Review
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/101
Play
Full screen (f)
Review
1
If the wood used to produce houses rises in price, then the houses shifts .
A) supply curve of; leftward
B) supply curve of; rightward
C) demand curve for; leftward
D) demand curve for; rightward
A) supply curve of; leftward
B) supply curve of; rightward
C) demand curve for; leftward
D) demand curve for; rightward
A
2
According to the principle of comparative advantage, if the United States trades with Mexico, most likely,
A) the United States will benefit and Mexico will lose.
B) neither of the countries will benefit.
C) both countries will benefit.
D) the United States will lose and Mexico will benefit.
A) the United States will benefit and Mexico will lose.
B) neither of the countries will benefit.
C) both countries will benefit.
D) the United States will lose and Mexico will benefit.
C
3
The opportunity cost of a good is
A) the lowest valued alternative you give up to get it.
B) all alternatives you give up to get it.
C) the highest valued alternative you give up to get it.
D) the income you forgo to get it.
A) the lowest valued alternative you give up to get it.
B) all alternatives you give up to get it.
C) the highest valued alternative you give up to get it.
D) the income you forgo to get it.
C
4
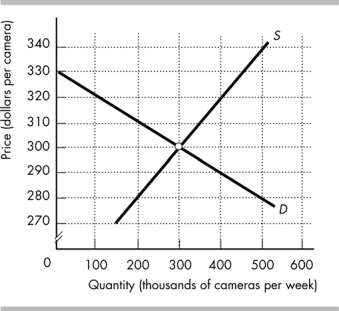
The figure above shows the market for film cameras. If the price of digital cameras falls, the equilibrium quantity of film cameras will be thousand cameras and the price of a film camera will be .
A) greater than 300; less than $300
B) greater than 400; greater than $310
C) less than 300; less than $300
D) 300; greater than $300

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A processor of alligator hides can produce either purses or shoes. If the demand for alligator shoes increases, then the alligator purses will .
A) supply of; increase
B) demand for; increase
C) demand for; decrease
D) supply of; decrease
A) supply of; increase
B) demand for; increase
C) demand for; decrease
D) supply of; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is NOT a factor of production?
A) a commercial aircraft
B) a computer programmer
C) money
D) mineral resources
A) a commercial aircraft
B) a computer programmer
C) money
D) mineral resources

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If pizza is a normal good, then an increase in peopleʹs incomes shifts the curve .
A) supply; rightward
B) demand; leftward
C) supply; leftward
D) demand; rightward
A) supply; rightward
B) demand; leftward
C) supply; leftward
D) demand; rightward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8

The figure above shows the market for digital cameras. If consumersʹ incomes rise and a digital camera is a normal good, the equilibrium quantity of digital cameras will be thousand cameras and the price of a digital camera will be .
A) greater than 300; greater than $300
B) less than 300; less than $300
C) greater than 300; less than $300
D) 300; greater than $300

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
All economic questions arise because
A) our wants are limited.
B) production possibilities are unlimited.
C) people are irrational.
D) of scarcity.
A) our wants are limited.
B) production possibilities are unlimited.
C) people are irrational.
D) of scarcity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following increases the demand for chicken?
A) an increase in the price of the grain used to feed chickens
B) a fall in the price of chicken
C) an increase in the number of chicken farmers
D) an increase in the price of beef, a substitute for chicken
A) an increase in the price of the grain used to feed chickens
B) a fall in the price of chicken
C) an increase in the number of chicken farmers
D) an increase in the price of beef, a substitute for chicken

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
-The table above lists six points on the production possibilities frontier for cheese and DVDs. Given this information, which of the following combinations is unattainable?
A) 6 tons of cheese and 34 thousand DVDs
B) 7 tons of cheese and 20 thousand DVDs
C) 2 tons of cheese and 56 thousand DVDs
D) 8 tons of cheese and 21 thousand DVDs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Lizzie takes 20 seconds to stuff an envelope and 10 seconds to seal it. Arnold takes 15 seconds to stuff an envelope and 5 seconds to seal it. Lizzie has a comparative advantage in and Arnold has a comparative advantage in .
A) stuffing envelopes; sealing them
B) neither of these activities; both activities
C) both activities; neither of these activities
D) sealing envelopes; stuffing them
A) stuffing envelopes; sealing them
B) neither of these activities; both activities
C) both activities; neither of these activities
D) sealing envelopes; stuffing them

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If OPEC cuts oil production, then the
A) price of gasoline will fall.
B) demand for gasoline will decrease.
C) supply of gasoline will decrease.
D) demand for gasoline will increase.
A) price of gasoline will fall.
B) demand for gasoline will decrease.
C) supply of gasoline will decrease.
D) demand for gasoline will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Jen won $900 in a lottery. She has a choice between using the money to buy a sofa, a television, or going on a vacation. If she chooses to buy a television, the opportunity cost of this decision is
A) zero because she won the money.
B) the sofa if that was her second choice.
C) the sofa and the vacation trip.
D) the sofa, the vacation trip, and $900.
A) zero because she won the money.
B) the sofa if that was her second choice.
C) the sofa and the vacation trip.
D) the sofa, the vacation trip, and $900.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
-The table above lists six points on the production possibilities frontier for cheese and DVDs. From this information you can conclude that production is inefficient if this economy produces
A) 5 tons of cheese and 48 thousand DVDs.
B) 2 tons of cheese and 56 thousand DVDs.
C) 8 tons of cheese and 21 thousand DVDs.
D) 7 tons of cheese and 20 thousand DVDs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If the wood used to produce houses rises in price, then the houses .
A) demand for; decreases
B) supply of; increases
C) supply of; decreases
D) demand for; increases
A) demand for; decreases
B) supply of; increases
C) supply of; decreases
D) demand for; increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
-The table above lists six points on the production possibilities frontier for cheese and DVDs. What is the opportunity cost of producing the 7th ton of cheese?
A) 8 DVDs per ton of cheese
B) 28 DVDs per ton of cheese
C) 20 DVDs per ton of cheese
D) 16 DVDs per ton of cheese

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An opportunity cost of economic growth is
A) the capital accumulation given up to increase present consumption.
B) the present consumption given up to accumulate capital.
C) the increased future consumption.
D) None of the above because there is no opportunity cost since if an economy grows, it can produce more of all goods.
A) the capital accumulation given up to increase present consumption.
B) the present consumption given up to accumulate capital.
C) the increased future consumption.
D) None of the above because there is no opportunity cost since if an economy grows, it can produce more of all goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Jelly beans and popcorn are substitutes. A fall in the price of a bag of jelly beans will the demand for popcorn and the price of popcorn will .
A) increase; rise
B) decrease; rise
C) decrease; fall
D) increase; fall
A) increase; rise
B) decrease; rise
C) decrease; fall
D) increase; fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Country X devoted 70 percent of its resources to consumption, while Country Y devoted 80 percent to consumption. Other things being equal, you can predict that
A) Country Xʹs economy will grow faster than Country Yʹs.
B) Country Yʹs economy will grow faster than Country Xʹs.
C) Country Xʹs opportunity cost of economic growth is lower than Country Yʹs.
D) Country Yʹs rate of capital accumulation is higher than Country Xʹs
A) Country Xʹs economy will grow faster than Country Yʹs.
B) Country Yʹs economy will grow faster than Country Xʹs.
C) Country Xʹs opportunity cost of economic growth is lower than Country Yʹs.
D) Country Yʹs rate of capital accumulation is higher than Country Xʹs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Shoes are a normal good and peopleʹs incomes rise. As a result, the equilibrium price of a pair of shoes and the equilibrium quantity .
A) rises; increases
B) falls; decreases
C) falls; increases
D) rises; decreases
A) rises; increases
B) falls; decreases
C) falls; increases
D) rises; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An increase in the amount of capital leads to the aggregate production function
And a technological advance leads to the aggregate production function.
A) a movement along; a movement along
B) an upward shift; an upward shift
C) a movement along; an upward shift
D) a downward shift; an upward shift
And a technological advance leads to the aggregate production function.
A) a movement along; a movement along
B) an upward shift; an upward shift
C) a movement along; an upward shift
D) a downward shift; an upward shift

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The accumulated loss of output that results from a slowdown in the growth rate of GDP per person is called the
A) Lucas wedge.
B) unemployment wedge.
C) Okun gap.
D) Keynesian gap.
A) Lucas wedge.
B) unemployment wedge.
C) Okun gap.
D) Keynesian gap.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The number of companies making shoes decreases. As a result, the equilibrium price of a pair of shoes and the equilibrium quantity .
A) rises; decreases
B) falls; increases
C) falls; decreases
D) rises; increases
A) rises; decreases
B) falls; increases
C) falls; decreases
D) rises; increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
An increase in the population will potential GDP, employment, and
The real wage.
A) increase; increase; raise.
B) increase; increase; lower
C) decrease; increase; raise
D) increase; decrease; lower
The real wage.
A) increase; increase; raise.
B) increase; increase; lower
C) decrease; increase; raise
D) increase; decrease; lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The circular flow model shows that GDP can be calculated by
A) only the expenditure method in which the four components of aggregate expenditure must be measured in the aggregate.
B) only the income method in which the four components of aggregate income must be measured separately.
C) both the expenditure and income methods, even though aggregate expenditure is usually less than aggregate income.
D) both the expenditure and income methods because aggregate expenditure equals aggregate income.
A) only the expenditure method in which the four components of aggregate expenditure must be measured in the aggregate.
B) only the income method in which the four components of aggregate income must be measured separately.
C) both the expenditure and income methods, even though aggregate expenditure is usually less than aggregate income.
D) both the expenditure and income methods because aggregate expenditure equals aggregate income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The labor force is defined as
A) all people aged 16 and over and not institutionalized.
B) those people employed and unemployed.
C) the entire population.
D) only those people with jobs.
A) all people aged 16 and over and not institutionalized.
B) those people employed and unemployed.
C) the entire population.
D) only those people with jobs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
increases real GDP.
A) An increase in employment
B) A decrease in government spending
C) A fall in the price level
D) An increase in the natural rate of unemployment
A) An increase in employment
B) A decrease in government spending
C) A fall in the price level
D) An increase in the natural rate of unemployment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
GDP is defined as
A) generally demanded product.
B) gross domestic product.
C) generally demanded prices.
D) gross demanded prices.
A) generally demanded product.
B) gross domestic product.
C) generally demanded prices.
D) gross demanded prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An increase in the productivity will potential GDP, employment, and
The real wage.
A) increase; increase; raise.
B) decrease; increase; raise
C) increase; decrease; lower
D) increase; increase; lower
The real wage.
A) increase; increase; raise.
B) decrease; increase; raise
C) increase; decrease; lower
D) increase; increase; lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The difference between nominal GDP and real GDP is that real GDP eliminates the effects from
A) inflation.
B) changes in productivity.
C) depreciation.
D) the unemployment rate.
A) inflation.
B) changes in productivity.
C) depreciation.
D) the unemployment rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The demand for labor and the accumulated skill and knowledge of human is called
)
A) is independent of technology; the marginal product of labor
B) increases when productivity rises; technology
C) depends on the nominal wage rate; human capital
D) depends on the real wage rate; human capital
)
A) is independent of technology; the marginal product of labor
B) increases when productivity rises; technology
C) depends on the nominal wage rate; human capital
D) depends on the real wage rate; human capital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Comparing the unemployment rate and the business cycle we see that
A) higher unemployment rates are the cause of most business cycles.
B) there is virtually no relationship between the business cycle and the unemployment rate.
C) the unemployment rate eventually falls during expansions and rises during recessions.
D) the unemployment rate generally increases during expansions and generally decreases during recessions.
A) higher unemployment rates are the cause of most business cycles.
B) there is virtually no relationship between the business cycle and the unemployment rate.
C) the unemployment rate eventually falls during expansions and rises during recessions.
D) the unemployment rate generally increases during expansions and generally decreases during recessions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Shoes are a normal good and peopleʹs incomes rise. Simultaneously the number of companies making shoes decreases. As a result, the equilibrium price of a pair of shoes________and the equilibrium quantity ________.
A) definitely rises; might increase, decrease, or not change
B) might rise, fall, or not change; might increase, decrease, or not change
C) definitely rises; definitely increases
D) None of the above answers is correct.
A) definitely rises; might increase, decrease, or not change
B) might rise, fall, or not change; might increase, decrease, or not change
C) definitely rises; definitely increases
D) None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In the United States over the past 40 years, the
A) unemployment rate has fluctuated and the labor force participation rate has risen.
B) labor force participation rate has remained relatively constant and the unemployment rate has trended upwards.
C) labor force participation rate has fallen and real GDP has increased.
D) both the unemployment rate and real GDP have tended to increase.
A) unemployment rate has fluctuated and the labor force participation rate has risen.
B) labor force participation rate has remained relatively constant and the unemployment rate has trended upwards.
C) labor force participation rate has fallen and real GDP has increased.
D) both the unemployment rate and real GDP have tended to increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A significant decline in activity spread across the economy, lasting more than a few months is called
A) a recession.
B) inflation.
C) an expansion.
D) a peak.
A) a recession.
B) inflation.
C) an expansion.
D) a peak.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
At full employment,
A) the unemployment rate is zero.
B) real GDP is above potential GDP.
C) real GDP equals potential GDP.
D) the business cycle is at its peak.
A) the unemployment rate is zero.
B) real GDP is above potential GDP.
C) real GDP equals potential GDP.
D) the business cycle is at its peak.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In the expenditure approach to measuring GDP, the components of GDP are
A) consumption, investment, government expenditure, and net exports.
B) consumption, taxes, saving, and investment.
C) frictional unemployment, structural unemployment, and cyclical unemployment.
D) inflation, unemployment, saving, and investment.
A) consumption, investment, government expenditure, and net exports.
B) consumption, taxes, saving, and investment.
C) frictional unemployment, structural unemployment, and cyclical unemployment.
D) inflation, unemployment, saving, and investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Purchasing new capital .
A) shifts the aggregate production function downward
B) creates an upward movement along the aggregate production function
C) shifts the aggregate production function upward
D) creates a downward movement along the aggregate production function
A) shifts the aggregate production function downward
B) creates an upward movement along the aggregate production function
C) shifts the aggregate production function upward
D) creates a downward movement along the aggregate production function

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In the United States, over time GDP
A) stays relatively constant with occasional increases.
B) increases most of the time and decreases occasionally.
C) decreases more often than it increases.
D) increases and decreases roughly about the same amount.
A) stays relatively constant with occasional increases.
B) increases most of the time and decreases occasionally.
C) decreases more often than it increases.
D) increases and decreases roughly about the same amount.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If the economy is at the natural unemployment rate,
A) real GDP = potential GDP.
B) real GDP < potential GDP.
C) real GDP > potential GDP.
D) All of the above can occur when the economy is at the natural unemployment rate.
A) real GDP = potential GDP.
B) real GDP < potential GDP.
C) real GDP > potential GDP.
D) All of the above can occur when the economy is at the natural unemployment rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In the foreign exchange market, if the supply of dollars and simultaneously the demand for dollars , then the exchange rate definitely .
A) increases; decreases; depreciates
B) decreases; increases; depreciates
C) increases; increases; depreciates
D) decreases; decreases; appreciates
A) increases; decreases; depreciates
B) decreases; increases; depreciates
C) increases; increases; depreciates
D) decreases; decreases; appreciates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If the Fed makes an open market of securities, in the quantity theory M and V
)
A) sale; decreases; does not change
B) purchase; does not change; does not change
C) purchase; increases; increases
D) sale; increases; decreases
)
A) sale; decreases; does not change
B) purchase; does not change; does not change
C) purchase; increases; increases
D) sale; increases; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The level of potential GDP
A) determines the location of the long-run aggregate supply curve.
B) rises and falls with the business cycle.
C) increases when the inflation rate rises.
D) changes when cyclical unemployment changes.
A) determines the location of the long-run aggregate supply curve.
B) rises and falls with the business cycle.
C) increases when the inflation rate rises.
D) changes when cyclical unemployment changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The velocity of circulation is
A) the same as the aggregate demand curve.
B) equal to the price level multiplied by real GDP.
C) increased when the Fed lowers the required reserve ratio.
D) the average number of times a dollar bill is used in a year to buy the goods and services in GDP.
A) the same as the aggregate demand curve.
B) equal to the price level multiplied by real GDP.
C) increased when the Fed lowers the required reserve ratio.
D) the average number of times a dollar bill is used in a year to buy the goods and services in GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The major component of the capital and finance account is
A) the official settlements account.
B) net exports.
C) imports and exports of services.
D) investment both abroad and domestically.
A) the official settlements account.
B) net exports.
C) imports and exports of services.
D) investment both abroad and domestically.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If two currencies allow for the equal value of money so that the same bundle of goods cost the same in two countries, there is
A) purchasing power parity.
B) interest rate parity.
C) tariff application parity.
D) trade equalization parity.
A) purchasing power parity.
B) interest rate parity.
C) tariff application parity.
D) trade equalization parity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
When money is accepted as payment in a market transaction, it is functioning as
A) the real interest rate.
B) a medium of exchange.
C) a factor that shifts the aggregate production function
D) the velocity of circulation.
A) the real interest rate.
B) a medium of exchange.
C) a factor that shifts the aggregate production function
D) the velocity of circulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The main component of the current account is
A) net exports.
B) the official settlements account.
C) investment both abroad and domestically.
D) net interest income.
A) net exports.
B) the official settlements account.
C) investment both abroad and domestically.
D) net interest income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Business cycles result when
A) the labor force participation rate changes.
B) aggregate demand grows faster than potential GDP.
C) real GDP equals potential GDP.
D) aggregate supply and aggregate demand change at an uneven pace.
A) the labor force participation rate changes.
B) aggregate demand grows faster than potential GDP.
C) real GDP equals potential GDP.
D) aggregate supply and aggregate demand change at an uneven pace.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Japanʹs population increased by 3 percent in 2010. As a result, which of the following occurred?
i. an increase in potential GDP
ii. a rightward shift in the long-run aggregate supply curve
iii. a rightward shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve.
A) ii and iii.
B) i, ii and iii.
C) i and ii only.
D) iii only.
i. an increase in potential GDP
ii. a rightward shift in the long-run aggregate supply curve
iii. a rightward shift in the short-run aggregate supply curve.
A) ii and iii.
B) i, ii and iii.
C) i and ii only.
D) iii only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Long-run macroeconomic equilibrium occurs when
A) real GDP is at a point along the short-run aggregate supply curve.
B) the unemployment rate is zero.
C) real GDP is equal to potential GDP.
D) all able-bodied adults have jobs.
A) real GDP is at a point along the short-run aggregate supply curve.
B) the unemployment rate is zero.
C) real GDP is equal to potential GDP.
D) all able-bodied adults have jobs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If the U.S. interest rate differential , the demand for dollars and the U.S. exchange rate .
A) decreases; increase; appreciates
B) increases; decrease; depreciates
C) decreases; decreases; appreciates
D) increases; increase; appreciates
A) decreases; increase; appreciates
B) increases; decrease; depreciates
C) decreases; decreases; appreciates
D) increases; increase; appreciates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The growth theory assumes that population growth is not driven by real GDP per person and the growth theory predicts that differences in the economic growth rate can last indefinitely.
A) neoclassical; new
B) neoclassical; neoclassical
C) new; classical
D) classical; neoclassical
A) neoclassical; new
B) neoclassical; neoclassical
C) new; classical
D) classical; neoclassical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Keynesian economists believe that
A) activist government policy is needed to get the economy to full employment.
B) there are no business cycles.
C) monetary policy causes business cycles.
D) the economy automatically adjusts towards full employment.
A) activist government policy is needed to get the economy to full employment.
B) there are no business cycles.
C) monetary policy causes business cycles.
D) the economy automatically adjusts towards full employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If the Fed hikes the U.S. interest rate relative to interest rates in other countries, in the foreign exchange market the demand for dollars will , the supply of dollars will , and the exchange rate will .
A) increase; increase; rise
B) increase; decrease; rise
C) decrease; decrease; fall
D) decrease; increase; fall
A) increase; increase; rise
B) increase; decrease; rise
C) decrease; decrease; fall
D) decrease; increase; fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
At potential GDP
A) unemployment is at its natural rate.
B) there is no unemployment but there is not necessarily full employment.
C) there is no unemployment and there is full employment.
D) None of the above is correct.
A) unemployment is at its natural rate.
B) there is no unemployment but there is not necessarily full employment.
C) there is no unemployment and there is full employment.
D) None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
If productivity constantly increases, then the real wage rate and employment .
A) constantly decreases; does not change
B) does not change; constantly decreases
C) constantly rises; does not change
D) constantly rises; constantly increases
A) constantly decreases; does not change
B) does not change; constantly decreases
C) constantly rises; does not change
D) constantly rises; constantly increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
According to the quantity theory of money,
A) a decrease in the quantity of money will decrease the price level.
B) a decrease in the quantity of money will decrease the velocity of circulation.
C) a change in the discount rate changes real GDP.
D) the only way the Fed can change the quantity of money without affecting the velocity of circulation is by using open market operations.
A) a decrease in the quantity of money will decrease the price level.
B) a decrease in the quantity of money will decrease the velocity of circulation.
C) a change in the discount rate changes real GDP.
D) the only way the Fed can change the quantity of money without affecting the velocity of circulation is by using open market operations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The opportunity cost of holding money is the
A) real interest rate.
B) velocity of circulation.
C) price level.
D) nominal interest rate.
A) real interest rate.
B) velocity of circulation.
C) price level.
D) nominal interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
If the Fed increases the quantity of money, economists believe that the .
A) monetarist; aggregate demand curve shifts rightward
B) monetarist; cyclical deficit increases
C) Keynesian; aggregate supply curve shifts rightward
D) Keynesian; structural deficit increases
A) monetarist; aggregate demand curve shifts rightward
B) monetarist; cyclical deficit increases
C) Keynesian; aggregate supply curve shifts rightward
D) Keynesian; structural deficit increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following is true?
A) The structural deficit changes over the business cycle.
B) At equilibrium expenditure, unplanned changes in inventory must be positive.
C) In the real business cycle model, there is no AD curve.
D) MPS + MPC = 1.
A) The structural deficit changes over the business cycle.
B) At equilibrium expenditure, unplanned changes in inventory must be positive.
C) In the real business cycle model, there is no AD curve.
D) MPS + MPC = 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If we compare the United States to France, we see that potential GDP per person in France is
Than that in the United States because the French is greater than that in the United States.
A) less; structural deficit
B) less; MPC
C) greater; tax wedge
D) less; tax wedge
Than that in the United States because the French is greater than that in the United States.
A) less; structural deficit
B) less; MPC
C) greater; tax wedge
D) less; tax wedge

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following leads to an rightward shift in the short-run Phillips curve?
I. a reduction in inflationary expectations.
II. an increase in the natural rate of unemployment.
III. an increase in the velocity of circulation
A) II only
B) I only
C) I and II
D) I and III
I. a reduction in inflationary expectations.
II. an increase in the natural rate of unemployment.
III. an increase in the velocity of circulation
A) II only
B) I only
C) I and II
D) I and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Suppose that a severe shock that decreases investment demand hits the United States. Which of the following can we expect to occur according to the real business cycle model?
A) The real wage rate will rise.
B) The real interest rate will fall.
C) The Fed will lower the federal funds rate.
D) The structural deficit will increase.
A) The real wage rate will rise.
B) The real interest rate will fall.
C) The Fed will lower the federal funds rate.
D) The structural deficit will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A recessionary gap occurs when
A) the economy is at its long-run equilibrium.
B) the short-run aggregate supply curve shifts rightward.
C) government interferes with the economy.
D) real GDP is less than potential GDP.
A) the economy is at its long-run equilibrium.
B) the short-run aggregate supply curve shifts rightward.
C) government interferes with the economy.
D) real GDP is less than potential GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The marginal propensity to consume measures
A) how much consumption expenditure occurs at the equilibrium level of income.
B) how much of a change in consumption expenditure results from a change in disposable income.
C) the cyclical deficit.
D) the structural deficit.
A) how much consumption expenditure occurs at the equilibrium level of income.
B) how much of a change in consumption expenditure results from a change in disposable income.
C) the cyclical deficit.
D) the structural deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The order for the chain of events for the Keynesian model is for a change in to lead to a change in , which is then multiplied resulting in a change in .
A) business confidence; investment; real GDP
B) investment; animal spirits; the price level
C) the Fedʹs intermediate targets; the Fedʹs goals; real GDP
D) real GDP; income; consumption
A) business confidence; investment; real GDP
B) investment; animal spirits; the price level
C) the Fedʹs intermediate targets; the Fedʹs goals; real GDP
D) real GDP; income; consumption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The growth rate of productivity is a major feature of
A) monetarist economists.
B) real business cycle economists.
C) Keynesian and monetarist economists.
D) why the marginal propensity to consume is less than 1.0.
A) monetarist economists.
B) real business cycle economists.
C) Keynesian and monetarist economists.
D) why the marginal propensity to consume is less than 1.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The presence of imports the size of the .
A) increases; multiplier
B) decreases; multiplier
C) decreases; government budget deficit
D) increases; government budget deficit
A) increases; multiplier
B) decreases; multiplier
C) decreases; government budget deficit
D) increases; government budget deficit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The impulse leading to business cycles in the Keynesian model is changes in
A) the expected future price level.
B) open market operations.
C) business confidence.
D) the structural deficit.
A) the expected future price level.
B) open market operations.
C) business confidence.
D) the structural deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Suppose disposable income increases from $11 trillion to $12 trillion. At the same time, consumption expenditure increases from $4.2 trillion to . Thus the MPC must equal
)
A) $5.0 trillion; 0.50
B) $5.5 trillion; 0.50
C) $5.0 trillion; 0.80
D) $4.4 trillion; 0.40
)
A) $5.0 trillion; 0.50
B) $5.5 trillion; 0.50
C) $5.0 trillion; 0.80
D) $4.4 trillion; 0.40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Fiscal policy entails changes in
A) the multiplier.
B) government spending and taxes.
C) the quantity of money.
D) the MPC.
A) the multiplier.
B) government spending and taxes.
C) the quantity of money.
D) the MPC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The Keynesian aggregate expenditure model best describes the economy in the run when prices are .
A) long; variable
B) short; fixed
C) long; fixed
D) short; variable
A) long; variable
B) short; fixed
C) long; fixed
D) short; variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The Keynesian aggregate expenditure model focuses on changes in
A) real GDP.
B) potential GDP.
C) the price level.
D) the SAS curve.
A) real GDP.
B) potential GDP.
C) the price level.
D) the SAS curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
An example of a fiscal policy designed to decrease real GDP is
A) an increase in taxes.
B) an increase in government expenditure.
C) a cut in taxes.
D) None of the above answers is correct.
A) an increase in taxes.
B) an increase in government expenditure.
C) a cut in taxes.
D) None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Classical economists believe that the economy
A) requires activist government intervention to reach its potential level of GDP.
B) is persistently below its potential level of GDP.
C) is self-regulating and does not require government intervention.
D) can be affected by only monetary policy.
A) requires activist government intervention to reach its potential level of GDP.
B) is persistently below its potential level of GDP.
C) is self-regulating and does not require government intervention.
D) can be affected by only monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Keynesians and monetarists believe that economic fluctuations are caused
A) by fiscal policy.
B) largely by shifts in the AD curve.
C) by shifts in both the AS and AD curves.
D) changes in the structural deficit.
A) by fiscal policy.
B) largely by shifts in the AD curve.
C) by shifts in both the AS and AD curves.
D) changes in the structural deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A fiscal action that is triggered by the state of the economy is called
A) monetarist policy.
B) the tax wedge.
C) the multiplier.
D) automatic fiscal policy.
A) monetarist policy.
B) the tax wedge.
C) the multiplier.
D) automatic fiscal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The multiplier effect
A) has no effect if the cyclical deficit is positive.
B) increases the MPC.
C) is nonexistent in the Keynesian model.
D) magnifies small changes in spending into larger changes in output and income.
A) has no effect if the cyclical deficit is positive.
B) increases the MPC.
C) is nonexistent in the Keynesian model.
D) magnifies small changes in spending into larger changes in output and income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



