Deck 32: The Gains From International Trade
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/50
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 32: The Gains From International Trade
1
A country that engages in no foreign trade is said to be in a situation of
A)comparative advantage.
B)absolute advantage.
C)reciprocal absolute advantage.
D)autarky.
E)isolation.
A)comparative advantage.
B)absolute advantage.
C)reciprocal absolute advantage.
D)autarky.
E)isolation.
autarky.
2
The existence of any ʺgains from tradeʺ relies on
A)closed economies.
B)absolute advantage.
C)comparative advantage.
D)both absolute and comparative advantage.
E)tariffs.
A)closed economies.
B)absolute advantage.
C)comparative advantage.
D)both absolute and comparative advantage.
E)tariffs.
comparative advantage.
3
One region is said to have an absolute advantage over another region in the production of good X when
A)the first region has a more productive labour force than the second.
B)the first region has a larger supply of the raw materials required to produce good X.
C)an equal quantity of resources can produce more of good X in the first region than in the second region.
D)there is no demand for good X in the second region.
E)the opportunity cost of one unit of X is lower in the first region than in the second region.
A)the first region has a more productive labour force than the second.
B)the first region has a larger supply of the raw materials required to produce good X.
C)an equal quantity of resources can produce more of good X in the first region than in the second region.
D)there is no demand for good X in the second region.
E)the opportunity cost of one unit of X is lower in the first region than in the second region.
an equal quantity of resources can produce more of good X in the first region than in the second region.
4
The diagram below shows the domestic demand and supply curves in the market for newsprint in Paperland.
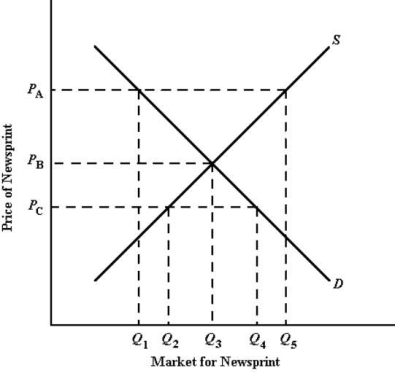 FIGURE 32-5
FIGURE 32-5
Refer to Figure 32-5.If Paperland engages in international trade and the world price is PA,the amount of newsprint produced by Paperland will be
A)Q1.
B)Q2.
C)Q3.
D)Q4.
E)Q5.
 FIGURE 32-5
FIGURE 32-5Refer to Figure 32-5.If Paperland engages in international trade and the world price is PA,the amount of newsprint produced by Paperland will be
A)Q1.
B)Q2.
C)Q3.
D)Q4.
E)Q5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The diagram below shows the domestic demand and supply curves in the market for newsprint in Paperland.
 FIGURE 32-5
FIGURE 32-5
Refer to Figure 32-5.If Paperland engages in international trade and the world price is PA,the amount of newsprint ________ will be ________.
A)imported; Q5 - Q1
B)exported; Q5
C)imported; Q1
D)exported; Q5 - Q1
E)imported; Q5 - Q3
 FIGURE 32-5
FIGURE 32-5Refer to Figure 32-5.If Paperland engages in international trade and the world price is PA,the amount of newsprint ________ will be ________.
A)imported; Q5 - Q1
B)exported; Q5
C)imported; Q1
D)exported; Q5 - Q1
E)imported; Q5 - Q3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Trade,whether between individuals or nations,generally promotes
A)self-sufficiency.
B)specialization.
C)lower living standards.
D)higher product prices.
E)autarky.
A)self-sufficiency.
B)specialization.
C)lower living standards.
D)higher product prices.
E)autarky.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Suppose Canada could produce all goods and services more cheaply than all other countries.In that case,
A)no trade would occur because Canada would have an absolute advantage in producing everything.
B)no trade would occur because Canada would not have a comparative advantage in producing anything.
C)trade would probably take place because Canada would still have a comparative disadvantage in producing some goods.
D)trade would occur but only if other countries also have an absolute advantage.
E)trade would occur but only if other countries subsidize the import of Canadian goods and services.
A)no trade would occur because Canada would have an absolute advantage in producing everything.
B)no trade would occur because Canada would not have a comparative advantage in producing anything.
C)trade would probably take place because Canada would still have a comparative disadvantage in producing some goods.
D)trade would occur but only if other countries also have an absolute advantage.
E)trade would occur but only if other countries subsidize the import of Canadian goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
According to what economists call the ʺlaw of one price,ʺ
A)the world price of a commodity is established by the country with the highest relative demand for that product without respect to the cost of production.
B)the world price of a commodity is established by the country with the highest opportunity cost in producing the product without respect to the domestic or world demand for the product.
C)the price of a specific product will be the same in any two markets in which the cost of labour is the same.
D)the lower the costs to move a product from one market to the other,the more equal the prices for the same product when it is sold in different markets.
E)the price of a given product will never be equal in two different markets because of differences in the patterns of demand.
A)the world price of a commodity is established by the country with the highest relative demand for that product without respect to the cost of production.
B)the world price of a commodity is established by the country with the highest opportunity cost in producing the product without respect to the domestic or world demand for the product.
C)the price of a specific product will be the same in any two markets in which the cost of labour is the same.
D)the lower the costs to move a product from one market to the other,the more equal the prices for the same product when it is sold in different markets.
E)the price of a given product will never be equal in two different markets because of differences in the patterns of demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The hypothesis that the price of some given internationally traded product in one country will be equal to the price of the same product in some other country is known as
A)absolute advantage.
B)comparative advantage.
C)gains from trade.
D)the law of one price.
E)the Big Mac index.
A)absolute advantage.
B)comparative advantage.
C)gains from trade.
D)the law of one price.
E)the Big Mac index.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The diagram below shows the domestic demand and supply curves in the market for newsprint in Paperland.
 FIGURE 32-5
FIGURE 32-5
Refer to Figure 32-5.If Paperland does not engage in international trade,the equilibrium quantity of newsprint produced domestically will be
A)Q1.
B)Q2.
C)Q3.
D)Q4.
E)Q5.
 FIGURE 32-5
FIGURE 32-5Refer to Figure 32-5.If Paperland does not engage in international trade,the equilibrium quantity of newsprint produced domestically will be
A)Q1.
B)Q2.
C)Q3.
D)Q4.
E)Q5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The increases in a nationʹs output and consumption that result from specialization and trade are called
A)the terms of trade.
B)the gains from trade.
C)autarky.
D)absolute advantage.
E)comparative advantage.
A)the terms of trade.
B)the gains from trade.
C)autarky.
D)absolute advantage.
E)comparative advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Suppose Spain is currently producing 90 units of wine and 10 units of cheese,but to produce 10 more units of cheese it must sacrifice 30 units of wine.Further,suppose that Portugal produces 45 units of wine and 45 units of cheese,but to produce 10 more units of cheese it must sacrifice only 10 units of wine.It can be concluded that
A)Portugal has an absolute advantage in both wine and cheese production.
B)Portugal has an absolute advantage in wine production and Spain has an absolute advantage in cheese production.
C)Spain has an absolute advantage in both wine and cheese production.
D)Spain has a comparative advantage in the production of wine and Portugal has a comparative advantage in the production of cheese.
E)more information is needed to conclude anything about comparative advantage in either country.
A)Portugal has an absolute advantage in both wine and cheese production.
B)Portugal has an absolute advantage in wine production and Spain has an absolute advantage in cheese production.
C)Spain has an absolute advantage in both wine and cheese production.
D)Spain has a comparative advantage in the production of wine and Portugal has a comparative advantage in the production of cheese.
E)more information is needed to conclude anything about comparative advantage in either country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The ʺlaw of one priceʺ states that the price of
A)labour,measured in terms of its opportunity cost,is the same in all markets.
B)a product is always equal to the absolute cost of the resources that went into its production in any country.
C)a product worldwide is always equal to the cost of production from the country with the lowest opportunity cost to make the product.
D)a product that is costless to transport will be the same in all markets.
E)natural resources is the same in all markets.
A)labour,measured in terms of its opportunity cost,is the same in all markets.
B)a product is always equal to the absolute cost of the resources that went into its production in any country.
C)a product worldwide is always equal to the cost of production from the country with the lowest opportunity cost to make the product.
D)a product that is costless to transport will be the same in all markets.
E)natural resources is the same in all markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Consider the trade of a product between two regions.If it is very inexpensive to move the product from one regional market to another,then the
A)ʺlaw of one priceʺ argues that it will sell for the same price in all markets.
B)price it sells for in every country will depend on the cost of labour in the single low-cost country in which the product was produced.
C)difference in the price from one market to another will depend on the relative elasticities of supply in the separate markets.
D)absolute cost of producing the product must be the same in all markets.
E)production of the world supply will be from the single country with the lowest absolute cost of producing it.
A)ʺlaw of one priceʺ argues that it will sell for the same price in all markets.
B)price it sells for in every country will depend on the cost of labour in the single low-cost country in which the product was produced.
C)difference in the price from one market to another will depend on the relative elasticities of supply in the separate markets.
D)absolute cost of producing the product must be the same in all markets.
E)production of the world supply will be from the single country with the lowest absolute cost of producing it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The diagram below shows the domestic demand and supply curves in the market for newsprint in Paperland.
 FIGURE 32-5
FIGURE 32-5
Refer to Figure 32-5.If Paperland engages in international trade and the world price is PC,the amount of newsprint produced by Paperland will be
A)Q1.
B)Q2.
C)Q3.
D)Q4.
E)Q5.
 FIGURE 32-5
FIGURE 32-5Refer to Figure 32-5.If Paperland engages in international trade and the world price is PC,the amount of newsprint produced by Paperland will be
A)Q1.
B)Q2.
C)Q3.
D)Q4.
E)Q5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The existence of ʺabsolute advantageʺ
A)implies that there will be no benefits from trade between two nations.
B)refers to a situation where one country can produce one unit of a given product with fewer resources than the other country.
C)fosters the self-sufficiency of nations.
D)refers to a situation where one country can produce one unit of all goods with fewer resources than can another country.
E)is not physically possible.
A)implies that there will be no benefits from trade between two nations.
B)refers to a situation where one country can produce one unit of a given product with fewer resources than the other country.
C)fosters the self-sufficiency of nations.
D)refers to a situation where one country can produce one unit of all goods with fewer resources than can another country.
E)is not physically possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Since 1950,the worldʹs real GDP has increased by seven times and the volume of world trade has increased by roughly
A)the same amount.
B)two times.
C)ten times.
D)fifteen times.
E)thirty-five times.
A)the same amount.
B)two times.
C)ten times.
D)fifteen times.
E)thirty-five times.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The diagram below shows the domestic demand and supply curves in the market for newsprint in Paperland.
 FIGURE 32-5
FIGURE 32-5
Refer to Figure 32-5.If Paperland engages in international trade and the world price is PC,the amount of newsprint ________ will be ________.
A)imported; Q4
B)exported; Q2
C)imported; Q4 - Q2
D)exported; Q4 - Q2
E)imported; Q3
 FIGURE 32-5
FIGURE 32-5Refer to Figure 32-5.If Paperland engages in international trade and the world price is PC,the amount of newsprint ________ will be ________.
A)imported; Q4
B)exported; Q2
C)imported; Q4 - Q2
D)exported; Q4 - Q2
E)imported; Q3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In 2014 the value of goods exported from Canada was approximately $________ while the value of goods imported was approximately $________. Each of these flows represents ________% of Canadaʹs GDP.
A)50 billion; 30 billion; 6
B)530 billion; 525 billion; 32
C)12 billion; 12 billion; 1
D)100 billion; 100 billion; 15
E)25 billion; 25 billion; 10
A)50 billion; 30 billion; 6
B)530 billion; 525 billion; 32
C)12 billion; 12 billion; 1
D)100 billion; 100 billion; 15
E)25 billion; 25 billion; 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
According to the Heckscher-Ohlin theory,national comparative advantages exist because of
A)differences in national factor endowments.
B)differences in saving and investment.
C)differences in climate alone.
D)economies of scale.
E)international factor mobility.
A)differences in national factor endowments.
B)differences in saving and investment.
C)differences in climate alone.
D)economies of scale.
E)international factor mobility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If Canadaʹs terms of trade rise from 212 to 236,then the change is said to be
A)favourable.
B)unfavourable.
C)neutral.
D)prudent,since the rule of 72 is not violated.
E)a deterioration.
A)favourable.
B)unfavourable.
C)neutral.
D)prudent,since the rule of 72 is not violated.
E)a deterioration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The diagram below shows the domestic demand and supply curves in the market for newsprint in Paperland.
 FIGURE 32-5
FIGURE 32-5
Refer to Figure 32-5.If Paperland engages in trade and the world price is PB,the residents of Paperland will consume ________ units of newsprint, and the net exports of newsprint from Paperland will be ________ units.
A)Q1; Q5 - Q1
B)Q2; zero
C)Q3; zero
D)Q4; Q5 - Q1
E)Q5; zero
 FIGURE 32-5
FIGURE 32-5Refer to Figure 32-5.If Paperland engages in trade and the world price is PB,the residents of Paperland will consume ________ units of newsprint, and the net exports of newsprint from Paperland will be ________ units.
A)Q1; Q5 - Q1
B)Q2; zero
C)Q3; zero
D)Q4; Q5 - Q1
E)Q5; zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The diagram below shows the (hypothetical)demand and supply curves for regional jets in Canada.Assume that the market is competitive,all jets are identical,and that Canada engages in international trade.
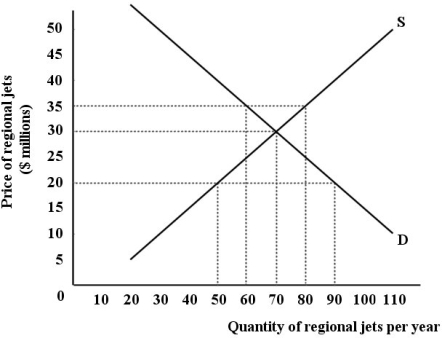 FIGURE 32-6
FIGURE 32-6
Refer to Figure 32-6.If the world price of a regional jet is $35 million,Canada will
A)neither import nor export any jets.
B)import 60 jets per year.
C)import 20 jets per year.
D)export 80 jets per year.
E)export 20 jets per year.
 FIGURE 32-6
FIGURE 32-6Refer to Figure 32-6.If the world price of a regional jet is $35 million,Canada will
A)neither import nor export any jets.
B)import 60 jets per year.
C)import 20 jets per year.
D)export 80 jets per year.
E)export 20 jets per year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The division of the gains from trade between two trading countries depends on the
A)difference between the terms of trade and the countriesʹ autarkic relative prices.
B)long-run costs.
C)quantity of resources held by each country.
D)level of unemployment in both countries.
E)size of the absolute advantages possessed by each country.
A)difference between the terms of trade and the countriesʹ autarkic relative prices.
B)long-run costs.
C)quantity of resources held by each country.
D)level of unemployment in both countries.
E)size of the absolute advantages possessed by each country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
There will be a favourable change in a nationʹs terms of trade if the
A)export and import prices rise by the same amount.
B)export price index rises by more than the import price index.
C)import price index rises by more than the export price index.
D)export and import prices fall by the same amount.
E)export and import prices stay the same.
A)export and import prices rise by the same amount.
B)export price index rises by more than the import price index.
C)import price index rises by more than the export price index.
D)export and import prices fall by the same amount.
E)export and import prices stay the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The diagram below shows the (hypothetical)demand and supply curves for regional jets in Canada.Assume that the market is competitive,all jets are identical,and that Canada engages in international trade.
 FIGURE 32-6
FIGURE 32-6
Refer to Figure 32-6.If the world price of a regional jet is $30 million,Canada will
A)neither import nor export any jets.
B)import 70 jets per year.
C)import 90 jets per year.
D)export 50 jets per year.
E)export 70 jets per year.
 FIGURE 32-6
FIGURE 32-6Refer to Figure 32-6.If the world price of a regional jet is $30 million,Canada will
A)neither import nor export any jets.
B)import 70 jets per year.
C)import 90 jets per year.
D)export 50 jets per year.
E)export 70 jets per year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The diagram below shows the (hypothetical)demand and supply curves for regional jets in Canada.Assume that the market is competitive,all jets are identical,and that Canada engages in international trade.
 FIGURE 32-6
FIGURE 32-6
Refer to Figure 32-6.Assume the world price of a regional jet is $20 million.Further,suppose that Canada disallowed international trade in regional jets.With no trade in regional jets,Canadian consumers will spend ________ at the domestic equilibrium price and quantity versus ________ for the same quantity at the world price.
A)$1000 million; $1800 million
B)$1800 million; $1000 million
C)$1400 million; $2100 million
D)$2100 million; $2100 million
E)$2100 million; $1400 million
 FIGURE 32-6
FIGURE 32-6Refer to Figure 32-6.Assume the world price of a regional jet is $20 million.Further,suppose that Canada disallowed international trade in regional jets.With no trade in regional jets,Canadian consumers will spend ________ at the domestic equilibrium price and quantity versus ________ for the same quantity at the world price.
A)$1000 million; $1800 million
B)$1800 million; $1000 million
C)$1400 million; $2100 million
D)$2100 million; $2100 million
E)$2100 million; $1400 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If Canadaʹs index of export prices is 250 and the index of import prices is 200,then the index of the terms of trade is
A)125.
B)80.
C)50
D)1.25.
E)0.8.
A)125.
B)80.
C)50
D)1.25.
E)0.8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The diagram below shows the (hypothetical)demand and supply curves for regional jets in Canada.Assume that the market is competitive,all jets are identical,and that Canada engages in international trade.
 FIGURE 32-6
FIGURE 32-6
Refer to Figure 32-6.If the world price of a regional jet is $20 million,Canada will
A)export 50 jets per year.
B)export 70 jets per year.
C)import 70 jets per year.
D)import 40 jets per year.
E)import 90 jets per year.
 FIGURE 32-6
FIGURE 32-6Refer to Figure 32-6.If the world price of a regional jet is $20 million,Canada will
A)export 50 jets per year.
B)export 70 jets per year.
C)import 70 jets per year.
D)import 40 jets per year.
E)import 90 jets per year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The diagram below shows the (hypothetical)demand and supply curves for regional jets in Canada.Assume that the market is competitive,all jets are identical,and that Canada engages in international trade.
 FIGURE 32-6
FIGURE 32-6
Refer to Figure 32-6.At what price is the total domestic demand for regional jets met completely by domestic supply?
A)exactly $30 million
B)$30 million and below
C)$30 million and above
D)$35 million
E)no price - there will always be some imported jets in this market.
 FIGURE 32-6
FIGURE 32-6Refer to Figure 32-6.At what price is the total domestic demand for regional jets met completely by domestic supply?
A)exactly $30 million
B)$30 million and below
C)$30 million and above
D)$35 million
E)no price - there will always be some imported jets in this market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The diagram below shows the (hypothetical)demand and supply curves for regional jets in Canada.Assume that the market is competitive,all jets are identical,and that Canada engages in international trade.
 FIGURE 32-6
FIGURE 32-6
Refer to Figure 32-6.Assume the world price of a regional jet is $20 million.Further,suppose that Canada disallowed international trade in regional jets and Canadian consumers purchase the domestic equilibrium quantity of jets from domestic suppliers.What is the total additional expenditure Canadian consumers will pay in this no-trade situation versus the amount they would pay for the same quantity at the world price?
A)$10 million
B)$700 million
C)$1400
D)$1800 million
E)$2100
 FIGURE 32-6
FIGURE 32-6Refer to Figure 32-6.Assume the world price of a regional jet is $20 million.Further,suppose that Canada disallowed international trade in regional jets and Canadian consumers purchase the domestic equilibrium quantity of jets from domestic suppliers.What is the total additional expenditure Canadian consumers will pay in this no-trade situation versus the amount they would pay for the same quantity at the world price?
A)$10 million
B)$700 million
C)$1400
D)$1800 million
E)$2100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The ʺterms of tradeʺ reflect the
A)amount of absolute advantage held by one country over another.
B)conditions under which trade takes place,as established by the World Trade Organization.
C)difference in opportunity costs between two countries.
D)quantity of domestic goods that must be exported to get a unit of imported goods.
E)quantity of imports that must be purchased to sell a unit of exported goods.
A)amount of absolute advantage held by one country over another.
B)conditions under which trade takes place,as established by the World Trade Organization.
C)difference in opportunity costs between two countries.
D)quantity of domestic goods that must be exported to get a unit of imported goods.
E)quantity of imports that must be purchased to sell a unit of exported goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The diagram below shows the domestic demand and supply curves in the market for newsprint in Paperland.
 FIGURE 32-5
FIGURE 32-5
Refer to Figure 32-5.If Paperland engages in trade and the world price is PA,the residents of Paperland will consume ________ units of newsprint.
A)Q1
B)Q2
C)Q3
D)Q4
E)Q5
 FIGURE 32-5
FIGURE 32-5Refer to Figure 32-5.If Paperland engages in trade and the world price is PA,the residents of Paperland will consume ________ units of newsprint.
A)Q1
B)Q2
C)Q3
D)Q4
E)Q5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If Canadaʹs index of import prices is 250 and the index of export prices is 200,then the index of the terms of trade is
A)0.80.
B)1.25.
C)12.50.
D)80.00.
E)125.00.
A)0.80.
B)1.25.
C)12.50.
D)80.00.
E)125.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The table below shows hypothetical Canadian domestic demand and supply schedules for granite.Assume there are no restrictions on trade. 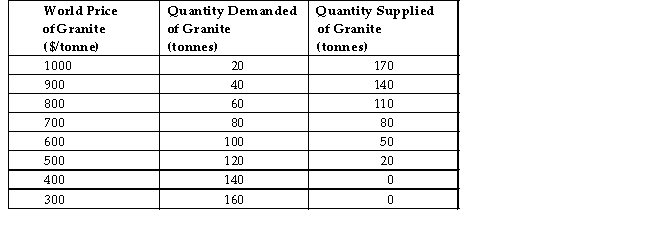 TABLE 32-6
TABLE 32-6
Refer to Table 32-6.At what price and quantity combination will Canada not engage in international trade in granite?
A)$1000 and 20 tonnes
B)$1000 and 170 tonnes
C)$700 and 80 tonnes
D)$400 and 140 tonnes
E)$400 and 0 tonnes
 TABLE 32-6
TABLE 32-6Refer to Table 32-6.At what price and quantity combination will Canada not engage in international trade in granite?
A)$1000 and 20 tonnes
B)$1000 and 170 tonnes
C)$700 and 80 tonnes
D)$400 and 140 tonnes
E)$400 and 0 tonnes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
There is an unfavourable change in a nationʹs terms of trade whenever its
A)import prices rise more than its export prices.
B)export prices rise more than its import prices.
C)import prices fall while its export prices remain constant.
D)export prices rise while its import prices remain constant.
E)export and import prices stay the same.
A)import prices rise more than its export prices.
B)export prices rise more than its import prices.
C)import prices fall while its export prices remain constant.
D)export prices rise while its import prices remain constant.
E)export and import prices stay the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The index for a countryʹs terms of trade is computed as
A)index of export prices/index of import prices.
B)(index of import prices/index of export prices)× 100.
C)index of import prices/index of export prices.
D)(index of import prices + index of export prices)× 100.
E)(index of export prices/index of import prices)× 100.
A)index of export prices/index of import prices.
B)(index of import prices/index of export prices)× 100.
C)index of import prices/index of export prices.
D)(index of import prices + index of export prices)× 100.
E)(index of export prices/index of import prices)× 100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The table below shows hypothetical Canadian domestic demand and supply schedules for granite.Assume there are no restrictions on trade.  TABLE 32-6
TABLE 32-6
Refer to Table 32-6.Suppose the world price of granite is $350 per tonne.What quantity will Canada import or export?
A)Canada will import 0 tonnes
B)Canada will import 150 tonnes
C)Canada will export 160 tonnes
D)Canada will neither import nor export
E)Canada will export 140 tonnes
 TABLE 32-6
TABLE 32-6Refer to Table 32-6.Suppose the world price of granite is $350 per tonne.What quantity will Canada import or export?
A)Canada will import 0 tonnes
B)Canada will import 150 tonnes
C)Canada will export 160 tonnes
D)Canada will neither import nor export
E)Canada will export 140 tonnes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The diagram below shows the (hypothetical)demand and supply curves for regional jets in Canada.Assume that the market is competitive,all jets are identical,and that Canada engages in international trade.
 FIGURE 32-6
FIGURE 32-6
Refer to Figure 32-6.Assume the world price of a regional jet is $20 million.How many jets are not produced in Canada that would have been if Canada did not engage in international trade?
A)20
B)40
C)50
D)70
E)90
 FIGURE 32-6
FIGURE 32-6Refer to Figure 32-6.Assume the world price of a regional jet is $20 million.How many jets are not produced in Canada that would have been if Canada did not engage in international trade?
A)20
B)40
C)50
D)70
E)90

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The table below shows hypothetical Canadian domestic demand and supply schedules for granite.Assume there are no restrictions on trade.  TABLE 32-6
TABLE 32-6
Refer to Table 32-6.Suppose the world price of granite is $900.What quantity will Canada import or export?
A)Canada will export 100 tonnes
B)Canada will export 140 tonnes
C)Canada will neither import nor export
D)Canada will import 40 tonnes
E)Canada will import 100 tonnes
 TABLE 32-6
TABLE 32-6Refer to Table 32-6.Suppose the world price of granite is $900.What quantity will Canada import or export?
A)Canada will export 100 tonnes
B)Canada will export 140 tonnes
C)Canada will neither import nor export
D)Canada will import 40 tonnes
E)Canada will import 100 tonnes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The diagram below shows Robinson Crusoeʹs annual production possibilities boundary for the production of bananas and coconuts.
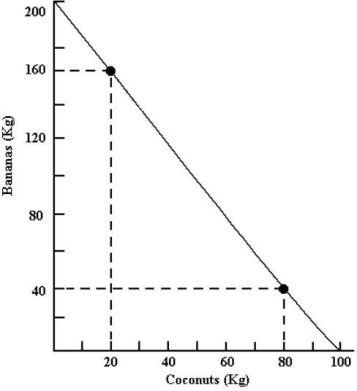 FIGURE 32-3
FIGURE 32-3
Refer to Figure 32-3.Suppose a trading partner offers to give coconuts to Robinson Crusoe in exchange for his bananas.If Robinson Crusoe is to improve his consumption possibilities,the terms of trade must be 1 kg coconuts for
A)5 kg bananas.
B)4 kg bananas.
C)3 kg bananas.
D)2 kg bananas.
E)1 kg bananas.
 FIGURE 32-3
FIGURE 32-3Refer to Figure 32-3.Suppose a trading partner offers to give coconuts to Robinson Crusoe in exchange for his bananas.If Robinson Crusoe is to improve his consumption possibilities,the terms of trade must be 1 kg coconuts for
A)5 kg bananas.
B)4 kg bananas.
C)3 kg bananas.
D)2 kg bananas.
E)1 kg bananas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The figure below shows Arcticlandʹs annual production possibilities boundary for the production of fish and ice.
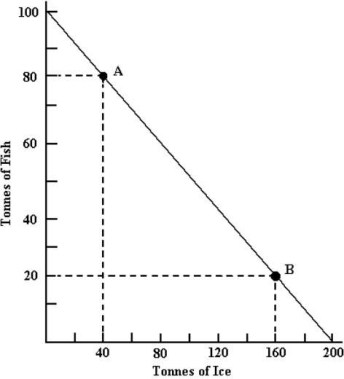 FIGURE 32-4
FIGURE 32-4
Refer to Figure 32-4.Suppose a trading partner offers to give Arcticland ice in exchange for its fish.If Arcticland is to improve its consumption possibilities from this trade,the terms of trade must be 1 tonne of ice for:
A)3 tonnes of fish.
B)2 tonnes of fish.
C)1 tonne of fish.
D)0.5 tonne of fish.
E)0.33 tonne of fish.
 FIGURE 32-4
FIGURE 32-4Refer to Figure 32-4.Suppose a trading partner offers to give Arcticland ice in exchange for its fish.If Arcticland is to improve its consumption possibilities from this trade,the terms of trade must be 1 tonne of ice for:
A)3 tonnes of fish.
B)2 tonnes of fish.
C)1 tonne of fish.
D)0.5 tonne of fish.
E)0.33 tonne of fish.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Consider Canadaʹs terms of trade.Canada is a net importer of citrus fruit.If severe weather in Florida wipes out the fruit crop for one season,Canadaʹs terms of trade will likely
A)deteriorate.
B)improve.
C)not change.
D)improve as long as Canada stops importing citrus fruit from Florida.
E)indeterminable with the information provided.
A)deteriorate.
B)improve.
C)not change.
D)improve as long as Canada stops importing citrus fruit from Florida.
E)indeterminable with the information provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The diagram below shows Robinson Crusoeʹs annual production possibilities boundary for the production of bananas and coconuts.
 FIGURE 32-3
FIGURE 32-3
Refer to Figure 32-3.Suppose a trading partner offers to give bananas to Robinson Crusoe in exchange for his coconuts.If Robinson Crusoe is to improve his consumption possibilities from this trade,the terms of trade must be 1 kg bananas for
A)3.0 kg coconuts.
B)2.0 kg coconuts.
C)1.0 kg coconuts.
D)0.5 kg coconuts.
E)0.33 kg coconuts.
 FIGURE 32-3
FIGURE 32-3Refer to Figure 32-3.Suppose a trading partner offers to give bananas to Robinson Crusoe in exchange for his coconuts.If Robinson Crusoe is to improve his consumption possibilities from this trade,the terms of trade must be 1 kg bananas for
A)3.0 kg coconuts.
B)2.0 kg coconuts.
C)1.0 kg coconuts.
D)0.5 kg coconuts.
E)0.33 kg coconuts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Canada is both an importer and an exporter of automobiles.If Canada exports more automobiles than it imports,and the price of automobiles rises,then ceteris paribus,Canadaʹs terms of trade will likely
A)improve because the index of export prices would rise and the index of import prices would fall.
B)remain the same because the index of export prices would rise by the same amount as the index of import prices.
C)deteriorate because of the loss of exports that would result.
D)deteriorate because the loss of exports would be more than offset by the gain in imports.
E)improve because the index of export prices will rise more than the index of import prices.
A)improve because the index of export prices would rise and the index of import prices would fall.
B)remain the same because the index of export prices would rise by the same amount as the index of import prices.
C)deteriorate because of the loss of exports that would result.
D)deteriorate because the loss of exports would be more than offset by the gain in imports.
E)improve because the index of export prices will rise more than the index of import prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Consider Canadaʹs terms of trade.Canadians consume millions of cups of Tim Hortonʹs coffee each year.If Tim Hortonʹs reduced the price per cup of coffee (because of a decrease in administration and transportation costs),ceteris paribus,Canadaʹs terms of trade will
A)deteriorate.
B)improve.
C)not change.
D)improve as long as consumption of coffee decreases.
E)deteriorate as long as consumption of coffee increases.
A)deteriorate.
B)improve.
C)not change.
D)improve as long as consumption of coffee decreases.
E)deteriorate as long as consumption of coffee increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Consider Canadaʹs terms of trade.Canada is a net exporter of oil.An increase in the world price of oil,ceteris paribus,means that Canadaʹs terms of trade will
A)deteriorate.
B)improve.
C)not change.
D)improve as long as all of Canadaʹs production of oil is being exported.
E)deteriorate as long as Canada exports more oil than it imports.
A)deteriorate.
B)improve.
C)not change.
D)improve as long as all of Canadaʹs production of oil is being exported.
E)deteriorate as long as Canada exports more oil than it imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The figure below shows Arcticlandʹs annual production possibilities boundary for the production of fish and ice.
 FIGURE 32-4
FIGURE 32-4
Refer to Figure 32-4.Suppose a trading partner offers to give Arcticland some fish in exchange for its ice.If Arcticland is to improve its consumption possibilities,the terms of trade must be 1 tonne of fish for
A)5 tonnes of ice.
B)4 tonnes of ice.
C)3 tonnes of ice.
D)2 tonne of ice.
E)1 tonne of ice.
 FIGURE 32-4
FIGURE 32-4Refer to Figure 32-4.Suppose a trading partner offers to give Arcticland some fish in exchange for its ice.If Arcticland is to improve its consumption possibilities,the terms of trade must be 1 tonne of fish for
A)5 tonnes of ice.
B)4 tonnes of ice.
C)3 tonnes of ice.
D)2 tonne of ice.
E)1 tonne of ice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If,over a period of a year,a countryʹs import price index rises from 100 to 120 and its export price index rises from 100 to 110,its index for the terms of trade has
A)risen from 100 to 120.
B)risen from 100 to 110.
C)risen to 109.09.
D)fallen to 91.67.
E)fallen from 110 to 100.
A)risen from 100 to 120.
B)risen from 100 to 110.
C)risen to 109.09.
D)fallen to 91.67.
E)fallen from 110 to 100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If the index of export prices for Country X increases from 120 to 150 and the index of import prices increases from 100 to 125,it may be said that
A)the terms of trade have improved.
B)the terms of trade have deteriorated.
C)there has been no change in the terms of trade.
D)the terms of trade have improved by 10%.
E)there is insufficient information to calculate the terms of trade.
A)the terms of trade have improved.
B)the terms of trade have deteriorated.
C)there has been no change in the terms of trade.
D)the terms of trade have improved by 10%.
E)there is insufficient information to calculate the terms of trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



