Deck 4: Protein Structure
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/100
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Protein Structure
1
If the isoelectric point (pI) for an amino acid is at point A, what is the charge on the amino acid at point B? 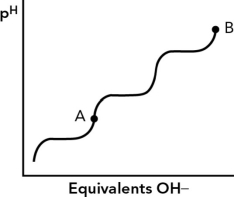
A) "0"
B) "-2"
C) "+2
D) "-1"

A) "0"
B) "-2"
C) "+2
D) "-1"
"-2"
2
For the alanine titration curve shown below, which best describes point A? 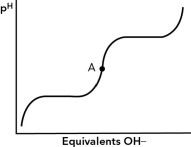
A) a buffer region
B) isoelectric point
C) second equivalence point
D) pH = pKa

A) a buffer region
B) isoelectric point
C) second equivalence point
D) pH = pKa
isoelectric point
3
What is the peptide sequence Asp-Gln-Gly-Ser, using one-letter abbreviations for the amino acids?
A) AGYS
B) DNGC
C) DQGS
D) EGYS
A) AGYS
B) DNGC
C) DQGS
D) EGYS
DQGS
4
The amino acid with the neutral side chain at neutral pH is
A) asparagine.
B) aspartate.
C) arginine.
D) glutamate.
A) asparagine.
B) aspartate.
C) arginine.
D) glutamate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The chirality of naturally occurring amino acids in proteins is
A) R.
B) L.
C) D.
D) the same as glyceraldehyde.
A) R.
B) L.
C) D.
D) the same as glyceraldehyde.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which amino acid side chain from the list below is the most polar?
A) Gln
B) Ala
C) Leu
D) Phe
A) Gln
B) Ala
C) Leu
D) Phe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the pI of the dipeptide shown? (Use the pK as given.) 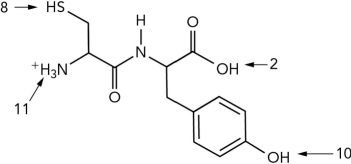
A) 0
B) 5
C) 9
D) 10.5

A) 0
B) 5
C) 9
D) 10.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which statement about amino acids is true?
A) Most common natural amino acids in proteins are L-amino acids.
B) All naturally occurring amino acids in proteins are chiral.
C) Most naturally occurring amino acids in proteins are D-amino acids.
D) Naturally occurring amino acids in proteins occur as a mixture of enantiomers.
A) Most common natural amino acids in proteins are L-amino acids.
B) All naturally occurring amino acids in proteins are chiral.
C) Most naturally occurring amino acids in proteins are D-amino acids.
D) Naturally occurring amino acids in proteins occur as a mixture of enantiomers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If the titration curve shown below is for the amino acid glycine, at which point in the curve is the pI? 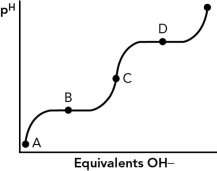
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Using the pKas shown, what is the isoelectric point of the amino acid tyrosine? 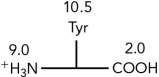
A) <1.0
B) 5.5
C) 7.0
D) 9.75

A) <1.0
B) 5.5
C) 7.0
D) 9.75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which amino acid has the highest pKa?
A) glutamate
B) asparagine
C) cysteine
D) lysine
A) glutamate
B) asparagine
C) cysteine
D) lysine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
At what point does the isoelectric point or pI occur?
A) when all of the acidic protons are neutralized with base
B) at pH = 7.0
C) at the pH when all negative charges on a zwitterion counter the positive charges
D) when the molecule has a single electric charge
A) when all of the acidic protons are neutralized with base
B) at pH = 7.0
C) at the pH when all negative charges on a zwitterion counter the positive charges
D) when the molecule has a single electric charge

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which amino acid contains a hydroxyl group?
A) valine
B) cysteine
C) threonine
D) aspartate
A) valine
B) cysteine
C) threonine
D) aspartate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What are the three-letter and one-letter abbreviations for the amino acid tyrosine?
A) Tyo, T
B) Tyr, R
C) Tro, Y
D) Tyr, Y
A) Tyo, T
B) Tyr, R
C) Tro, Y
D) Tyr, Y

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following are negatively charged amino acids at pH = 7?
A) Glu, Asp
B) Gln, Asn
C) Thr, Tyr
D) Cys, Asn
A) Glu, Asp
B) Gln, Asn
C) Thr, Tyr
D) Cys, Asn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Consider the whole amino acid alanine at pH =7. How many atoms (including Hs) are found in the molecule?
A) 15
B) 13
C) 10
D) 8
A) 15
B) 13
C) 10
D) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Of the 20 common amino acids, how many have a chiral -carbon?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 19
D) 20
A) 0
B) 1
C) 19
D) 20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The amino acid with the most hydrophobic side chain is
A) asparagine.
B) aspartate.
C) valine.
D) threonine.
A) asparagine.
B) aspartate.
C) valine.
D) threonine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A polypeptide has a high pI value. Which amino acids might comprise it?
A) arginine and lysine residues
B) aspartate and glutamate residues
C) the large nonpolar amino acids
D) a mixture of aspartate and arginine residues
A) arginine and lysine residues
B) aspartate and glutamate residues
C) the large nonpolar amino acids
D) a mixture of aspartate and arginine residues

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the approximate net charge of the molecule shown below at pH 7? 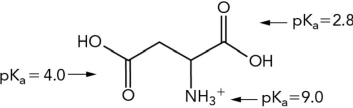
A) "+1"
B) "0"
C) "-1"
D) "-2"

A) "+1"
B) "0"
C) "-1"
D) "-2"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
To what organic reaction class does peptide bond formation belong?
A) condensation
B) isomerization
C) oxidation
D) addition
A) condensation
B) isomerization
C) oxidation
D) addition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which statement regarding protein secondary structures is correct?
A) " -strands allow -helices to interact with one another."
B) "Protein -helices alternate with -strands in stabilizing protein structure."
C) "Protein -helices are left handed, whereas -sheets are right handed in arrangement."
D) "Protein -helices and -strands differ in that -helices are stabilized by intrahelical hydrogen bonds, whereas -strands are stabilized by hydrogen bonds across adjacent strands."
A) " -strands allow -helices to interact with one another."
B) "Protein -helices alternate with -strands in stabilizing protein structure."
C) "Protein -helices are left handed, whereas -sheets are right handed in arrangement."
D) "Protein -helices and -strands differ in that -helices are stabilized by intrahelical hydrogen bonds, whereas -strands are stabilized by hydrogen bonds across adjacent strands."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The peptide bond is stronger than the ester bond. What structural feature of the peptide bond gives it additional bond strength?
A) Resonance structures give the peptide bond some double bond character.
B) The peptide bond is between carbon and nitrogen instead of carbon and oxygen atoms.
C) The peptide bond is more polar.
D) Peptide bonds can hydrogen bond.
A) Resonance structures give the peptide bond some double bond character.
B) The peptide bond is between carbon and nitrogen instead of carbon and oxygen atoms.
C) The peptide bond is more polar.
D) Peptide bonds can hydrogen bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
How many possible unique triplet codons could there be in a genome?
A) 3
B) 20
C) 36
D) 64
A) 3
B) 20
C) 36
D) 64

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which interaction largely stabilizes protein secondary (2 ) structures?
A) disulfide bonds
B) hydrogen bonding
C) hydrophobic packing
D) metal ions
A) disulfide bonds
B) hydrogen bonding
C) hydrophobic packing
D) metal ions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which linear sequence of bonded atoms can be found in the backbone of polypeptides?
A) C-N-N-C
B) C-C-N-C
C) N-C-C-C
D) C-O-C-N
A) C-N-N-C
B) C-C-N-C
C) N-C-C-C
D) C-O-C-N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Protein secondary structures such as -helices and -sheets are stabilized mainly by
A) ionic interactions.
B) disulfide bond formation.
C) van der Waals forces.
D) hydrogen bond formation.
A) ionic interactions.
B) disulfide bond formation.
C) van der Waals forces.
D) hydrogen bond formation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which represents the correct arrangement of bonding in a peptide bond?
A)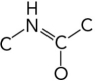
B)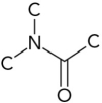
C)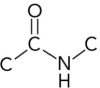
D)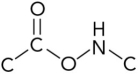
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What do Ramachandran plots show?
A) Only some and angles are commonly found in proteins.
B) The chiral carbon in amino acids is found largely in the S configuration.
C) Peptide backbones form mostly linear chains.
D) The -carbon is chiral.
A) Only some and angles are commonly found in proteins.
B) The chiral carbon in amino acids is found largely in the S configuration.
C) Peptide backbones form mostly linear chains.
D) The -carbon is chiral.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The dipole moment associated with a peptide bond proceeds from which amide?
A) the C to the O atom
B) the C to the N atom
C) the O to the H atom
D) the H to the O atom
A) the C to the O atom
B) the C to the N atom
C) the O to the H atom
D) the H to the O atom

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
All of the following are stabilizing forces in maintaining a stable protein tertiary (3 ) structure, EXCEPT
A) H bonds.
B) temperature.
C) hydrophobic interactions.
D) electrostatic attractions.
A) H bonds.
B) temperature.
C) hydrophobic interactions.
D) electrostatic attractions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The peptide bond
A) is most stable in the cis configuration.
B) has a mix of single and double bond characters.
C) can rotate around the carbonyl and N bond but not around the -carbon and N bond.
D) can function as a weak acid and weak base.
A) is most stable in the cis configuration.
B) has a mix of single and double bond characters.
C) can rotate around the carbonyl and N bond but not around the -carbon and N bond.
D) can function as a weak acid and weak base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The and angles are the
A) flatness of the peptide bond.
B) torsion angles on either side of the -carbon.
C) angles of each amino acid side chain.
D) peptide bond plane angle.
A) flatness of the peptide bond.
B) torsion angles on either side of the -carbon.
C) angles of each amino acid side chain.
D) peptide bond plane angle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A mutation in a gene results in the least amount of damage to the resulting protein.
A) missense
B) nonsense
C) frameshift
D) silent
A) missense
B) nonsense
C) frameshift
D) silent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
All of the following are types of protein secondary structure EXCEPT
A) " -sheets."
B) " -helixes."
C) " -helixes."
D) " -turns."
A) " -sheets."
B) " -helixes."
C) " -helixes."
D) " -turns."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
How many possible protein primary structures are there for a tripeptide given the 20 amino acids?
A) 320
B) 400
C) 203
D) 1.27 *10130
A) 320
B) 400
C) 203
D) 1.27 *10130

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Trace directly the covalently bonded backbone atoms from the N to C terminus of a dipeptide. Which atoms are found in this trace?
A) NCCNCC
B) NCCONCCO
C) NCONCO
D) CNCCNC
A) NCCNCC
B) NCCONCCO
C) NCONCO
D) CNCCNC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Use the table below to determine how many possible RNA sequences could code for the dipeptide Pro-Ala. 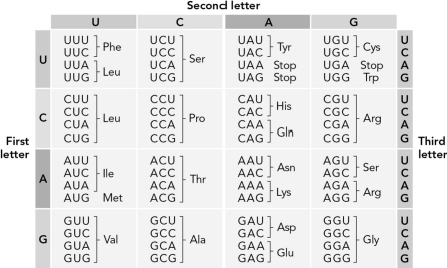
A) 1
B) 16
C) 8
D) 64

A) 1
B) 16
C) 8
D) 64

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Using the table below, determine the kind of gene mutation illustrated. ATG_AAT_CAC ATG_AAG_CAC

A) missense mutation
B) nonsense mutation
C) frameshift mutation
D) silent mutation

A) missense mutation
B) nonsense mutation
C) frameshift mutation
D) silent mutation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The points in the Ramachandran plot are derived by 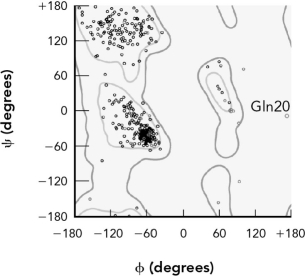
A) counting the number of amino acids and placing points in allowed regions.
B) measuring the and angles in an experimentally determined protein crystal structure.
C) placing each amino acid in regions commonly occupied by that amino acid.
D) experimentally measuring the optical rotation of polarized light.

A) counting the number of amino acids and placing points in allowed regions.
B) measuring the and angles in an experimentally determined protein crystal structure.
C) placing each amino acid in regions commonly occupied by that amino acid.
D) experimentally measuring the optical rotation of polarized light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
An -helix has the sequence: NH3+-Ser-Glu-Gly-Asp-Trp-Gln-Leu-His-Val-Phe-Ala-Lys-Val-Glu-COO-. The carbonyl oxygen (in the peptide bond) of the histidine residue is hydrogen bonded to the amide nitrogen of
A) Asp.
B) Lys.
C) Trp.
D) Ala.
A) Asp.
B) Lys.
C) Trp.
D) Ala.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which one of the following statements comparing alpha keratin and silk fibroin is true?
A) Both have covalently cross-linked strands.
B) Both are primarily -helical in character.
C) Both fibers are intracellularly located.
D) Both fibers are heavily stabilized by hydrogen bonds.
A) Both have covalently cross-linked strands.
B) Both are primarily -helical in character.
C) Both fibers are intracellularly located.
D) Both fibers are heavily stabilized by hydrogen bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
How many -turns or -loops are required to construct a -sheet composed of four antiparallel strands?
A) 0
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
A) 0
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which statement about the -helix is true?
A) "The hydrophobic interior of -helices is stabilized by the side chains of hydrophobic amino acids."
B) "The amino acid side chains point out to the sides with every third amino acid roughly lining up on one side of the helix."
C) " -Helices have backbone amide groups that are hydrogen bonded to amino acid side chains."
D) " -Helices have 5 amino acids per one turn of the helix."
A) "The hydrophobic interior of -helices is stabilized by the side chains of hydrophobic amino acids."
B) "The amino acid side chains point out to the sides with every third amino acid roughly lining up on one side of the helix."
C) " -Helices have backbone amide groups that are hydrogen bonded to amino acid side chains."
D) " -Helices have 5 amino acids per one turn of the helix."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Protein tertiary structures
A) require the formation of disulfide bonds in order to achieve their native state.
B) are always irreversibly destroyed by the addition of denaturants, such as urea and salts, even when the denaturants are subsequently removed.
C) are often disrupted by the either very low pH or very high pH values as a result of alterations in the ionization states of acidic or basic amino acids.
D) are generally poorly defined and cannot be determined experimentally.
A) require the formation of disulfide bonds in order to achieve their native state.
B) are always irreversibly destroyed by the addition of denaturants, such as urea and salts, even when the denaturants are subsequently removed.
C) are often disrupted by the either very low pH or very high pH values as a result of alterations in the ionization states of acidic or basic amino acids.
D) are generally poorly defined and cannot be determined experimentally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following statements about -sheet structures is true?
A) The individual strands of all -sheet structures are connected by turns, helices, or loops.
B) All amino acid side chains in antiparallel and parallel -sheet structures point to one side of the sheet.
C) Parallel -sheet structures have backbone amides that directly hydrogen bond between strands, whereas antiparallel -sheets have hydrogen bonds that are offset.
D) All -sheet structures form a spiraling backbone chain.
A) The individual strands of all -sheet structures are connected by turns, helices, or loops.
B) All amino acid side chains in antiparallel and parallel -sheet structures point to one side of the sheet.
C) Parallel -sheet structures have backbone amides that directly hydrogen bond between strands, whereas antiparallel -sheets have hydrogen bonds that are offset.
D) All -sheet structures form a spiraling backbone chain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The common protein fold shown below is the fold. 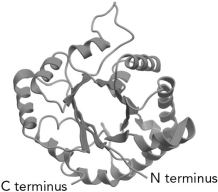
A) "Greek key"
B) "Rossman"
C) "FERM domain"
D) " / barrel"

A) "Greek key"
B) "Rossman"
C) "FERM domain"
D) " / barrel"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is the dominant secondary structure found in hair keratin?
A) " -helices"
B) "disulfide bonds"
C) " -sheets"
D) "loop structures"
A) " -helices"
B) "disulfide bonds"
C) " -sheets"
D) "loop structures"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The proteins collagen, silk fibroin, and hair keratin have all of the following in common, EXCEPT that they
A) are fibrous proteins.
B) are composed of repeating amino acid sequences.
C) are composed of -helical structures.
D) play important structural roles in biology.
A) are fibrous proteins.
B) are composed of repeating amino acid sequences.
C) are composed of -helical structures.
D) play important structural roles in biology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
How many different protein folds are recognized in the formal system of organization, referred to as SCOP: Structure Organization of Proteins?
A) 4
B) >10
C) >100
D) >1000
A) 4
B) >10
C) >100
D) >1000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following statements regarding protein domains is true?
A) Each protein has one unique domain.
B) Multiple domains require multiple subunits and a quaternary structure.
C) A domain can be composed of smaller structural units called motifs.
D) A domain is a region absent of -helices and -sheets.
A) Each protein has one unique domain.
B) Multiple domains require multiple subunits and a quaternary structure.
C) A domain can be composed of smaller structural units called motifs.
D) A domain is a region absent of -helices and -sheets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which class of protein structures does the protein shown below fit into? 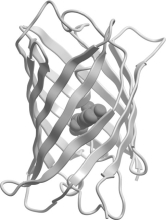
A) predominantly -helical
B) predominantly -sheet
C) intermixed -helix and -sheet
D) domains of -helix adjacent to domains of -sheet

A) predominantly -helical
B) predominantly -sheet
C) intermixed -helix and -sheet
D) domains of -helix adjacent to domains of -sheet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What is the minimum number of amino acids needed to make one turn of an -helix?
A) 3
B) 4
C) 6
D) 7
A) 3
B) 4
C) 6
D) 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What is a difference between parallel and antiparallel -sheet secondary structures?
A) Antiparallel -sheets have a larger number of stabilizing H bonds between backbone amides than parallel -sheets.
B) Parallel -sheets require a larger loop connecting together the individual peptide strands in the sheet.
C) Parallel -sheets are longer than antiparallel sheets.
D) Parallel -sheets have amino acid side chains alternating up and down, whereas antiparallel side chains alternate down and up.
A) Antiparallel -sheets have a larger number of stabilizing H bonds between backbone amides than parallel -sheets.
B) Parallel -sheets require a larger loop connecting together the individual peptide strands in the sheet.
C) Parallel -sheets are longer than antiparallel sheets.
D) Parallel -sheets have amino acid side chains alternating up and down, whereas antiparallel side chains alternate down and up.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In a standard -helix, __________ H bonds and dipole moments are found per amino acid, which stabilizes the -helical structure.
A) 1; 1
B) 1; 2
C) 2; 1
D) 2; 2
A) 1; 1
B) 1; 2
C) 2; 1
D) 2; 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following statements about -helices and -sheets are FALSE?
A) They are both incompatible with the amino acid proline.
B) They both interact with other protein elements through amino acid side chains that stick out.
C) They both contain a recurring pattern of hydrogen bonds from one peptide bond to another peptide bond.
D) They both give rise to similar tertiary structures.
A) They are both incompatible with the amino acid proline.
B) They both interact with other protein elements through amino acid side chains that stick out.
C) They both contain a recurring pattern of hydrogen bonds from one peptide bond to another peptide bond.
D) They both give rise to similar tertiary structures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which stabilizing force in protein tertiary structures is a covalent bonding force?
A) ionic bonding
B) disulfide bonding
C) hydrophobic interactions
D) van der Waals bonding
A) ionic bonding
B) disulfide bonding
C) hydrophobic interactions
D) van der Waals bonding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following statements is true about -helices?
A) The center of the helix is an open channel.
B) There are about seven amino acids per helical turn.
C) The amide backbone dipoles line up in one direction.
D) The helical backbone structure is stabilized by ionic interactions.
A) The center of the helix is an open channel.
B) There are about seven amino acids per helical turn.
C) The amide backbone dipoles line up in one direction.
D) The helical backbone structure is stabilized by ionic interactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The protein fold known as the Rossman fold is found in proteins that commonly bind
A) " -helices."
B) "nucleotides."
C) "cytochromes."
D) "membranes."
A) " -helices."
B) "nucleotides."
C) "cytochromes."
D) "membranes."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following statements about Ramachandran plots is true?
A) They are good predictors of protein tertiary structure.
B) They are needed to determine the secondary structure of a protein.
C) They show equal distributions of and angles for -helical and -sheet containing proteins.
D) They show that -sheets and -helices occupy different and angles.
A) They are good predictors of protein tertiary structure.
B) They are needed to determine the secondary structure of a protein.
C) They show equal distributions of and angles for -helical and -sheet containing proteins.
D) They show that -sheets and -helices occupy different and angles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Calculate the pI for the following dipeptide using the pKas shown.
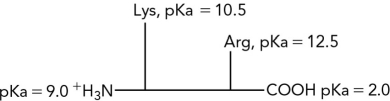


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What is believed to be the underlying cause of prion protein plaque formation?
A) The PrPSc proteins are misfolded and aggregated from PrPc proteins.
B) The unstructured N-terminal region of PrPc is thought to remain unfolded.
C) The normal PrPc proteins are aggregated.
D) The PrPSc protein adheres to and inhibits cell membranes.
A) The PrPSc proteins are misfolded and aggregated from PrPc proteins.
B) The unstructured N-terminal region of PrPc is thought to remain unfolded.
C) The normal PrPc proteins are aggregated.
D) The PrPSc protein adheres to and inhibits cell membranes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In multi-subunit proteins, such as hemoglobin, the different subunits are usually bound to one another by all of the following EXCEPT
A) hydrogen bonds.
B) electrostatic interactions.
C) hydrophobic interactions.
D) peptide bonds.
A) hydrogen bonds.
B) electrostatic interactions.
C) hydrophobic interactions.
D) peptide bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following statements about the clamp-type chaperone protein Hsp70 is correct?
A) Hsp70 uses ATP binding and hydrolysis energy to assist in the folding of a protein.
B) Hsp70 is a multi-subunit protein shaped like a large barrel, inside of which the folding protein is protected.
C) Hsp70 is most active during cell division phases.
D) Hsp70 assists in protein unfolding by hydrolyzing and remaking the protein peptide bonds.
A) Hsp70 uses ATP binding and hydrolysis energy to assist in the folding of a protein.
B) Hsp70 is a multi-subunit protein shaped like a large barrel, inside of which the folding protein is protected.
C) Hsp70 is most active during cell division phases.
D) Hsp70 assists in protein unfolding by hydrolyzing and remaking the protein peptide bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Of the three proposed models of globular protein folding, which one describes formation of an initial disordered protein interior, followed next by ordering of secondary and tertiary structures?
A) mutant globule
B) hydrophobic collapse model
C) framework model
D) nucleation model
A) mutant globule
B) hydrophobic collapse model
C) framework model
D) nucleation model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which gives rise to a favorable enthalpic ( S) driving force for protein folding?
A) The lining up of hydrogen bonds as the protein folds.
B) The limiting of possible conformations as the protein folds.
C) The decrease in ordered water molecules as hydrophobic amino acids pack together.
D) The stabilization caused by favorable electrostatic interactions of amino acid side chains.
A) The lining up of hydrogen bonds as the protein folds.
B) The limiting of possible conformations as the protein folds.
C) The decrease in ordered water molecules as hydrophobic amino acids pack together.
D) The stabilization caused by favorable electrostatic interactions of amino acid side chains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The essential amino acids in adult humans are those that are required in our diet because of a lack of the biosynthetic pathway in our cells. The single-letter abbreviations for these amino acids are WVMILKFHT. Name these amino acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Draw the structure of the amino acid glutamate showing the predominant form found at pH
7.0 (assume -NH3+ pKa 9.0; Glu pKR 4.0; -COOH pKa 2.0).
7.0 (assume -NH3+ pKa 9.0; Glu pKR 4.0; -COOH pKa 2.0).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Of the three proposed models of globular protein folding, which one describes the initial formation of all secondary structures, followed by the arrangement of those secondary structures into a final tertiary structure?
A) mutant globule
B) hydrophobic collapse model
C) framework model
D) nucleation model
A) mutant globule
B) hydrophobic collapse model
C) framework model
D) nucleation model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following statements about the chamber-type chaperone protein GroEL-GroES is correct?
A) GroEL-GroES requires the hydrolysis of multiple ATPs to assist in the folding of a protein.
B) GroEL-GroES recycles misfolded proteins by recovering individual amino acids.
C) GroEL-GroES assists in protein unfolding by hydrolyzing and remaking the protein peptide bonds.
D) GroEL-GroES uses GroEL as a cap, trapping an unfolded protein in the GroES chamber.
A) GroEL-GroES requires the hydrolysis of multiple ATPs to assist in the folding of a protein.
B) GroEL-GroES recycles misfolded proteins by recovering individual amino acids.
C) GroEL-GroES assists in protein unfolding by hydrolyzing and remaking the protein peptide bonds.
D) GroEL-GroES uses GroEL as a cap, trapping an unfolded protein in the GroES chamber.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
At the interface between subunits of a protein with quaternary structure, which of the following interactions between amino acid side chains would contribute to the stability of the dimer?
A) glutamate-aspartate.
B) leucine-aspartate.
C) glutamate-lysine.
D) phenylalaninelysine.
A) glutamate-aspartate.
B) leucine-aspartate.
C) glutamate-lysine.
D) phenylalaninelysine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What is the difference between clamp-type and chamber-type chaperone proteins?
A) One uses ATP and the other does not.
B) One folds proteins, whereas the other just protects them from unfolding.
C) They are shaped differently.
D) One type is found extracellularly and one intracellularly.
A) One uses ATP and the other does not.
B) One folds proteins, whereas the other just protects them from unfolding.
C) They are shaped differently.
D) One type is found extracellularly and one intracellularly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
In the Anfinsen experiment with the unfolding of RNaseA, what order could the chemical reagents be removed in order to achieve an inactive protein?
A) Remove denaturant first and reductant second.
B) Simultaneously remove denaturant and reductant.
C) Remove reductant first, denaturant second, and then finally add back reductant.
D) Remove reductant first and denaturant second.
A) Remove denaturant first and reductant second.
B) Simultaneously remove denaturant and reductant.
C) Remove reductant first, denaturant second, and then finally add back reductant.
D) Remove reductant first and denaturant second.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Christian Anfinsen showed in a famous experiment that it is possible to unfold a protein and refold it to obtain a functional protein. Which two reagents were used in this experiment to unfold the protein?
A) detergent and salt
B) urea and -mercaptoethanol
C) acid and base
D) ethanol and -mercaptoethanol
A) detergent and salt
B) urea and -mercaptoethanol
C) acid and base
D) ethanol and -mercaptoethanol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Cells deal with misfolded proteins by
A) storing them for later energy use.
B) collecting and excreting them from the cell.
C) aggregating them to maintain the cell's structural integrity.
D) degrading them to individual amino acids.
A) storing them for later energy use.
B) collecting and excreting them from the cell.
C) aggregating them to maintain the cell's structural integrity.
D) degrading them to individual amino acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Cystic fibrosis results from the misfolding of proteins that never get the chance to properly insert into the membranes of lung epithelial cells and perform their function. This is generally referred to as a disease.
A) loss-of-function protein folding
B) chaperonin-unassisted folding
C) gain-of-function protein folding
D) amyloid plaque-forming
A) loss-of-function protein folding
B) chaperonin-unassisted folding
C) gain-of-function protein folding
D) amyloid plaque-forming

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
It is important for cells to degrade misfolded proteins. If misfolded proteins are not degraded, the misfolded proteins may
A) waste excessive ATP in attempts to refold them.
B) aggregate and interfere with normal cellular function.
C) eventually refold, but not until excessive and sometimes fatal levels of cellular energy are spent.
D) be excreted from the cell rather than recycled for building blocks.
A) waste excessive ATP in attempts to refold them.
B) aggregate and interfere with normal cellular function.
C) eventually refold, but not until excessive and sometimes fatal levels of cellular energy are spent.
D) be excreted from the cell rather than recycled for building blocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
What is a current hypothesis that explains the infectious nature of prion diseases?
A) The virus responsible for prion diseases is transmissible.
B) Unfavorable environmental factors negatively influence healthy cells.
C) The small molecule denaturants found in infected cells are passed on to healthy cells.
D) The presence of an improperly folded prion protein promotes the misfolding of normal prion proteins.
A) The virus responsible for prion diseases is transmissible.
B) Unfavorable environmental factors negatively influence healthy cells.
C) The small molecule denaturants found in infected cells are passed on to healthy cells.
D) The presence of an improperly folded prion protein promotes the misfolding of normal prion proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The following amino acid is discovered in a newly isolated protein. What would it be called, and does it represent a new amino acid?
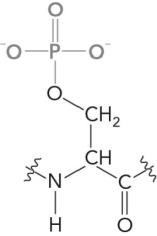


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Shown is the titration curve for the amino acid aspartic acid. Draw the predominant protonation state of aspartic acid found at point A in the curve.
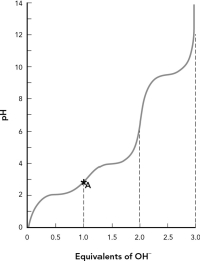


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



