cycle and fatty acid synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What does glycolysis accomplish for the cell?
A) It generates ADP for the cell to be used in other cycles.
B) It generates ATP and pyruvate for the cell to be used in other cycles.
C) It generates glucose to be used for storage.
D) It generates CO2 that is exhaled.
A) It generates ADP for the cell to be used in other cycles.
B) It generates ATP and pyruvate for the cell to be used in other cycles.
C) It generates glucose to be used for storage.
D) It generates CO2 that is exhaled.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the relationship between the molecules in the figure below? 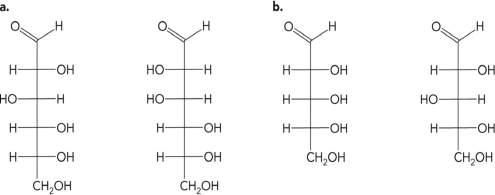
A) They are isomers.
B) They are anomers.
C) They are epimers.
D) They are identical.

A) They are isomers.
B) They are anomers.
C) They are epimers.
D) They are identical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The test using copper to determine blood glucose levels is called a test.
A) glycolysis
B) phosphorylation
C) Benedict's
D) McKee's
A) glycolysis
B) phosphorylation
C) Benedict's
D) McKee's

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following best defines substrate-level phosphorylation?
A) direct transfer of a Pi to an ADP
B) direct transfer of a Pi to an ATP
C) indirect transfer of a Pi to an ATP
D) indirect transfer of a Pi to glucose
A) direct transfer of a Pi to an ADP
B) direct transfer of a Pi to an ATP
C) indirect transfer of a Pi to an ATP
D) indirect transfer of a Pi to glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Define aldose.
A) Only aldose molecules have CH2OH.
B) Aldose molecules have ketone functional groups.
C) Aldose molecules have aldehyde functional groups.
D) Aldose molecules are all five-membered rings.
A) Only aldose molecules have CH2OH.
B) Aldose molecules have ketone functional groups.
C) Aldose molecules have aldehyde functional groups.
D) Aldose molecules are all five-membered rings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following compounds contains a "high-energy" bond and is used to produce ATP by substrate-level phosphorylation in glycolysis?
A) glucose
B) fructose-1,6-BP
C) 3-phosphoglycerate
D) 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
A) glucose
B) fructose-1,6-BP
C) 3-phosphoglycerate
D) 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Anomers differ from each other by changes at the carbon.
A) chiral
B) C-2
C) C-3
D) C-1
A) chiral
B) C-2
C) C-3
D) C-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is the correct net reaction for glycolysis?
A) glucose + 2 ATP 2 lactate + 2 ADP + 2 Pi
B) glucose + 2 ADP + 2 Pi + 2 NAD+ 2 pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 4 H+
C) glucose + 2 ADP + 2 Pi 2 CH3CH2OH + 2 CO2 + 2 ATP
D) glucose + 2 ADP + 2 Pi + 2 NAD+ 2 pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + 2H2O
A) glucose + 2 ATP 2 lactate + 2 ADP + 2 Pi
B) glucose + 2 ADP + 2 Pi + 2 NAD+ 2 pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 4 H+
C) glucose + 2 ADP + 2 Pi 2 CH3CH2OH + 2 CO2 + 2 ATP
D) glucose + 2 ADP + 2 Pi + 2 NAD+ 2 pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + 2H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A carbohydrate that reacts with oxidizing agents such as Cu+2 is called a(n) sugar.
A) oxidizing
B) reducing
C) rentose
D) aldose
A) oxidizing
B) reducing
C) rentose
D) aldose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Distinguish between D and L isomers.
A) D is right handed and L is left handed.
B) D is left handed and L is right handed.
C) D and L only differ in the position of one chiral center.
D) D is the boat conformation and L is the chair conformation.
A) D is right handed and L is left handed.
B) D is left handed and L is right handed.
C) D and L only differ in the position of one chiral center.
D) D is the boat conformation and L is the chair conformation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Name the following disaccharide using descriptive nomenclature. 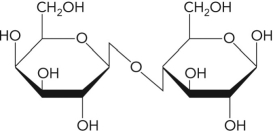
A) Glc( 1 2)Fru
B) Glc( 1 2)Glc
C) Gal( 1 4)Glc
D) Glc( 1 4)Glc

A) Glc( 1 2)Fru
B) Glc( 1 2)Glc
C) Gal( 1 4)Glc
D) Glc( 1 4)Glc

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Where in the body is glucokinase found?
A) small intestine
B) liver
C) heart
D) thyroid
A) small intestine
B) liver
C) heart
D) thyroid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In glycolysis, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate is converted to two products with a standard free-energy change ( G ' ) of 23.8 kJ/mol. Under what conditions (encountered in erythrocytes) will the free-energy change ( G) be negative, enabling the reaction to proceed to products?
A) The free-energy change will be negative if the concentrations of the two products are high relative to that of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate.
B) The reaction will not go to the right spontaneously under any conditions because the G ' is positive.
C) Under standard conditions, enough energy is released to drive the reaction to the right.
D) The free-energy change will be negative when there is a high concentration of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate relative to the concentration of products.
A) The free-energy change will be negative if the concentrations of the two products are high relative to that of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate.
B) The reaction will not go to the right spontaneously under any conditions because the G ' is positive.
C) Under standard conditions, enough energy is released to drive the reaction to the right.
D) The free-energy change will be negative when there is a high concentration of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate relative to the concentration of products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
How does phosphoglycerate kinase make glycolysis energy neutral at this step?
A) It uses ATP to produce 3-phosphoglycerate.
B) It produces 2 ATP along with 3-phosphoglycerate.
C) It results in a reaction at equilibrium.
D) It results in a reaction is endergonic.
A) It uses ATP to produce 3-phosphoglycerate.
B) It produces 2 ATP along with 3-phosphoglycerate.
C) It results in a reaction at equilibrium.
D) It results in a reaction is endergonic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In the presence of high concentrations of ADP and F6P, how does the equilibrium shift between the T state and R state of PFK-1? High concentrations of ADP and F6P
A) shift equilibrium to the R state.
B) shift equilibrium to the T state.
C) do not bind to PFK.
D) dancel each other out and have no effect.
A) shift equilibrium to the R state.
B) shift equilibrium to the T state.
C) do not bind to PFK.
D) dancel each other out and have no effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The first reaction in glycolysis that produces a high-energy compound is catalyzed by
A) aldolase.
B) triose phosphate isomerase.
C) enolase.
D) phosphofructokinase-1.
A) aldolase.
B) triose phosphate isomerase.
C) enolase.
D) phosphofructokinase-1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In the presence of lactase, lactose is cleaved into the monosaccharides glucose and
A) glucose.
B) fructose.
C) galactose.
D) maltose.
A) glucose.
B) fructose.
C) galactose.
D) maltose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If blood glucose levels are elevated, what does glucokinase do in response?
A) inhibits glycolysis
B) stimulates the production of more hexokinase
C) stimulates the release of insulin
D) inhibits production of 2,3-BPG
A) inhibits glycolysis
B) stimulates the production of more hexokinase
C) stimulates the release of insulin
D) inhibits production of 2,3-BPG

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If you are unable to digest milk products, what is the metabolic root of that issue?
A) maltase
B) lactase
C) sucrose
D) glucose oxidase
A) maltase
B) lactase
C) sucrose
D) glucose oxidase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following metabolic conversions is considered to be the major control point of glycolysis?
A) fructose-1,6-bisphosphate dihydroxyacetone phosphate + glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
B) 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate + ADP 3-Phosphoglycerate + ATP
C) 2-phosphoglyerate phosphoenolpyruvate
D) fructose-6-phosphate fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
A) fructose-1,6-bisphosphate dihydroxyacetone phosphate + glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
B) 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate + ADP 3-Phosphoglycerate + ATP
C) 2-phosphoglyerate phosphoenolpyruvate
D) fructose-6-phosphate fructose-1,6-bisphosphate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which coenzyme is required to convert glyceraldehyde-3-P into 1,3-bisphosphosphoglycerate?
A) FAD+
B) NAD+
C) ATP
D) Pi
A) FAD+
B) NAD+
C) ATP
D) Pi

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If a person has a deficiency in fructose-1-P, what effects does that have on the body?
A) Fructose-6-P concentrations increase.
B) Fructose-6-P is depleted.
C) ATP concentrations increase.
D) Glucose-6-P concentrations increase.
A) Fructose-6-P concentrations increase.
B) Fructose-6-P is depleted.
C) ATP concentrations increase.
D) Glucose-6-P concentrations increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What advantage is there to phosphoglycerate kinase having an open and closed configuration?
A) It allows water to be trapped in the active site along with the substrate.
B) It forces covalent binding of the substrate to the enzyme active site.
C) The induced-fit mechanism maximizes accessibility of active site without sacrificing hydrophobic environment.
D) Changing of the configuration of the enzyme makes the reaction exergonic.
A) It allows water to be trapped in the active site along with the substrate.
B) It forces covalent binding of the substrate to the enzyme active site.
C) The induced-fit mechanism maximizes accessibility of active site without sacrificing hydrophobic environment.
D) Changing of the configuration of the enzyme makes the reaction exergonic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
To produce 4 ATP requires 122 kJ/mol. Which reactions in the glycolytic pathway produce enough energy to be able to overcome this deficit?
A) hexokinase, phosphofructokinase-1, and pyruvate kina
B) hexokinase, phosphofructokinase-1, and pyruvate kinase
C) phosphofructokinase-1, aldolase, and pyruvate kinase
D) hexokinase, enolase, and pyruvate kinase
A) hexokinase, phosphofructokinase-1, and pyruvate kina
B) hexokinase, phosphofructokinase-1, and pyruvate kinase
C) phosphofructokinase-1, aldolase, and pyruvate kinase
D) hexokinase, enolase, and pyruvate kinase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The enzyme phosphoglycerate mutase operates at G ≈ 0 kJ/mol. That indicates that the reversibility of that reaction
A) is spontaneous.
B) occurs rapidly.
C) occurs at equilibrium.
D) is nonspontaneous.
A) is spontaneous.
B) occurs rapidly.
C) occurs at equilibrium.
D) is nonspontaneous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What effect do elevated levels of ATP have on glycolysis?
A) decrease the affinity of PFK-1 for fructose-6-P and slow rate of the pathway
B) increase the affinity of PFK-1 for fructose-6-P and increase the rate of the pathway
C) increase the concentration of PFK-1 in the R-state
D) increase the concentration of glucose entering glycolysis
A) decrease the affinity of PFK-1 for fructose-6-P and slow rate of the pathway
B) increase the affinity of PFK-1 for fructose-6-P and increase the rate of the pathway
C) increase the concentration of PFK-1 in the R-state
D) increase the concentration of glucose entering glycolysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is cleaved by aldolase. What is required for the reaction to proceed?
A) production of endergonic intermediate
B) substrate phosphorylation
C) cleaving of high-energy phosphate bond
D) formation of Schiff base intermediate
A) production of endergonic intermediate
B) substrate phosphorylation
C) cleaving of high-energy phosphate bond
D) formation of Schiff base intermediate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Predict how oxygen saturation would be affected if an individual has defective hexokinase enzymes.
A) 2,3-BPG levels are elevated and oxygen binding decreases.
B) 2,3-BPG levels are reduced and oxygen binding increases.
C) 2,3-BPG levels are elevated and oxygen binding increases.
D) 2,3-BPG levels are reduced and oxygen binding decreases.
A) 2,3-BPG levels are elevated and oxygen binding decreases.
B) 2,3-BPG levels are reduced and oxygen binding increases.
C) 2,3-BPG levels are elevated and oxygen binding increases.
D) 2,3-BPG levels are reduced and oxygen binding decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Hexokinase has a Km of 0.1 mM for glucose, whereas glucokinase has a Km of 10 mM for glucose. What does that mean for their relative affinities for glucose?
A) Glucokinase has a higher affinity.
B) Hexokinase has a higher affinity.
C) Km does not measure affinity.
D) They are different enzymes and affinity cannot be compared between enzymes.
A) Glucokinase has a higher affinity.
B) Hexokinase has a higher affinity.
C) Km does not measure affinity.
D) They are different enzymes and affinity cannot be compared between enzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The rate limiting step can be defined as a level of enzyme activity that can be regulated to be __________ even when substrate levels are _.
A) high; high
B) low; high
C) high; low
D) low; low
A) high; high
B) low; high
C) high; low
D) low; low

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Using the table below, explain why glycolysis is an overall favorable reaction pathway. 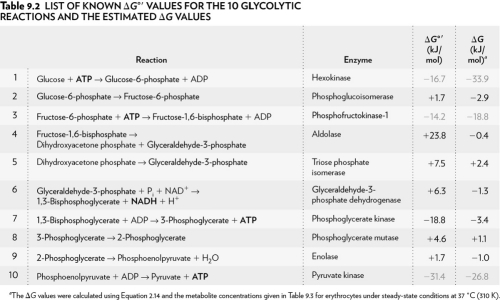
A) Overall the pathway is G > 0.
B) Overall the pathway is G = 0.
C) Overall the pathway is G < 0.
D) Overall the pathway is G < 1.

A) Overall the pathway is G > 0.
B) Overall the pathway is G = 0.
C) Overall the pathway is G < 0.
D) Overall the pathway is G < 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
During glycolysis, the steps between glucose and formation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
A) consume 2 ATP and 2 NADH.
B) consume 2 ATP.
C) produce 2 ADP and 2 NADH.
D) produce 2 ATP and 2 NADH.
A) consume 2 ATP and 2 NADH.
B) consume 2 ATP.
C) produce 2 ADP and 2 NADH.
D) produce 2 ATP and 2 NADH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which reaction in glycolysis is a redox reaction?
A) glyceraldehyde-3-P 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
B) glucose glucose-6-P
C) 2-phosphoglycerate phosphoenolpyruvate
D) fructose-6-P fructose-1,6-BP
A) glyceraldehyde-3-P 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
B) glucose glucose-6-P
C) 2-phosphoglycerate phosphoenolpyruvate
D) fructose-6-P fructose-1,6-BP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
List three ways in which flux is controlled through glycolysis.
A) regulation of aldolase, PFK-1, and supply and demand of intermediates
B) regulation of glucokinase, fructokinase, and number of intermediates
C) regulation of glucokinase, PFK-1, and concentration of glucose
D) regulation of glucokinase, PFK-1, and supply and demand of intermediates
A) regulation of aldolase, PFK-1, and supply and demand of intermediates
B) regulation of glucokinase, fructokinase, and number of intermediates
C) regulation of glucokinase, PFK-1, and concentration of glucose
D) regulation of glucokinase, PFK-1, and supply and demand of intermediates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate is converted to two products with a standard free energy of 23.8 kJ/mol. Under what condition(s) will this reaction become spontaneous?
A) spontaneous under any conditions
B) spontaneous under all conditions
C) when there is a high concentration of products relative to the concentration of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
D) when there is a low concentration of products relative to the concentration of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
A) spontaneous under any conditions
B) spontaneous under all conditions
C) when there is a high concentration of products relative to the concentration of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
D) when there is a low concentration of products relative to the concentration of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What would the effect be of a lack of lactate dehydrogenase?
A) buildup of glucose
B) buildup of CO2
C) deficiency of ATP
D) deficiency of pyruvate
A) buildup of glucose
B) buildup of CO2
C) deficiency of ATP
D) deficiency of pyruvate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The NADH that is produced by glycolysis under anaerobic conditions is regenerated to NAD+ by the conversion of
A) acetaldehyde ethanol.
B) lactate pyruvate.
C) phosphoenolpyruvate pyruvate.
D) pyruvate lactate.
A) acetaldehyde ethanol.
B) lactate pyruvate.
C) phosphoenolpyruvate pyruvate.
D) pyruvate lactate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Using glucose metabolism, justify the following statement: Metabolic pathways are highly interdependent and are exquisitely controlled by enzyme activity levels and substrate bioavailability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
An infant who obtains nourishment from milk and who has galactosemia is unable to convert
A) galactose-1-P to glucose-6-P.
B) glucose-6-P to galactose-1-P.
C) galactose-1-P to glucose-1-P.
D) glucose-1-P to galactose-1-P.
A) galactose-1-P to glucose-6-P.
B) glucose-6-P to galactose-1-P.
C) galactose-1-P to glucose-1-P.
D) glucose-1-P to galactose-1-P.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Given figures A and B below, label the chiral center on each and state if the molecule is a D or L enantiomer.
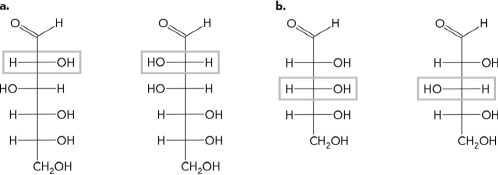


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Illustrate both the Fisher and Haworth projections for glucose and fructose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Galactosemia is deficiency in which enzyme?
A) galactokinase
B) galactose-1-P uridyltransferase
C) UDP-galactose 4-epimerase
D) phosphoglucomutase
A) galactokinase
B) galactose-1-P uridyltransferase
C) UDP-galactose 4-epimerase
D) phosphoglucomutase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
List the major metabolic pathways in animals and classify each as either an energy conversion pathway or a synthesis/degradation pathway

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
List the major metabolic pathways in plants and classify each as either an energy conversion pathway or a synthesis/degradation pathway.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What is the potential metabolic fate of pyruvate under aerobic conditions?
A) produce lactate
B) produce ethanol
C) produce carbon dioxide and water
D) produce glucose
A) produce lactate
B) produce ethanol
C) produce carbon dioxide and water
D) produce glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of these cofactors participates directly in MOST of the redox reactions in the fermentation of glucose to lactate?
A) ADP
B) ATP
C) NAD+/NADH
D) FAD/FADH2
A) ADP
B) ATP
C) NAD+/NADH
D) FAD/FADH2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
What is the potential metabolic fate of pyruvate during strenuous exercise?
A) produce lactate
B) produce ethanol
C) produce carbon dioxide and water
D) produce glucose
A) produce lactate
B) produce ethanol
C) produce carbon dioxide and water
D) produce glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Glucokinase is a molecular sensor for which molecule?
A) glucose
B) lactose
C) galactose
D) maltose
A) glucose
B) lactose
C) galactose
D) maltose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which enzyme is the main regulator of glycolysis?
A) hexokinase
B) PFK-1
C) pyruvate kinase
D) aldolase
A) hexokinase
B) PFK-1
C) pyruvate kinase
D) aldolase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What is the fate of pyruvate in the presence of yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae?
A) converts to CO2 and ethanol
B) converts to H2O and CO2
C) converts to lactate and ethanol
D) converts to lactate and glucose
A) converts to CO2 and ethanol
B) converts to H2O and CO2
C) converts to lactate and ethanol
D) converts to lactate and glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
When a mixture of glucose 6-phosphate and fructose 6-phosphate is incubated with the enzyme phosphohexose isomerase, the final mixture contains twice as much glucose 6-phosphate as fructose 6-phosphate. Which one of the following statements is MOST correct, when applied to the reaction below (R = 8.315 J/mol·K and T = 298 K)?
Glucose 6-phosphate fructose 6-phosphate
A) " G ' is +1.7 kJ/mol."
B) " G ' is -1.7 kJ/mol."
C) " G ' is zero."
D) "It is not possible to calculate G ' "
Glucose 6-phosphate fructose 6-phosphate
A) " G ' is +1.7 kJ/mol."
B) " G ' is -1.7 kJ/mol."
C) " G ' is zero."
D) "It is not possible to calculate G ' "

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



