Deck 10: Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/452
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand
1
Aggregate supply describes the behavior of
A) households.
B) producers.
C) government.
D) foreign buyers.
A) households.
B) producers.
C) government.
D) foreign buyers.
B
2
When talking about aggregate supply, it is necessary to
A) distinguish between long- run full employment and short- run full- employment.
B) distinguish between long- run aggregate supply and short- run aggregate supply.
C) focus on the short run.
D) focus on the long run.
A) distinguish between long- run full employment and short- run full- employment.
B) distinguish between long- run aggregate supply and short- run aggregate supply.
C) focus on the short run.
D) focus on the long run.
B
3
In the macroeconomic long run,
A) real GDP equals potential GDP.
B) regardless of the price level, the economy is producing at potential GDP.
C) the economy is at full employment.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) real GDP equals potential GDP.
B) regardless of the price level, the economy is producing at potential GDP.
C) the economy is at full employment.
D) All of the above are correct.
D
4
The supply of real GDP is a function of
A) the quantities of labor, capital and the state of technology.
B) the total expenditures of consumers, investors and government.
C) only the state of technology.
D) the sum of wages, salaries, corporate profits, rents and interest.
A) the quantities of labor, capital and the state of technology.
B) the total expenditures of consumers, investors and government.
C) only the state of technology.
D) the sum of wages, salaries, corporate profits, rents and interest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The long- run aggregate supply (LAS) curve
A) has a positive slope.
B) is horizontal.
C) has a negative slope.
D) is vertical.
A) has a positive slope.
B) is horizontal.
C) has a negative slope.
D) is vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The quantity of real GDP supplied depends on the
A) level of aggregate demand.
B) quantity of labor, the quantity of capital, and the state of technology.
C) quantity of capital, bonds, and stocks.
D) price level, the unemployment rate, and the quantity of government expenditures on goods and services.
A) level of aggregate demand.
B) quantity of labor, the quantity of capital, and the state of technology.
C) quantity of capital, bonds, and stocks.
D) price level, the unemployment rate, and the quantity of government expenditures on goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If the economy is at the natural unemployment rate,
A) real GDP < potential GDP.
B) real GDP > potential GDP.
C) real GDP = potential GDP.
D) All of the above can occur when the economy is at the natural unemployment rate.
A) real GDP < potential GDP.
B) real GDP > potential GDP.
C) real GDP = potential GDP.
D) All of the above can occur when the economy is at the natural unemployment rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
At potential GDP
A) unemployment is at its natural rate.
B) there is no unemployment but there is not necessarily full employment.
C) there is no unemployment and there is full employment.
D) None of the above is correct.
A) unemployment is at its natural rate.
B) there is no unemployment but there is not necessarily full employment.
C) there is no unemployment and there is full employment.
D) None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The aggregate supply/aggregate demand model is used to help understand all of the following EXCEPT
A) inflation.
B) growth of potential GDP.
C) the aggregate value of stock traded in the stock market.
D) business cycle fluctuations.
A) inflation.
B) growth of potential GDP.
C) the aggregate value of stock traded in the stock market.
D) business cycle fluctuations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The macroeconomic long run is best defined as
A) the time period sufficiently long so that real GDP has adjusted to equal potential GDP.
B) a time period of less than 1 year.
C) the time period sufficiently long so that real GDP has adjusted to exceed potential GDP.
D) a time period of more than 1 year.
A) the time period sufficiently long so that real GDP has adjusted to equal potential GDP.
B) a time period of less than 1 year.
C) the time period sufficiently long so that real GDP has adjusted to exceed potential GDP.
D) a time period of more than 1 year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In the long- run
A) real GDP is equal to potential GDP.
B) the aggregate supply curve is upward sloping.
C) aggregate supply depends on the price level.
D) All of the above answers are correct.
A) real GDP is equal to potential GDP.
B) the aggregate supply curve is upward sloping.
C) aggregate supply depends on the price level.
D) All of the above answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following variables does NOT directly influence the supply of real GDP?
A) the quantity of labor
B) the state of technology
C) the quantity demanded
D) the quantity of capital
A) the quantity of labor
B) the state of technology
C) the quantity demanded
D) the quantity of capital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The quantity of real GDP supplied at different price levels is reflected by the
A) aggregate supply curve.
B) total expenditure curve.
C) aggregate demand curve.
D) real wealth curve.
A) aggregate supply curve.
B) total expenditure curve.
C) aggregate demand curve.
D) real wealth curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
We distinguish between the long- run aggregate supply curve and the short- run aggregate supply curve. In the long run
A) the aggregate supply curve is horizontal while in the short run it is upward sloping.
B) real GDP equals potential GDP.
C) the price level is constant but in the short run it fluctuates.
D) technology is fixed but not in the short run.
A) the aggregate supply curve is horizontal while in the short run it is upward sloping.
B) real GDP equals potential GDP.
C) the price level is constant but in the short run it fluctuates.
D) technology is fixed but not in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The quantity of real GDP supplied _ _ the amount of _.
A) decreases as; capital and labor input decreases
B) decreases as; capital input increases
C) increases as; labor input decreases
D) is unaffected by; technology
A) decreases as; capital and labor input decreases
B) decreases as; capital input increases
C) increases as; labor input decreases
D) is unaffected by; technology

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Aggregate supply is
A) the relationship between the unemployment rate and real GDP.
B) the relationship between labor employment and the real (inflation adjusted) wage rate.
C) desired spending on output at different price levels.
D) the relationship between the quantity of real GDP and the price level.
A) the relationship between the unemployment rate and real GDP.
B) the relationship between labor employment and the real (inflation adjusted) wage rate.
C) desired spending on output at different price levels.
D) the relationship between the quantity of real GDP and the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When the labor market is in equilibrium,
A) the price level equals potential prices.
B) real GDP equals potential GDP.
C) the SAS curve is horizontal.
D) the price level is stable.
A) the price level equals potential prices.
B) real GDP equals potential GDP.
C) the SAS curve is horizontal.
D) the price level is stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In the macroeconomic long run,
A) output always is above potential GDP.
B) there is full employment and real GDP is equal to potential GDP.
C) there is full employment with no unemployment.
D) GDP always is below potential GDP.
A) output always is above potential GDP.
B) there is full employment and real GDP is equal to potential GDP.
C) there is full employment with no unemployment.
D) GDP always is below potential GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An aggregate supply curve depicts the relationship between
A) household expenditures and household income.
B) the price level and the aggregate quantity demanded.
C) the price level and nominal GDP.
D) the price level and the aggregate quantity supplied.
A) household expenditures and household income.
B) the price level and the aggregate quantity demanded.
C) the price level and nominal GDP.
D) the price level and the aggregate quantity supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the macroeconomic short run,
A) actual real GDP may be less than or more than potential GDP.
B) actual real GDP always equals potential GDP.
C) the unemployment rate is zero.
D) the economy is always moving away from full employment.
A) actual real GDP may be less than or more than potential GDP.
B) actual real GDP always equals potential GDP.
C) the unemployment rate is zero.
D) the economy is always moving away from full employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The long- run aggregate supply curve is because along it, as prices rise, the money wage rate .
A) vertical; rises
B) upward sloping; stays constant
C) vertical; falls
D) upward sloping; falls
A) vertical; rises
B) upward sloping; stays constant
C) vertical; falls
D) upward sloping; falls

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The long- run aggregate supply curve illustrates the
A) amount of products producers offer at various prices when money wages and other resource prices do not change.
B) relationship of prices with the level of GDP when real GDP equals potential GDP.
C) relationship of aggregate supply and aggregate demand.
D) surpluses, shortages and equilibrium level of GDP.
A) amount of products producers offer at various prices when money wages and other resource prices do not change.
B) relationship of prices with the level of GDP when real GDP equals potential GDP.
C) relationship of aggregate supply and aggregate demand.
D) surpluses, shortages and equilibrium level of GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The long- run aggregate supply curve shows the
A) maximum GDP the nation will ever produce.
B) level of output for which real GDP equals nominal GDP.
C) level of real GDP associated with a constant price level.
D) full- employment level of real GDP.
A) maximum GDP the nation will ever produce.
B) level of output for which real GDP equals nominal GDP.
C) level of real GDP associated with a constant price level.
D) full- employment level of real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In the short run, the aggregate supply curve is
A) vertical.
B) downward sloping.
C) horizontal.
D) upward sloping.
A) vertical.
B) downward sloping.
C) horizontal.
D) upward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is true about the long- run aggregate supply curve?
A) It is vertical at the level of potential GDP.
B) It does not shift in response to temporary changes in aggregate demand.
C) It shows the relationship between the price level and real GDP when wages and other costs are at an equilibrium level.
D) All of the above are true.
A) It is vertical at the level of potential GDP.
B) It does not shift in response to temporary changes in aggregate demand.
C) It shows the relationship between the price level and real GDP when wages and other costs are at an equilibrium level.
D) All of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The long- run aggregate supply curve
A) is positively sloped.
B) is horizontal at the level of potential GDP.
C) is negatively sloped.
D) is vertical at the level of potential GDP.
A) is positively sloped.
B) is horizontal at the level of potential GDP.
C) is negatively sloped.
D) is vertical at the level of potential GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The long- run aggregate supply curve is
A) the same as the short- run aggregate supply curve.
B) horizontal at the full employment price level.
C) vertical at the full employment level of real GDP.
D) upward sloping because of the effects of price level changes on real GDP.
A) the same as the short- run aggregate supply curve.
B) horizontal at the full employment price level.
C) vertical at the full employment level of real GDP.
D) upward sloping because of the effects of price level changes on real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
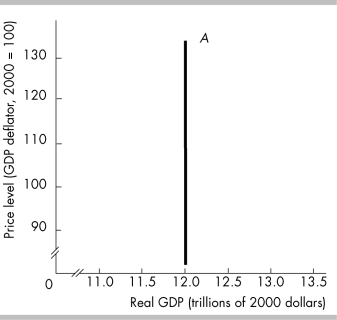
The curve labeled A in the above figure will shift rightward when
A) the price level rises.
B) population falls.
C) technology increases.
D) the price level falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The long- run aggregate supply curve is
A) horizontal.
B) upward sloping.
C) downward sloping
D) vertical.
A) horizontal.
B) upward sloping.
C) downward sloping
D) vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The long- run aggregate supply curve is the relationship between the quantity of real GDP supplied and _ _ when _ .
A) the price level; real GDP equals potential GDP
B) real GDP demanded; the wage rate is constant
C) real GDP demanded; the price level does not change
D) the price level; real GDP equals nominal GDP
A) the price level; real GDP equals potential GDP
B) real GDP demanded; the wage rate is constant
C) real GDP demanded; the price level does not change
D) the price level; real GDP equals nominal GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The positive relationship between short- run aggregate supply and the price level indicates that, in the short run,
A) firms produce more output as the price level falls.
B) the money wage rate increases when moving along the short- run aggregate supply curve.
C) lower price levels are more profitable for firms.
D) firms produce more output as the price level rises.
A) firms produce more output as the price level falls.
B) the money wage rate increases when moving along the short- run aggregate supply curve.
C) lower price levels are more profitable for firms.
D) firms produce more output as the price level rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The short- run aggregate supply curve is upward sloping because in the short run the
A) both the money wage rate and the price level change.
B) neither the money wage rate nor the price level can change.
C) price level changes but the money wage rate does not.
D) money wage rate changes but the price level does not.
A) both the money wage rate and the price level change.
B) neither the money wage rate nor the price level can change.
C) price level changes but the money wage rate does not.
D) money wage rate changes but the price level does not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) The long- run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
B) The long- run aggregate supply curve is upward sloping.
C) The short- run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
D) The long- run aggregate demand curve is upward sloping.
A) The long- run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
B) The long- run aggregate supply curve is upward sloping.
C) The short- run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
D) The long- run aggregate demand curve is upward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34

The curve labeled A in the above figure is a
A) short- run aggregate demand curve.
B) long- run aggregate supply curve.
C) short- run aggregate supply curve.
D) long- run aggregate demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
When the price level rises, the long- run aggregate supply curve .
A) does not shift
B) shifts leftward
C) slopes upward
D) shifts rightward
A) does not shift
B) shifts leftward
C) slopes upward
D) shifts rightward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The long- run aggregate supply curve is vertical because
A) at full employment prices are stable.
B) potential GDP is independent of the price level.
C) there is no cyclical inflation.
D) the money wage rate increases faster than the price level.
A) at full employment prices are stable.
B) potential GDP is independent of the price level.
C) there is no cyclical inflation.
D) the money wage rate increases faster than the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
For movements along the long- run aggregate supply curve,
A) the prices of goods and services change while the prices of productive resources hold steady.
B) potential GDP is dependent on the price level.
C) the price level and the money wage rate change by the same percentage.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) the prices of goods and services change while the prices of productive resources hold steady.
B) potential GDP is dependent on the price level.
C) the price level and the money wage rate change by the same percentage.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The short- run aggregate supply curve
A) is vertical.
B) has a positive slope.
C) has a negative slope.
D) is horizontal.
A) is vertical.
B) has a positive slope.
C) has a negative slope.
D) is horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following events will increase long- run aggregate supply?
A) a decrease in expected profit
B) an increase in the interest rate
C) an advance in technology
D) an increase in resource prices
A) a decrease in expected profit
B) an increase in the interest rate
C) an advance in technology
D) an increase in resource prices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The short- run aggregate supply curve
A) becomes vertical if there is excess production capacity within the economy.
B) shows a negative relationship between the price level and real national income holding constant potential GDP and all resource prices.
C) shows what each producer is willing and able to produce at each level of income holding constant potential GDP and all resource prices.
D) relates aggregate production and the price level holding constant potential GDP and all resource prices.
A) becomes vertical if there is excess production capacity within the economy.
B) shows a negative relationship between the price level and real national income holding constant potential GDP and all resource prices.
C) shows what each producer is willing and able to produce at each level of income holding constant potential GDP and all resource prices.
D) relates aggregate production and the price level holding constant potential GDP and all resource prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Suppose the price level rises and the money wage remains constant. This set of changes leads to
A) a leftward shift of the SAS curve.
B) an upward movement along the LAS curve.
C) an upward movement along the SAS curve.
D) a leftward shift of the SAS curve and the LAS curve.
A) a leftward shift of the SAS curve.
B) an upward movement along the LAS curve.
C) an upward movement along the SAS curve.
D) a leftward shift of the SAS curve and the LAS curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Moving along the short- run aggregate supply curve, _ .
A) real GDP equals potential GDP
B) the money wage rate, the prices of other resources, and potential GDP remain constant
C) the real wage rate is constant
D) real GDP equals nominal GDP
A) real GDP equals potential GDP
B) the money wage rate, the prices of other resources, and potential GDP remain constant
C) the real wage rate is constant
D) real GDP equals nominal GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If the money wage and other resource prices do not change when the price level rises by 10 percent,
)
A) there is movement along the short- run aggregate supply curve
B) the long- run aggregate supply curve shifts leftward
C) massive labor lay- offs occur
D) the short- run aggregate supply curve shifts leftward
)
A) there is movement along the short- run aggregate supply curve
B) the long- run aggregate supply curve shifts leftward
C) massive labor lay- offs occur
D) the short- run aggregate supply curve shifts leftward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In the short- run
A) the price level does not change.
B) the aggregate supply curve is upward sloping.
C) the money wage rate can change.
D) real GDP is always equal to potential GDP.
A) the price level does not change.
B) the aggregate supply curve is upward sloping.
C) the money wage rate can change.
D) real GDP is always equal to potential GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Moving along a short- run aggregate supply curve, resource prices , the money rate wage
, and potential GDP _ .
A) change; does not change; does not change
B) do not change; does not change; does not change
C) do not change; changes; does not change
D) do not change; does not change; changes
, and potential GDP _ .
A) change; does not change; does not change
B) do not change; does not change; does not change
C) do not change; changes; does not change
D) do not change; does not change; changes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
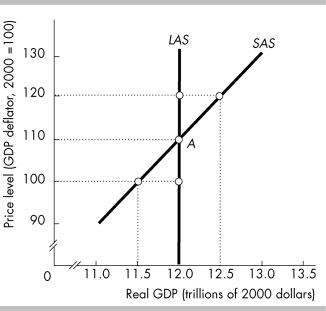
In the figure above, potential GDP equals
A) $12.0 trillion.
B) $11.5 trillion.
C) $12.5 trillion.
D) None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Along a short- run aggregate supply curve, a decrease in the price level means that
A) output does not change because firms do not change the quantity they produce.
B) more output is produced as firms increase production because wages fall more than the price level falls, making it profitable to hire more workers.
C) less output is produced as firms decrease production.
D) more output is produced as consumer demand increases.
A) output does not change because firms do not change the quantity they produce.
B) more output is produced as firms increase production because wages fall more than the price level falls, making it profitable to hire more workers.
C) less output is produced as firms decrease production.
D) more output is produced as consumer demand increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Moving upward along the SAS results in a in the price level and in real GDP.
A) rise; a decrease
B) fall; a decrease
C) fall; an increase
D) rise; an increase
A) rise; a decrease
B) fall; a decrease
C) fall; an increase
D) rise; an increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The short- run aggregate supply curve is upward sloping because
A) capital is scarce.
B) potential GDP is less than real GDP when the price level falls.
C) firms need to receive higher prices to cover the higher costs of producing increasing levels of output.
D) technology is scarce.
A) capital is scarce.
B) potential GDP is less than real GDP when the price level falls.
C) firms need to receive higher prices to cover the higher costs of producing increasing levels of output.
D) technology is scarce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following statements regarding aggregate supply are correct?
A) Moving along the long- run aggregate supply curve, the money wage rate changes but the price level is constant.
B) Moving along the long- run aggregate supply curve, both the price level and the money wage rate change by the same percentage.
C) Moving along the short- run aggregate supply curve, both the price level and the money wage rate change by the same percentage.
D) Moving along the short- run aggregate supply curve, the money wage rate changes but the price level is constant.
A) Moving along the long- run aggregate supply curve, the money wage rate changes but the price level is constant.
B) Moving along the long- run aggregate supply curve, both the price level and the money wage rate change by the same percentage.
C) Moving along the short- run aggregate supply curve, both the price level and the money wage rate change by the same percentage.
D) Moving along the short- run aggregate supply curve, the money wage rate changes but the price level is constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Suppose the price level, the money wage, and the price of all other resources rise by 10 percent. This set of changes leads to
A) an upward movement along the SAS curve.
B) a downward movement along the LAS curve.
C) a leftward shift of the LAS curve.
D) an upward movement along the LAS curve.
A) an upward movement along the SAS curve.
B) a downward movement along the LAS curve.
C) a leftward shift of the LAS curve.
D) an upward movement along the LAS curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A decrease in the price level accompanied by no change in the money wage rate leads to movement along the _ aggregate supply curve.
A) an upward; long- run
B) an upward; short- run
C) a downward; short- run
D) a downward; long- run
A) an upward; long- run
B) an upward; short- run
C) a downward; short- run
D) a downward; long- run

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A change in results in a movement along the short- run aggregate supply curve but no shift in the short- run aggregate supply curve.
A) technology
B) the quantity of capital
C) the price level
D) the money wage rate
A) technology
B) the quantity of capital
C) the price level
D) the money wage rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following does NOT shift the short- run aggregate supply curve?
A) a reduction in the price of a raw material
B) a change in the price level
C) a change in the money wage rate
D) technological progress
A) a reduction in the price of a raw material
B) a change in the price level
C) a change in the money wage rate
D) technological progress

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The short- run aggregate supply curve is upward sloping because
A) a lower price level creates a wealth effect.
B) most business firms operate with long- term contracts for output but not labor.
C) money wage rates do not immediately change when the price level changes.
D) lower taxes motivate people to work more.
A) a lower price level creates a wealth effect.
B) most business firms operate with long- term contracts for output but not labor.
C) money wage rates do not immediately change when the price level changes.
D) lower taxes motivate people to work more.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
For movements along the short- run aggregate supply curve,
A) the money wage rate is constant.
B) potential GDP remains constant.
C) the real wage rate changes.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) the money wage rate is constant.
B) potential GDP remains constant.
C) the real wage rate changes.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The short- run aggregate supply curve
A) shifts because of changes in the price level.
B) shows the impact changes in the price level have on the quantity of real GDP when resource prices are constant.
C) illustrates the level of potential real GDP.
D) is vertical.
A) shifts because of changes in the price level.
B) shows the impact changes in the price level have on the quantity of real GDP when resource prices are constant.
C) illustrates the level of potential real GDP.
D) is vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In the short run, firms expand their production when the price level rises because
A) the higher prices allow the firm to hire more workers by offering higher wages, thereby increasing productivity and profits.
B) each firm must keep its production up to the level of its rivals, and some firms will expand production as the price level increases.
C) firms can increase their profits by increasing their maintenance.
D) the money wage rate remains constant so the higher prices for their product makes it profitable for firms to expand production.
A) the higher prices allow the firm to hire more workers by offering higher wages, thereby increasing productivity and profits.
B) each firm must keep its production up to the level of its rivals, and some firms will expand production as the price level increases.
C) firms can increase their profits by increasing their maintenance.
D) the money wage rate remains constant so the higher prices for their product makes it profitable for firms to expand production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following occurs while moving along a short- run aggregate supply curve?
A) Neither the price level nor the money wage rate changes.
B) The price level changes and the money wage rate is constant.
C) The money wage rate and the price level change by the same percentage.
D) The money wage rate changes and the price level is constant.
A) Neither the price level nor the money wage rate changes.
B) The price level changes and the money wage rate is constant.
C) The money wage rate and the price level change by the same percentage.
D) The money wage rate changes and the price level is constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The SAS curve and the LAS curve
A) are perpendicular to one another at potential GDP.
B) are parallel at potential GDP.
C) intersect at potential GDP.
D) None of the above answers is correct.
A) are perpendicular to one another at potential GDP.
B) are parallel at potential GDP.
C) intersect at potential GDP.
D) None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
All of the following shift the LAS curve EXCEPT
A) an increase in the stock of human capital.
B) technological progress.
C) a change in the capital stock.
D) an increase in the money wage rate.
A) an increase in the stock of human capital.
B) technological progress.
C) a change in the capital stock.
D) an increase in the money wage rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
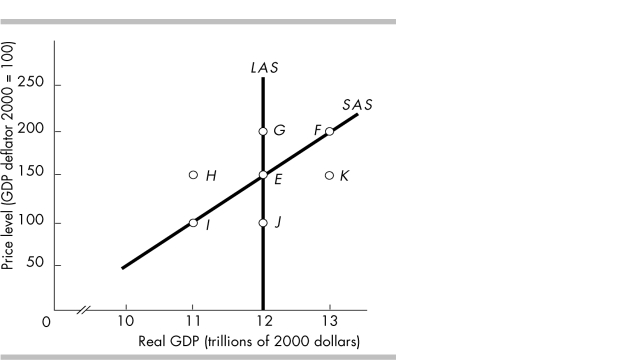
In the above figure, which movement illustrates the impact of a falling price level and a constant money wage rate?
A) E to I
B) E to H
C) E to J
D) E to F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following shifts the short- run aggregate supply curve?
I) changes in the size of the labor force
II) changes in the money wage rate
A) I only
B) II only
C) both I and II
D) neither I nor II
I) changes in the size of the labor force
II) changes in the money wage rate
A) I only
B) II only
C) both I and II
D) neither I nor II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following events will increase short- run aggregate supply?
A) an increase in foreign income
B) an increase in resource prices
C) an advance in technology
D) an increase in the natural unemployment rate
A) an increase in foreign income
B) an increase in resource prices
C) an advance in technology
D) an increase in the natural unemployment rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following directly shifts the short- run aggregate supply curve?
A) a change in resource prices
B) a change in the price level
C) a change in aggregate demand
D) all of the above
A) a change in resource prices
B) a change in the price level
C) a change in aggregate demand
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66

In the above figure, which movement illustrates the impact of a rising price level and a constant money wage rate?
A) E to G
B) E to K
C) E to I
D) E to F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
All of the following shift the short- run aggregate supply curve EXCEPT
A) technological progress.
B) a change in the money wage rate.
C) a change in the price of a raw material.
D) a change in the price level.
A) technological progress.
B) a change in the money wage rate.
C) a change in the price of a raw material.
D) a change in the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68

In the figure above, the economy is at point A when the price level falls to 100. Money wage rates and all other resource prices remain constant. Firms are willing to supply output equal to
A) $11.5 trillion.
B) $12.5 trillion.
C) $12.0 trillion.
D) None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A change in which of the following shifts the short- run aggregate supply curve?
A) an advance in technology
B) a change in the quantity of capital
C) a change in the money wage rate
D) All of the above shift the short- run aggregate supply curve.
A) an advance in technology
B) a change in the quantity of capital
C) a change in the money wage rate
D) All of the above shift the short- run aggregate supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70

In the above figure, which movement illustrates the impact of the price level and money wage rate falling at the same rate?
A) E to J
B) E to K
C) E to H
D) E to G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71

In the figure above, the economy is at point A when the price level rises to 120. Money wage rates and other resource prices remain constant. Firms are willing to supply output equal to
A) $12.0 trillion.
B) $11.5 trillion.
C) $12.5 trillion.
D) None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72

In the above figure, which movement illustrates the impact of a constant price level and a rising money wage rate?
A) E to H
B) E to F
C) E to J
D) E to I

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following changes does NOT shift the short- run aggregate supply curve?
A) an increase in technology
B) an increase in the money wage rate
C) an increase in the price level
D) an increase in the quantity of capital
A) an increase in technology
B) an increase in the money wage rate
C) an increase in the price level
D) an increase in the quantity of capital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
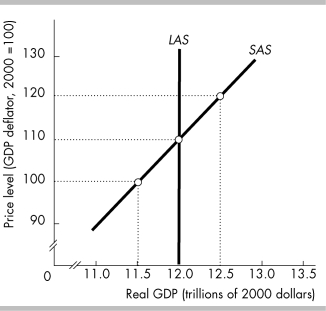
In the above figure, the economy will be at full employment if the price level
A) is below 100.
B) is above 110.
C) is 110.
D) All of the above are possible because the economy will be at full employment at any price level at, above, or below 110.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Suppose there is a temporary increase in the price of oil. This is represented by
A) a leftward shift of the SAS and the LAS curve.
B) a rightward shift of the SAS curve.
C) a leftward shift of the LAS curve.
D) a leftward shift of the SAS curve.
A) a leftward shift of the SAS and the LAS curve.
B) a rightward shift of the SAS curve.
C) a leftward shift of the LAS curve.
D) a leftward shift of the SAS curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following shift the LAS curve rightward?
A) a decrease in the labor force
B) a decrease in the money wage
C) an increase in the price level
D) a increase in the education level of the labor force
A) a decrease in the labor force
B) a decrease in the money wage
C) an increase in the price level
D) a increase in the education level of the labor force

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The SAS curve shifts if there is a change in
A) nominal GDP.
B) the price level.
C) real GDP.
D) potential GDP.
A) nominal GDP.
B) the price level.
C) real GDP.
D) potential GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The short- run aggregate supply curve shifts leftward when the
A) general level of technology advances.
B) price level increases.
C) availability of on- the- job training expands to all workers.
D) money wage rate increases.
A) general level of technology advances.
B) price level increases.
C) availability of on- the- job training expands to all workers.
D) money wage rate increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following changes does NOT shift the long- run aggregate supply curve?
A) a tax hike that reduces the capital stock
B) a rise in number of college graduates in the labor force
C) a fall in the price level
D) a decrease in the labor force
A) a tax hike that reduces the capital stock
B) a rise in number of college graduates in the labor force
C) a fall in the price level
D) a decrease in the labor force

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The short- run aggregate supply curve shifts when
A) the quantity of capital changes.
B) advances in technology occur.
C) the full- employment quantity of labor changes.
D) All of the above answers are correct.
A) the quantity of capital changes.
B) advances in technology occur.
C) the full- employment quantity of labor changes.
D) All of the above answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 452 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



