Deck 3: Nucleic Acid Structure and Function
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/100
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Nucleic Acid Structure and Function
1
Increasing the ion concentration increases the Tm because the ions
A) bind to the phosphate groups of the DNA backbone and increase stability.
B) bind to the nucleic acids and disrupt the base pairs, decreasing stability.
C) increase the base length of the DNA, increasing stability.
D) associate with the ribose sugars, decreasing stability.
A) bind to the phosphate groups of the DNA backbone and increase stability.
B) bind to the nucleic acids and disrupt the base pairs, decreasing stability.
C) increase the base length of the DNA, increasing stability.
D) associate with the ribose sugars, decreasing stability.
bind to the phosphate groups of the DNA backbone and increase stability.
2
Which form(s) of DNA exhibit(s) a zigzag arrangement?
A) A-DNA
B) B-DNA
C) Z-DNA
D) A-DNA and B-DNA
A) A-DNA
B) B-DNA
C) Z-DNA
D) A-DNA and B-DNA
Z-DNA
3
The K+ ion concentration in a DNA sample is increased from 50 mM to 100 mM. The Tm will
A) remain the same.
B) decrease.
C) increase.
D) vary unpredictably.
A) remain the same.
B) decrease.
C) increase.
D) vary unpredictably.
increase.
4
The DNA of a bacteria was isolated and it was determined that 15% of the DNA is composed of cytosine. What percentage of the DNA is guanine?
A) 15%
B) 30%
C) 35%
D) 70%
A) 15%
B) 30%
C) 35%
D) 70%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
DNA strands are considered to be antiparallel. This means the
A) phosphodiester bonds run in the same direction.
B) phosphodiester bonds run in different directions.
C) base pairs form hydrogen bonds.
D) phosphate backbone is on the outside of the helix.
A) phosphodiester bonds run in the same direction.
B) phosphodiester bonds run in different directions.
C) base pairs form hydrogen bonds.
D) phosphate backbone is on the outside of the helix.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When DNA is transcribed into RNA, the strand has the same base sequences as the RNA transcript.
A) antiparallel
B) parallel
C) coding
D) template
A) antiparallel
B) parallel
C) coding
D) template

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which form(s) of DNA exhibit(s) a right-handed helical structure?
A) A-DNA
B) B-DNA
C) Z-DNA
D) A-DNA and B-DNA
A) A-DNA
B) B-DNA
C) Z-DNA
D) A-DNA and B-DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When DNA is transcribed into RNA, the strand has the complementary sequence to the transcribed RNA.
A) antiparallel
B) parallel
C) coding
D) template
A) antiparallel
B) parallel
C) coding
D) template

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The ability to monitor the denaturation of DNA using absorbance is referred to as
A) annealing.
B) supercoiling.
C) melting temperature.
D) hyperchromic effect.
A) annealing.
B) supercoiling.
C) melting temperature.
D) hyperchromic effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
As DNA unwinds and denatures, absorbance is predicted to
A) remain the same.
B) decrease.
C) increase.
D) vary unpredictably.
A) remain the same.
B) decrease.
C) increase.
D) vary unpredictably.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The figure below shows part of the primary structure of DNA. Identify the nucleotide. 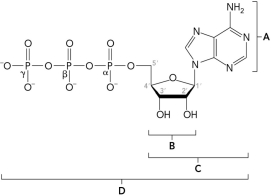
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The basic structure of DNA is a right-handed helix formed by two strands of DNA.
A) antiparallel
B) parallel
C) coding
D) template
A) antiparallel
B) parallel
C) coding
D) template

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Predict the complementary strand of the following DNA sequence: 5 ' -ATCTGAATCT-3 '
A) 5 ' -TCTAAGTCTA-3 '
B) 5 ' -TAGACTTAGA-3 '
C) 5 ' -ATCTGAATCT-3 '
D) 5 ' -AGATTCAGAT-3 '
A) 5 ' -TCTAAGTCTA-3 '
B) 5 ' -TAGACTTAGA-3 '
C) 5 ' -ATCTGAATCT-3 '
D) 5 ' -AGATTCAGAT-3 '

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The figure below shows part of the primary structure of DNA. Identify the nucleoside. 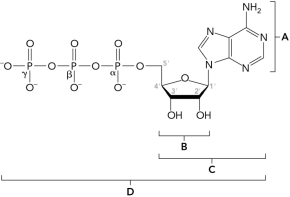
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Chargaff's rule is that the amount of
A) A = G and the amount of C = T.
B) A = C = G = T.
C) A = T and the amount of C = G.
D) A = C and the amount of G = T.
A) A = G and the amount of C = T.
B) A = C = G = T.
C) A = T and the amount of C = G.
D) A = C and the amount of G = T.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
How many base pairs per turn does B-DNA contain?
A) 10.0
B) 10.5
C) 11.0
D) 12.0
A) 10.0
B) 10.5
C) 11.0
D) 12.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The DNA double helix is considered to be a structure.
A) primary
B) secondary
C) tertiary
D) quaternary
A) primary
B) secondary
C) tertiary
D) quaternary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The DNA of a bacteria was isolated and it was determined that 15% of the DNA is composed of cytosine. What percentage of the DNA is adenine?
A) 15%
B) 30%
C) 35%
D) 70%
A) 15%
B) 30%
C) 35%
D) 70%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the melting temperature from the DNA absorbance shown in the figure below? 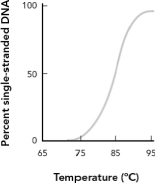
A) 80 C
B) 85 C
C) 90 C
D) 95 C

A) 80 C
B) 85 C
C) 90 C
D) 95 C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The interior stacking of the DNA bases in the double helix provides stability through
A) hydrophobic and van der Waals interactions.
B) hydrophilic and van der Waals interactions.
C) hydrophilic and ion-dipole interactions.
D) hydrophobic and ion-dipole interactions.
A) hydrophobic and van der Waals interactions.
B) hydrophilic and van der Waals interactions.
C) hydrophilic and ion-dipole interactions.
D) hydrophobic and ion-dipole interactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Predict how type II topoisomerases change the supercoil region.
A) Lk = 2
B) Lk = 1
C) Lk = -1
D) Lk = -2
A) Lk = 2
B) Lk = 1
C) Lk = -1
D) Lk = -2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Type I topoisomerase activity results in a region of DNA.
A) semiconservative
B) spliced
C) relaxed
D) unrepaired
A) semiconservative
B) spliced
C) relaxed
D) unrepaired

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following binds to DNA using a specific sequence?
A) histones
B) Lac repressor protein
C) double-stranded binding proteins
D) single-stranded binding proteins
A) histones
B) Lac repressor protein
C) double-stranded binding proteins
D) single-stranded binding proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following expresses the relationship among the linking number, twist, and writhe?
A) Tw = Lk + Wr
B) Lk = Tw - Wr
C) Lk = Wr - Tw
D) Lk = Tw + Wr
A) Tw = Lk + Wr
B) Lk = Tw - Wr
C) Lk = Wr - Tw
D) Lk = Tw + Wr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Several histones can bind to one DNA molecule, forming a repeating unit called a
A) ribozyme.
B) nucleosome.
C) topoisomerase.
D) nucleoside.
A) ribozyme.
B) nucleosome.
C) topoisomerase.
D) nucleoside.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What mediates the binding of histone proteins to DNA?
A) ionic attractions
B) London dispersion forces
C) hydrophilic interactions
D) hydrophobic interactions
A) ionic attractions
B) London dispersion forces
C) hydrophilic interactions
D) hydrophobic interactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The linking number of a relaxed DNA strand whose axis is not coiling is 30. Predict the twist and writhe of the DNA stand.
A) Wr = 0, Tw = 30
B) Wr = 30, Tw = 0
C) Wr = 15, Tw = 15
D) Wr = 30, Tw = -30
A) Wr = 0, Tw = 30
B) Wr = 30, Tw = 0
C) Wr = 15, Tw = 15
D) Wr = 30, Tw = -30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Less condensed, gene-rich chromatin is referred to as
A) nucleosomes.
B) histones.
C) heterochromatin.
D) euchromatin.
A) nucleosomes.
B) histones.
C) heterochromatin.
D) euchromatin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Type II topoisomerase enzymes are important in replication and transcription because they
A) prevent autocleavage.
B) prevent DNA cleavage.
C) relieve the positive supercoiling.
D) stabilize the cleaved complex.
A) prevent autocleavage.
B) prevent DNA cleavage.
C) relieve the positive supercoiling.
D) stabilize the cleaved complex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Calculate the linking number for a B-DNA strand that contains 735 total base pairs.
A) 50
B) 61
C) 67
D) 70
A) 50
B) 61
C) 67
D) 70

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
DNA strands containing 20 base pairs, 40 base pairs, and 60 base pairs were denatured and the results were graphed below. Identify the curve from the 60 base pair DNA strand. 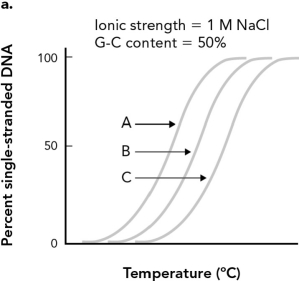
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) Not enough information is included to determine the curve.

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) Not enough information is included to determine the curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A double helix that crosses itself in a right-handed twist is referred to as a
A) positive supercoil.
B) negative supercoil.
C) topoisomer.
D) linking number.
A) positive supercoil.
B) negative supercoil.
C) topoisomer.
D) linking number.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Chromatin that consists of more condensed regions of mostly noncoding DNA are referred to as
A) nucleosomes.
B) histones.
C) heterochromatin.
D) euchromatin.
A) nucleosomes.
B) histones.
C) heterochromatin.
D) euchromatin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The proteins that bind to DNA in a sequence-independent manner are
A) histones.
B) single-stranded binding proteins.
C) Lac repressor proteins.
D) histones and single-stranded binding proteins.
A) histones.
B) single-stranded binding proteins.
C) Lac repressor proteins.
D) histones and single-stranded binding proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
During eukaryotic DNA condensation, nucleosomes are packed together to form
A) histones.
B) chromatin.
C) chromosomes.
D) genes.
A) histones.
B) chromatin.
C) chromosomes.
D) genes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A double helix that crosses itself in a left-handed twist is referred to as a
A) positive supercoil.
B) negative supercoil.
C) topoisomer.
D) linking number.
A) positive supercoil.
B) negative supercoil.
C) topoisomer.
D) linking number.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The process of condensation reduced the size of DNA by
A) 100-fold.
B) 1,000-fold.
C) 10,000-fold.
D) 100,000-fold.
A) 100-fold.
B) 1,000-fold.
C) 10,000-fold.
D) 100,000-fold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The A-T content for several DNA strands is reported below. Which strand would have the highest Tm?
A) 40% A-T
B) 50% A-T
C) 60% A-T
D) 70% A-T
A) 40% A-T
B) 50% A-T
C) 60% A-T
D) 70% A-T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Predict how type I topoisomerases change the supercoil region.
A) Lk = 2
B) Lk = 1
C) Lk = -1
D) Lk = -2
A) Lk = 2
B) Lk = 1
C) Lk = -1
D) Lk = -2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
RNA only contains which of the following bases?
A) thymine
B) adenine
C) uracil
D) guanine
A) thymine
B) adenine
C) uracil
D) guanine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The mixing and matching of novel genes in eukaryotic cells occurs through
A) operons.
B) exon shuffling.
C) promoter regions.
D) untranslated regions.
A) operons.
B) exon shuffling.
C) promoter regions.
D) untranslated regions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Identify the kinetochore in the following figure. 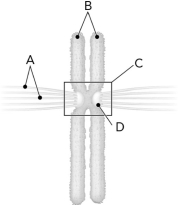
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In the eukaryotic cell, the NONcoding sequences on a gene are referred to as
A) exons.
B) operons.
C) introns.
D) promoter.
A) exons.
B) operons.
C) introns.
D) promoter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Genes found in prokaryotes that only contain a single coding sequence are referred to as
A) exons.
B) introns.
C) polycistronic.
D) monocistronic.
A) exons.
B) introns.
C) polycistronic.
D) monocistronic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In plasmid transformation, DNA is transferred when
A) bacteriophages infect bacteria.
B) foreign DNA fragments are inserted into the plasmid using multiple cloning sites.
C) there is a horizontal gene transfer during the bacteria mating process.
D) a dead bacterium releases DNA into the environment and it is obtained by another bacterium.
A) bacteriophages infect bacteria.
B) foreign DNA fragments are inserted into the plasmid using multiple cloning sites.
C) there is a horizontal gene transfer during the bacteria mating process.
D) a dead bacterium releases DNA into the environment and it is obtained by another bacterium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In plasmid conjugation, DNA is transferred when
A) bacteriophages infect bacteria.
B) foreign DNA fragments are inserted into the plasmid using multiple cloning sites.
C) there is a horizontal gene transfer during the bacteria mating process.
D) a dead bacterium releases DNA into the environment and it is obtained by another bacterium.
A) bacteriophages infect bacteria.
B) foreign DNA fragments are inserted into the plasmid using multiple cloning sites.
C) there is a horizontal gene transfer during the bacteria mating process.
D) a dead bacterium releases DNA into the environment and it is obtained by another bacterium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Individual nucleotide changes to the genome cause a polymorphism called
A) short tandem repeats.
B) variable number tandem repeats.
C) long tandem repeats.
D) single nucleotide polymorphism.
A) short tandem repeats.
B) variable number tandem repeats.
C) long tandem repeats.
D) single nucleotide polymorphism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Foreign DNA fragments can be inserted into plasmids using
A) promoters.
B) cloning vectors.
C) cloning sites.
D) recombinant DNA.
A) promoters.
B) cloning vectors.
C) cloning sites.
D) recombinant DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Not all single nucleotide polymorphisms cause a phenotypic change because sometimes the changes occur in the
A) coding region.
B) noncoding region.
C) promoter sequence.
D) telomeres.
A) coding region.
B) noncoding region.
C) promoter sequence.
D) telomeres.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Polycistronic genes that contain a coding sequence for proteins that are only involved in one biochemical process are called
A) exons.
B) operons.
C) introns.
D) promoters.
A) exons.
B) operons.
C) introns.
D) promoters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
__________ maintain the length of the chromosome after replication.
A) Telomeres
B) Centromeres
C) Kinetochores
D) Sister chromatids
A) Telomeres
B) Centromeres
C) Kinetochores
D) Sister chromatids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The exons of a single gene often encode for different functional domains of a protein, which can result in
A) genetic recombination.
B) gene regulation.
C) untranslated regions.
D) termination of transcription.
A) genetic recombination.
B) gene regulation.
C) untranslated regions.
D) termination of transcription.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In viral transduction, DNA is transferred when
A) bacteriophages infect bacteria.
B) foreign DNA fragments are inserted into the plasmid using multiple cloning sites.
C) there is a horizontal gene transfer during the bacteria mating process.
D) a dead bacterium releases DNA into the environment and it is obtained by another bacterium.
A) bacteriophages infect bacteria.
B) foreign DNA fragments are inserted into the plasmid using multiple cloning sites.
C) there is a horizontal gene transfer during the bacteria mating process.
D) a dead bacterium releases DNA into the environment and it is obtained by another bacterium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When DNA molecules from multiple sources have been connected in the laboratory, the result is referred to as
A) promoters.
B) cloning vectors.
C) cloning sites.
D) recombinant DNA.
A) promoters.
B) cloning vectors.
C) cloning sites.
D) recombinant DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Deletions or insertions into the genome cause a polymorphism called
A) short tandem repeats.
B) variable number tandem repeats.
C) long tandem repeats.
D) single nucleotide polymorphism.
A) short tandem repeats.
B) variable number tandem repeats.
C) long tandem repeats.
D) single nucleotide polymorphism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A common database tool used to determine homologous genomic sequences is called
A) the National Center for Biotechnology Information.
B) the National Human Genome Research Institute.
C) Computational Analysis.
D) Basic Local Alignment Search Tool.
A) the National Center for Biotechnology Information.
B) the National Human Genome Research Institute.
C) Computational Analysis.
D) Basic Local Alignment Search Tool.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which protein is responsible for the proper separation of the chromosomes during cell division?
A) telomeres
B) centromeres
C) kinetochores
D) sister chromatids
A) telomeres
B) centromeres
C) kinetochores
D) sister chromatids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Two identical copies of replicated DNA that remain attached until cell division are referred to as
A) telomeres.
B) centromeres.
C) kinetochores.
D) sister chromatids.
A) telomeres.
B) centromeres.
C) kinetochores.
D) sister chromatids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In the eukaryotic cell, the coding sequences on a gene are referred to as
A) exons.
B) operons.
C) introns.
D) promoter.
A) exons.
B) operons.
C) introns.
D) promoter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In a single RNA transcript, polycistronic prokaryotic genes encode protein(s).
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) multiple
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) multiple

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which enzyme is used to cleave DNA at specific sequences during the production of recombinant DNA?
A) DNA methylase
B) restriction endonucleases
C) reverse transcriptase
D) DNA ligase
A) DNA methylase
B) restriction endonucleases
C) reverse transcriptase
D) DNA ligase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The most common purpose for cloning a gene sequence using mRNA is to
A) disrupt antibiotic resistance.
B) determine homologous genomic sequences.
C) generate a library of actively transcribed genes.
D) disrupt the lacZ gene, resulting in blue-white screening.
A) disrupt antibiotic resistance.
B) determine homologous genomic sequences.
C) generate a library of actively transcribed genes.
D) disrupt the lacZ gene, resulting in blue-white screening.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In the production of recombinant DNA, which enzyme links matching cohesive ends using covalent interactions?
A) DNA methylase
B) restriction endonucleases
C) reverse transcriptase
D) DNA ligase
A) DNA methylase
B) restriction endonucleases
C) reverse transcriptase
D) DNA ligase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In the second temperature phase of PCR, why does the temperature vary from 55 C to 65 C?
A) different ionic strengths
B) different primer concentrations
C) G-C content
D) different amount of hydrogen bonds
A) different ionic strengths
B) different primer concentrations
C) G-C content
D) different amount of hydrogen bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Identify the phase of PCR amplification where DNA synthesis occurs. 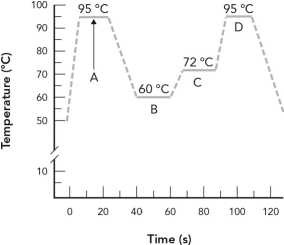
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Compare and contrast the arrangements of A-DNA, B-DNA, and Z-DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
When a gene sequence is cloned using mRNA, the mRNA is isolated from the cell and converted into a double-stranded sequence using which enzyme?
A) DNA methylase
B) restriction endonucleases
C) reverse transcriptase
D) DNA ligase
A) DNA methylase
B) restriction endonucleases
C) reverse transcriptase
D) DNA ligase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Identify the phase of PCR amplification where DNA is denatured and the strands are separated. 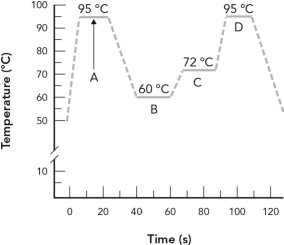
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The -galactosidase gene that is inserted into plasmid cloning vectors is used to
A) cleave the DNA in a sequence-specific fashion.
B) disrupt the antibiotic-resistance gene, making it nonfunctional.
C) determine if the cloning has been successful.
D) protect the bacteria from bacteriophage infection.
A) cleave the DNA in a sequence-specific fashion.
B) disrupt the antibiotic-resistance gene, making it nonfunctional.
C) determine if the cloning has been successful.
D) protect the bacteria from bacteriophage infection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Below are the steps involved in cloning gene sequences using mRNA. Arrange the steps in the appropriate order. 1. The double-stranded cDNA is treated with a restriction endonuclease to generate compatible ends for annealing and ligation.
2) mRNA is isolated from the cell and converted back into double-stranded sequences using reverse transcriptase to generate complementary DNA.
3) The RNA-DNA hybrid is treated with a nuclease to cleave the RNA strand, producing RNA fragments.
4) Reverse transcriptase completes the single-stranded cDNA when it reaches the 5 ' end of the mRNA transcript.
5) RNA fragments serve as primers for DNA synthesis of the second strand of cDNA using DNA polymerase.
A) 4, 2, 1, 5, 3
B) 2, 4, 3, 5, 1
C) 2, 3, 5, 4, 1
D) 3, 2, 5, 4, 1
2) mRNA is isolated from the cell and converted back into double-stranded sequences using reverse transcriptase to generate complementary DNA.
3) The RNA-DNA hybrid is treated with a nuclease to cleave the RNA strand, producing RNA fragments.
4) Reverse transcriptase completes the single-stranded cDNA when it reaches the 5 ' end of the mRNA transcript.
5) RNA fragments serve as primers for DNA synthesis of the second strand of cDNA using DNA polymerase.
A) 4, 2, 1, 5, 3
B) 2, 4, 3, 5, 1
C) 2, 3, 5, 4, 1
D) 3, 2, 5, 4, 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Explain the difference between the coding strand and the template strand of DNA as it relates to RNA transcription.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Compare the primary and secondary structures of DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
This method of analyzing RNA transcripts relies on a predetermined collection of complementary DNA sequences.
A) plasmid cloning
B) viral transduction
C) RNA-seq
D) gene-expression microarrays
A) plasmid cloning
B) viral transduction
C) RNA-seq
D) gene-expression microarrays

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
When a gene sequence is cloned using mRNA, which enzyme is used to seal the single-strand gaps left behind in the second strand of DNA?
A) DNA methylase
B) restriction endonucleases
C) reverse transcriptase
D) DNA ligase
A) DNA methylase
B) restriction endonucleases
C) reverse transcriptase
D) DNA ligase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Identify the phase of PCR amplification where the primer is annealed. 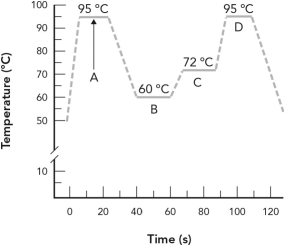
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
DNA regions rich in A-T are more easily denatured than regions with a higher G-C content. Why is this biologically significant?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Identify the products when Sm al cleaves the following DNA sequence. 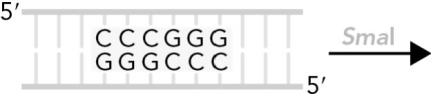
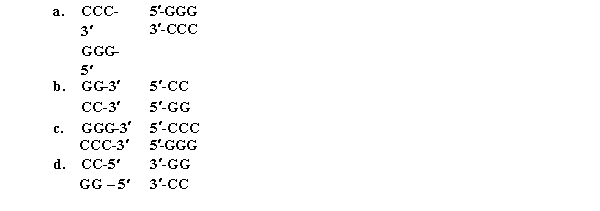
A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d

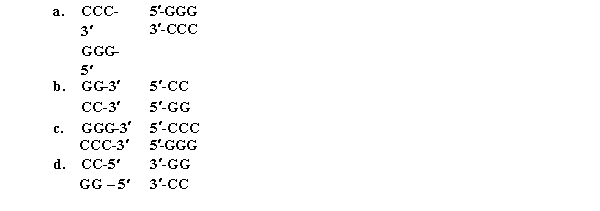
A)a
B)b
C)c
D)d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
When DNA is sequenced, which analytical technique is used to separate the chain-terminated DNA fragments?
A) gel electrophoresis
B) blue-white screening
C) antibiotic resistance
D) fluorescent labeling
A) gel electrophoresis
B) blue-white screening
C) antibiotic resistance
D) fluorescent labeling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which method of analyzing RNA transcripts is considered to be an unbiased approach because it does not use a predetermined collection of complementary DNA sequence?
A) plasmid cloning
B) viral transduction
C) RNA-seq
D) gene-expression microarrays
A) plasmid cloning
B) viral transduction
C) RNA-seq
D) gene-expression microarrays

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A sequence of B-DNA contains 78,000 base pairs. Analysis shows that 42% are C-G base pairs. Answer the following questions and show your mathematical work.
a. How many pyrimidine bases are in this sequence?
b. How many nucleotides are cytosines?
c. How many nucleotides are thymines?
d. How many hydrogen bonds does this sequence contain?
e. How many turns of the double helix occur in this sequence?
a. How many pyrimidine bases are in this sequence?
b. How many nucleotides are cytosines?
c. How many nucleotides are thymines?
d. How many hydrogen bonds does this sequence contain?
e. How many turns of the double helix occur in this sequence?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



