Deck 9: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/189
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
1
A decrease in personal income taxes will lead to:
A) no change in aggregate demand.
B) a decrease in aggregate supply.
C) an increase in aggregate demand.
D) a decrease in aggregate demand.
A) no change in aggregate demand.
B) a decrease in aggregate supply.
C) an increase in aggregate demand.
D) a decrease in aggregate demand.
an increase in aggregate demand.
2
The "short run" in macroeconomics is a period in which prices
A) reflect the equilibrium price.
B) do not change or change very little.
C) change by a lot.
D) are determined by changes in the supply.
A) reflect the equilibrium price.
B) do not change or change very little.
C) change by a lot.
D) are determined by changes in the supply.
do not change or change very little.
3
A decrease in government purchases shifts the _______ curve to the _______.
A) aggregate demand; right
B) aggregate supply; left
C) aggregate supply; right
D) aggregate demand; left
A) aggregate demand; right
B) aggregate supply; left
C) aggregate supply; right
D) aggregate demand; left
aggregate demand; left
4
When output falls below full employment output, we expect that the:
A) wages and prices decrease as the short run aggregate supply curve shifts upward over time.
B) wages and prices decrease as short run aggregate supply curve shifts downward over time.
C) wages and prices increase as the long run aggregate supply curve shifts upward over time.
D) wages and prices decrease as the long run aggregate supply curve shifts downward over time.
A) wages and prices decrease as the short run aggregate supply curve shifts upward over time.
B) wages and prices decrease as short run aggregate supply curve shifts downward over time.
C) wages and prices increase as the long run aggregate supply curve shifts upward over time.
D) wages and prices decrease as the long run aggregate supply curve shifts downward over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A leftward shift in the aggregate demand curve cannot be caused by:
A) an increase in taxes.
B) a decrease in the money supply.
C) a decrease in government spending.
D) a decrease in imports.
A) an increase in taxes.
B) a decrease in the money supply.
C) a decrease in government spending.
D) a decrease in imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Following Keynes' work in explaining the Great Depression, economists started to make a distinction between
A) nominal and real GDP.
B) recessions and booms.
C) positive and normative economics.
D) GDP in the short run and in the long run.
A) nominal and real GDP.
B) recessions and booms.
C) positive and normative economics.
D) GDP in the short run and in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Rank these three goods in the order of least sticky to most sticky: fresh fish, used cars, steel rods.
A) fresh fish, used cars, steel rods
B) steel rods, cars, fresh fish
C) steel rods, fresh fish, used cars
D) used cars, fresh fish, steel rods
A) fresh fish, used cars, steel rods
B) steel rods, cars, fresh fish
C) steel rods, fresh fish, used cars
D) used cars, fresh fish, steel rods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The economy moves from a short- run equilibrium to the long- run equilibrium through:
A) improvements in technology.
B) demand shocks.
C) adjustments in wages and prices.
D) supply shocks.
A) improvements in technology.
B) demand shocks.
C) adjustments in wages and prices.
D) supply shocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In the short run, the formal or informal contracts between firms mean that changes in demand will be reflected primarily in changes in _______ .
A) future equilibrium price.
B) prices.
C) output.
D) future price.
A) future equilibrium price.
B) prices.
C) output.
D) future price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
As the marginal propensity to consume decreases, the value of the multiplier
A) stays the same.
B) can increase or decrease.
C) increases.
D) decreases.
A) stays the same.
B) can increase or decrease.
C) increases.
D) decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Suppose an automobile maker producing a certain kind of car suddenly experiences an increase in the demand for the car. In the short run,
A) the demand for steel goes down and the price of steel goes down.
B) the demand for steel goes down but the price of steel stays the same.
C) the demand for steel goes up and the price of steel goes up very quickly.
D) the demand for steel goes up but the steel prices remain the same.
A) the demand for steel goes down and the price of steel goes down.
B) the demand for steel goes down but the price of steel stays the same.
C) the demand for steel goes up and the price of steel goes up very quickly.
D) the demand for steel goes up but the steel prices remain the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Suppose there are three economies with 3 different consumption functions: Country A: C = 100 + 0.8Y Country B: C = 200 + 0.75 Y
Country C: C = 75 + 0.9Y
In which of these countries is autonomous consumption the largest?
A) Country C
B) Country B
C) Country A
D) All countries have the same autonomous consumption levels.
Country C: C = 75 + 0.9Y
In which of these countries is autonomous consumption the largest?
A) Country C
B) Country B
C) Country A
D) All countries have the same autonomous consumption levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Suppose there are three economies with 3 different consumption functions: Country A: C = 100 + 0.8Y Country B: C = 200 + 0.75 Y
Country C: C = 75 + 0.9Y
In which of these countries is the marginal propensity to consume the largest?
A) Country B
B) Country C
C) Country A
D) All countries have the same marginal propensity to consume.
Country C: C = 75 + 0.9Y
In which of these countries is the marginal propensity to consume the largest?
A) Country B
B) Country C
C) Country A
D) All countries have the same marginal propensity to consume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Recall Application 2, "Two Approaches to Determining the Causes of Recessions," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, a recession caused by a decrease in aggregate supply occurred in:
A) 1981
B) 1929
C) 1979
D) All of the above were caused by a decrease in aggregate supply.
According to the application, a recession caused by a decrease in aggregate supply occurred in:
A) 1981
B) 1929
C) 1979
D) All of the above were caused by a decrease in aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
An increase in the price level results in a decline in aggregate demand because people's "net worth" decreases and will spend less. This effect is called the:
A) interest rate effect.
B) income effect.
C) wealth effect.
D) trade effect.
A) interest rate effect.
B) income effect.
C) wealth effect.
D) trade effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If the marginal propensity to consume is 0.5, a decrease in consumption by $100 will shift the aggregate demand curve horizontally to the left by
A) $400.
B) $100.5.
C) $200.
D) $100.
A) $400.
B) $100.5.
C) $200.
D) $100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Recall Application 1, "Measuring Price Stickiness in Consumer Markets," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, Bils and Klenow found that between 1995- 1997, prices in more than half of the 350 goods that they were studying showed frequent price changes. This finding was contrary to Kashyap's finding because:
A) custom auction prices.
B) the economy during that time was in a recession.
C) unemployment rates during that time were rising.
D) the inflation during that period was low.
According to the application, Bils and Klenow found that between 1995- 1997, prices in more than half of the 350 goods that they were studying showed frequent price changes. This finding was contrary to Kashyap's finding because:
A) custom auction prices.
B) the economy during that time was in a recession.
C) unemployment rates during that time were rising.
D) the inflation during that period was low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
According to the international effect explanation of the downward slope of the AD curve, a higher price level in the U.S. economy causes:
A) U.S. imports and U.S. exports to increase.
B) U.S. imports to decrease and U.S. exports to increase.
C) U.S. imports and U.S. exports to decrease.
D) US imports to increase and U.S. exports to decrease.
A) U.S. imports and U.S. exports to increase.
B) U.S. imports to decrease and U.S. exports to increase.
C) U.S. imports and U.S. exports to decrease.
D) US imports to increase and U.S. exports to decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Recall Application 3, "How the U.S. Economy has Coped with Oil Price Fluctuations," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, surge in the price of oil was caused by the increase in the demand for oil by fast growing countries such as:
A) Mexico and Iceland.
B) the U.S. and Japan.
C) Japan and China.
D) India and China.
According to the application, surge in the price of oil was caused by the increase in the demand for oil by fast growing countries such as:
A) Mexico and Iceland.
B) the U.S. and Japan.
C) Japan and China.
D) India and China.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Suppose there are three economies with 3 different consumption functions: Country A: C = 100 + 0.8Y Country B: C = 200 + 0.75 Y
Country C: C = 75 + 0.9Y
If the government spending increases by 10, in which of these countries would the shift of the AD curve be the largest?
A) Country B
B) Country C
C) Country A
D) All countries have the same shifts in the aggregate demand.
Country C: C = 75 + 0.9Y
If the government spending increases by 10, in which of these countries would the shift of the AD curve be the largest?
A) Country B
B) Country C
C) Country A
D) All countries have the same shifts in the aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In the long- run, the amount of output that the economy can produce will depend on:
A) the price level.
B) the supply of labor and capital.
C) the money supply.
D) the nominal interest rate.
A) the price level.
B) the supply of labor and capital.
C) the money supply.
D) the nominal interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
_______ is a curve that shows the relationship between the price level and the quantity of real GDP demanded.
A) The aggregate supply curve
B) The market demand curve
C) The product demand curve
D) The aggregate demand curve
A) The aggregate supply curve
B) The market demand curve
C) The product demand curve
D) The aggregate demand curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The relationship between the level of prices and the total quantity of goods and services that firms supply in the short- run is:
A) positive.
B) negative.
C) marginally decreasing.
D) similar in the long run and in the short run due to the existence of sticky prices.
A) positive.
B) negative.
C) marginally decreasing.
D) similar in the long run and in the short run due to the existence of sticky prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If the marginal propensity to consume is 0.8, the value of the marginal propensity to save is:
A) 5.
B) 0.8.
C) 1.25.
D) 0.2.
A) 5.
B) 0.8.
C) 1.25.
D) 0.2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following will not cause the price level to increase in the long- run?
A) a decrease in income taxes
B) an increase in government spending
C) a decrease in the money supply
D) a decrease in the interest rates
A) a decrease in income taxes
B) an increase in government spending
C) a decrease in the money supply
D) a decrease in the interest rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Recall Application 1, "Measuring Price Stickiness in Consumer Markets," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, during periods of high inflation, catalog prices tend to show
A) more stickiness.
B) no change in stickiness.
C) stickiness equal to the level of inflation.
D) less stickiness.
According to the application, during periods of high inflation, catalog prices tend to show
A) more stickiness.
B) no change in stickiness.
C) stickiness equal to the level of inflation.
D) less stickiness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If the economy is in equilibrium at full employment, a decrease in aggregate demand will:
A) increase both the price level and the level of output in the long run.
B) decrease both the price level and the level of output in the long run.
C) decrease the price level and leave the level of output unchanged in the long run.
D) increase the price level and leave the level of output unchanged in the long run.
A) increase both the price level and the level of output in the long run.
B) decrease both the price level and the level of output in the long run.
C) decrease the price level and leave the level of output unchanged in the long run.
D) increase the price level and leave the level of output unchanged in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The international effect explanation of the downward slope of the AD operates through which component of aggregate demand?
A) consumption
B) net exports
C) investment
D) government purchases.
A) consumption
B) net exports
C) investment
D) government purchases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When the economy is in a boom, the intersection between the:
A) short run AS and the AD occurs at an output level lower than potential output.
B) long run AS and the AD occurs at an output level higher than potential output.
C) short run AS and the AD occurs at an output level higher than potential output.
D) long run AS and the AD occurs at an output level lower than potential output.
A) short run AS and the AD occurs at an output level lower than potential output.
B) long run AS and the AD occurs at an output level higher than potential output.
C) short run AS and the AD occurs at an output level higher than potential output.
D) long run AS and the AD occurs at an output level lower than potential output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following are the factors that affect the short- run aggregate supply curve?
A) input prices
B) taxes and subsidies
C) the state of technology
D) All of the above can affect the SRAS curve.
A) input prices
B) taxes and subsidies
C) the state of technology
D) All of the above can affect the SRAS curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Recall Application 2, "Two Approaches to Determining the Causes of Recessions," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, a recession is likely to be caused by a decrease in aggregate supply if:
A) prices change but output does not change in the long run.
B) both prices and output do not change in the long run.
C) both prices and output change in the long run.
D) prices do not change but output changes in the long run.
According to the application, a recession is likely to be caused by a decrease in aggregate supply if:
A) prices change but output does not change in the long run.
B) both prices and output do not change in the long run.
C) both prices and output change in the long run.
D) prices do not change but output changes in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Recall Application 3, "How the U.S. Economy has Coped with Oil Price Fluctuations," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, when the price of oil increases, the aggregate supply curve shifts up because:
A) oil is a by- product of the production processes in the economy.
B) oil is a complement to the production of most goods and services.
C) oil is an input to the production processes in the economy.
D) oil is a major source of export revenues in the economy.
According to the application, when the price of oil increases, the aggregate supply curve shifts up because:
A) oil is a by- product of the production processes in the economy.
B) oil is a complement to the production of most goods and services.
C) oil is an input to the production processes in the economy.
D) oil is a major source of export revenues in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When the economy is in a recession, the intersection between the:
A) long run AS and the AD occurs at an output level lower than potential output.
B) long run AS and the AD occurs at an output level higher than potential output.
C) short run AS and the AD occurs at an output level higher than potential output.
D) short run AS and the AD occurs at an output level lower than potential output.
A) long run AS and the AD occurs at an output level lower than potential output.
B) long run AS and the AD occurs at an output level higher than potential output.
C) short run AS and the AD occurs at an output level higher than potential output.
D) short run AS and the AD occurs at an output level lower than potential output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
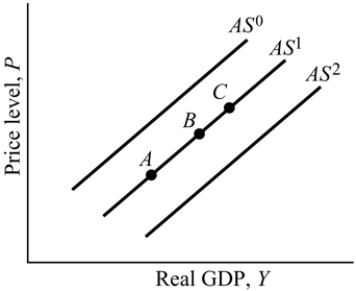
Figure 9.5
Refer to Figure 9.5. Suppose the economy is a point B. A large in the price of crude oil leads to a shift from _______ to _______.
A) increase; AS1; AS0
B) increase; AS1; AS2
C) decrease; AS2; AS1
D) increase; AS2; AS1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Can the aggregate demand curve slope upwards?
A) Yes, always.
B) No.
C) Yes, if the economy experiences inflation.
D) Yes, if the aggregate supply curve is downward sloping.
A) Yes, always.
B) No.
C) Yes, if the economy experiences inflation.
D) Yes, if the aggregate supply curve is downward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A large reduction in oil prices will cause:
A) a rightward shift in the aggregate supply curve.
B) a rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve.
C) a leftward shift in the aggregate demand curve.
D) a leftward shift in the aggregate supply curve.
A) a rightward shift in the aggregate supply curve.
B) a rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve.
C) a leftward shift in the aggregate demand curve.
D) a leftward shift in the aggregate supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
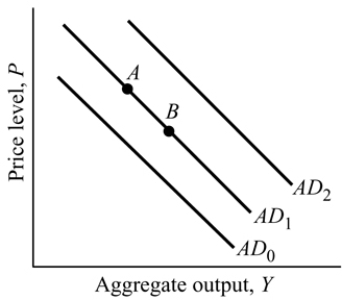
Figure 9.1
Refer to Figure 9.1. A reduction in government spending causes:
A) the aggregate demand curve to shift from AD1 to AD2.
B) the economy to move from Point A to Point B, but will not shift the aggregate demand curve.
C) the aggregate demand curve to shift from AD1 to AD0.
D) neither a shift of the aggregate demand curve nor a change in real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Custom prices are also known as:
A) flexible prices.
B) auction prices.
C) equilibrium prices.
D) sticky prices.
A) flexible prices.
B) auction prices.
C) equilibrium prices.
D) sticky prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The aggregate demand curve shows a(n) _______ relationship between the _______.
A) positive; price level and real GDP
B) positive; interest rate and investment
C) negative; level of real GDP and investment
D) negative; price level and real GDP
A) positive; price level and real GDP
B) positive; interest rate and investment
C) negative; level of real GDP and investment
D) negative; price level and real GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Recall Application 1, "Measuring Price Stickiness in Consumer Markets," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, which of the following goods showed considerable price stickiness?
A) fishing rod and fly
B) shoes
C) binoculars
D) All the goods above showed price stickiness.
According to the application, which of the following goods showed considerable price stickiness?
A) fishing rod and fly
B) shoes
C) binoculars
D) All the goods above showed price stickiness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In the long run, the aggregate supply curve is:
A) downward sloping.
B) horizontal at the full employment level of GDP.
C) upward sloping.
D) vertical at the full employment level of GDP.
A) downward sloping.
B) horizontal at the full employment level of GDP.
C) upward sloping.
D) vertical at the full employment level of GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The four components of the aggregate demand curve are:
A) consumption, inventories, government purchases and net exports.
B) consumption, inventories, government spending and exports.
C) land, labor, capital, and technology.
D) consumption, investment, government purchases and net exports.
A) consumption, inventories, government purchases and net exports.
B) consumption, inventories, government spending and exports.
C) land, labor, capital, and technology.
D) consumption, investment, government purchases and net exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In the long run, an increase in the money supply will cause prices:
A) to increase.
B) not to change.
C) to decrease.
D) to fluctuate up and then down.
A) to increase.
B) not to change.
C) to decrease.
D) to fluctuate up and then down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Because the long run aggregate supply curve is vertical at the full employment level of GDP, then this would imply that the long run aggregate supply curve:
A) decreases as the price level increases.
B) is independent of changes in the price level.
C) shifts to the right when the price level increases.
D) increases as the price level increases.
A) decreases as the price level increases.
B) is independent of changes in the price level.
C) shifts to the right when the price level increases.
D) increases as the price level increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
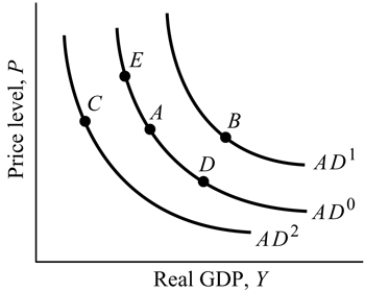 Figure 9.2
Figure 9.2Refer to Figure 9.2. Suppose the economy is at Point A, an increase in the price level causes a movement to Point:
A) E.
B) C.
C) D.
D) B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In the short run, the primary determinant of output of firms is the:
A) level of demand.
B) future price.
C) availability of inputs.
D) level of prices.
A) level of demand.
B) future price.
C) availability of inputs.
D) level of prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
When output exceeds the full employment level of output, we expect that the
A) wages and prices increase as the long- run aggregate supply curve shifts upward over time.
B) wages and prices increase as the short- run aggregate supply curve shifts upward over time.
C) wages and prices decrease as the short- run aggregate supply curve shifts downward over time.
D) wages and prices increase as the long- run aggregate supply curve shifts downward over time.
A) wages and prices increase as the long- run aggregate supply curve shifts upward over time.
B) wages and prices increase as the short- run aggregate supply curve shifts upward over time.
C) wages and prices decrease as the short- run aggregate supply curve shifts downward over time.
D) wages and prices increase as the long- run aggregate supply curve shifts downward over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Recall Application 3, "How the U.S. Economy has Coped with Oil Price Fluctuations," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, oil prices in 2008 shot up as high as per barrel.
A) $110
B) $60
C) $190
D) $145
According to the application, oil prices in 2008 shot up as high as per barrel.
A) $110
B) $60
C) $190
D) $145

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In the short run, an increase in the money supply will cause output:
A) to remain the same.
B) to decrease.
C) to become zero.
D) to increase.
A) to remain the same.
B) to decrease.
C) to become zero.
D) to increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following will cause output to increase in the long- run?
A) a decrease in the money supply
B) a decrease in government spending
C) an increase in income taxes
D) None of the above will increase output in the long run.
A) a decrease in the money supply
B) a decrease in government spending
C) an increase in income taxes
D) None of the above will increase output in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The aggregate demand curve slopes downward because at a higher price level:
A) the purchasing power of consumers' assets declines and consumption increases.
B) the purchasing power of consumers' wealth declines and consumption decreases.
C) producers can get more for what they produce, and they increase production.
D) the purchasing power of consumers' wealth increases and consumption increases.
A) the purchasing power of consumers' assets declines and consumption increases.
B) the purchasing power of consumers' wealth declines and consumption decreases.
C) producers can get more for what they produce, and they increase production.
D) the purchasing power of consumers' wealth increases and consumption increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The aggregate demand curve shifts to the left if:
A) the government decreases taxes.
B) household consumption falls.
C) the government increases spending.
D) the supply of money rises.
A) the government decreases taxes.
B) household consumption falls.
C) the government increases spending.
D) the supply of money rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Recall Application 1, "Measuring Price Stickiness in Consumer Markets," to answer the following questions:
Based on what you learned from the application, coin- operated laundry prices behave as:
A) auction prices.
B) flexible prices
C) custom prices.
D) custom auction prices.
Based on what you learned from the application, coin- operated laundry prices behave as:
A) auction prices.
B) flexible prices
C) custom prices.
D) custom auction prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Suppose there are three economies with 3 different consumption functions: Country A: C = 100 + 0.8Y Country B: C = 200 + 0.75 Y
Country C: C = 75 + 0.9Y
In which of these countries is the multiplier the largest?
A) Country A
B) Country C
C) Country B
D) All countries have the same multipliers.
Country C: C = 75 + 0.9Y
In which of these countries is the multiplier the largest?
A) Country A
B) Country C
C) Country B
D) All countries have the same multipliers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Compared to the long run aggregate supply curve, the short- run aggregate supply curve is relatively:
A) more vertical.
B) less elastic.
C) steeper.
D) flatter.
A) more vertical.
B) less elastic.
C) steeper.
D) flatter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Rank these three wage rates in the order of least sticky to most sticky: minimum wage workers, nurses, movie stars.
A) minimum wage workers, movie stars, nurses
B) movie stars, minimum wage workers, nurses
C) minimum wage workers, nurses, movie stars
D) movie stars, nurses, minimum wage workers
A) minimum wage workers, movie stars, nurses
B) movie stars, minimum wage workers, nurses
C) minimum wage workers, nurses, movie stars
D) movie stars, nurses, minimum wage workers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The curve that depicts aggregate demand slopes downward because:
A) as the overall price level (P) falls, real GDP (y) falls.
B) as the overall price level (P) rises, real GDP (y) does not change.
C) as the overall price level (P) rises, real GDP (y) rises.
D) as the overall price level (P) rises, real GDP (y) falls.
A) as the overall price level (P) falls, real GDP (y) falls.
B) as the overall price level (P) rises, real GDP (y) does not change.
C) as the overall price level (P) rises, real GDP (y) rises.
D) as the overall price level (P) rises, real GDP (y) falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
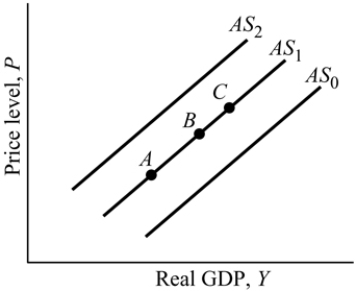 Figure 9.4
Figure 9.4Refer to Figure 9.4. An increase in aggregate supply is represented by:
A) a movement from Point C to Point A along AS1.
B) a shift from AS1 to AS2.
C) a movement from Point B to Point A along AS1.
D) a shift from AS1 to AS0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Steel rod prices are an example of:
A) custom prices.
B) regulated prices.
C) auction prices.
D) personal prices.
A) custom prices.
B) regulated prices.
C) auction prices.
D) personal prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The aggregate demand curve:
A) slopes upward.
B) slopes downward.
C) is horizontal.
D) may slope upward or downward.
A) slopes upward.
B) slopes downward.
C) is horizontal.
D) may slope upward or downward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
If the economy is in equilibrium at full employment, a decrease in aggregate demand will:
A) decrease both the price level and the level of output in the short run.
B) decrease the price level and leave the level of output unchanged in the short run.
C) increase both the price level and the level of output in the short run.
D) increase the price level and leave the level of output unchanged in the short run.
A) decrease both the price level and the level of output in the short run.
B) decrease the price level and leave the level of output unchanged in the short run.
C) increase both the price level and the level of output in the short run.
D) increase the price level and leave the level of output unchanged in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The aggregate supply curve depicts the relationship between:
A) the unemployment rate and the total quantity of goods and services that firms supply.
B) the cost of inputs and the total quantity of goods and services that firms supply.
C) the cost of labor and the total quantity of goods and services that firms supply.
D) the level of prices and the total quantity of goods and services that firms supply.
A) the unemployment rate and the total quantity of goods and services that firms supply.
B) the cost of inputs and the total quantity of goods and services that firms supply.
C) the cost of labor and the total quantity of goods and services that firms supply.
D) the level of prices and the total quantity of goods and services that firms supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
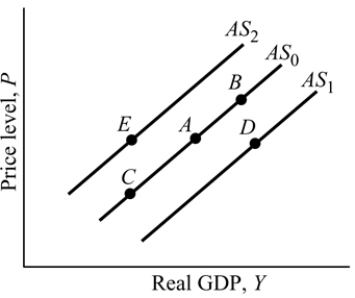 Figure 9.3
Figure 9.3Refer to Figure 9.3. Suppose the economy is at Point A, an increase in the price level moves the economy in the short run to Point:
A) B.
B) D.
C) E.
D) C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In the short run, the aggregate supply curve is relatively flat because at any point in time:
A) firms are assumed to supply all the output demanded with relatively small changes in prices.
B) the labor costs faced by firms are slower to adjust than final prices.
C) technology advances faster than production costs.
D) firms can not face increases in the output demanded without experiencing small reductions in profits.
A) firms are assumed to supply all the output demanded with relatively small changes in prices.
B) the labor costs faced by firms are slower to adjust than final prices.
C) technology advances faster than production costs.
D) firms can not face increases in the output demanded without experiencing small reductions in profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Recall Application 2, "Two Approaches to Determining the Causes of Recessions," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, a recession can be caused by:
A) a decrease in aggregate demand or an increase in aggregate supply.
B) a decrease in ether aggregate demand or aggregate supply.
C) an increase in aggregate demand or a decrease in aggregate supply.
D) an increase in either aggregate demand or aggregate supply.
According to the application, a recession can be caused by:
A) a decrease in aggregate demand or an increase in aggregate supply.
B) a decrease in ether aggregate demand or aggregate supply.
C) an increase in aggregate demand or a decrease in aggregate supply.
D) an increase in either aggregate demand or aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If the consumption function is C = 200 + 0.8Y and there is a $10 million increase in investment spending, then the aggregate demand curve will shift horizontally to the right by:
A) $8 million.
B) $12.5 million.
C) $2 million.
D) $50 million.
A) $8 million.
B) $12.5 million.
C) $2 million.
D) $50 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
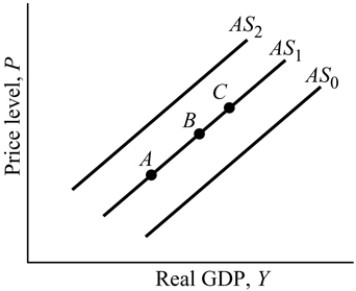 Figure 9.4
Figure 9.4Refer to Figure 9.4. The flooding in the Midwest during the summer of 1993 destroyed a large portion of the agricultural crop in the United States. This caused:
A) the economy to move from Point B to Point A along AS1.
B) the aggregate supply curve to shift from AS1 to AS2.
C) the economy to move from Point C to Point B along AS1.
D) the aggregate supply curve to shift from AS1 to AS0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If the marginal propensity to consume is 0.2, the value of the marginal propensity to save is:
A) 2.
B) 5.
C) 1.25.
D) 0.8.
A) 2.
B) 5.
C) 1.25.
D) 0.8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The aggregate demand curve would shift to the left if:
A) the cost of energy was to decrease.
B) taxes were increased.
C) the money supply was increased.
D) government spending was increased.
A) the cost of energy was to decrease.
B) taxes were increased.
C) the money supply was increased.
D) government spending was increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The _______ is one reason why the aggregate demand curve is downward sloping.
A) paradox of thrift
B) natural rate of unemployment
C) wealth effect
D) presence of sticky prices
A) paradox of thrift
B) natural rate of unemployment
C) wealth effect
D) presence of sticky prices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Sticky prices cause an economic coordination problem for the economy because:
A) they are likely to cause the CPI to understate the actual increase in the cost of living.
B) they increase the transaction costs in open market auctions.
C) they confuse the signal system that brings together consumers and producers.
D) they confuse the system of custom prices.
A) they are likely to cause the CPI to understate the actual increase in the cost of living.
B) they increase the transaction costs in open market auctions.
C) they confuse the signal system that brings together consumers and producers.
D) they confuse the system of custom prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If prices are slow to adjust, then it is possible that:
A) some markets will not be in equilibrium.
B) there will be a demand surplus.
C) there will be a supply shortage.
D) all of the above are true.
A) some markets will not be in equilibrium.
B) there will be a demand surplus.
C) there will be a supply shortage.
D) all of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
According to the international effect explanation of the downward slope of the AD curve, a lower price level in the U.S. economy causes:
A) U.S. imports and U.S. exports to decrease.
B) U.S. imports and U.S. exports to increase.
C) U.S. imports to increase and U.S. exports to decrease.
D) U.S. imports to decrease and U.S. exports to increase.
A) U.S. imports and U.S. exports to decrease.
B) U.S. imports and U.S. exports to increase.
C) U.S. imports to increase and U.S. exports to decrease.
D) U.S. imports to decrease and U.S. exports to increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In the consumption function C = Ca + bY, the term b represents:
A) the marginal propensity to consume.
B) the multiplier effect.
C) the autonomous consumption spending.
D) the marginal propensity to save.
A) the marginal propensity to consume.
B) the multiplier effect.
C) the autonomous consumption spending.
D) the marginal propensity to save.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
In the long- run, an increase in the money supply will cause output:
A) to remain the same.
B) to increase.
C) to fluctuate up and down.
D) to decrease.
A) to remain the same.
B) to increase.
C) to fluctuate up and down.
D) to decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
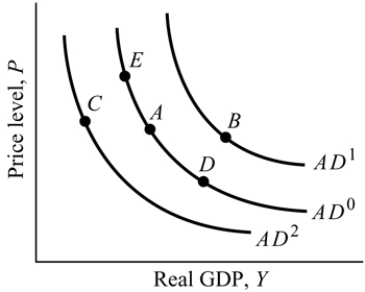 Figure 9.2
Figure 9.2Refer to Figure 9.2. Suppose the economy is at Point A, a decrease in taxes causes a movement to Point:
A) B.
B) D.
C) C.
D) E.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
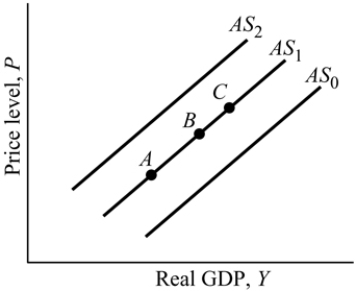 Figure 9.4
Figure 9.4Refer to Figure 9.4. A decrease in aggregate supply is represented by:
A) a movement from Point B to Point A along AS1.
B) a shift from AS1 to AS2.
C) a movement from Point A to Point B along AS1.
D) a shift from AS1 to AS0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following will cause the price level to increase in the long- run?
A) a decrease in government spending
B) an increase in income taxes
C) a decrease in the money supply
D) an increase in the interest rates
A) a decrease in government spending
B) an increase in income taxes
C) a decrease in the money supply
D) an increase in the interest rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
An example of a good/service that has custom prices is
A) labor.
B) gasoline.
C) steel rods.
D) oil.
A) labor.
B) gasoline.
C) steel rods.
D) oil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
If the marginal propensity to consume is 0.5, an increase in consumption by $200 will shift the aggregate demand curve horizontally to the right by
A) $200.
B) $400.
C) $100.
D) $200.5.
A) $200.
B) $400.
C) $100.
D) $200.5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



