Deck 12: The Business Cycle, Inflation, and Deflation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/105
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: The Business Cycle, Inflation, and Deflation
1
Both new Keynesian and new classical cycle theories claim that
A)a change in the price of oil is the major cause of a business cycle.
B)expected changes in the quantity of money can trigger a business cycle.
C)unexpected changes in aggregate demand trigger a business cycle.
D)shifts in the SAS curve are the main impulse for a business cycle.
E)animal spirits can trigger a business cycle.
A)a change in the price of oil is the major cause of a business cycle.
B)expected changes in the quantity of money can trigger a business cycle.
C)unexpected changes in aggregate demand trigger a business cycle.
D)shifts in the SAS curve are the main impulse for a business cycle.
E)animal spirits can trigger a business cycle.
unexpected changes in aggregate demand trigger a business cycle.
2
Which business cycle theory emphasizes that, because of previously negotiated wage agreements, both expected and unexpected fluctuations in aggregate demand can change real GDP?
A)the new classical cycle theory
B)the monetarist cycle theory
C)the new Keynesian cycle theory
D)the real business cycle theory
E)the Keynesian cycle theory
A)the new classical cycle theory
B)the monetarist cycle theory
C)the new Keynesian cycle theory
D)the real business cycle theory
E)the Keynesian cycle theory
the new Keynesian cycle theory
3
Which of the following are business cycle theories that regard fluctuations in aggregate demand as the factor tha business cycles? I.Keynesian cycle theory
II.real business cycle theory
III.monetarist cycle theory
A)I, II and III
B)I and III
C)I only
D)I and II
E)II and III
II.real business cycle theory
III.monetarist cycle theory
A)I, II and III
B)I and III
C)I only
D)I and II
E)II and III
I and III
4
The _______ cycle theory states that only unexpected fluctuations in aggregate demand bring fluctuations in real GDP around potential GDP.
A)new Keynesian
B)monetarist
C)Keynesian
D)real business
E)new classical
A)new Keynesian
B)monetarist
C)Keynesian
D)real business
E)new classical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
According to _______ theory, a decrease in productivity growth shifts the _______.
A)real business cycle; AD curve leftward
B)real business cycle; demand for loanable funds curve leftward
C)real business cycle; AD curve rightward
D)Keynesian cycle; SAS curve leftward
E)Keynesian cycle; SAS curve rightward
A)real business cycle; AD curve leftward
B)real business cycle; demand for loanable funds curve leftward
C)real business cycle; AD curve rightward
D)Keynesian cycle; SAS curve leftward
E)Keynesian cycle; SAS curve rightward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is not a mainstream theory of the business cycle?
A)real business cycle theory
B)new Keynesian cycle theory
C)Keynesian cycle theory
D)new classical cycle theory
E)monetarist cycle theory
A)real business cycle theory
B)new Keynesian cycle theory
C)Keynesian cycle theory
D)new classical cycle theory
E)monetarist cycle theory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The key ripple effect in real business cycle theory is the _______ decision and it depends on the _______.
A)when- to- invest; real interest rate
B)when- to- work; real interest rate
C)where- to- work; real wage rate
D)what- to- save; nominal interest rate
E)when- to- work; rigidity of the money wage rate
A)when- to- invest; real interest rate
B)when- to- work; real interest rate
C)where- to- work; real wage rate
D)what- to- save; nominal interest rate
E)when- to- work; rigidity of the money wage rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
According to the real business cycle theory, what effects follow from a change in productivity? I.Investment demand changes.
II.The demand for labour changes.
III.Government expenditure changes.
A)I
B)I and II
C)I and III
D)II and III
E)I, II and III
II.The demand for labour changes.
III.Government expenditure changes.
A)I
B)I and II
C)I and III
D)II and III
E)I, II and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
New Keynesian economists believe that _______ is influenced by _______.
A)today's money wage rate; today's rational expectations of the price level
B)yesterday's money wage rate; today's rational expectations of the money wage
C)today's money wage rate; yesterday's rational expectations of the price level
D)today's money wage rate; animal spirits
E)yesterday's rational expectations of the price level; today's money wage rate
A)today's money wage rate; today's rational expectations of the price level
B)yesterday's money wage rate; today's rational expectations of the money wage
C)today's money wage rate; yesterday's rational expectations of the price level
D)today's money wage rate; animal spirits
E)yesterday's rational expectations of the price level; today's money wage rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The factor leading to business cycles in the _______ cycle theory is unexpected fluctuations in aggregate demand while in the _______ cycle theory both unexpected and expected fluctuations in aggregate demand are factors that lead to business cycles.
A)new classical; monetarist
B)new Keynesian; Keynesian
C)real business; monetarist
D)monetarist; new Keynesian
E)new classical; new Keynesian
A)new classical; monetarist
B)new Keynesian; Keynesian
C)real business; monetarist
D)monetarist; new Keynesian
E)new classical; new Keynesian

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
_______ states that the main source of economic fluctuations is fluctuations in business confidence.
A)Monetarist cycle theory
B)Real business cycle theory
C)New classical cycle theory
D)Keynesian cycle theory
E)None of the above
A)Monetarist cycle theory
B)Real business cycle theory
C)New classical cycle theory
D)Keynesian cycle theory
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In new classical cycle theory, _______ bring fluctuations in real GDP around potential GDP.
A)unexpected changes in aggregate demand
B)expected changes in labour productivity
C)expected changes in aggregate demand
D)fluctuations in investment coupled with rigid wages
E)fluctuations in money growth with rigid wages
A)unexpected changes in aggregate demand
B)expected changes in labour productivity
C)expected changes in aggregate demand
D)fluctuations in investment coupled with rigid wages
E)fluctuations in money growth with rigid wages

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
According to _______, the business cycle is the result of aggregate demand growing at a fluctuating rate.
A)the Keynesian, monetarist, and real business cycle theories
B)real business cycle theory
C)the Keynesian, monetarist, and new classical cycle theories
D)only the Keynesian and monetarist cycle theories
E)the Keynesian cycle theory only
A)the Keynesian, monetarist, and real business cycle theories
B)real business cycle theory
C)the Keynesian, monetarist, and new classical cycle theories
D)only the Keynesian and monetarist cycle theories
E)the Keynesian cycle theory only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The key difference between new classical cycle theory and new Keynesian cycle theory is that the new classical cycle theory believes that _______ while the new Keynesian cycle theory believes that _______.
A)expected and unexpected changes in aggregate demand change real GDP; only changes in labour productivity change aggregate demand
B)only unexpected changes in aggregate demand change real GDP; only expected changes in aggregate demand change real GDP
C)the short- run aggregate supply curve is horizontal; the short- run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
D)expected changes in aggregate demand change real GDP; expected changes in aggregate demand do not change real GDP
E)only unexpected changes in aggregate demand change real GDP; both expected and unexpected changes in aggregate demand change real GDP
A)expected and unexpected changes in aggregate demand change real GDP; only changes in labour productivity change aggregate demand
B)only unexpected changes in aggregate demand change real GDP; only expected changes in aggregate demand change real GDP
C)the short- run aggregate supply curve is horizontal; the short- run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
D)expected changes in aggregate demand change real GDP; expected changes in aggregate demand do not change real GDP
E)only unexpected changes in aggregate demand change real GDP; both expected and unexpected changes in aggregate demand change real GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
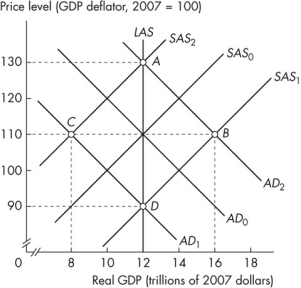 Figure 12.1.1
Figure 12.1.1
Refer to Figure 12.1.1.Suppose the economy moves from point D to point B.According to the monetarist theory of the business cycle, what could have caused this movement?
A)an increase in uncertainty about future sales and profits
B)an increase in the growth rate of the quantity of money
C)a decrease in the money wage rate
D)a decrease in exports
E)an increase in the money wage rate
 Figure 12.1.1
Figure 12.1.1Refer to Figure 12.1.1.Suppose the economy moves from point D to point B.According to the monetarist theory of the business cycle, what could have caused this movement?
A)an increase in uncertainty about future sales and profits
B)an increase in the growth rate of the quantity of money
C)a decrease in the money wage rate
D)a decrease in exports
E)an increase in the money wage rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In real business cycle theory, a decrease in productivity leads to all of the following events except
A)a decrease in the demand for loanable funds.
B)a decrease in the demand for labour.
C)a fall in the real interest rate.
D)a decrease in the supply of labour.
E)a rise in the real wage rate.
A)a decrease in the demand for loanable funds.
B)a decrease in the demand for labour.
C)a fall in the real interest rate.
D)a decrease in the supply of labour.
E)a rise in the real wage rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the Keynesian business cycle theory, business cycles begin with a change in
A)government expenditure.
B)the money wage rate.
C)business confidence.
D)inflation expectations.
E)monetary policy.
A)government expenditure.
B)the money wage rate.
C)business confidence.
D)inflation expectations.
E)monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The new classical theory argues that the primary factor leading to business cycles is
A)unexpected fluctuations in short- run aggregate supply.
B)expected fluctuations in aggregate demand.
C)unexpected fluctuations in long- run aggregate supply.
D)unexpected fluctuations in aggregate demand.
E)expected fluctuations in short- run aggregate supply.
A)unexpected fluctuations in short- run aggregate supply.
B)expected fluctuations in aggregate demand.
C)unexpected fluctuations in long- run aggregate supply.
D)unexpected fluctuations in aggregate demand.
E)expected fluctuations in short- run aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
"Intertemporal substitution" in real business cycle theory refers to the change in the _______ as a result of the change in the real interest rate.
A)demand for labour
B)demand for loanable funds
C)consumer demand for goods
D)personal tax rate
E)supply of labour
A)demand for labour
B)demand for loanable funds
C)consumer demand for goods
D)personal tax rate
E)supply of labour

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
 Figure 12.1.1
Figure 12.1.1
Refer to Figure 12.1.1.Suppose the economy moves from point A to point C.According to the monetarist theory of the business cycle, what could have caused this movement?
A)an increase in the growth rate of the quantity of money
B)animal spirits
C)an increase in uncertainty
D)an increase in the money wage rate
E)a decrease in the growth rate of the quantity of money
 Figure 12.1.1
Figure 12.1.1Refer to Figure 12.1.1.Suppose the economy moves from point A to point C.According to the monetarist theory of the business cycle, what could have caused this movement?
A)an increase in the growth rate of the quantity of money
B)animal spirits
C)an increase in uncertainty
D)an increase in the money wage rate
E)a decrease in the growth rate of the quantity of money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In real business cycle theory, _______ are the main source of economic fluctuations.
A)unexpected changes in the full- employment quantity of labour
B)changes in the quantity of money
C)random fluctuations in productivity
D)random fluctuations in investment
E)unexpected changes in government expenditure
A)unexpected changes in the full- employment quantity of labour
B)changes in the quantity of money
C)random fluctuations in productivity
D)random fluctuations in investment
E)unexpected changes in government expenditure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following would cause the aggregate demand curve to keep shifting rightward year after year?
A)inflation
B)excess wage demands
C)a one- time increase in government expenditures on goods and services
D)a one- time tax cut
E)a persistent increase in the quantity of money
A)inflation
B)excess wage demands
C)a one- time increase in government expenditures on goods and services
D)a one- time tax cut
E)a persistent increase in the quantity of money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Real business cycle theorists believe that the intertemporal substitution effect _______.Many other economists believe that the intertemporal substitution effect _______.
A)is negligible; is large
B)occurs in the money market; occurs in the labour market
C)occurs in the labour market; occurs in the money market
D)occurs in foreign markets; occurs in domestic markets
E)is large; is negligible
A)is negligible; is large
B)occurs in the money market; occurs in the labour market
C)occurs in the labour market; occurs in the money market
D)occurs in foreign markets; occurs in domestic markets
E)is large; is negligible

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
According to real business cycle theory, an increase in productivity _______ the demand for loanable funds, _______ the demand for labour, and _______ the supply of labour.The real interest rate will _______.
A)increases; increases; does not change; rise
B)increases; increases; does not change; fall
C)increases; increases; increases; rise
D)decreases; decreases; decreases; fall
E)increases; increases; increases; fall
A)increases; increases; does not change; rise
B)increases; increases; does not change; fall
C)increases; increases; increases; rise
D)decreases; decreases; decreases; fall
E)increases; increases; increases; fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
According to real business cycle theory, if the Bank of Canada increases the quantity of money when real GDP decreases, real GDP
A)will increase but only temporarily.
B)and the price level will both be unaffected.
C)will increase permanently.
D)will be unaffected, but the price level will rise.
E)will decrease due to the inefficiencies introduced into production as a result.
A)will increase but only temporarily.
B)and the price level will both be unaffected.
C)will increase permanently.
D)will be unaffected, but the price level will rise.
E)will decrease due to the inefficiencies introduced into production as a result.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
According to real business cycle theory, workers' decisions to work now versus later depend on
A)labour productivity.
B)the money wage rate.
C)the real wage rate today but not the real wage rate in the future.
D)human capital.
E)the real interest rate.
A)labour productivity.
B)the money wage rate.
C)the real wage rate today but not the real wage rate in the future.
D)human capital.
E)the real interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Suppose that the business cycle in Canada is best described by RBC theory.An advance in technology increases productivity.The when- to- work decision depends on the real interest rate.The _______ the real interest rate, other things remaining the same, the _______ is the supply of labour today.RBC theorists believe the when- to- work effect is _______.
A)higher; smaller; small
B)lower; smaller; small
C)higher; larger; small
D)higher; larger; large
E)lower; larger; large
A)higher; smaller; small
B)lower; smaller; small
C)higher; larger; small
D)higher; larger; large
E)lower; larger; large

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which one of the following can start a demand- pull inflation?
A)a sharp increase in the price of oil
B)a decrease in investment as a result of a decrease in expected future profits
C)a decrease in government expenditure on goods and services
D)a cut in the interest rate
E)higher wages negotiated by unions
A)a sharp increase in the price of oil
B)a decrease in investment as a result of a decrease in expected future profits
C)a decrease in government expenditure on goods and services
D)a cut in the interest rate
E)higher wages negotiated by unions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
According to the real business cycle theory, during a recession the demand for labour _______ and the supply of labour _______.
A)decreases; increases
B)decreases; does not change
C)does not change; decreases
D)increases; decreases
E)decreases; decreases
A)decreases; increases
B)decreases; does not change
C)does not change; decreases
D)increases; decreases
E)decreases; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Suppose that a severe shock that decreases the demand for loanable funds hits Canada.Which of the following can we expect to occur according to real business cycle theory?
A)People will work fewer hours.
B)The real wage rate will fall.
C)The demand for loanable funds will decrease.
D)The real interest rate will fall.
E)All of the above are true.
A)People will work fewer hours.
B)The real wage rate will fall.
C)The demand for loanable funds will decrease.
D)The real interest rate will fall.
E)All of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
According to mainstream business cycle theory, _______ grows at a steady rate and _______ grows at a fluctuating rate.
A)aggregate demand; long- run aggregate supply
B)potential GDP; short- run aggregate supply
C)short- run aggregate supply; long- run aggregate supply
D)short- run aggregate supply; aggregate demand
E)potential GDP; aggregate demand
A)aggregate demand; long- run aggregate supply
B)potential GDP; short- run aggregate supply
C)short- run aggregate supply; long- run aggregate supply
D)short- run aggregate supply; aggregate demand
E)potential GDP; aggregate demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In real business cycle theory, the supply of labour
A)decreases if the real interest rate rises.
B)increases if the nominal interest rate rises.
C)decreases if the real wage rate decreases.
D)decreases if the real interest rate falls.
E)is independent of the real interest rate.
A)decreases if the real interest rate rises.
B)increases if the nominal interest rate rises.
C)decreases if the real wage rate decreases.
D)decreases if the real interest rate falls.
E)is independent of the real interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
At full employment, an increase in the quantity of money ceteris paribus) can start
A)demand- pull inflation, as can an increase in government expenditure.
B)cost- push inflation, but an increase in government expenditure cannot.
C)demand- pull and a cost- push inflation, as can an increase in government expenditure.
D)cost- push inflation, as can an increase in government expenditure.
E)demand- pull inflation, but an increase in government expenditure cannot.
A)demand- pull inflation, as can an increase in government expenditure.
B)cost- push inflation, but an increase in government expenditure cannot.
C)demand- pull and a cost- push inflation, as can an increase in government expenditure.
D)cost- push inflation, as can an increase in government expenditure.
E)demand- pull inflation, but an increase in government expenditure cannot.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Suppose that in response to a decrease in real interest rates, a person decides to reduce his supply of labour today and increase it in the future.This behaviour is most consistent with the
A)new Keynesian cycle theory.
B)new classical cycle theory.
C)monetarist cycle theory.
D)real business cycle theory.
E)Keynesian cycle theory.
A)new Keynesian cycle theory.
B)new classical cycle theory.
C)monetarist cycle theory.
D)real business cycle theory.
E)Keynesian cycle theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Stagflation occurs when the economy experiences both a
A)low exports and low imports.
B)rising price level and decreasing real GDP.
C)falling price level and decreasing real GDP.
D)falling price level and increasing real GDP.
E)rising price level and increasing real GDP.
A)low exports and low imports.
B)rising price level and decreasing real GDP.
C)falling price level and decreasing real GDP.
D)falling price level and increasing real GDP.
E)rising price level and increasing real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Suppose the economy is in long- run equilibrium when the price of oil rises.Which one of the following is not a short- run effect of this situation?
A)an increase in the price level
B)an increase in unemployment
C)a decrease in short- run aggregate supply
D)an increase in real GDP above long- run real GDP
E)a decrease in consumer spending
A)an increase in the price level
B)an increase in unemployment
C)a decrease in short- run aggregate supply
D)an increase in real GDP above long- run real GDP
E)a decrease in consumer spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
According to real business cycle theory, a fall in the real interest rate _______ the supply of labour and _______ employment.
A)decreases; increases
B)increases; increases
C)increases; decreases
D)decreases; decreases
E)does not change; does not change
A)decreases; increases
B)increases; increases
C)increases; decreases
D)decreases; decreases
E)does not change; does not change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Inflation that starts because aggregate demand increases is called
A)anticipated inflation.
B)cost- push inflation.
C)demand- pull inflation.
D)political inflation.
E)unanticipated inflation.
A)anticipated inflation.
B)cost- push inflation.
C)demand- pull inflation.
D)political inflation.
E)unanticipated inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Demand- pull inflation can start when
A)input costs rise.
B)aggregate supply decreases.
C)aggregate demand increases.
D)unemployment is above the natural rate.
E)people incorrectly forecast inflation.
A)input costs rise.
B)aggregate supply decreases.
C)aggregate demand increases.
D)unemployment is above the natural rate.
E)people incorrectly forecast inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In real business cycle theory, the supply of labour
A)increases if the demand for labour decreases.
B)increases if the real interest rate falls.
C)increases if the demand for loanable funds decreases.
D)is not influenced by changes in the real interest rate.
E)increases if the real interest rate rises.
A)increases if the demand for labour decreases.
B)increases if the real interest rate falls.
C)increases if the demand for loanable funds decreases.
D)is not influenced by changes in the real interest rate.
E)increases if the real interest rate rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
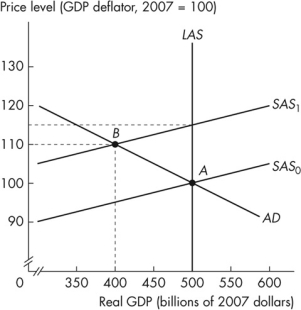 Figure 12.2.2
Figure 12.2.2
Refer to Figure 12.2.2.The economy is in long- run equilibrium.If the short- run aggregate supply curve shifts leftward from SAS0 to SAS1, ceteris paribus, then the actual inflation rate
A)cannot be determined without more information.
B)depends on what happens to wage settlements.
C)is less than the expected inflation rate.
D)is greater than the expected inflation rate.
E)is the same as the expected inflation rate.
 Figure 12.2.2
Figure 12.2.2Refer to Figure 12.2.2.The economy is in long- run equilibrium.If the short- run aggregate supply curve shifts leftward from SAS0 to SAS1, ceteris paribus, then the actual inflation rate
A)cannot be determined without more information.
B)depends on what happens to wage settlements.
C)is less than the expected inflation rate.
D)is greater than the expected inflation rate.
E)is the same as the expected inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
An economy is in long- run equilibrium when aggregate supply unexpectedly decreases.Then real GDP ceteris paribus) will be
A)below potential GDP.
B)above potential GDP.
C)equal to potential GDP.
D)either above, below, or equal to potential GDP depending on the position of the aggregate demand curve.
E)either above or equal to potential GDP depending on the position of the aggregate demand curve.
A)below potential GDP.
B)above potential GDP.
C)equal to potential GDP.
D)either above, below, or equal to potential GDP depending on the position of the aggregate demand curve.
E)either above or equal to potential GDP depending on the position of the aggregate demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
 Figure 12.2.2
Figure 12.2.2
Refer to Figure 12.2.2.Complete the following sentence.The figure illustrates
A)cost- push inflation.
B)demand- pull inflation.
C)a one- time rise in the price level.
D)a cost- push inflation spiral.
E)a deflation.
 Figure 12.2.2
Figure 12.2.2Refer to Figure 12.2.2.Complete the following sentence.The figure illustrates
A)cost- push inflation.
B)demand- pull inflation.
C)a one- time rise in the price level.
D)a cost- push inflation spiral.
E)a deflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A cost- price inflation spiral results if the policy response to stagflation is to keep
A)decreasing aggregate demand.
B)increasing aggregate demand.
C)increasing short- run aggregate supply.
D)decreasing short- run aggregate supply.
E)doing nothing.
A)decreasing aggregate demand.
B)increasing aggregate demand.
C)increasing short- run aggregate supply.
D)decreasing short- run aggregate supply.
E)doing nothing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Stagflation can result from
A)a rightward shift of the short- run aggregate supply curve.
B)a rightward shift of the long- run aggregate supply curve.
C)a rightward shift of the demand curve.
D)a leftward shift of the short- run aggregate supply curve.
E)a leftward shift of the demand curve.
A)a rightward shift of the short- run aggregate supply curve.
B)a rightward shift of the long- run aggregate supply curve.
C)a rightward shift of the demand curve.
D)a leftward shift of the short- run aggregate supply curve.
E)a leftward shift of the demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
 Figure 12.2.2
Figure 12.2.2
Refer to Figure 12.2.2.If the short- run aggregate supply curve does not shift, and remains at SAS0, then the expected inflation rate is
A)15 percent.
B)zero.
C)10 percent.
D)- 10 percent.
E)5 percent.
 Figure 12.2.2
Figure 12.2.2Refer to Figure 12.2.2.If the short- run aggregate supply curve does not shift, and remains at SAS0, then the expected inflation rate is
A)15 percent.
B)zero.
C)10 percent.
D)- 10 percent.
E)5 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A correctly anticipated increase in the quantity of money, in an economy with an unchanging long- run aggregate supply, will result in
A)no change in the price level and no change in real GDP.
B)a rise in the price level and a decrease in real GDP.
C)no change in the price level and an increase in real GDP.
D)a rise in the price level and an increase in real GDP.
E)a proportional rise in the price level and no change in real GDP.
A)no change in the price level and no change in real GDP.
B)a rise in the price level and a decrease in real GDP.
C)no change in the price level and an increase in real GDP.
D)a rise in the price level and an increase in real GDP.
E)a proportional rise in the price level and no change in real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Use the figure below to answer the following question.
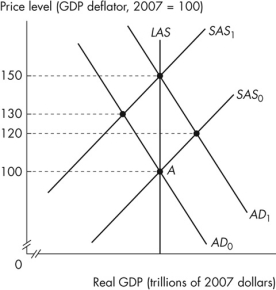 Figure 12.2.4
Figure 12.2.4
Refer to Figure 12.2.4.The figure illustrates an economy initially in equilibrium at point A.If the quantity of money is expected to increase by 50 percent, what is the rational expectation of the price level?
A)100
B)120
C)150
D)130
E)We cannot tell without more information on wage negotiations.
 Figure 12.2.4
Figure 12.2.4Refer to Figure 12.2.4.The figure illustrates an economy initially in equilibrium at point A.If the quantity of money is expected to increase by 50 percent, what is the rational expectation of the price level?
A)100
B)120
C)150
D)130
E)We cannot tell without more information on wage negotiations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
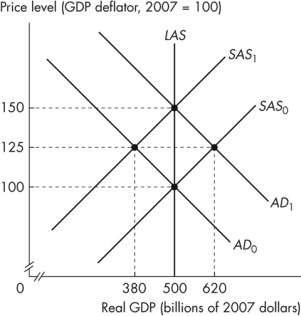 Figure 12.2.3
Figure 12.2.3
Refer to Figure 12.2.3.Assume that the figure illustrates an economy initially in equilibrium at the intersection of the SAS0 curve and the AD0 curve.If the aggregate demand curve is expected to remain at AD0 but shifts to AD1, the new equilibrium real GDP is _______ and the new equilibrium price level is _______.
A)$500 billion; 100
B)$380 billion; 125
C)$500 billion; 125
D)$620 billion; 125
E)$500 billion; 150
 Figure 12.2.3
Figure 12.2.3Refer to Figure 12.2.3.Assume that the figure illustrates an economy initially in equilibrium at the intersection of the SAS0 curve and the AD0 curve.If the aggregate demand curve is expected to remain at AD0 but shifts to AD1, the new equilibrium real GDP is _______ and the new equilibrium price level is _______.
A)$500 billion; 100
B)$380 billion; 125
C)$500 billion; 125
D)$620 billion; 125
E)$500 billion; 150

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Cost- push inflation can result from an initial
A)increase in the money wage rate.
B)increase in transfer payments.
C)decrease in personal income taxes.
D)increase in government expenditure.
E)increase in personal income taxes.
A)increase in the money wage rate.
B)increase in transfer payments.
C)decrease in personal income taxes.
D)increase in government expenditure.
E)increase in personal income taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
 Figure 12.2.2
Figure 12.2.2
Refer to Figure 12.2.2.Consider the market for labour as the short- run aggregate supply curve shifts leftward from SAS0 to SAS1.This shift could have been the result of an agreement between workers and employers for a
A)10 percent increase in the money wage rate.
B)15 percent decrease in the money wage rate.
C)10 percent increase in the real wage rate.
D)15 percent increase in the money wage rate.
E)10 percent decrease in the money wage rate.
 Figure 12.2.2
Figure 12.2.2Refer to Figure 12.2.2.Consider the market for labour as the short- run aggregate supply curve shifts leftward from SAS0 to SAS1.This shift could have been the result of an agreement between workers and employers for a
A)10 percent increase in the money wage rate.
B)15 percent decrease in the money wage rate.
C)10 percent increase in the real wage rate.
D)15 percent increase in the money wage rate.
E)10 percent decrease in the money wage rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Suppose the quantity of money is expected to remain unchanged but it actually increases.The price level
A)rises and real GDP stays the same.
B)falls and real GDP increases.
C)rises and real GDP increases.
D)rises and real GDP decreases.
E)falls and real GDP decreases.
A)rises and real GDP stays the same.
B)falls and real GDP increases.
C)rises and real GDP increases.
D)rises and real GDP decreases.
E)falls and real GDP decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
 Figure 12.2.3
Figure 12.2.3
Refer to Figure 12.2.3.Assume that the figure illustrates an economy initially in equilibrium at the intersection of the SAS0 curve and the AD0 curve.If the aggregate demand curve is expected to shift to AD1 but remains at AD0, the new equilibrium real GDP is _______ and the new equilibrium price level is _______.
A)$500 billion; 100
B)$380 billion; 100
C)$500 billion; 150
D)$620 billion; 125
E)$380 billion; 125
 Figure 12.2.3
Figure 12.2.3Refer to Figure 12.2.3.Assume that the figure illustrates an economy initially in equilibrium at the intersection of the SAS0 curve and the AD0 curve.If the aggregate demand curve is expected to shift to AD1 but remains at AD0, the new equilibrium real GDP is _______ and the new equilibrium price level is _______.
A)$500 billion; 100
B)$380 billion; 100
C)$500 billion; 150
D)$620 billion; 125
E)$380 billion; 125

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
 Figure 12.2.2
Figure 12.2.2
Refer to Figure 12.2.2.The vertical distance between SAS0 and SAS1 represents the
A)actual decrease in real GDP.
B)expected decrease in the real wage rate.
C)actual inflation rate.
D)expected increase in real GDP.
E)expected inflation rate.
 Figure 12.2.2
Figure 12.2.2Refer to Figure 12.2.2.The vertical distance between SAS0 and SAS1 represents the
A)actual decrease in real GDP.
B)expected decrease in the real wage rate.
C)actual inflation rate.
D)expected increase in real GDP.
E)expected inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
 Figure 12.2.2
Figure 12.2.2
Refer to Figure 12.2.2.If SAS shifts from SAS0 to SAS1, then
A)inflation will be 10 percent.
B)unemployment will fall.
C)potential GDP will decrease
D)deflation occurs.
E)inflation is expected to be 10 percent.
 Figure 12.2.2
Figure 12.2.2Refer to Figure 12.2.2.If SAS shifts from SAS0 to SAS1, then
A)inflation will be 10 percent.
B)unemployment will fall.
C)potential GDP will decrease
D)deflation occurs.
E)inflation is expected to be 10 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A forecast based on all the relevant information is
A)a perfect forecast.
B)always a correct expectation.
C)an adaptive expectation.
D)a future expectation.
E)a rational expectation.
A)a perfect forecast.
B)always a correct expectation.
C)an adaptive expectation.
D)a future expectation.
E)a rational expectation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
 Figure 12.2.2
Figure 12.2.2
Refer to Figure 12.2.2.The economy is in long- run equilibrium.If the short- run aggregate supply curve shifts leftward from SAS0 to SAS1, ceteris paribus, then people expect
A)a real GDP decrease of $50 billion.
B)a 10 percent inflation.
C)the price level to rise to 110.
D)the real wage rate to fall by 10 percent.
E)a 15 percent inflation.
 Figure 12.2.2
Figure 12.2.2Refer to Figure 12.2.2.The economy is in long- run equilibrium.If the short- run aggregate supply curve shifts leftward from SAS0 to SAS1, ceteris paribus, then people expect
A)a real GDP decrease of $50 billion.
B)a 10 percent inflation.
C)the price level to rise to 110.
D)the real wage rate to fall by 10 percent.
E)a 15 percent inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Use the figure below to answer the following question.
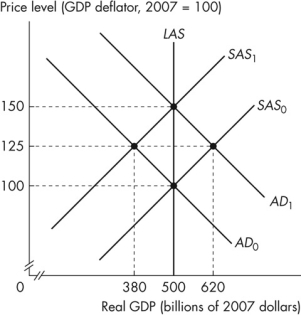 Figure 12.2.1
Figure 12.2.1
Refer to Figure 12.2.1.The figure illustrates an economy initially in equilibrium at the intersection of the SAS0 curve and the AD0 curve.Which of the following shifts the short- run aggregate supply curve from SAS0 to SAS1?
A)an increase in the demand for money
B)a decrease in the money wage rate
C)an increase in the marginal product of labour
D)an increase in the price level
E)an increase in the price of oil
 Figure 12.2.1
Figure 12.2.1Refer to Figure 12.2.1.The figure illustrates an economy initially in equilibrium at the intersection of the SAS0 curve and the AD0 curve.Which of the following shifts the short- run aggregate supply curve from SAS0 to SAS1?
A)an increase in the demand for money
B)a decrease in the money wage rate
C)an increase in the marginal product of labour
D)an increase in the price level
E)an increase in the price of oil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
 Figure 12.2.3
Figure 12.2.3
Refer to Figure 12.2.3.Assume that the figure illustrates an economy initially in equilibrium at the intersection of the SAS0 curve and the AD0 curve.If the aggregate demand curve is correctly expected to shift to AD1, new equilibrium real GDP is _______ and the new equilibrium price level is _______.
A)$500 billion; 150
B)$620 billion; 125
C)$380 billion; 125
D)$500 billion; 100
E)$500 billion; 125
 Figure 12.2.3
Figure 12.2.3Refer to Figure 12.2.3.Assume that the figure illustrates an economy initially in equilibrium at the intersection of the SAS0 curve and the AD0 curve.If the aggregate demand curve is correctly expected to shift to AD1, new equilibrium real GDP is _______ and the new equilibrium price level is _______.
A)$500 billion; 150
B)$620 billion; 125
C)$380 billion; 125
D)$500 billion; 100
E)$500 billion; 125

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
An increase in the price level due to an increase in the price of oil
A)leads to an increase in the money wage rate.
B)increases output above potential GDP.
C)creates stagflation in the short- run and will trigger a cost- push inflation.
D)creates stagflation in the short- run and may trigger a cost- push inflation.
E)leads to a decrease in the money wage rate.
A)leads to an increase in the money wage rate.
B)increases output above potential GDP.
C)creates stagflation in the short- run and will trigger a cost- push inflation.
D)creates stagflation in the short- run and may trigger a cost- push inflation.
E)leads to a decrease in the money wage rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A correctly anticipated increase in the quantity of money
A)increases the price level and increases real GDP.
B)increases the price level with no change in real GDP.
C)does not change the price level but increases real GDP.
D)does not change the price level or real GDP.
E)does not change the price level but decreases real GDP.
A)increases the price level and increases real GDP.
B)increases the price level with no change in real GDP.
C)does not change the price level but increases real GDP.
D)does not change the price level or real GDP.
E)does not change the price level but decreases real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The short- run Phillips curve shows the relationship between _______, holding constant the expected inflation rate and the natural unemployment rate.
A)the inflation rate and the growth of the money wage rate.
B)the inflation rate and the unemployment rate
C)the inflation rate and the economic growth rate
D)growth and potential GDP.
E)unemployment and the economic growth rate
A)the inflation rate and the growth of the money wage rate.
B)the inflation rate and the unemployment rate
C)the inflation rate and the economic growth rate
D)growth and potential GDP.
E)unemployment and the economic growth rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A forecast that is based on all the relevant information available is
A)usually accurate.
B)usually no better than a random guess given that the future bears many uncertainties.
C)useful only in the prediction of cost- push inflation.
D)called a rational expectation.
E)useful only in the prediction of demand- pull inflation.
A)usually accurate.
B)usually no better than a random guess given that the future bears many uncertainties.
C)useful only in the prediction of cost- push inflation.
D)called a rational expectation.
E)useful only in the prediction of demand- pull inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Deflation ends with
A)a rise in the interest rate.
B)a one- time decrease in the quantity of money.
C)a one- time increase in the quantity of money.
D)an increase in the growth rate of the money stock.
E)a decrease in the growth rate of the money stock.
A)a rise in the interest rate.
B)a one- time decrease in the quantity of money.
C)a one- time increase in the quantity of money.
D)an increase in the growth rate of the money stock.
E)a decrease in the growth rate of the money stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The economy starts out at a full- employment equilibrium.Some events then occur that generate a cost- push inflation.Which of the following events might start a cost- push inflation?
A)an increase in taxes
B)an increase in the money wage rate or an increase in the money prices of raw materials
C)an increase in the quantity of money
D)a decrease in government expenditure
E)a decrease in exports
A)an increase in taxes
B)an increase in the money wage rate or an increase in the money prices of raw materials
C)an increase in the quantity of money
D)a decrease in government expenditure
E)a decrease in exports

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
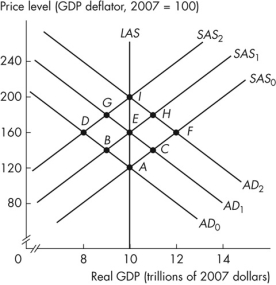 Figure 12.2.6
Figure 12.2.6
Refer to Figure 12.2.6.Starting at point A, the initial effect of a cost- push inflation is a move to point _______.As a cost- push inflation spiral proceeds, it follows the path _______.
A)C; E, H, I
B)B; D, G, I
C)E; I
D)C; B, H, G, I
E)B; E, G, I
 Figure 12.2.6
Figure 12.2.6Refer to Figure 12.2.6.Starting at point A, the initial effect of a cost- push inflation is a move to point _______.As a cost- push inflation spiral proceeds, it follows the path _______.
A)C; E, H, I
B)B; D, G, I
C)E; I
D)C; B, H, G, I
E)B; E, G, I

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Suppose aggregate demand increases by more than expected.Which of the following does not occur?
A)Unemployment falls.
B)The price level rises.
C)The natural unemployment rate does not change.
D)Real GDP is greater than potential GDP.
E)Stagflation occurs.
A)Unemployment falls.
B)The price level rises.
C)The natural unemployment rate does not change.
D)Real GDP is greater than potential GDP.
E)Stagflation occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Stagflation is the result of
A)an increase in short- run aggregate supply.
B)a decrease in short- run aggregate supply.
C)a decrease in aggregate demand.
D)a decrease in short- run aggregate supply combined with a simultaneous increase in aggregate supply.
E)an increase in aggregate demand.
A)an increase in short- run aggregate supply.
B)a decrease in short- run aggregate supply.
C)a decrease in aggregate demand.
D)a decrease in short- run aggregate supply combined with a simultaneous increase in aggregate supply.
E)an increase in aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Suppose OPEC unexpectedly collapses, which leads to a fall in the price of oil.As a result, the price level
A)rises, and real GDP increases.
B)rises, and real GDP decreases.
C)falls, and real GDP decreases.
D)rises, and real GDP remains the same.
E)falls, and real GDP increases.
A)rises, and real GDP increases.
B)rises, and real GDP decreases.
C)falls, and real GDP decreases.
D)rises, and real GDP remains the same.
E)falls, and real GDP increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Suppose that the money prices of raw materials rise.With no action by the Bank of Canada, I.the aggregate demand curve shifts rightward and the price level rises.
II.the aggregate demand curve shifts rightward and the aggregate supply curve shifts leftward.
III.the initial outcome is lower employment and a rise in the price level.
A)I only
B)II only
C)III only
D)I and II only
E)I, II, and III
II.the aggregate demand curve shifts rightward and the aggregate supply curve shifts leftward.
III.the initial outcome is lower employment and a rise in the price level.
A)I only
B)II only
C)III only
D)I and II only
E)I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The economy starts out at a full- employment equilibrium.Some events then occur that generate a demand- pull inflation.All of the following events except an increase in _______ might start a demand- pull inflation.
A)government expenditure
B)transfer payments
C)the quantity of money
D)exports
E)the money wage rate
A)government expenditure
B)transfer payments
C)the quantity of money
D)exports
E)the money wage rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
An unanticipated deflation does all of the following except
A)redistributes wealth.
B)decreases the real wages of workers with long- term wage contracts.
C)lowers real GDP.
D)lowers employment.
E)redistributes income.
A)redistributes wealth.
B)decreases the real wages of workers with long- term wage contracts.
C)lowers real GDP.
D)lowers employment.
E)redistributes income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
 Figure 12.2.6
Figure 12.2.6
Refer to Figure 12.2.6.Starting at point A, the initial effect of a demand- pull inflation is a move to point _______.As a demand- pull inflation spiral proceeds, it follows the path _______.
A)C; B, H, G, I
B)B; E, G, I
C)C; F, H, I
D)E; I
E)C; E, H, I
 Figure 12.2.6
Figure 12.2.6Refer to Figure 12.2.6.Starting at point A, the initial effect of a demand- pull inflation is a move to point _______.As a demand- pull inflation spiral proceeds, it follows the path _______.
A)C; B, H, G, I
B)B; E, G, I
C)C; F, H, I
D)E; I
E)C; E, H, I

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Choose the statement that is incorrect.
A)A one- time fall in the price level occurs either because aggregate demand decreases or because short- run aggregate supply increases.
B)In a deflation, the inflation rate is positive but decreasing in consequent years.
C)A one- time fall in the price level occurs when there is an increase in capital that increases potential GDP.
D)In a deflation, the price level persistently falls.
E)A one- time fall in the price level is not a deflation.
A)A one- time fall in the price level occurs either because aggregate demand decreases or because short- run aggregate supply increases.
B)In a deflation, the inflation rate is positive but decreasing in consequent years.
C)A one- time fall in the price level occurs when there is an increase in capital that increases potential GDP.
D)In a deflation, the price level persistently falls.
E)A one- time fall in the price level is not a deflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Deflation occurs when
A)the growth rate of potential GDP slows.
B)aggregate demand increases at a persistently faster rate than aggregate supply.
C)aggregate demand increases at a persistently slower rate than aggregate supply.
D)the quantity of money remains constant.
E)the quantity theory of money is disregarded.
A)the growth rate of potential GDP slows.
B)aggregate demand increases at a persistently faster rate than aggregate supply.
C)aggregate demand increases at a persistently slower rate than aggregate supply.
D)the quantity of money remains constant.
E)the quantity theory of money is disregarded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Deflation is
A)a persistent and ongoing falling price level.
B)always accompanied by a decrease in the natural unemployment rate.
C)unknown in the twenty- first century.
D)always accompanied by an increase in the natural unemployment rate.
E)a one- time fall in the price level.
A)a persistent and ongoing falling price level.
B)always accompanied by a decrease in the natural unemployment rate.
C)unknown in the twenty- first century.
D)always accompanied by an increase in the natural unemployment rate.
E)a one- time fall in the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
When the price level is rising and, simultaneously, real GDP is decreasing,
A)potential GDP is decreasing.
B)the natural unemployment rate is rising.
C)stagflation is occurring.
D)the economy is experiencing an expansionary gap.
E)the natural unemployment rate is falling.
A)potential GDP is decreasing.
B)the natural unemployment rate is rising.
C)stagflation is occurring.
D)the economy is experiencing an expansionary gap.
E)the natural unemployment rate is falling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Use the figure below to answer the following question.
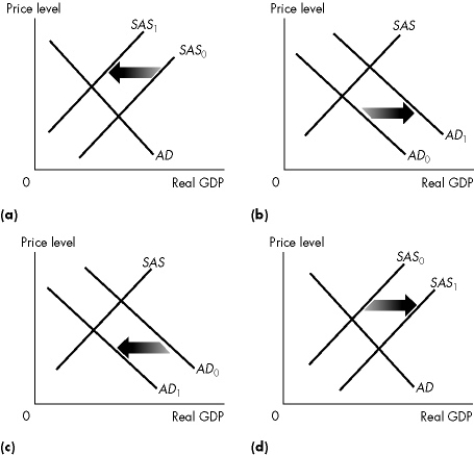 Figure 12.2.5
Figure 12.2.5
Refer to Figure 12.2.5.Which one of the graphs in the figure represents an economy experiencing stagflation?
A)a only
B)b only
C)c only
D)d only
E)Both a and c
 Figure 12.2.5
Figure 12.2.5Refer to Figure 12.2.5.Which one of the graphs in the figure represents an economy experiencing stagflation?
A)a only
B)b only
C)c only
D)d only
E)Both a and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Along the short- run Phillips curve, everything remaining the same, the higher the
A)quantity of money, the lower the unemployment rate.
B)growth rate of the quantity of money, the higher the inflation rate.
C)unemployment rate, the lower the inflation rate.
D)money wage rate, the lower is the unemployment rate.
E)price level, the lower the inflation rate.
A)quantity of money, the lower the unemployment rate.
B)growth rate of the quantity of money, the higher the inflation rate.
C)unemployment rate, the lower the inflation rate.
D)money wage rate, the lower is the unemployment rate.
E)price level, the lower the inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Choose the statement that is incorrect.
A)The price level falls if aggregate supply increases at a persistently slower rate than aggregate demand.
B)Deflation can end if the central bank ensures that the quantity of money grows at the target inflation rate plus the growth rate of potential GDP minus the growth rate of the velocity of circulation.
C)A one- time fall in the price level is not deflation.
D)An economy experiences deflation when it has a persistently falling price level.
E)During a period of deflation, the inflation rate is negative.
A)The price level falls if aggregate supply increases at a persistently slower rate than aggregate demand.
B)Deflation can end if the central bank ensures that the quantity of money grows at the target inflation rate plus the growth rate of potential GDP minus the growth rate of the velocity of circulation.
C)A one- time fall in the price level is not deflation.
D)An economy experiences deflation when it has a persistently falling price level.
E)During a period of deflation, the inflation rate is negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



