Deck 30: Unemployment Fluctuations and the Nairu
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/111
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 30: Unemployment Fluctuations and the Nairu
1
One reason that economists are interested in gross flows in the labour market as well as in the stock of unemployment is that examining the gross flows
A)gives a better estimate of NAIRU.
B)gives a good estimate of the incidence of unemployment.
C)excludes only the new entrants and retirements of people moving into and out of the labour force.
D)in relation to the stock of unemployment can indicate the amount of time the average person spends unemployed.
E)provides a better indication of the total number of people unemployed at any one time.
A)gives a better estimate of NAIRU.
B)gives a good estimate of the incidence of unemployment.
C)excludes only the new entrants and retirements of people moving into and out of the labour force.
D)in relation to the stock of unemployment can indicate the amount of time the average person spends unemployed.
E)provides a better indication of the total number of people unemployed at any one time.
in relation to the stock of unemployment can indicate the amount of time the average person spends unemployed.
2
Suppose John finishes school and immediately gets a part-time job.The measured unemployment rate would
A)rise because he was not in the labour force when in school.
B)not change since he is now employed.
C)fall because he was considered unemployed when in school.
D)fall because he was not in the labour force when in school.
E)not change because part-time jobs arenʹt counted in the labour force.
A)rise because he was not in the labour force when in school.
B)not change since he is now employed.
C)fall because he was considered unemployed when in school.
D)fall because he was not in the labour force when in school.
E)not change because part-time jobs arenʹt counted in the labour force.
fall because he was not in the labour force when in school.
3
Suppose the official rate of unemployment reported by Statistics Canada is 7.2%.One reason this is likely to be an understatement of the amount of ʺtrueʺ unemployment is that
A)the official rate is a measure of gross flows into and out of unemployment rather than net flows.
B)discouraged workers who have given up searching for a job,but would take one if offered,are not included.
C)the official rate is a measure of net flows into and out of unemployment rather than gross flows.
D)Statistics Canada does not have a good measure of the numbers of people entering the labour force.
E)seasonal workers are not included at all in the official data.
A)the official rate is a measure of gross flows into and out of unemployment rather than net flows.
B)discouraged workers who have given up searching for a job,but would take one if offered,are not included.
C)the official rate is a measure of net flows into and out of unemployment rather than gross flows.
D)Statistics Canada does not have a good measure of the numbers of people entering the labour force.
E)seasonal workers are not included at all in the official data.
discouraged workers who have given up searching for a job,but would take one if offered,are not included.
4
If the actual unemployment rate is equal to the NAIRU,then
A)actual GDP will be higher than potential GDP.
B)actual GDP will be below potential GDP.
C)potential GDP will expand permanently.
D)the unemployment rate is 0%.
E)actual and potential GDP are equal.
A)actual GDP will be higher than potential GDP.
B)actual GDP will be below potential GDP.
C)potential GDP will expand permanently.
D)the unemployment rate is 0%.
E)actual and potential GDP are equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The total amount of unemployment in the economy is constant when the flows of individuals
A)into unemployment are positive.
B)into unemployment exceed the flows out of unemployment.
C)out of unemployment exceed the flows into unemployment.
D)out of unemployment are negative.
E)out of unemployment are equal to the flows into unemployment.
A)into unemployment are positive.
B)into unemployment exceed the flows out of unemployment.
C)out of unemployment exceed the flows into unemployment.
D)out of unemployment are negative.
E)out of unemployment are equal to the flows into unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If there are more job vacancies in the economy than there are unemployed workers,it is likely that
A)fiscal policy aimed at increasing aggregate demand would cause the actual unemployment rate to move toward the NAIRU.
B)the actual unemployment rate is less than the NAIRU.
C)the economy has a high NAIRU.
D)there is excessive involuntary unemployment in this economy.
E)there is no structural unemployment in this economy.
A)fiscal policy aimed at increasing aggregate demand would cause the actual unemployment rate to move toward the NAIRU.
B)the actual unemployment rate is less than the NAIRU.
C)the economy has a high NAIRU.
D)there is excessive involuntary unemployment in this economy.
E)there is no structural unemployment in this economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Suppose the official rate of unemployment reported by Statistics Canada declines from one month to the next from 7.5% to 7.2%,but we also know that the stock of unemployed workers has not changed.How is this possible?
A)The labour force has declined due to out-migration of working-age people.
B)The labour force has grown as previously discouraged workers re-start their job-search process as unemployed individuals.
C)Some individuals who were previously outside the labour force have joined the labour force and immediately found jobs.
D)We have gone from a month with high seasonal unemployment to a month with low seasonal unemployment.
E)We have gone from a month with low seasonal unemployment to a month with high seasonal unemployment.
A)The labour force has declined due to out-migration of working-age people.
B)The labour force has grown as previously discouraged workers re-start their job-search process as unemployed individuals.
C)Some individuals who were previously outside the labour force have joined the labour force and immediately found jobs.
D)We have gone from a month with high seasonal unemployment to a month with low seasonal unemployment.
E)We have gone from a month with low seasonal unemployment to a month with high seasonal unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Suppose that next year 300 000 existing jobs in the economy are eliminated through layoffs and plant closures,and 400 000 new jobs are created through expansions and the creation of new firms.The amount of unemployment will rise over that year if
A)more than 300 000 people drop out of the labour force.
B)more than 100 000 people drop out of the labour force.
C)less than 100 000 people drop out of the labour force.
D)less than 100 000 people join the labour force.
E)more than 100 000 people join the labour force.
A)more than 300 000 people drop out of the labour force.
B)more than 100 000 people drop out of the labour force.
C)less than 100 000 people drop out of the labour force.
D)less than 100 000 people join the labour force.
E)more than 100 000 people join the labour force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When the actual unemployment rate is equal to the NAIRU,we can say that
A)all remaining unemployment is structural.
B)the economy is experiencing no lost output due to frictional unemployment.
C)the economy is at full employment.
D)frictional unemployment is zero.
E)frictional and structural unemployment are both zero.
A)all remaining unemployment is structural.
B)the economy is experiencing no lost output due to frictional unemployment.
C)the economy is at full employment.
D)frictional unemployment is zero.
E)frictional and structural unemployment are both zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The total amount of unemployment in the economy decreases when the flows of individuals
A)into unemployment are positive.
B)into unemployment exceed the flows out of unemployment.
C)out of unemployment exceed the flows into unemployment.
D)out of unemployment are negative.
E)out of unemployment are equal to the flows into unemployment.
A)into unemployment are positive.
B)into unemployment exceed the flows out of unemployment.
C)out of unemployment exceed the flows into unemployment.
D)out of unemployment are negative.
E)out of unemployment are equal to the flows into unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When the growth rate of the labour force is greater than the growth rate of total employment,the unemployment rate
A)decreases.
B)increases.
C)is below NAIRU.
D)is above NAIRU.
E)is equal to NAIRU.
A)decreases.
B)increases.
C)is below NAIRU.
D)is above NAIRU.
E)is equal to NAIRU.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When the growth rate of the labour force is less than the growth rate of total employment,the unemployment rate
A)decreases.
B)increases.
C)is below NAIRU.
D)is above NAIRU.
E)is equal to NAIRU.
A)decreases.
B)increases.
C)is below NAIRU.
D)is above NAIRU.
E)is equal to NAIRU.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
One reason that economists are interested in the gross flows in the labour market as well as the stocks of unemployed is that examining the flows
A)gives us a better estimate of NAIRU.
B)gives more insight into the amount of labour-market turnover.
C)provides a better indication of the total number of people unemployed at any one time rather than just looking at the stocks.
D)provides a good estimate of the overall level of employment.
E)provides the only reliable way to measure cyclical unemployment.
A)gives us a better estimate of NAIRU.
B)gives more insight into the amount of labour-market turnover.
C)provides a better indication of the total number of people unemployed at any one time rather than just looking at the stocks.
D)provides a good estimate of the overall level of employment.
E)provides the only reliable way to measure cyclical unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Suppose in a given month the flow out of unemployment equals 300 000 per month,and the flow into unemployment equals 330 000 per month.The rate of unemployment has
A)increased by 30 000.
B)decreased by 30 000.
C)increased by 10%.
D)decreased by 10%.
E)Not enough information to determine.
A)increased by 30 000.
B)decreased by 30 000.
C)increased by 10%.
D)decreased by 10%.
E)Not enough information to determine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The total amount of unemployment in the economy rises when the flows of individuals
A)into unemployment are positive.
B)into unemployment exceed the flows out of unemployment.
C)out of unemployment exceed the flows into unemployment.
D)out of unemployment are negative.
E)out of unemployment are equal to the flows into unemployment.
A)into unemployment are positive.
B)into unemployment exceed the flows out of unemployment.
C)out of unemployment exceed the flows into unemployment.
D)out of unemployment are negative.
E)out of unemployment are equal to the flows into unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When real GDP is greater than potential output,the unemployment rate the NAIRU.
A)falls toward
B)falls below
C)rises toward but never exceeds
D)is equal to
E)rises above
A)falls toward
B)falls below
C)rises toward but never exceeds
D)is equal to
E)rises above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Suppose that next year 300 000 existing jobs in the economy are eliminated and 200 000 new jobs are created.The amount of unemployment will decline over that year if
A)more than 100 000 people drop out of the labour force.
B)less than 100 000 people drop out of the labour force.
C)less than 100 000 people join the labour force.
D)more than 100 000 people join the labour force.
E)more than 300 000 people join the labour force.
A)more than 100 000 people drop out of the labour force.
B)less than 100 000 people drop out of the labour force.
C)less than 100 000 people join the labour force.
D)more than 100 000 people join the labour force.
E)more than 300 000 people join the labour force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When one worker is unemployed for one year,
A)we no longer include that worker in labour-force statistics.
B)there may be significant personal costs,but there is no cost to the economy.
C)it is not a problem because as soon as the worker is employed again,any loss of output goes away.
D)there is no effect on national income.
E)the output this worker would have produced is lost forever.
A)we no longer include that worker in labour-force statistics.
B)there may be significant personal costs,but there is no cost to the economy.
C)it is not a problem because as soon as the worker is employed again,any loss of output goes away.
D)there is no effect on national income.
E)the output this worker would have produced is lost forever.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If the actual unemployment rate is one percentage point less than the NAIRU,then
A)actual and potential GDP are equal.
B)actual GDP is greater than potential GDP.
C)actual GDP is less than potential GDP.
D)potential GDP will expand permanently.
E)potential GDP will contract until it equals actual GDP.
A)actual and potential GDP are equal.
B)actual GDP is greater than potential GDP.
C)actual GDP is less than potential GDP.
D)potential GDP will expand permanently.
E)potential GDP will contract until it equals actual GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When real GDP is less than potential output,the unemployment rate ________ the NAIRU.
A)falls toward
B)falls below
C)rises toward but never exceeds
D)is equal to
E)rises above
A)falls toward
B)falls below
C)rises toward but never exceeds
D)is equal to
E)rises above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If,as market-clearing theories of the labour market suggest,all labour markets had perfectly flexible wages,real wages would rise when labour demand
A)rises and fall when labour supply rises.
B)rises and fall when labour supply falls.
C)falls and rise when labour supply falls.
D)rises and rise when labour supply rises.
E)falls and falls when labour supply rises.
A)rises and fall when labour supply rises.
B)rises and fall when labour supply falls.
C)falls and rise when labour supply falls.
D)rises and rise when labour supply rises.
E)falls and falls when labour supply rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Market-clearing theories of the labour market feature ________ wages, and thus involuntary unemployment________.
A)perfectly flexible; exists
B)sticky; does not exist
C)sticky; exists
D)perfectly flexible; does not exist
A)perfectly flexible; exists
B)sticky; does not exist
C)sticky; exists
D)perfectly flexible; does not exist

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What economists sometimes call ʺvoluntary unemploymentʺ occurs when
A)a job is available but the worker has not yet found it.
B)the level of real GDP is at or above the economyʹs potential output.
C)a person is willing to accept a job at the going wage rate but cannot find one.
D)a worker enters the job market for the first time.
E)a worker is not willing to accept an available job at the going wage rate.
A)a job is available but the worker has not yet found it.
B)the level of real GDP is at or above the economyʹs potential output.
C)a person is willing to accept a job at the going wage rate but cannot find one.
D)a worker enters the job market for the first time.
E)a worker is not willing to accept an available job at the going wage rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Empirical observation of employment and real-wage fluctuations over the business cycle in Canada and other developed countries
A)is not able to refute the market-clearing theory of unemployment.
B)shows that employment is volatile and real wages are not.
C)shows that real wages are volatile and employment levels are not.
D)supports the market-clearing theory that there is no involuntary unemployment.
E)supports the market-clearing theory that labour markets always clear.
A)is not able to refute the market-clearing theory of unemployment.
B)shows that employment is volatile and real wages are not.
C)shows that real wages are volatile and employment levels are not.
D)supports the market-clearing theory that there is no involuntary unemployment.
E)supports the market-clearing theory that labour markets always clear.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The table below provides hypothetical unemployment,employment,and labour force data for a small economy over a 3 -month period.The unemployment rate on January 1 is 6%. 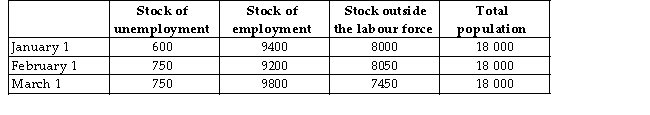 TABLE 30-1
TABLE 30-1
Refer to Table 30-1.What is the unemployment rate on February 1?
A)4.17%
B)6.0%
C)7.54%
D)8.15%
E)9.32%
 TABLE 30-1
TABLE 30-1Refer to Table 30-1.What is the unemployment rate on February 1?
A)4.17%
B)6.0%
C)7.54%
D)8.15%
E)9.32%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Market-clearing theories of the labour market argue that
A)competitive labour markets can be relied upon to eliminate all unemployment.
B)labour markets will clear and involuntary unemployment will thereby be eliminated.
C)all unemployment is most easily corrected by government intervention in the economy.
D)all unemployment arises from firms being unwilling to demand labour services.
E)labour unions are necessary elements in reducing unemployment.
A)competitive labour markets can be relied upon to eliminate all unemployment.
B)labour markets will clear and involuntary unemployment will thereby be eliminated.
C)all unemployment is most easily corrected by government intervention in the economy.
D)all unemployment arises from firms being unwilling to demand labour services.
E)labour unions are necessary elements in reducing unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The labour market in the diagram below begins in equilibrium with a real wage of $10 and quantity employed of 1000.
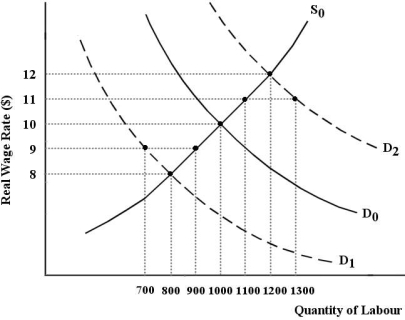 FIGURE 30-1
FIGURE 30-1
Refer to Figure 30-1.Given the labour supply and labour demand curves,D0 and S0,which of the following statements is true in the market-clearing theory of unemployment?
A)At any wage above $10,there is an excess demand for labour,and the wage will be driven down.
B)At any wage above $10,there is an excess supply of labour,and the wage will be driven down.
C)At any wage above $10,there is persistent,involuntary unemployment.
D)At any wage below $10,there is an excess supply of labour,and the wage will be driven up.
E)At any wage below $10,there is an excess demand for labour,and the wage will be driven down.
 FIGURE 30-1
FIGURE 30-1Refer to Figure 30-1.Given the labour supply and labour demand curves,D0 and S0,which of the following statements is true in the market-clearing theory of unemployment?
A)At any wage above $10,there is an excess demand for labour,and the wage will be driven down.
B)At any wage above $10,there is an excess supply of labour,and the wage will be driven down.
C)At any wage above $10,there is persistent,involuntary unemployment.
D)At any wage below $10,there is an excess supply of labour,and the wage will be driven up.
E)At any wage below $10,there is an excess demand for labour,and the wage will be driven down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The table below provides hypothetical unemployment,employment,and labour force data for an economy over a 3 -month period. 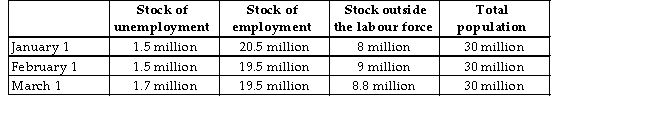 TABLE 30-2
TABLE 30-2
Refer to Table 30-2.What is the unemployment rate on March 1?
A)19.3%
B)5.6%
C)6.0%
D)8.7%
E)8.0%
 TABLE 30-2
TABLE 30-2Refer to Table 30-2.What is the unemployment rate on March 1?
A)19.3%
B)5.6%
C)6.0%
D)8.7%
E)8.0%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The table below provides hypothetical unemployment,employment,and labour force data for an economy over a 3 -month period.  TABLE 30-2
TABLE 30-2
Refer to Table 30-2.What is the unemployment rate on February 1?
A)7.7%
B)7.1%
C)16.7%
D)6.0%
E)5.0%
 TABLE 30-2
TABLE 30-2Refer to Table 30-2.What is the unemployment rate on February 1?
A)7.7%
B)7.1%
C)16.7%
D)6.0%
E)5.0%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The table below provides hypothetical unemployment,employment,and labour force data for an economy over a 3 -month period.  TABLE 30-2
TABLE 30-2
Refer to Table 30-2.Something unusual happened in this countryʹs labour force between January 1 and February 1.What was it?
A)The unemployment rate declined,even though the stock of unemployment remained stable.
B)The labour force grew by one million workers,which represents over 3 percent of the countryʹs total population.
C)The unemployment rate declined because workers left the labour force.
D)The number of workers employed rose,even though workers left the labour force.
E)One million workers (net)left their jobs and also left the labour force.
 TABLE 30-2
TABLE 30-2Refer to Table 30-2.Something unusual happened in this countryʹs labour force between January 1 and February 1.What was it?
A)The unemployment rate declined,even though the stock of unemployment remained stable.
B)The labour force grew by one million workers,which represents over 3 percent of the countryʹs total population.
C)The unemployment rate declined because workers left the labour force.
D)The number of workers employed rose,even though workers left the labour force.
E)One million workers (net)left their jobs and also left the labour force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The table below provides hypothetical unemployment,employment,and labour force data for an economy over a 3 -month period.  TABLE 30-2
TABLE 30-2
Refer to Table 30-2.Which of the following changes occurred in this economy between February 1 and March 1?
A)The labour force remained stable.
B)The unemployment rate declined.
C)The unemployment rate remained stable.
D)200 000 (net)workers entered the labour force.
E)200 000 (net)workers left the labour force.
 TABLE 30-2
TABLE 30-2Refer to Table 30-2.Which of the following changes occurred in this economy between February 1 and March 1?
A)The labour force remained stable.
B)The unemployment rate declined.
C)The unemployment rate remained stable.
D)200 000 (net)workers entered the labour force.
E)200 000 (net)workers left the labour force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Market-clearing theories of the labour market assume that labour markets
A)always clear.
B)are inefficient.
C)have asymmetrically rigid wages.
D)should be regulated to produce an efficient wage rate.
E)will always provide a subsistence wage.
A)always clear.
B)are inefficient.
C)have asymmetrically rigid wages.
D)should be regulated to produce an efficient wage rate.
E)will always provide a subsistence wage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If labour markets had perfectly flexible wages,as the market-clearing theories suggest,involuntary unemployment would
A)not exist.
B)rise when the labour demand curve shifts to the left.
C)rise when the labour demand curve shifts to the right.
D)rise when the labour supply curve shifts to the left.
E)rise when the labour supply curve shifts to the right.
A)not exist.
B)rise when the labour demand curve shifts to the left.
C)rise when the labour demand curve shifts to the right.
D)rise when the labour supply curve shifts to the left.
E)rise when the labour supply curve shifts to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Suppose we know the following information about the labour market.Over a one-month period: -total number of previously unemployed workers that found jobs = 150 000
-total number of previously employed workers that became unemployed = 150 000
During this month the gross flow into unemployment was ________ and the net flow into unemployment was________.
A)150 000; zero
B)150 000; 150 000
C)zero; 150 000
D)zero; zero
E)300 000; 150 000
-total number of previously employed workers that became unemployed = 150 000
During this month the gross flow into unemployment was ________ and the net flow into unemployment was________.
A)150 000; zero
B)150 000; 150 000
C)zero; 150 000
D)zero; zero
E)300 000; 150 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The table below provides hypothetical unemployment,employment,and labour force data for a small economy over a 3 -month period.The unemployment rate on January 1 is 6%.  TABLE 30-1
TABLE 30-1
Refer to Table 30-1.What is the unemployment rate on March 1?
A)6.0%
B)7.11%
C)10.07%
D)7.65%
E)4.17%
 TABLE 30-1
TABLE 30-1Refer to Table 30-1.What is the unemployment rate on March 1?
A)6.0%
B)7.11%
C)10.07%
D)7.65%
E)4.17%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Market-clearing theories of the labour market suggest that fluctuations in employment and wages can be caused by the supply side of the market through changes in the
A)price level.
B)level of net exports in the economy.
C)marginal efficiency of investment.
D)willingness of firms to hire workers.
E)willingness of workers to supply their labour.
A)price level.
B)level of net exports in the economy.
C)marginal efficiency of investment.
D)willingness of firms to hire workers.
E)willingness of workers to supply their labour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The table below provides hypothetical unemployment,employment,and labour force data for a small economy over a 3 -month period.The unemployment rate on January 1 is 6%.  TABLE 30-1
TABLE 30-1
Refer to Table 30-1.Between February 1 and March 1 the stock of unemployment remained stable at 750,and the unemployment rate ________ because ________.
A)decreased; the labour force grew by 600
B)decreased; the labour force shrank by 600
C)remained stable; the stock of unemployment did not change
D)increased; the labour force grew by 600
E)increased; the labour force shrank by 600
 TABLE 30-1
TABLE 30-1Refer to Table 30-1.Between February 1 and March 1 the stock of unemployment remained stable at 750,and the unemployment rate ________ because ________.
A)decreased; the labour force grew by 600
B)decreased; the labour force shrank by 600
C)remained stable; the stock of unemployment did not change
D)increased; the labour force grew by 600
E)increased; the labour force shrank by 600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which statement by an employer is consistent with the market-clearing theory of unemployment?
A)ʺI pay more than the going rate so I can hire good workers.ʺ
B)ʺI pay only enough to attract workers who are at the bottom of the pay scale.ʺ
C)ʺI love it when inflation goes up because that drives down my wage costs.ʺ
D)ʺWorkers can always find jobs,if only they lower their expectations.ʺ
E)ʺUnions have only their current membersʹ interests at heart.ʺ
A)ʺI pay more than the going rate so I can hire good workers.ʺ
B)ʺI pay only enough to attract workers who are at the bottom of the pay scale.ʺ
C)ʺI love it when inflation goes up because that drives down my wage costs.ʺ
D)ʺWorkers can always find jobs,if only they lower their expectations.ʺ
E)ʺUnions have only their current membersʹ interests at heart.ʺ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The table below provides hypothetical unemployment,employment,and labour force data for an economy over a 3 -month period.  TABLE 30-2
TABLE 30-2
Refer to Table 30-2.What is the unemployment rate on January 1?
A)5.3%
B)5.0%
C)7.3%
D)6.8%
E)18.7%
 TABLE 30-2
TABLE 30-2Refer to Table 30-2.What is the unemployment rate on January 1?
A)5.3%
B)5.0%
C)7.3%
D)6.8%
E)18.7%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Suppose we know the following information about the labour market.Over a one-month period: -total number of previously unemployed workers that found jobs = 500 000
-total number of individuals that became unemployed = 500 000
During the same month the unemployment rate increased from 7.1% to 7.3%.It must be the case that
A)the population increased during that month.
B)the population decreased during that month.
C)a certain number of people entered the labour force during that month.
D)the gross flow and the net flow into unemployment are equal.
E)a certain number of people left the labour force during that month.
-total number of individuals that became unemployed = 500 000
During the same month the unemployment rate increased from 7.1% to 7.3%.It must be the case that
A)the population increased during that month.
B)the population decreased during that month.
C)a certain number of people entered the labour force during that month.
D)the gross flow and the net flow into unemployment are equal.
E)a certain number of people left the labour force during that month.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The concept of ʺfull employmentʺ refers to a situation in which there exists
A)an unemployment rate of less than 5%.
B)no job vacancies at the time.
C)only structural and/or frictional unemployment.
D)only involuntary unemployment.
E)a measured unemployment rate of zero.
A)an unemployment rate of less than 5%.
B)no job vacancies at the time.
C)only structural and/or frictional unemployment.
D)only involuntary unemployment.
E)a measured unemployment rate of zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
When the total number of unfilled job openings in the economy is equal to the total number of persons unemployed,________ is zero.
A)cyclical unemployment
B)frictional unemployment
C)involuntary unemployment
D)the NAIRU
E)structural unemployment
A)cyclical unemployment
B)frictional unemployment
C)involuntary unemployment
D)the NAIRU
E)structural unemployment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
ʺEfficiency wagesʺ are said to exist when wages are
A)such that cyclical unemployment is zero.
B)such that the NAIRU is zero.
C)high enough above market levels that workers increase their productivity.
D)equal to the market wage.
E)just high enough to induce a worker to take a job.
A)such that cyclical unemployment is zero.
B)such that the NAIRU is zero.
C)high enough above market levels that workers increase their productivity.
D)equal to the market wage.
E)just high enough to induce a worker to take a job.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Non-market-clearing theories of the labour market feature ________ wages, and thus involuntary unemployment ________.
A)perfectly flexible; cannot exist
B)perfectly flexible; can exist
C)sticky; cannot exist
D)sticky; can exist
E)efficiency wages; cannot exist
A)perfectly flexible; cannot exist
B)perfectly flexible; can exist
C)sticky; cannot exist
D)sticky; can exist
E)efficiency wages; cannot exist

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The labour market in the diagram below begins in equilibrium with a real wage of $10 and quantity employed of 1000.
 FIGURE 30-1
FIGURE 30-1
Refer to Figure 30-1.The economy begins with D0 and S0.Suppose there is a negative shock to the economy,which shifts the demand for labour curve to D1.In the market-clearing theory of unemployment,
A)wages would be sticky and would adjust downward to,perhaps $9,causing involuntary unemployment of 200 workers.
B)the wage rate would fall to $8,employment would fall to 800,causing involuntary unemployment of 200 workers.
C)wages would be sticky and would adjust downward to,perhaps $9,causing involuntary unemployment of 300 workers.
D)the wage rate would fall to $8,employment would fall to 800 and there would be no unemployment.
E)all markets would clear,causing the demand for labour curve to shift back to D 0 and the wage rate and employment levels would return to their original levels.
 FIGURE 30-1
FIGURE 30-1Refer to Figure 30-1.The economy begins with D0 and S0.Suppose there is a negative shock to the economy,which shifts the demand for labour curve to D1.In the market-clearing theory of unemployment,
A)wages would be sticky and would adjust downward to,perhaps $9,causing involuntary unemployment of 200 workers.
B)the wage rate would fall to $8,employment would fall to 800,causing involuntary unemployment of 200 workers.
C)wages would be sticky and would adjust downward to,perhaps $9,causing involuntary unemployment of 300 workers.
D)the wage rate would fall to $8,employment would fall to 800 and there would be no unemployment.
E)all markets would clear,causing the demand for labour curve to shift back to D 0 and the wage rate and employment levels would return to their original levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The labour market in the diagram below begins in equilibrium with a real wage of $10 and quantity employed of 1000.
 FIGURE 30-1
FIGURE 30-1
Refer to Figure 30-1.The economy begins with D0 and S0.Suppose there is a negative shock to the economy,which shifts the demand for labour curve to D1.An outcome consistent with non-market-clearing theories of unemployment is
A)the wage rate would fall to $8,employment would fall to 800,causing involuntary unemployment of 200 workers.
B)wages would be sticky and would adjust downward to,perhaps $9,causing involuntary unemployment of 300 workers at that wage.
C)the wage rate would fall to $8,employment would fall to 800 and there would be no unemployment.
D)wages would be sticky and would adjust downward to,perhaps $9,causing involuntary unemployment of 200 workers at that wage.
E)all markets would clear,causing the demand for labour curve to shift back to D 0 and the wage rate and employment levels would return to their original levels.
 FIGURE 30-1
FIGURE 30-1Refer to Figure 30-1.The economy begins with D0 and S0.Suppose there is a negative shock to the economy,which shifts the demand for labour curve to D1.An outcome consistent with non-market-clearing theories of unemployment is
A)the wage rate would fall to $8,employment would fall to 800,causing involuntary unemployment of 200 workers.
B)wages would be sticky and would adjust downward to,perhaps $9,causing involuntary unemployment of 300 workers at that wage.
C)the wage rate would fall to $8,employment would fall to 800 and there would be no unemployment.
D)wages would be sticky and would adjust downward to,perhaps $9,causing involuntary unemployment of 200 workers at that wage.
E)all markets would clear,causing the demand for labour curve to shift back to D 0 and the wage rate and employment levels would return to their original levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In macroeconomic theories of national-income determination,short-run changes in real GDP are typically associated with changes in ________ unemployment.
A)frictional
B)structural
C)cyclical
D)voluntary
E)efficiency-wage
A)frictional
B)structural
C)cyclical
D)voluntary
E)efficiency-wage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The market-clearing and non-market-clearing theories of unemployment both agree that
A)actual unemployment rates will equal the NAIRU in the long run.
B)wages and prices are perfectly flexible.
C)unemployment is always voluntary.
D)actual output adjusts only gradually to potential output.
E)wages are rigid and adjust only over the long run.
A)actual unemployment rates will equal the NAIRU in the long run.
B)wages and prices are perfectly flexible.
C)unemployment is always voluntary.
D)actual output adjusts only gradually to potential output.
E)wages are rigid and adjust only over the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Retaining a core group of experienced employees that feels entitled to some degree of job security requires that in a recession firms hold wages ________ the market-clearing level, thus ________ involuntary unemployment.
A)above; avoiding
B)above; creating
C)equal to; avoiding
D)below; avoiding
E)below; creating
A)above; avoiding
B)above; creating
C)equal to; avoiding
D)below; avoiding
E)below; creating

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Long-term labour contracts are an important feature of ________ theories of the labour market. In contrast to aworld with continuous bargaining of wages and employment, the existence of such contracts leads to a labour market in which involuntary unemployment is ________.
A)non-market-clearing; possible
B)non-market-clearing; impossible
C)market-clearing; possible
D)market-clearing; impossible
E)market-clearing; always present
A)non-market-clearing; possible
B)non-market-clearing; impossible
C)market-clearing; possible
D)market-clearing; impossible
E)market-clearing; always present

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Involuntary unemployment in a labour market is said to exist when the wage is ________ the market -clearing wage, this creating an excess ________ labour.
A)greater than; demand for
B)greater than; supply of
C)equal to; employment of
D)less than; supply of
E)less than; demand for
A)greater than; demand for
B)greater than; supply of
C)equal to; employment of
D)less than; supply of
E)less than; demand for

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A likely consequence of firms paying ʺefficiency wagesʺ is
A)decreased unemployment.
B)increased unemployment.
C)lower real wages for employed workers.
D)more competitive labour markets.
E)rapid wage adjustment in the face of labour-market changes.
A)decreased unemployment.
B)increased unemployment.
C)lower real wages for employed workers.
D)more competitive labour markets.
E)rapid wage adjustment in the face of labour-market changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The theory of ʺefficiency wagesʺ provides
A)a way in which firms can pay workers less than the market -clearing wage.
B)an explanation for the high wages that unions are able to extract from firms.
C)many firms with a good reason to dismiss workers.
D)most workers with a good reason to quit.
E)one explanation for why wages do not readily fall in response to excess supply in labour markets.
A)a way in which firms can pay workers less than the market -clearing wage.
B)an explanation for the high wages that unions are able to extract from firms.
C)many firms with a good reason to dismiss workers.
D)most workers with a good reason to quit.
E)one explanation for why wages do not readily fall in response to excess supply in labour markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The kind of unemployment that results when actual real GDP is less than potential GDP is known as ________unemployment.
A)cyclical
B)frictional
C)natural
D)structural
E)voluntary
A)cyclical
B)frictional
C)natural
D)structural
E)voluntary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In non-market-clearing theories of the labour market an important explanation for the existence of involuntary unemployment is that labour markets exhibit
A)an elastic labour demand curve.
B)perfectly flexible wages.
C)rigid or sticky wages.
D)unshifting labour demand.
E)unshifting labour supply.
A)an elastic labour demand curve.
B)perfectly flexible wages.
C)rigid or sticky wages.
D)unshifting labour demand.
E)unshifting labour supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The main difference between market-clearing and non-market-clearing models of the economy is
A)the long-run path of wages.
B)the long-run path of employment.
C)the degree of wage and price flexibility in the short run.
D)the long-run path of output.
E)the tendency for output to return to potential in the long run.
A)the long-run path of wages.
B)the long-run path of employment.
C)the degree of wage and price flexibility in the short run.
D)the long-run path of output.
E)the tendency for output to return to potential in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Wage contracts are often set for periods of up to three years.As a result,fluctuations in aggregate demand and aggregate supply tend to
A)cause changes in the amount of involuntary unemployment.
B)cause greater inflexibility of wages.
C)have no effect in labour markets until wages are renegotiated.
D)clear the labour market.
E)either increase or decrease the NAIRU.
A)cause changes in the amount of involuntary unemployment.
B)cause greater inflexibility of wages.
C)have no effect in labour markets until wages are renegotiated.
D)clear the labour market.
E)either increase or decrease the NAIRU.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The theory of ʺefficiency wagesʺ suggests that a pool of involuntarily unemployed workers
A)quickly disappears because perfectly-flexible wages eliminates this inefficient waste of resources.
B)exists only between sessions of wage re-negotiation.
C)is comprised solely of workers who have failed to meet the productivity standards of potential employers.
D)is irrelevant to the behaviour of employed workers.
E)provides an incentive for employees to work hard so they are not laid off.
A)quickly disappears because perfectly-flexible wages eliminates this inefficient waste of resources.
B)exists only between sessions of wage re-negotiation.
C)is comprised solely of workers who have failed to meet the productivity standards of potential employers.
D)is irrelevant to the behaviour of employed workers.
E)provides an incentive for employees to work hard so they are not laid off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which statement by an employer is consistent with the efficiency wage theory?
A)ʺI pay more than the going rate so that my employees work hard.ʺ
B)ʺI pay only enough to attract workers who are at the bottom of the pay scale.ʺ
C)ʺI love it when unemployment goes up because that drives down my wage costs.ʺ
D)ʺWorkers can always find jobs,if only they lower their expectations.ʺ
E)ʺUnions have only their current membersʹ interests at heart.ʺ
A)ʺI pay more than the going rate so that my employees work hard.ʺ
B)ʺI pay only enough to attract workers who are at the bottom of the pay scale.ʺ
C)ʺI love it when unemployment goes up because that drives down my wage costs.ʺ
D)ʺWorkers can always find jobs,if only they lower their expectations.ʺ
E)ʺUnions have only their current membersʹ interests at heart.ʺ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The labour market in the diagram below begins in equilibrium with a real wage of $10 and quantity employed of 1000.
 FIGURE 30-1
FIGURE 30-1
Refer to Figure 30-1.The economy begins with D0 and S0.Suppose there is a positive shock to the economy,which shifts the demand for labour curve to D2,and the wage rate rises to $11.The result is
A)cyclical unemployment of 200 workers.
B)excess supply of labour of 300 workers.
C)excess demand for labour of 300 workers.
D)excess supply of labour of 200 workers.
E)excess demand for labour of 200 workers.
 FIGURE 30-1
FIGURE 30-1Refer to Figure 30-1.The economy begins with D0 and S0.Suppose there is a positive shock to the economy,which shifts the demand for labour curve to D2,and the wage rate rises to $11.The result is
A)cyclical unemployment of 200 workers.
B)excess supply of labour of 300 workers.
C)excess demand for labour of 300 workers.
D)excess supply of labour of 200 workers.
E)excess demand for labour of 200 workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Suppose that in PetroLand the oil fields in the western region suddenly stop producing,causing oil companies to shift activities to their fields in the eastern region.This is bound to cause some ________ unemployment in the western region of the countryʹs economy.
A)cyclical
B)efficiency-wage
C)frictional
D)structural
E)voluntary
A)cyclical
B)efficiency-wage
C)frictional
D)structural
E)voluntary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Some economists argue that increases in labour-force participation rates by young people and females in the 1970s and 1980s caused
A)a decrease in frictional unemployment.
B)a decrease in cyclical unemployment.
C)a decrease in NAIRU.
D)an increase in NAIRU.
E)an increase in cyclical unemployment.
A)a decrease in frictional unemployment.
B)a decrease in cyclical unemployment.
C)a decrease in NAIRU.
D)an increase in NAIRU.
E)an increase in cyclical unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Other things being equal,a macroeconomic shock that leads to an inflationary output gap results in
A)a decrease in cyclical unemployment.
B)a decrease in NAIRU.
C)an increase in NAIRU.
D)a decrease in frictional unemployment.
E)a decrease in structural unemployment.
A)a decrease in cyclical unemployment.
B)a decrease in NAIRU.
C)an increase in NAIRU.
D)a decrease in frictional unemployment.
E)a decrease in structural unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
An unemployed worker can be identified as being ʺstructurallyʺ unemployed if
A)minimum wage laws prevent the worker from finding a job.
B)the worker has a different set of skills than what is desired by firms.
C)the worker quits a job in order to search for a better one.
D)the worker wants to work only during certain months of the year.
E)there is a recession and the worker is laid off.
A)minimum wage laws prevent the worker from finding a job.
B)the worker has a different set of skills than what is desired by firms.
C)the worker quits a job in order to search for a better one.
D)the worker wants to work only during certain months of the year.
E)there is a recession and the worker is laid off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Other things being equal,improvements in the efficiency of labour markets that make it easier for firms to advertise prospective jobs and which reduce the effort of workers to search for jobs will
A)decrease cyclical unemployment.
B)decrease frictional unemployment.
C)increase frictional unemployment.
D)increase structural unemployment.
E)increase NAIRU.
A)decrease cyclical unemployment.
B)decrease frictional unemployment.
C)increase frictional unemployment.
D)increase structural unemployment.
E)increase NAIRU.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A good example of an outcome that could lead to ʺhysteresisʺ in the labour market is
A)new entrants to the labour market have a high rate of unemployment due to technological change.
B)new entrants to the labour market have difficulty finding jobs,and as a result have a higher rate of unemployment throughout their working lives.
C)unemployment is generated by an increase in the minimum wage.
D)a negative supply shock persists.
E)a negative demand shock persists.
A)new entrants to the labour market have a high rate of unemployment due to technological change.
B)new entrants to the labour market have difficulty finding jobs,and as a result have a higher rate of unemployment throughout their working lives.
C)unemployment is generated by an increase in the minimum wage.
D)a negative supply shock persists.
E)a negative demand shock persists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following statements about frictional unemployment is most accurate?
A)The only way to reduce it is to shift the AD curve to the left.
B)The only way to reduce it is to shift the AD curve to the right.
C)Its source is that unemployed workers and the employers with suitable job vacancies have not yet found each other.
D)It exists when only there are no jobs for the unemployed people in the economy.
E)Its source is a mismatch between the needs of employers with job vacancies and the unemployed workers.
A)The only way to reduce it is to shift the AD curve to the left.
B)The only way to reduce it is to shift the AD curve to the right.
C)Its source is that unemployed workers and the employers with suitable job vacancies have not yet found each other.
D)It exists when only there are no jobs for the unemployed people in the economy.
E)Its source is a mismatch between the needs of employers with job vacancies and the unemployed workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Technological changes over time caused workers who in the past produced such things as telephone books,video cassettes,or worked as travel agents to become ________ unemployed,at least until they could be re-employed in other industries.
A)frictionally
B)cyclically
C)seasonally
D)structurally
E)voluntarily
A)frictionally
B)cyclically
C)seasonally
D)structurally
E)voluntarily

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The normal turnover of workers and the usual time it takes to find a satisfactory job causes ________ unemployment to persist even at potential GDP.
A)excess
B)cyclical
C)frictional
D)involuntary
E)structural
A)excess
B)cyclical
C)frictional
D)involuntary
E)structural

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The best description of the cause of ʺcyclicalʺ unemployment is that
A)firms engage in race,gender and sex discrimination in their hiring practices.
B)some individuals do not have marketable skills for the jobs that do exist.
C)the AD curve shifts to the right.
D)the level of overall economic activity falls below its potential level.
E)workers often voluntarily quit a job to look for a better job.
A)firms engage in race,gender and sex discrimination in their hiring practices.
B)some individuals do not have marketable skills for the jobs that do exist.
C)the AD curve shifts to the right.
D)the level of overall economic activity falls below its potential level.
E)workers often voluntarily quit a job to look for a better job.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Suppose the NAIRU in April,2015 is 7.2%.If the actual unemployment rate is 8.1%,then
A)there is an inflationary gap.
B)0.9 percentage points are due to cyclical factors.
C)the sum of frictional and structural unemployment is greater than the NAIRU.
D)the NAIRU has increased by 0.9 percentage points.
E)cyclical unemployment is 8.1%.
A)there is an inflationary gap.
B)0.9 percentage points are due to cyclical factors.
C)the sum of frictional and structural unemployment is greater than the NAIRU.
D)the NAIRU has increased by 0.9 percentage points.
E)cyclical unemployment is 8.1%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In macroeconomic models,the idea that NAIRU can be influenced by the actual rate of unemployment is referred to as
A)efficiency-wage unemployment.
B)hysteresis.
C)the market-clearing theory.
D)rational expectations.
E)the Phillips curve.
A)efficiency-wage unemployment.
B)hysteresis.
C)the market-clearing theory.
D)rational expectations.
E)the Phillips curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
An increase in the rate of aggregate economic growth usually speeds up the rate of change in the structure of labour demand.As a result,we can expect that structural unemployment will ________,and will therefore cause the NAIRU to ________ .
A)decrease; increase
B)decrease; decrease
C)remain constant; remain constant
D)increase; increase
E)increase; decrease
A)decrease; increase
B)decrease; decrease
C)remain constant; remain constant
D)increase; increase
E)increase; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Another name for ʺfrictionalʺ unemployment is
A)economic unemployment.
B)real-wage unemployment.
C)recessional unemployment.
D)search unemployment.
E)structural unemployment.
A)economic unemployment.
B)real-wage unemployment.
C)recessional unemployment.
D)search unemployment.
E)structural unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Suppose a free-trade agreement with Central America eliminates all tariffs on imported textiles from those countries.Which type of unemployment will be affected in Canada?
A)frictional unemployment
B)structural unemployment
C)cyclical unemployment
D)seasonal unemployment
E)hidden unemployment
A)frictional unemployment
B)structural unemployment
C)cyclical unemployment
D)seasonal unemployment
E)hidden unemployment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Other things being equal,when changes in technology cause some industries to decline and other industries to expand the result is
A)a decrease in cyclical unemployment.
B)a decrease in NAIRU.
C)an increase in NAIRU.
D)an increase in frictional unemployment.
E)an increase in structural unemployment.
A)a decrease in cyclical unemployment.
B)a decrease in NAIRU.
C)an increase in NAIRU.
D)an increase in frictional unemployment.
E)an increase in structural unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Suppose that unemployed workers searching to replace their lost jobs become discouraged and so decide to temporarily give up the search.Such a decision
A)increases the NAIRU.
B)decreases the NAIRU.
C)increases the official unemployment rate.
D)decreases the official unemployment rate.
E)has no effect on the official unemployment rate.
A)increases the NAIRU.
B)decreases the NAIRU.
C)increases the official unemployment rate.
D)decreases the official unemployment rate.
E)has no effect on the official unemployment rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
An unemployed worker can be identified as being ʺfrictionallyʺ unemployed if
A)minimum wage laws prevent the worker from finding a job.
B)the worker has a different set of skills than what is desired by firms.
C)the worker quits a job in order to search for a better one.
D)the worker wants to work only during certain months of the year.
E)there is a recession and the worker is laid off.
A)minimum wage laws prevent the worker from finding a job.
B)the worker has a different set of skills than what is desired by firms.
C)the worker quits a job in order to search for a better one.
D)the worker wants to work only during certain months of the year.
E)there is a recession and the worker is laid off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
An unemployed worker can be identified as being ʺcyclicallyʺ unemployed if
A)minimum wage laws prevent the worker from finding a job.
B)the worker has a different set of skills than what is desired by firms.
C)the worker quits a job in order to search for a better one.
D)the worker wants to work only during certain months of the year.
E)there is an economic downturn and the worker is laid off.
A)minimum wage laws prevent the worker from finding a job.
B)the worker has a different set of skills than what is desired by firms.
C)the worker quits a job in order to search for a better one.
D)the worker wants to work only during certain months of the year.
E)there is an economic downturn and the worker is laid off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Consider Canadaʹs employment insurance (EI)program,which provides benefits to eligible unemployed workers.If the program is designed such that benefits are more generous in regions with higher rates of unemployment,then we can expect that
A)cyclical unemployment will increase.
B)frictional unemployment will decrease because workers have more time to find a well-suited job.
C)the NAIRU will decrease.
D)labour markets will adapt to changes more quickly as a result.
E)structural unemployment will increase and the NAIRU will be higher than otherwise.
A)cyclical unemployment will increase.
B)frictional unemployment will decrease because workers have more time to find a well-suited job.
C)the NAIRU will decrease.
D)labour markets will adapt to changes more quickly as a result.
E)structural unemployment will increase and the NAIRU will be higher than otherwise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 111 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



