Deck 4: Chemical Reactions and Stoichiometry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/261
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Chemical Reactions and Stoichiometry
1
What element is being oxidized in the following (unbalanced) redox reaction? MnO4⁻ (aq) + H2C2O4(aq) → Mn2+(aq) + CO2(g)
A) C
B) O
C) Mn
D) H
A) C
B) O
C) Mn
D) H
C
2
Balance the following redox reaction if it occurs in acidic solution. What are the coefficients in front of Cd and Ag+ in the balanced reaction? Cd(s) + Ag+(aq) → Ag(s) + Cd2+(aq)
A) Cd = 1, Ag⁺ = 2
B) Cd = 1, Ag⁺ = 1
C) Cd = 2, Ag⁺ = 1
D) Cd = 2, Ag⁺ = 2
E) Cd = 3, Ag⁺ = 1
A) Cd = 1, Ag⁺ = 2
B) Cd = 1, Ag⁺ = 1
C) Cd = 2, Ag⁺ = 1
D) Cd = 2, Ag⁺ = 2
E) Cd = 3, Ag⁺ = 1
Cd = 1, Ag⁺ = 2
3
Balance the following redox reaction if it occurs in acidic solution. What are the coefficients in front of Zn and H+ in the balanced reaction? Zn2+(aq) + NH4+(aq) → Zn(s) + NO3⁻(aq)
A) Zn = 1, H⁺ = 8
B) Zn = 1, H⁺ = 4
C) Zn = 4, H⁺ = 10
D) Zn = 2, H⁺ = 4
E) Zn = 3, H⁺ = 5
A) Zn = 1, H⁺ = 8
B) Zn = 1, H⁺ = 4
C) Zn = 4, H⁺ = 10
D) Zn = 2, H⁺ = 4
E) Zn = 3, H⁺ = 5
Zn = 4, H⁺ = 10
4
Identify the location of oxidation in an electrochemical cell.
A) the anode
B) the cathode
C) the electrode
D) the salt bridge
E) the socket
A) the anode
B) the cathode
C) the electrode
D) the salt bridge
E) the socket

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Identify the location of reduction in an electrochemical cell.
A) the anode
B) the cathode
C) the electrode
D) the salt bridge
E) the socket
A) the anode
B) the cathode
C) the electrode
D) the salt bridge
E) the socket

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What element is being reduced in the following (unbalanced) redox reaction? H2O2(l) + ClO2(aq) → ClO2⁻(aq) + O2(g)
A) H
B) O
C) Cl
D) N
E) C
A) H
B) O
C) Cl
D) N
E) C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What element is being oxidized in the following (unbalanced) redox reaction? Cr(OH)4⁻(aq) + ClO⁻(aq) → CrO42-(aq) + Cl⁻(aq)
A) Cr
B) O
C) H
D) Cl
A) Cr
B) O
C) H
D) Cl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Define a salt bridge.
A) A pathway, composed of salt water, that ions pass through.
B) A pathway in which no ions flow.
C) A pathway between the cathode and anode in which ions are reduced.
D) A pathway between the cathode and anode in which ions are oxidized.
E) A pathway through which counterions can flow between the half-cells without the solutions in the half-cell totally mixing.
A) A pathway, composed of salt water, that ions pass through.
B) A pathway in which no ions flow.
C) A pathway between the cathode and anode in which ions are reduced.
D) A pathway between the cathode and anode in which ions are oxidized.
E) A pathway through which counterions can flow between the half-cells without the solutions in the half-cell totally mixing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Balance the following redox reaction if it occurs in acidic solution. What are the coefficients in front of H⁺ and Fe3+ in the balanced reaction? Fe2+(aq) + MnO4⁻(aq) → Fe3+(aq) + Mn2+(aq)
A) H⁺ = 2, Fe3+ = 3
B) H⁺ = 8, Fe3+ = 5
C) H⁺ = 3, Fe3+ = 2
D) H⁺ = 5, Fe3+ = 1
E) H⁺ = 8, Fe3+ = 1
A) H⁺ = 2, Fe3+ = 3
B) H⁺ = 8, Fe3+ = 5
C) H⁺ = 3, Fe3+ = 2
D) H⁺ = 5, Fe3+ = 1
E) H⁺ = 8, Fe3+ = 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Balance the following redox reaction if it occurs in acidic solution. What are the coefficients in front of H2C2O4 and H2O in the balanced reaction? MnO4⁻ (aq) + H2C2O4(aq) → Mn2+(aq) + CO2(g)
A) H2C2O4 = 5, H2O = 8
B) H2C2O4 = 1, H2O = 1
C) H2C2O4 = 5, H2O = 1
D) H2C2O4 = 1, H2O = 4
E) H2C2O4 = 3, H2O = 2
A) H2C2O4 = 5, H2O = 8
B) H2C2O4 = 1, H2O = 1
C) H2C2O4 = 5, H2O = 1
D) H2C2O4 = 1, H2O = 4
E) H2C2O4 = 3, H2O = 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What element is being oxidized in the following (unbalanced) redox reaction? H2O2(l) + ClO2(aq) → ClO2⁻(aq) + O2(g)
A) H
B) O
C) Cl
D) N
E) C
A) H
B) O
C) Cl
D) N
E) C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What element is being reduced in the following (unbalanced) redox reaction? MnO4⁻ (aq) + H2C2O4(aq) → Mn2+(aq) + CO2(g)
A) C
B) O
C) Mn
D) H
A) C
B) O
C) Mn
D) H

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What element is being oxidized in the following (unbalanced) redox reaction? Zn2+(aq) + NH4+(aq) → Zn(s) + NO3⁻(aq)
A) Zn
B) N
C) H
D) O
A) Zn
B) N
C) H
D) O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which one of the following is the best electrolyte?
A) C12H22O11(aq)
B) NaCl(aq)
C) AgCl(aq)
D) CaSO4(aq)
E) CH3COOH(aq)
A) C12H22O11(aq)
B) NaCl(aq)
C) AgCl(aq)
D) CaSO4(aq)
E) CH3COOH(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) A reduction process corresponds to an increase in oxidation state as a result of loss of electrons.
B) An oxidation process involves the loss of electrons resulting in an increase in oxidation state.
C) An oxidation process corresponds to a decrease in oxidation state as a result of a gain of electrons.
D) During a reduction process electrons are lost, while during an oxidation they are gained.
E) During a reduction process an oxidation state increases, while in an oxidation process an oxidation state decreases.
A) A reduction process corresponds to an increase in oxidation state as a result of loss of electrons.
B) An oxidation process involves the loss of electrons resulting in an increase in oxidation state.
C) An oxidation process corresponds to a decrease in oxidation state as a result of a gain of electrons.
D) During a reduction process electrons are lost, while during an oxidation they are gained.
E) During a reduction process an oxidation state increases, while in an oxidation process an oxidation state decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
How many electrons are transferred in the following reaction? (The reaction is unbalanced.) Mg(s) + Al3+(aq) → Al(s) + Mg2+(aq)
A) 6
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1
E) 4
A) 6
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) Electrolytes conduct electricity.
B) Strong acids are weak electrolytes.
C) Weak acids completely ionize in water.
D) Sugar solution conducts electricity.
E) AgNO3 is insoluble in water.
A) Electrolytes conduct electricity.
B) Strong acids are weak electrolytes.
C) Weak acids completely ionize in water.
D) Sugar solution conducts electricity.
E) AgNO3 is insoluble in water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What element is being reduced in the following (unbalanced) redox reaction? Cr(OH)4⁻(aq) + ClO⁻(aq) → CrO42-(aq) + Cl⁻(aq)
A) Cr
B) O
C) H
D) Cl
A) Cr
B) O
C) H
D) Cl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Balance the following redox reaction if it occurs in basic solution. What are the coefficients in front of Br2 and OH⁻ in the balanced reaction? Br2(l) → BrO3⁻(aq) + Br⁻(aq)
A) Br2 = 1, OH⁻ = 2
B) Br2 = 2, OH⁻ = 5
C) Br2 = 3, OH⁻ = 3
D) Br2 = 3, OH⁻ = 6
E) Br2 = 1, OH⁻ = 6
A) Br2 = 1, OH⁻ = 2
B) Br2 = 2, OH⁻ = 5
C) Br2 = 3, OH⁻ = 3
D) Br2 = 3, OH⁻ = 6
E) Br2 = 1, OH⁻ = 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A homogeneous mixture of two substances is known as ________.
A) a solute
B) a solvent
C) a solution
D) solute-solute interactions
E) solvent-solvent interactions
A) a solute
B) a solvent
C) a solution
D) solute-solute interactions
E) solvent-solvent interactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following is considered a strong electrolyte?
A) NH4NO3
B) C12H22O11
C) PbCl2
D) HC2H3O2
E) CH3OH
A) NH4NO3
B) C12H22O11
C) PbCl2
D) HC2H3O2
E) CH3OH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Balance the following redox reaction if it occurs in basic solution. What are the coefficients in front of Cr(OH)4⁻ and ClO⁻ in the balanced reaction? Cr(OH)4⁻(aq) + ClO⁻(aq) → CrO42-(aq) + Cl⁻(aq)
A) Cr(OH)4⁻ = 2, ClO⁻ = 3
B) Cr(OH)4⁻ = 1, ClO⁻ = 1
C) Cr(OH)4⁻ = 1, ClO⁻ = 2
D) Cr(OH)4⁻ = 2, ClO⁻ = 6
E) Cr(OH)4⁻ = 6, ClO⁻ = 5
A) Cr(OH)4⁻ = 2, ClO⁻ = 3
B) Cr(OH)4⁻ = 1, ClO⁻ = 1
C) Cr(OH)4⁻ = 1, ClO⁻ = 2
D) Cr(OH)4⁻ = 2, ClO⁻ = 6
E) Cr(OH)4⁻ = 6, ClO⁻ = 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What are the required coefficients to properly balance the following chemical reaction? CH4(g) + H2O(g) → CO(g) + H2(g)
A) 1, 2, 2, 3
B) 1, 1, 2, 2
C) 2, 1, 1, 3
D) 2, 2, 1, 1
E) 1, 1, 1, 3
A) 1, 2, 2, 3
B) 1, 1, 2, 2
C) 2, 1, 1, 3
D) 2, 2, 1, 1
E) 1, 1, 1, 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following describes sugar?
A) strong electrolyte, weak acid
B) weak electrolyte, weak acid
C) strong electrolyte, strong acid
D) weak electrolyte, strong acid
E) nonelectrolyte
A) strong electrolyte, weak acid
B) weak electrolyte, weak acid
C) strong electrolyte, strong acid
D) weak electrolyte, strong acid
E) nonelectrolyte

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What are the required coefficients to properly balance the following chemical reaction? NO(g) + H2O(g) → NH3(g) + O2(g)
A) 4, 6, 4,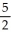
B) 4, 6, 4, 5
C) 2, 3, 2, 2
D) 2, 3, 2, 3
E) 4, 4, 6, 6
A) 4, 6, 4,
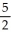
B) 4, 6, 4, 5
C) 2, 3, 2, 2
D) 2, 3, 2, 3
E) 4, 4, 6, 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following describes HCl?
A) strong electrolyte, weak acid
B) weak electrolyte, weak acid
C) strong electrolyte, strong acid
D) weak electrolyte, strong acid
E) nonelectrolyte
A) strong electrolyte, weak acid
B) weak electrolyte, weak acid
C) strong electrolyte, strong acid
D) weak electrolyte, strong acid
E) nonelectrolyte

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What are the required coefficients to properly balance the following chemical reaction? C6H12O6(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(l)
A) 1, 3, 3, 3
B) 2, 6, 6, 3
C) 1, 6, 6, 6
D) 1, 1, 3, 3
E) 2, 2, 6, 3
A) 1, 3, 3, 3
B) 2, 6, 6, 3
C) 1, 6, 6, 6
D) 1, 1, 3, 3
E) 2, 2, 6, 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What are the required coefficients to properly balance the following chemical reaction? SO2(g) + O2(g) + H2O(l) → H2SO4(aq)
A) 1, 1, 1, 1
B) 1, 2, 1, 2
C) 1, 2, 2, 1
D) 2, 1, 2, 2
E) 2, 1, 1, 2
A) 1, 1, 1, 1
B) 1, 2, 1, 2
C) 1, 2, 2, 1
D) 2, 1, 2, 2
E) 2, 1, 1, 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What are the required coefficients to properly balance the following chemical reaction? PbS(s) + HBr(aq) → PbBr2(s) + H2S(g)
A) 1, 1, 2, 2
B) 1, 2, 1, 1
C) 1, 2, 2, 1
D) 2, 1, 1, 1
E) 2, 2, 1, 2
A) 1, 1, 2, 2
B) 1, 2, 1, 1
C) 1, 2, 2, 1
D) 2, 1, 1, 1
E) 2, 2, 1, 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What are the required coefficients to properly balance the following chemical reaction? H2(g) + Cl2(g) → HCl(g)
A) 1, 1, 2
B) 2, 2,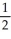
C) 1, 1, 1
D) 2, 1, 2
E) 1, 2, 1
A) 1, 1, 2
B) 2, 2,
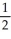
C) 1, 1, 1
D) 2, 1, 2
E) 1, 2, 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Identify the balanced equation to show the reaction of gaseous ethane with gaseous oxygen to form carbon monoxide gas and water vapour.
A) 2C2H6(g) + 7O2(g) → 4CO2(g) + 6H2O(g)
B) C2H6(g) + 5O(g) → 2CO(g) + 3H2O(g)
C) 2C2H6(g) + 5O2(g) → 4CO(g) + 6H2O(g)
D) C2H6(g) + 7O(g) → 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(g)
E) 2CH3(g) + 5O(g) → 2CO(g) + 3H2O(g)
A) 2C2H6(g) + 7O2(g) → 4CO2(g) + 6H2O(g)
B) C2H6(g) + 5O(g) → 2CO(g) + 3H2O(g)
C) 2C2H6(g) + 5O2(g) → 4CO(g) + 6H2O(g)
D) C2H6(g) + 7O(g) → 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(g)
E) 2CH3(g) + 5O(g) → 2CO(g) + 3H2O(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What are the required coefficients to properly balance the following chemical reaction? Cu(s) + S(s) → Cu2S(s)
A) 1, 1,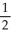
B) 1, 1, 1
C) 1, 1, 2
D) 2, 1, 1
E) 2, 1, 2
A) 1, 1,
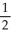
B) 1, 1, 1
C) 1, 1, 2
D) 2, 1, 1
E) 2, 1, 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What are the required coefficients to properly balance the following chemical reaction? MnCl2(s) + H2O(l) + Cl2(g) → HCl(aq) + MnO2(s)
A) 1, 2, 1, 4, 1
B) 2, 2, 1, 4, 2
C) 1, 1, 1, 2, 1
D) 1, 1, 1, 4, 1
E) 2, 1, 1, 4, 2
A) 1, 2, 1, 4, 1
B) 2, 2, 1, 4, 2
C) 1, 1, 1, 2, 1
D) 1, 1, 1, 4, 1
E) 2, 1, 1, 4, 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Balance the following redox reaction if it occurs in basic solution. What are the coefficients in front of Al and F2 in the balanced reaction? Al(s) + F2(g) → Al3+(aq) + F-(aq)
A) Al = 2, F2 = 3
B) Al = 2, F2 = 6
C) Al = 1, F2 = 1
D) Al = 2, F2 = 1
E) Al = 3, F2 = 2
A) Al = 2, F2 = 3
B) Al = 2, F2 = 6
C) Al = 1, F2 = 1
D) Al = 2, F2 = 1
E) Al = 3, F2 = 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What are the required coefficients to properly balance the following chemical reaction? Na(s) + H2O(l) → H2(g) + NaOH(aq)
A) 1, 2, 2, 1
B) 2, 2, 1, 1
C) 2, 1, 1, 1
D) 2, 1, 2, 1
E) 2, 2, 1, 2
A) 1, 2, 2, 1
B) 2, 2, 1, 1
C) 2, 1, 1, 1
D) 2, 1, 2, 1
E) 2, 2, 1, 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What are the required coefficients to properly balance the following chemical reaction? N2H4(l) → NH3(g) + N2(g)
A) 3, 4, 1
B) 2, 3, 2
C) 3, 4, 4
D) 1, 4, 3
E) 2, 2, 1
A) 3, 4, 1
B) 2, 3, 2
C) 3, 4, 4
D) 1, 4, 3
E) 2, 2, 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Identify the balanced equation to show the reaction of aqueous aluminum acetate with aqueous ammonium phosphate to form solid aluminum phosphate and aqueous ammonium acetate.
A) Al(C2H3O2)2(aq) + (NH4)2PO4(aq) → AlPO4(s) + 2NH4C2H3O2(aq)
B) Al(C2H3O2)2(aq) + (NH3)2PO4(aq) → AlPO4(s) + 2NH3C2H3O2(aq)
C) Al(CO3)2(aq) + (NH3)2PO4(aq) → AlPO4(s) + 2NH3CO3(aq)
D) Al(C2H3O2)3(aq) + (NH4)3PO4(aq) → AlPO4(s) + 3NH4C2H3O2(aq)
E) Al(CO2)3(aq) + (NH4)3PO3(aq) → AlPO3(s) + 3NH4CO2(aq)
A) Al(C2H3O2)2(aq) + (NH4)2PO4(aq) → AlPO4(s) + 2NH4C2H3O2(aq)
B) Al(C2H3O2)2(aq) + (NH3)2PO4(aq) → AlPO4(s) + 2NH3C2H3O2(aq)
C) Al(CO3)2(aq) + (NH3)2PO4(aq) → AlPO4(s) + 2NH3CO3(aq)
D) Al(C2H3O2)3(aq) + (NH4)3PO4(aq) → AlPO4(s) + 3NH4C2H3O2(aq)
E) Al(CO2)3(aq) + (NH4)3PO3(aq) → AlPO3(s) + 3NH4CO2(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Identify the balanced equation to show the reaction of sulfurous acid with lithium hydroxide to form water and lithium sulfite.
A) H2SO4(aq) + LiOH(aq) → H2O(l) + Li2SO4(aq)
B) H2SO3(aq) + 2LiOH(aq) → 2H2O(l) + Li2SO3(aq)
C) HSO3(aq) + LiOH(aq) → H2O(l) + LiSO3(aq)
D) HSO4(aq) + LiOH(aq) → H2O(l) + LiSO4(aq)
E) H2S(aq) + 2LiOH(aq) → 2H2O(l) + Li2S(aq)
A) H2SO4(aq) + LiOH(aq) → H2O(l) + Li2SO4(aq)
B) H2SO3(aq) + 2LiOH(aq) → 2H2O(l) + Li2SO3(aq)
C) HSO3(aq) + LiOH(aq) → H2O(l) + LiSO3(aq)
D) HSO4(aq) + LiOH(aq) → H2O(l) + LiSO4(aq)
E) H2S(aq) + 2LiOH(aq) → 2H2O(l) + Li2S(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Balance the following redox reaction if it occurs in basic solution. What are the coefficients in front of ClO2 and H2O in the balanced reaction? H2O2(l) + ClO2(aq) → ClO2⁻(aq) + O2(g)
A) ClO2 = 1, H2O = 1
B) ClO2 = 1, H2O = 2
C) ClO2 = 4, H2O = 3
D) ClO2 = 4, H2O = 2
E) ClO2 = 2, H2O = 2
A) ClO2 = 1, H2O = 1
B) ClO2 = 1, H2O = 2
C) ClO2 = 4, H2O = 3
D) ClO2 = 4, H2O = 2
E) ClO2 = 2, H2O = 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is a weak electrolyte?
A) LiOH
B) CaCl2
C) MgCO3
D) NaC2H3O2
E) Li2SO4
A) LiOH
B) CaCl2
C) MgCO3
D) NaC2H3O2
E) Li2SO4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
How many of the following compounds are soluble in water? Cu(OH)2 LiNO3 NH4Br K2S
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following compounds is insoluble in water?
A) Hg2I2
B) MgSO4
C) (NH4)2CO3
D) BaS
E) All of these compounds are soluble in water.
A) Hg2I2
B) MgSO4
C) (NH4)2CO3
D) BaS
E) All of these compounds are soluble in water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following compounds is soluble in water?
A) CaCl2
B) MgCO3
C) PbCl2
D) BaSO4
E) None of these compounds is soluble in water.
A) CaCl2
B) MgCO3
C) PbCl2
D) BaSO4
E) None of these compounds is soluble in water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) Aqueous reactions can be represented with a molecular equation.
B) Aqueous reactions can be represented with a complete ionic equation.
C) Aqueous reactions can be represented with a net ionic equation.
D) Precipitation reactions isoccur when two aqueous solutions are mixed a to form a solid precipitate.
E) Spectator ions change the course of the reaction and are included in the net ionic equation.
A) Aqueous reactions can be represented with a molecular equation.
B) Aqueous reactions can be represented with a complete ionic equation.
C) Aqueous reactions can be represented with a net ionic equation.
D) Precipitation reactions isoccur when two aqueous solutions are mixed a to form a solid precipitate.
E) Spectator ions change the course of the reaction and are included in the net ionic equation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following is a precipitation reaction?
A) 2HBr(aq) + NiS(s) →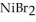 (aq) +
(aq) + 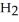 S(g)
S(g)
B)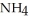 I(aq) + NaOH(aq) →
I(aq) + NaOH(aq) → 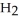 O(l) +
O(l) + 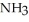 (g) + NaI(aq)
(g) + NaI(aq)
C) 2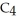
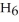 (g) + 11
(g) + 11 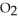 (g) → 8
(g) → 8 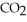 (g) + 6
(g) + 6 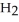 O(g)
O(g)
D) 4NO(g) + 6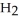 O(g) → 4
O(g) → 4 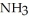 (g) +
(g) + 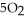 (g)
(g)
E)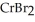 (aq) +
(aq) + 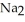
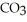 (aq) →
(aq) → 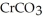 (s) + 2NaBr(aq)
(s) + 2NaBr(aq)
A) 2HBr(aq) + NiS(s) →
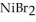 (aq) +
(aq) + 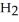 S(g)
S(g)B)
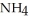 I(aq) + NaOH(aq) →
I(aq) + NaOH(aq) → 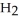 O(l) +
O(l) + 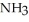 (g) + NaI(aq)
(g) + NaI(aq)C) 2
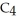
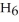 (g) + 11
(g) + 11 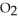 (g) → 8
(g) → 8 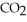 (g) + 6
(g) + 6 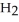 O(g)
O(g)D) 4NO(g) + 6
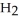 O(g) → 4
O(g) → 4 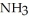 (g) +
(g) + 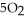 (g)
(g)E)
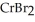 (aq) +
(aq) + 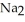
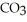 (aq) →
(aq) → 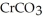 (s) + 2NaBr(aq)
(s) + 2NaBr(aq)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
How many of the following compounds are insoluble in water? KC2H3O2 CaSO4 SrS AlPO4
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Choose the statement below that is TRUE.
A) A weak acid solution consists of mostly nonionized acid molecules.
B) The term "strong electrolyte" means that the substance is extremely reactive.
C) A strong acid solution consists of only partially ionized acid molecules.
D) The term "weak electrolyte" means that the substance is inert.
E) A molecular compound that does not ionize in solution is considered a strong electrolyte.
A) A weak acid solution consists of mostly nonionized acid molecules.
B) The term "strong electrolyte" means that the substance is extremely reactive.
C) A strong acid solution consists of only partially ionized acid molecules.
D) The term "weak electrolyte" means that the substance is inert.
E) A molecular compound that does not ionize in solution is considered a strong electrolyte.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Identify the net ionic equation for the reaction (if any) that occurs when aqueous solutions of Na2CO3 and HCl are mixed.
A) 2H+(aq) + CO32-(aq) → H2CO3(s)
B) 2Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) + 2H+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) → H2CO3(s) + 2NaCl(aq)
C) 2H+(aq) + CO32-(aq) → H2O(l) + CO2(g)
D) 2Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) + 2H+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) → H2CO3(s) + 2Na+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq)
E) No reaction occurs.
A) 2H+(aq) + CO32-(aq) → H2CO3(s)
B) 2Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) + 2H+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) → H2CO3(s) + 2NaCl(aq)
C) 2H+(aq) + CO32-(aq) → H2O(l) + CO2(g)
D) 2Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) + 2H+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) → H2CO3(s) + 2Na+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq)
E) No reaction occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Identify the spectator ions in the following molecular equation: KBr(aq) + AgNO3(aq) → AgBr(s) + KNO3(aq)
A) Ag+ and Br-
B) K+ and NO3-
C) K+ and Br-
D) Ag+ and NO3-
E) There are no spectator ions in this reaction.
A) Ag+ and Br-
B) K+ and NO3-
C) K+ and Br-
D) Ag+ and NO3-
E) There are no spectator ions in this reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following pairs of aqueous solutions will form a precipitate when mixed?
A) NH4NO3 + Li2CO3
B) Hg2(NO3)2 + LiI
C) NaCl + Li3PO4
D) AgC2H3O2 + Cu(NO3)2
E) None of the above solution pairs will produce a precipitate.
A) NH4NO3 + Li2CO3
B) Hg2(NO3)2 + LiI
C) NaCl + Li3PO4
D) AgC2H3O2 + Cu(NO3)2
E) None of the above solution pairs will produce a precipitate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following describes acetic acid?
A) strong electrolyte, weak acid
B) weak electrolyte, weak acid
C) strong electrolyte, strong acid
D) weak electrolyte, strong acid
E) nonelectrolyte
A) strong electrolyte, weak acid
B) weak electrolyte, weak acid
C) strong electrolyte, strong acid
D) weak electrolyte, strong acid
E) nonelectrolyte

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Identify the net ionic equation for the reaction (if any) that occurs when aqueous solutions of H2SO4 and KOH are mixed.
A) H+(aq) + OH-(aq) → H2O(l)
B) 2K+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → K2SO4(s)
C) H+(aq) + OH-(aq) + 2K+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → H2O(l) + K2SO4(s)
D) H22+(aq) + OH-(aq) → H2(OH)2(l)
E) No reaction occurs.
A) H+(aq) + OH-(aq) → H2O(l)
B) 2K+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → K2SO4(s)
C) H+(aq) + OH-(aq) + 2K+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → H2O(l) + K2SO4(s)
D) H22+(aq) + OH-(aq) → H2(OH)2(l)
E) No reaction occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Identify the net ionic equation for the reaction (if any) that occurs when aqueous solutions of K2S and Fe(NO3)2 are mixed.
A) K+(aq) + NO3-(aq) → KNO3(s)
B) Fe2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2K+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) → FeS(s) + 2K+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq)
C) Fe2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2K+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) → Fe2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2KNO3(s)
D) Fe2+(aq) + S2-(aq) → FeS(s)
E) No reaction occurs.
A) K+(aq) + NO3-(aq) → KNO3(s)
B) Fe2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2K+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) → FeS(s) + 2K+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq)
C) Fe2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2K+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) → Fe2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2KNO3(s)
D) Fe2+(aq) + S2-(aq) → FeS(s)
E) No reaction occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What precipitate is most likely formed from a solution containing Ba2+, Na1+, OH1-, and CO32-.
A) NaOH
B) BaCO3
C) Na2CO3
D) Ba(OH)2
A) NaOH
B) BaCO3
C) Na2CO3
D) Ba(OH)2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following pairs of aqueous solutions will form a precipitate when mixed?
A) K2CO3 + NaCl
B) Na2SO4 + KOH
C) CaS + Na2SO4
D) None of these solution pairs will produce a precipitate.
E) All of these solution pairs will produce a precipitate.
A) K2CO3 + NaCl
B) Na2SO4 + KOH
C) CaS + Na2SO4
D) None of these solution pairs will produce a precipitate.
E) All of these solution pairs will produce a precipitate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Identify the complete ionic equation for the reaction (if any) that occurs when aqueous solutions of lithium sulfide and copper(II) nitrate are mixed.
A) Li+(aq) + SO42-(aq) + Cu+(aq) + NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + Li+(aq) + NO3-(aq)
B) Li+(aq) + S-(aq) + Cu+(aq) + NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + LiNO3(aq)
C) 2Li+(aq) + S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) → Cu2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2LiNO3(s)
D) 2Li+(aq) + S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + 2Li+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq)
E) No reaction occurs.
A) Li+(aq) + SO42-(aq) + Cu+(aq) + NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + Li+(aq) + NO3-(aq)
B) Li+(aq) + S-(aq) + Cu+(aq) + NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + LiNO3(aq)
C) 2Li+(aq) + S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) → Cu2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2LiNO3(s)
D) 2Li+(aq) + S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + 2Li+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq)
E) No reaction occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following pairs of aqueous solutions will form a precipitate when mixed?
A) LiOH + Na2S
B) (NH4)2SO4 + LiCl
C) Sr(C2H3O2)2 + Na2SO4
D) KNO3 + NaOH
E) None of the above solution pairs will produce a precipitate.
A) LiOH + Na2S
B) (NH4)2SO4 + LiCl
C) Sr(C2H3O2)2 + Na2SO4
D) KNO3 + NaOH
E) None of the above solution pairs will produce a precipitate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following is a precipitation reaction?
A) Zn(s) + 2AgNO3(aq) → 2Ag(s) + Zn(NO3)2(aq)
B) NaCl(aq) + LiI(aq) → NaI(aq) + LiCl(aq)
C) 2LiI(aq) + Hg2(NO3)2(aq) → Hg2I2(s) + 2LiNO3(aq)
D) HCl(aq) + KOH(aq) → KCl(aq) + H2O(l)
E) None of the above are precipitation reactions.
A) Zn(s) + 2AgNO3(aq) → 2Ag(s) + Zn(NO3)2(aq)
B) NaCl(aq) + LiI(aq) → NaI(aq) + LiCl(aq)
C) 2LiI(aq) + Hg2(NO3)2(aq) → Hg2I2(s) + 2LiNO3(aq)
D) HCl(aq) + KOH(aq) → KCl(aq) + H2O(l)
E) None of the above are precipitation reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following pairs of aqueous solutions will form a precipitate when mixed?
A) HCl + LiOH
B) Li2S + HCl
C) K2CO3 + HNO3
D) MgCl2 + KOH
E) All of these solution pairs will produce a precipitate.
A) HCl + LiOH
B) Li2S + HCl
C) K2CO3 + HNO3
D) MgCl2 + KOH
E) All of these solution pairs will produce a precipitate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following describes NaCl?
A) weak acid
B) weak electrolyte
C) strong acid
D) strong electrolyte
E) nonelectrolyte
A) weak acid
B) weak electrolyte
C) strong acid
D) strong electrolyte
E) nonelectrolyte

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What element is undergoing oxidation (if any) in the following reaction? CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(g)
A) O
B) H
C) C
D) both C and H
E) This is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.
A) O
B) H
C) C
D) both C and H
E) This is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Determine the oxidation state of Sn in Sn(SO4)2.
A) +2
B) +4
C) +6
D) 0
E) -2
A) +2
B) +4
C) +6
D) 0
E) -2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following is an oxidation-reduction reaction?
A) HCl(aq) + LiOH(aq) → LiCl(aq) + H2O(l)
B) NaI(aq) + AgNO3(aq) → AgI(s) + NaNO3(aq)
C) Pb(C2H3O2)2(aq) + 2NaCl(aq) → PbCl2(s) + 2NaC2H3O2(aq)
D) Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
E) All of the above are oxidation-reduction reactions.
A) HCl(aq) + LiOH(aq) → LiCl(aq) + H2O(l)
B) NaI(aq) + AgNO3(aq) → AgI(s) + NaNO3(aq)
C) Pb(C2H3O2)2(aq) + 2NaCl(aq) → PbCl2(s) + 2NaC2H3O2(aq)
D) Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
E) All of the above are oxidation-reduction reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What element is undergoing reduction (if any) in the following reaction? Zn(s) + 2AgNO3(aq) → Zn(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag(s)
A) Zn
B) N
C) O
D) Ag
E) This is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.
A) Zn
B) N
C) O
D) Ag
E) This is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Determine the oxidation state of C in CO32-.
A) +4
B) +2
C) -2
D) -4
E) +6
A) +4
B) +2
C) -2
D) -4
E) +6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Identify the oxidation state of Mg in Mg(s). Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
A) +1
B) +2
C) 0
D) -1
E) -2
A) +1
B) +2
C) 0
D) -1
E) -2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What element is undergoing oxidation (if any) in the following reaction? Zn(s) + 2AgNO3(aq) → Zn(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag(s)
A) Zn
B) N
C) O
D) Ag
E) This is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.
A) Zn
B) N
C) O
D) Ag
E) This is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Find the volume of 0.110 mol L-1 hydrochloric acid necessary to react completely with 1.52 g 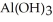 .
.
A) 0.658 L
B) 1.52 L
C) 1.88 L
D) 1.01 L
E) 0.531 L
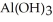 .
.A) 0.658 L
B) 1.52 L
C) 1.88 L
D) 1.01 L
E) 0.531 L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following is an acid-base reaction?
A) C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g)
B) 2HClO4(aq) + Ca(OH)2(aq) → 2 H2O(l) + Ca(ClO4)2(aq)
C) Fe(s) + 2AgNO3(aq) → 2Ag(s) + Fe(NO3)2(aq)
D) MgSO4(aq) + Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Mg(NO3)2(aq) + BaSO4(s)
E) None of the above is an acid-base reaction.
A) C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g)
B) 2HClO4(aq) + Ca(OH)2(aq) → 2 H2O(l) + Ca(ClO4)2(aq)
C) Fe(s) + 2AgNO3(aq) → 2Ag(s) + Fe(NO3)2(aq)
D) MgSO4(aq) + Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Mg(NO3)2(aq) + BaSO4(s)
E) None of the above is an acid-base reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Determine the oxidation state of P in PO33-.
A) +3
B) +6
C) +2
D) 0
E) -3
A) +3
B) +6
C) +2
D) 0
E) -3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Determine the oxidizing agent in the following reaction. Ni(s) + 2AgClO4(aq) → Ni(ClO4)2(aq) + 2Ag(s)
A) Ag+
B) Ni
C) Cl
D) O
E) This is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.
A) Ag+
B) Ni
C) Cl
D) O
E) This is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Identify the oxidation state of H in HCl(aq). Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
A) +1
B) +2
C) 0
D) -1
E) -2
A) +1
B) +2
C) 0
D) -1
E) -2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Identify the net ionic equation for the reaction (if any) that occurs when aqueous solutions of MgSO3 and HI are mixed.
A) 2H+(aq) + SO32-(aq) → H2SO3(s)
B) Mg2+(aq) + 2I-(aq) → MgI2(s)
C) 2H+(aq) + SO32-(aq) + Mg2+(aq) + 2I-(aq) → H2SO3(s) + MgI2(aq)
D) 2H+(aq) + SO32-(aq) → H2O(l) + SO2(g)
E) No reaction occurs.
A) 2H+(aq) + SO32-(aq) → H2SO3(s)
B) Mg2+(aq) + 2I-(aq) → MgI2(s)
C) 2H+(aq) + SO32-(aq) + Mg2+(aq) + 2I-(aq) → H2SO3(s) + MgI2(aq)
D) 2H+(aq) + SO32-(aq) → H2O(l) + SO2(g)
E) No reaction occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Identify the net ionic equation for the reaction (if any) that occurs when aqueous solutions of Al(C2H3O2)3 and LiNO3 are mixed.
A) Al3+(aq) + 3NO3-(aq) → Al(NO3)3(s)
B) Li+(aq) + C2H3O2-(aq) → LiC2H3O2(s)
C) Al3+(aq) + 3NO3-(aq) + Li+(aq) + C2H3O2-(aq) → Al(NO3)3(aq) + LiC2H3O2(s)
D) 3Li+(aq) + (C2H3O2)33-(aq) → Li3(C2H3O2)3(s)
E) No reaction occurs.
A) Al3+(aq) + 3NO3-(aq) → Al(NO3)3(s)
B) Li+(aq) + C2H3O2-(aq) → LiC2H3O2(s)
C) Al3+(aq) + 3NO3-(aq) + Li+(aq) + C2H3O2-(aq) → Al(NO3)3(aq) + LiC2H3O2(s)
D) 3Li+(aq) + (C2H3O2)33-(aq) → Li3(C2H3O2)3(s)
E) No reaction occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Identify the oxidation state of Mg in MgCl2(aq). Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
A) +1
B) +2
C) 0
D) -1
E) -2
A) +1
B) +2
C) 0
D) -1
E) -2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following is a gas-evolution reaction?
A) 2C2H6(l) + 7O2(g) → 4CO2(g) + 6H2O(g)
B) 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(g)
C) LiCl(aq) + NaNO3(aq) → LiNO3(aq) + NaCl(aq)
D) NH4Cl(aq) + KOH(aq) → KCl(aq) + NH3(g) + H2O(l)
E) None of the above is a gas-evolution reaction.
A) 2C2H6(l) + 7O2(g) → 4CO2(g) + 6H2O(g)
B) 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(g)
C) LiCl(aq) + NaNO3(aq) → LiNO3(aq) + NaCl(aq)
D) NH4Cl(aq) + KOH(aq) → KCl(aq) + NH3(g) + H2O(l)
E) None of the above is a gas-evolution reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Choose the reaction that represents the combustion of C6H12O2.
A) C6H12O2(l) + 8O2(g) → 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(g)
B) Mg(s) + C6H12O2(l) → MgC6H12O2(aq)
C) 6C(s) + 6H2(g) + O2(g) → C6H12O2(l)
D) C6H12O2(l) → 6C(s) + 6H2(g) + O2(g)
E) None of the above represents the combustion of C6H12O2.
A) C6H12O2(l) + 8O2(g) → 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(g)
B) Mg(s) + C6H12O2(l) → MgC6H12O2(aq)
C) 6C(s) + 6H2(g) + O2(g) → C6H12O2(l)
D) C6H12O2(l) → 6C(s) + 6H2(g) + O2(g)
E) None of the above represents the combustion of C6H12O2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Identify the polyprotic acid.
A) H2SO4
B) HCl
C) NaCl
D) NaOH
E) Li(OH)2
A) H2SO4
B) HCl
C) NaCl
D) NaOH
E) Li(OH)2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Determine the reducing agent in the following reaction. 2Li(s) + Fe(C2H3O2)2(aq) → 2LiC2H3O2(aq) + Fe(s)
A) O
B) H
C) C
D) Fe
E) Li
A) O
B) H
C) C
D) Fe
E) Li

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Determine the oxidation state of S in MgSO4.
A) -4
B) +2
C) +4
D) +6
E) -2
A) -4
B) +2
C) +4
D) +6
E) -2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 261 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



