Deck 1: Introduction: What Is Economics
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/144
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: Introduction: What Is Economics
1
Resources are all of the following except:
A) the things we use to produce goods and services.
B) scarce and therefore requiring choices to be made.
C) unlimited and in abundance.
D) limited in quantity and can be used in different ways.
A) the things we use to produce goods and services.
B) scarce and therefore requiring choices to be made.
C) unlimited and in abundance.
D) limited in quantity and can be used in different ways.
unlimited and in abundance.
2
A student has a D grade average in her accounting course and a B grade average in her economics course. She decides to study an extra hour for her accounting exam and one less hour for her economics exam hoping to improve her accounting grade while not hurting her economics grade. This is an example of:
A) using assumptions to simplify.
B) thinking at the margin.
C) ceteris paribus.
D) caveat emptor.
A) using assumptions to simplify.
B) thinking at the margin.
C) ceteris paribus.
D) caveat emptor.
thinking at the margin.
3
If a variable is 100 and then decreases to 60, then using the initial value approach its percentage decline is:
A) 160 percent.
B) - 40 percent.
C) 40 percent.
D) 50 percent.
A) 160 percent.
B) - 40 percent.
C) 40 percent.
D) 50 percent.
40 percent.
4
Deciding how products of a society are distributed among the citizens in an economy answers the economic question of:
A) Who consumes the products produced?
B) Where will the products produced be consumed?
C) What will be produced?
D) How will we produce it?
A) Who consumes the products produced?
B) Where will the products produced be consumed?
C) What will be produced?
D) How will we produce it?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Normative economic analysis:
A) answers the question "What ought to be?"
B) is the focus of most modern economic reasoning.
C) predicts the consequences of alternative actions.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) answers the question "What ought to be?"
B) is the focus of most modern economic reasoning.
C) predicts the consequences of alternative actions.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In a modern market economy, most of the answers to the questions of what to produce, how to produce it, and who should get the production are made by:
A) governments.
B) individuals.
C) firms.
D) both B and C
A) governments.
B) individuals.
C) firms.
D) both B and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
There is a negative relationship between two variables if the two variables :
A) are negative.
B) are positive.
C) move in the same direction.
D) move in opposite directions.
A) are negative.
B) are positive.
C) move in the same direction.
D) move in opposite directions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Economists use assumptions to:
A) focus on what really matters.
B) simplify decision- making.
C) make things simpler.
D) all of the above
A) focus on what really matters.
B) simplify decision- making.
C) make things simpler.
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If each extra driver on the road makes every other drivers commute last one minute longer and there are 600 drivers on the road, then one extra driver costs society
A) 10 hours extra in commuting time.
B) 10 extra minutes in commuting time.
C) 100 hours extra in commuting time.
D) 1 hour extra in commuting time.
A) 10 hours extra in commuting time.
B) 10 extra minutes in commuting time.
C) 100 hours extra in commuting time.
D) 1 hour extra in commuting time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is a microeconomic question?
A) Should the government prevent the merger of two large firms?
B) Why do some countries grow faster than others?
C) Should we have a constitutional amendment to balance the federal budget?
D) All of the above are microeconomic questions.
A) Should the government prevent the merger of two large firms?
B) Why do some countries grow faster than others?
C) Should we have a constitutional amendment to balance the federal budget?
D) All of the above are microeconomic questions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is an example of a marginal question?
A) What is the average cost of a college education?
B) What is the average income of a college graduate?
C) How much will my chances of a job improve if I raise my GPA from a C to a C+ grade average?
D) How many students borrow money in order to attend college?
A) What is the average cost of a college education?
B) What is the average income of a college graduate?
C) How much will my chances of a job improve if I raise my GPA from a C to a C+ grade average?
D) How many students borrow money in order to attend college?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Who is associated with the following summary of the economic way of thinking: "The theory of economics does not furnish a body of settled conclusions immediately acceptable to policy. It is a method rather than a doctrine, an apparatus of the mind, a technique of thinking which helps its processor draw correct conclusions."
A) President Harry Truman
B) Alfred Marshall
C) Adam Smith
D) John Maynard Keynes
A) President Harry Truman
B) Alfred Marshall
C) Adam Smith
D) John Maynard Keynes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Economists employ economic models:
A) to make reality more complex.
B) because economic theory is too easy without them.
C) because reality is complex.
D) to make the field more scientific.
A) to make reality more complex.
B) because economic theory is too easy without them.
C) because reality is complex.
D) to make the field more scientific.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The reason why spammers find it profitable to spam is because:
A) it does not cost nor benefit the spammer anything to send a million emails.
B) it does not benefit the spammer anything to send a million emails.
C) it does not cost the spammer anything to send a million emails.
D) it does not cost the spammer anything to receive a million emails.
A) it does not cost nor benefit the spammer anything to send a million emails.
B) it does not benefit the spammer anything to send a million emails.
C) it does not cost the spammer anything to send a million emails.
D) it does not cost the spammer anything to receive a million emails.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
_______ is a situation in which resources are limited in quantity and can be used in different ways.
A) Scarcity
B) Choice
C) Economics
D) Supply and demand
A) Scarcity
B) Choice
C) Economics
D) Supply and demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Imagine that an upward sloping line is depicted in a graph with income per week on the y- axis and hours worked per week on the x- axis. The slope of the line in the graph depicts the:
A) the total monthly income of the worker.
B) hourly wage of the worker.
C) minimum wage of the worker.
D) increase in income earned by the worker per every year of service.
A) the total monthly income of the worker.
B) hourly wage of the worker.
C) minimum wage of the worker.
D) increase in income earned by the worker per every year of service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
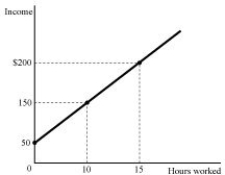 Figure 1.1
Figure 1.1Refer to Figure 1.1. The relationship between hours worked and income, as shown by the graph in Figure 1.1 is:
A) exponential.
B) nonlinear.
C) negative.
D) positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Because resources are limited:
A) people must make choices.
B) only the very wealthy can get everything they want.
C) firms will be forced out of business.
D) the availability of goods will be limited but the availability of services will not.
A) people must make choices.
B) only the very wealthy can get everything they want.
C) firms will be forced out of business.
D) the availability of goods will be limited but the availability of services will not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is not a factor of production?
A) money
B) labor
C) human capital
D) physical capital
A) money
B) labor
C) human capital
D) physical capital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The four elements of the economic way of thinking includes all of the following except:
A) economic analysis uses the key assumption that people act irrationally and that they are not motivated by self- interest.
B) economists use assumptions to make things simpler and focus attention on what really matters.
C) economic analysis often involves variables and how they affect one another.
D) economists often consider how a small change in one variable affects another variable.
A) economic analysis uses the key assumption that people act irrationally and that they are not motivated by self- interest.
B) economists use assumptions to make things simpler and focus attention on what really matters.
C) economic analysis often involves variables and how they affect one another.
D) economists often consider how a small change in one variable affects another variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Microeconomic analysis can be used to:
A) make personal or managerial decisions.
B) evaluate the merits of public policies.
C) better understand how markets work.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) make personal or managerial decisions.
B) evaluate the merits of public policies.
C) better understand how markets work.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A variable is:
A) something that cannot be measured.
B) something that always has the same value.
C) something that varies over time.
D) something that can take on different values.
A) something that cannot be measured.
B) something that always has the same value.
C) something that varies over time.
D) something that can take on different values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
London reduced its road congestion by
A) imposing a daytime driving tax.
B) making city buses free.
C) raising the fare for the London subway system, the Underground.
D) banning cars in the inner city during the daytime.
A) imposing a daytime driving tax.
B) making city buses free.
C) raising the fare for the London subway system, the Underground.
D) banning cars in the inner city during the daytime.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The study of the choices made by individual households, firms, and government is called:
A) microeconomics.
B) macroeconomics.
C) market economics.
D) managerial economics.
A) microeconomics.
B) macroeconomics.
C) market economics.
D) managerial economics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The effort used to coordinate the factors of production and produce goods and services is called:
A) capital accumulation.
B) land.
C) entrepreneurship.
D) land ownership.
A) capital accumulation.
B) land.
C) entrepreneurship.
D) land ownership.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A small change in a relevant variable is:
A) an average change.
B) an efficient change.
C) a marginal change.
D) a ceteris paribus change.
A) an average change.
B) an efficient change.
C) a marginal change.
D) a ceteris paribus change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is a question answered with positive economic analysis?
A) If we had more money, should the college offer free parking for students?
B) If the college increased tuition, by how much will class sizes decline?
C) As a result of the recession, should the college cut tuition to stimulate enrollments?
D) If we can afford it, should the college provide more financial aid assistance?
A) If we had more money, should the college offer free parking for students?
B) If the college increased tuition, by how much will class sizes decline?
C) As a result of the recession, should the college cut tuition to stimulate enrollments?
D) If we can afford it, should the college provide more financial aid assistance?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Ceteris paribus is the Latin expression meaning:
A) let buyer beware.
B) for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
C) think at the margin.
D) other variables are held fixed.
A) let buyer beware.
B) for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
C) think at the margin.
D) other variables are held fixed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The example about London's congestion problem illustrates which of the following economic ways of thinking?
A) Thinking at the Margin
B) Use of Assumptions to Simplify
C) Isolate Variables-Ceteris Paribus
D) all of the above
A) Thinking at the Margin
B) Use of Assumptions to Simplify
C) Isolate Variables-Ceteris Paribus
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Economists have found that as a nation's economy grows
A) the poorest families are left behind.
B) the poorest families share in the prosperity.
C) the poorest families have a decline in income.
D) the poorest families are unaffected.
A) the poorest families are left behind.
B) the poorest families share in the prosperity.
C) the poorest families have a decline in income.
D) the poorest families are unaffected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
An economic model is
A) a small but completely working economy.
B) any graph.
C) a simplified representation of an economic environment.
D) all of the above.
A) a small but completely working economy.
B) any graph.
C) a simplified representation of an economic environment.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is an example of how a business owner uses macroeconomics to make informed business decisions?
A) A business owner can use macroeconomics to predict whether the Fed will increase or decrease the interest rates in the future in order to determine whether to borrow money now or later.
B) A business owner can use macroeconomics to predict it should sell more red t- shirts as opposed to white t- shirts.
C) A business owner can use macroeconomics to determine whether college graduates are better employees than non- college graduates.
D) A business owner can use macroeconomics to predict whether television prices will be higher today or in the future.
A) A business owner can use macroeconomics to predict whether the Fed will increase or decrease the interest rates in the future in order to determine whether to borrow money now or later.
B) A business owner can use macroeconomics to predict it should sell more red t- shirts as opposed to white t- shirts.
C) A business owner can use macroeconomics to determine whether college graduates are better employees than non- college graduates.
D) A business owner can use macroeconomics to predict whether television prices will be higher today or in the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
One efficient solution to congestion is to:
A) give subsidies to drivers who use the road during the rush hour.
B) lower gasoline taxes.
C) prevent cars from using the roads during the rush hour.
D) impose a congestion tax on drivers who use the road during the rush hour.
A) give subsidies to drivers who use the road during the rush hour.
B) lower gasoline taxes.
C) prevent cars from using the roads during the rush hour.
D) impose a congestion tax on drivers who use the road during the rush hour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Adam Smith is:
A) responsible for a branch of economics bearing his name.
B) the author of this text.
C) responsible for refining the model of supply and demand.
D) considered the founder of economics.
A) responsible for a branch of economics bearing his name.
B) the author of this text.
C) responsible for refining the model of supply and demand.
D) considered the founder of economics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A straight line graph shows
A) the relationships among any number of variables.
B) the constant relationship between two variable.
C) one variable.
D) none of the above.
A) the relationships among any number of variables.
B) the constant relationship between two variable.
C) one variable.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In which of the following markets is a person's time and effort exchanged for money?
A) labor market
B) consumer market
C) capital market
D) goods market
A) labor market
B) consumer market
C) capital market
D) goods market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
An arrangement that allows buyers and sellers to exchange things is called:
A) a contract.
B) a market.
C) efficient.
D) money.
A) a contract.
B) a market.
C) efficient.
D) money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Studies that look into the effects of state education spending cuts on the poverty rates of minorities use:
A) microeconomics to make managerial and personal decisions.
B) microeconomics to evaluate the merits of public policies.
C) microeconomics to understand marginal changes in the macroeconomy.
D) microeconomics to understand markets and predict changes.
A) microeconomics to make managerial and personal decisions.
B) microeconomics to evaluate the merits of public policies.
C) microeconomics to understand marginal changes in the macroeconomy.
D) microeconomics to understand markets and predict changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Economics is the study of:
A) the role of money in markets.
B) how government officials decide which goods and services are produced.
C) how to invest in the stock market.
D) how society uses limited resources.
A) the role of money in markets.
B) how government officials decide which goods and services are produced.
C) how to invest in the stock market.
D) how society uses limited resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
There is a positive relationship between two variables if the two variables:
A) have positive values.
B) have negative values.
C) move in the same direction.
D) move in opposite directions.
A) have positive values.
B) have negative values.
C) move in the same direction.
D) move in opposite directions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When Bob, a recent college grad, took an internship at an accounting firm, he is accumulating which factor of production?
A) natural resources
B) human capital
C) physical capital
D) entrepreneurship
A) natural resources
B) human capital
C) physical capital
D) entrepreneurship

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Deciding if a college uses more PhDs to teach introductory classes answers the economic question of:
A) What will be produced?
B) Who consumes the products produced?
C) Where will the products produced be consumed?
D) How will we produce it?
A) What will be produced?
B) Who consumes the products produced?
C) Where will the products produced be consumed?
D) How will we produce it?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Printing presses, forklifts and assembly plants are examples of which factor of production?
A) human capital
B) labor
C) entrepreneurship
D) physical capital
A) human capital
B) labor
C) entrepreneurship
D) physical capital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An example of people acting in their own self- interest would include:
A) a teenager earns an A grade average in school in order to use his or her parent's car.
B) individuals joining a car pool to work when tolls are imposed on congested highways.
C) an adult, returning to college to pursue a degree to qualify for a promotion at work.
D) All of the above are examples of people acting in their own self- interest.
A) a teenager earns an A grade average in school in order to use his or her parent's car.
B) individuals joining a car pool to work when tolls are imposed on congested highways.
C) an adult, returning to college to pursue a degree to qualify for a promotion at work.
D) All of the above are examples of people acting in their own self- interest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
_______ is a simplified representation of an economic environment.
A) Scarcity
B) Normative Analysis.
C) An economic model
D) Microeconomics
A) Scarcity
B) Normative Analysis.
C) An economic model
D) Microeconomics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
When after seeing the current mortgage interest rates and immediately deciding to start the search for a new house, you are using:
A) microeconomics to understand marginal changes in the macroeconomy.
B) microeconomics to understand markets and predict changes.
C) microeconomics to make managerial and personal decisions.
D) microeconomics to evaluate the merits of public policies.
A) microeconomics to understand marginal changes in the macroeconomy.
B) microeconomics to understand markets and predict changes.
C) microeconomics to make managerial and personal decisions.
D) microeconomics to evaluate the merits of public policies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Macroeconomics is best described as the study of:
A) the relationship between inflation and wage inequality.
B) the nation's economy as a whole.
C) the choices made by individual households, firms, and governments.
D) very large issues.
A) the relationship between inflation and wage inequality.
B) the nation's economy as a whole.
C) the choices made by individual households, firms, and governments.
D) very large issues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following is a macroeconomic question?
A) Should the government prevent the merger of two large firms?
B) Will a constitutional amendment to balance the federal budget lead to good economic policy?
C) Should a firm decide to enter a particular market?
D) All of the above are macroeconomic questions.
A) Should the government prevent the merger of two large firms?
B) Will a constitutional amendment to balance the federal budget lead to good economic policy?
C) Should a firm decide to enter a particular market?
D) All of the above are macroeconomic questions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following is a country whose economy shrank between the 1960s and 2001?
A) Canada
B) Sierra Leone
C) Mexico
D) the United States
A) Canada
B) Sierra Leone
C) Mexico
D) the United States

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
When economists construct economic models,:
A) every detail found in reality must be included.
B) only mathematical equations are used.
C) all the essential features of the environment are eliminated.
D) all but the essential features of the environment are eliminated.
A) every detail found in reality must be included.
B) only mathematical equations are used.
C) all the essential features of the environment are eliminated.
D) all but the essential features of the environment are eliminated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is not an example of a marginal question?
A) How many more dollars will I earn in my lifetime if I get my Master's degree?
B) How many more points will I expect to have if I study an hour longer?
C) How many more years of education must I take if I want to get a Ph.D. in economics?
D) How many students borrow money in order to attend college?
A) How many more dollars will I earn in my lifetime if I get my Master's degree?
B) How many more points will I expect to have if I study an hour longer?
C) How many more years of education must I take if I want to get a Ph.D. in economics?
D) How many students borrow money in order to attend college?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is not an example of a question answered by positive analysis?
A) Should the government increase the minimum wage?
B) What fraction of an income- tax cut will be spent on consumer goods?
C) How will an increase in interest rates affect investment in factories?
D) How will an increase in the price of gasoline affect taxi drivers?
A) Should the government increase the minimum wage?
B) What fraction of an income- tax cut will be spent on consumer goods?
C) How will an increase in interest rates affect investment in factories?
D) How will an increase in the price of gasoline affect taxi drivers?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Recall Application 2,"Economic Solution to Spam," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, one economic solution to spam is to:
A) outlaw the use of the internet.
B) charge a $0.01 electronic stamp for each commercial email message.
C) require internet service providers to sue spammers.
D) subsidize spammers.
According to the application, one economic solution to spam is to:
A) outlaw the use of the internet.
B) charge a $0.01 electronic stamp for each commercial email message.
C) require internet service providers to sue spammers.
D) subsidize spammers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The slope of a straight line is:
A) constant.
B) increasing if the line is upward sloping.
C) increasing if the line is downward sloping.
D) increasing.
A) constant.
B) increasing if the line is upward sloping.
C) increasing if the line is downward sloping.
D) increasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Recall Application 1, "Responding to Production Rewards," to answer the following questions:
Based on the application, do incentives increase the average worker productivity?
A) Yes, but the increase in productivity was observed only in the "reward" group.
B) Yes, but the increase in productivity was observed only in the "punishment" group.
C) No. The control group produced 7% more than either "treatment" group.
D) Yes, workers in the treatment groups (those with bonuses or punishment stated in their contracts) produced 7% more than the control group.
Based on the application, do incentives increase the average worker productivity?
A) Yes, but the increase in productivity was observed only in the "reward" group.
B) Yes, but the increase in productivity was observed only in the "punishment" group.
C) No. The control group produced 7% more than either "treatment" group.
D) Yes, workers in the treatment groups (those with bonuses or punishment stated in their contracts) produced 7% more than the control group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following is a microeconomic question?
A) Should Congress and the president take action to reduce the unemployment rate?
B) Is it sensible for the government to subsidize college education?
C) Why do some countries grow faster than others?
D) All of the above are microeconomic questions.
A) Should Congress and the president take action to reduce the unemployment rate?
B) Is it sensible for the government to subsidize college education?
C) Why do some countries grow faster than others?
D) All of the above are microeconomic questions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following did not directly cause the worldwide recession in 2007- 2008?
A) the decision by the government to bailout banks in 2008
B) easy access to credit in the U.S.
C) booming housing prices that ultimately dropped
D) a large number of home purchasers who were unable to afford the homes
A) the decision by the government to bailout banks in 2008
B) easy access to credit in the U.S.
C) booming housing prices that ultimately dropped
D) a large number of home purchasers who were unable to afford the homes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following is a question that needs to be answered with normative economic reasoning?
A) Should the college reduce tuition to stimulate enrollment?
B) If the college increases tuition, would class size decline?
C) If the college offers free parking for students, will more students drive to campus?
D) If the college provided more financial aid assistance, would more students benefit?
A) Should the college reduce tuition to stimulate enrollment?
B) If the college increases tuition, would class size decline?
C) If the college offers free parking for students, will more students drive to campus?
D) If the college provided more financial aid assistance, would more students benefit?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following is not a macroeconomic question?
A) Do employers discriminate against women by paying them lower wages?
B) How does a political candidate's economic reform package affect the inflation rate?
C) Should we have a constitutional amendment to balance the federal budget?
D) All of the above are macroeconomic questions.
A) Do employers discriminate against women by paying them lower wages?
B) How does a political candidate's economic reform package affect the inflation rate?
C) Should we have a constitutional amendment to balance the federal budget?
D) All of the above are macroeconomic questions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In making stock buy or sell recommendations, most stock analysts use microeconomics:
A) to understand markets and predict changes.
B) to evaluate the merits of public policies.
C) to make managerial and personal decisions.
D) to understand marginal changes in the macroeconomy.
A) to understand markets and predict changes.
B) to evaluate the merits of public policies.
C) to make managerial and personal decisions.
D) to understand marginal changes in the macroeconomy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The Latin phrase ceteris paribus means that when a relationship between two variables is being studied:
A) all other variables are held fixed.
B) both are treated as unpredictable.
C) we recognize that some factors are unknown.
D) neither of those two variables is allowed to change.
A) all other variables are held fixed.
B) both are treated as unpredictable.
C) we recognize that some factors are unknown.
D) neither of those two variables is allowed to change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following is not a microeconomic question?
A) What would happen to gasoline consumption if the gasoline tax were increased?
B) How does a particular health care reform program affect physicians' incomes?
C) How should Judy decide how many hours to study for her economics exam?
D) All of the above are microeconomic questions.
A) What would happen to gasoline consumption if the gasoline tax were increased?
B) How does a particular health care reform program affect physicians' incomes?
C) How should Judy decide how many hours to study for her economics exam?
D) All of the above are microeconomic questions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Imagine that an upward sloping line is depicted in a graph with income per week on the y- axis and hours worked per week on the x- axis. From the graph, we can conclude that:
A) hours worked are not related.
B) income and hours worked are negatively related.
C) income and hours worked per week are positively related.
D) income and hours worked are equal.
A) hours worked are not related.
B) income and hours worked are negatively related.
C) income and hours worked per week are positively related.
D) income and hours worked are equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What assumption was used by the authors of the book when analyzing the traffic congestion problem in London?
A) They assumed that traffic congestion is the same during daytime and during nighttime.
B) They assumed that every car has the same effect on the travel time of other cars.
C) They assumed that all cars are of the same make and model.
D) They assumed that travel via public transportation is less costly that travel by car.
A) They assumed that traffic congestion is the same during daytime and during nighttime.
B) They assumed that every car has the same effect on the travel time of other cars.
C) They assumed that all cars are of the same make and model.
D) They assumed that travel via public transportation is less costly that travel by car.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Microeconomics is best described as the study of:
A) inflation, unemployment, gross national product, and the nation's economy as a whole.
B) how markets interact in the aggregate economy.
C) the choices made by individual households, firms, and governments.
D) marginal changes in the economy.
A) inflation, unemployment, gross national product, and the nation's economy as a whole.
B) how markets interact in the aggregate economy.
C) the choices made by individual households, firms, and governments.
D) marginal changes in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following is not a question answered with normative economic reasoning?
A) If we had more money, should the college offer free parking for students?
B) Given the additional funding that we received, should the college cut tuition to stimulate enrollments?
C) If the college increased tuition, what is the estimated decline in enrollments?
D) As a result of the recent recession, should the college offer more financial aid assistance?
A) If we had more money, should the college offer free parking for students?
B) Given the additional funding that we received, should the college cut tuition to stimulate enrollments?
C) If the college increased tuition, what is the estimated decline in enrollments?
D) As a result of the recent recession, should the college offer more financial aid assistance?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If a variable is 100 and then increases to 150, then using the initial value approach its percentage growth is:
A) 50 percent.
B) 15 percent.
C) - 50 percent.
D) 40 percent.
A) 50 percent.
B) 15 percent.
C) - 50 percent.
D) 40 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following is an example of scarcity?
A) If I decide to buy a new car I may not have enough money to go away on vacation this year.
B) If a city uses an acre of land to build a park there will be less land for houses.
C) If you choose to play video games you will not have as much time for exercise.
D) All of the above are examples of scarcity.
A) If I decide to buy a new car I may not have enough money to go away on vacation this year.
B) If a city uses an acre of land to build a park there will be less land for houses.
C) If you choose to play video games you will not have as much time for exercise.
D) All of the above are examples of scarcity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
We can use microeconomic analysis to:
A) evaluate the merits of public policies.
B) understand marginal changes in the macroeconomy.
C) learn how to balance a checkbook.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) evaluate the merits of public policies.
B) understand marginal changes in the macroeconomy.
C) learn how to balance a checkbook.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Economics is best defined as the study of:
A) how consumers make purchasing decisions.
B) choices made by people faced with scarcity.
C) inflation, unemployment, and economic growth.
D) financial decision- making.
A) how consumers make purchasing decisions.
B) choices made by people faced with scarcity.
C) inflation, unemployment, and economic growth.
D) financial decision- making.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following is not an economic decision in a modern economy?
A) Where will the products produced be consumed?
B) How will we produce it?
C) Who consumes the products produced?
D) What will be produced?
A) Where will the products produced be consumed?
B) How will we produce it?
C) Who consumes the products produced?
D) What will be produced?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The economic view of traffic congestion considers
A) that most drivers are not good defensive drivers.
B) that driving is a right.
C) that drivers ignore the costs they impose on other drivers by slowing other drivers' commute time.
D) that the amount of driving should be reduced.
A) that most drivers are not good defensive drivers.
B) that driving is a right.
C) that drivers ignore the costs they impose on other drivers by slowing other drivers' commute time.
D) that the amount of driving should be reduced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
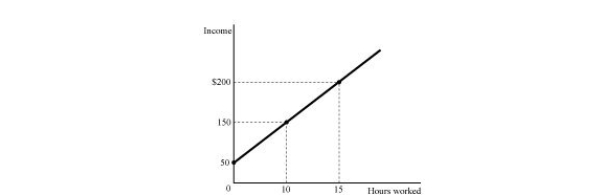 Figure 1.1
Figure 1.1Refer to Figure 1.1. Slope of the relationship or the wage rate shown in Figure 1.1 is
A) $15 per hour.
B) $10 per hour.
C) $13.33 per hour.
D) $5.15 per hour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following is not a market?
A) a cattle auction
B) a group of children trading Pokemon cards
C) your college bookstore
D) All of the above are markets.
A) a cattle auction
B) a group of children trading Pokemon cards
C) your college bookstore
D) All of the above are markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Scarcity can best be defined as a situation in which:
A) there are not enough goods to satisfy all of the buyers demands.
B) there is more than enough money to satisfy consumers wants.
C) there are no buyers willing to purchase what sellers have produced.
D) resources are limited in quantity and can be used in different ways.
A) there are not enough goods to satisfy all of the buyers demands.
B) there is more than enough money to satisfy consumers wants.
C) there are no buyers willing to purchase what sellers have produced.
D) resources are limited in quantity and can be used in different ways.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The factors of production include
A) labor.
B) entrepreneurship.
C) natural resources.
D) all of the above.
A) labor.
B) entrepreneurship.
C) natural resources.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
When we study the effect of how a beer tax may decrease the number of highway deaths, we use microeconomics to:
A) better understand how markets work.
B) make personal or managerial decisions.
C) evaluate the merits of public officials.
D) A and C are correct.
A) better understand how markets work.
B) make personal or managerial decisions.
C) evaluate the merits of public officials.
D) A and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Positive economics:
A) predicts the consequences of alternative actions.
B) concerns the forces that affect economic activity.
C) is the focus of most modern economic reasoning.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) predicts the consequences of alternative actions.
B) concerns the forces that affect economic activity.
C) is the focus of most modern economic reasoning.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A single variable can be illustrated as
A) a bar graph.
B) a time- series graph.
C) a pie chart.
D) all of the above.
A) a bar graph.
B) a time- series graph.
C) a pie chart.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
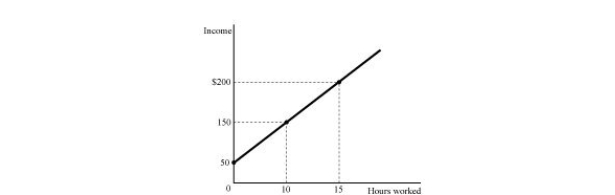 Figure 1.1
Figure 1.1Refer to Figure 1.1. If hours worked are zero in Figure 1.1, then income is
A) $100.
B) zero.
C) $200.
D) $50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 144 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



