Deck 6: Unemployment and Inflation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/206
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Unemployment and Inflation
1
Changes in the unemployment that occur as the economy expands and contracts are called _______ unemployment.
A) frictional
B) the natural rate of
C) structural
D) cyclical
A) frictional
B) the natural rate of
C) structural
D) cyclical
cyclical
2
A man is fired from his job because he was late for work too many times. While he is searching for another job he would be classified as:
A) cyclically unemployed.
B) not in the labor force because his employer had a legitimate reason for firing him.
C) structurally unemployed.
D) frictionally unemployed.
A) cyclically unemployed.
B) not in the labor force because his employer had a legitimate reason for firing him.
C) structurally unemployed.
D) frictionally unemployed.
frictionally unemployed.
3
Which of the following statements is false?
A) The consumer price index understates changes in the cost of living.
B) The chain index for GDP overstates actual changes in prices.
C) The best overall indicator of inflationary pressures in the economy is the GDP price index.
D) One problem with any fixed- bundle index as a measure of the cost of living is that it does not account for substitutions that consumers might make in response to price changes.
A) The consumer price index understates changes in the cost of living.
B) The chain index for GDP overstates actual changes in prices.
C) The best overall indicator of inflationary pressures in the economy is the GDP price index.
D) One problem with any fixed- bundle index as a measure of the cost of living is that it does not account for substitutions that consumers might make in response to price changes.
The consumer price index understates changes in the cost of living.
4
Sally works 10 hours a week, but would prefer to work more hours. According to the BLS, Sally is classified as:
A) employed but not "an individual working part time for economic reasons."
B) a discouraged worker.
C) unemployed and "an individual working part time for economic reason."
D) employed and "an individual working part time for economic reason."
A) employed but not "an individual working part time for economic reasons."
B) a discouraged worker.
C) unemployed and "an individual working part time for economic reason."
D) employed and "an individual working part time for economic reason."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
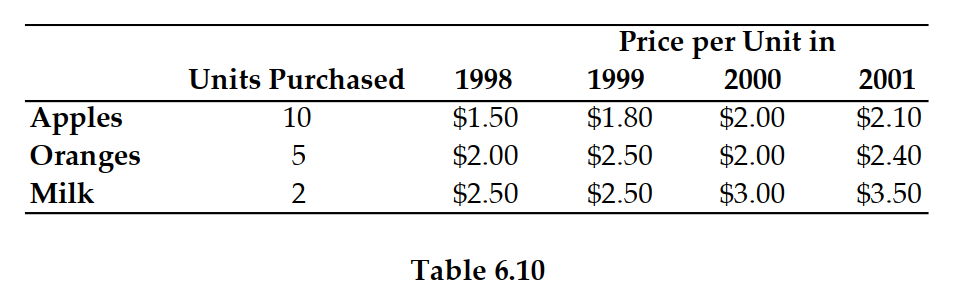
Refer to Table 6.10. If 1999 is the base year, then the inflation rate (i.e., the growth rate of the price index) between 2000 and 2001 is:
A) about 11 percent.
B) about 7 percent.
C) about 9 percent.
D) about 13 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When the economy slows down and real GDP falls, the type of unemployment that will be directly affected is the:
A) natural rate of unemployment.
B) cyclical unemployment.
C) frictional unemployment.
D) structural unemployment.
A) natural rate of unemployment.
B) cyclical unemployment.
C) frictional unemployment.
D) structural unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
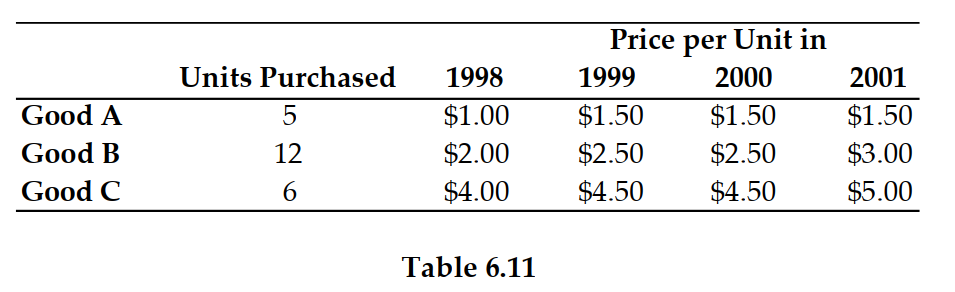
Refer to Table 6.11. If 1999 is the base year, the price index in 1999 is:
A) 138.7.
B) 121.7.
C) 1998.
D) 100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is correct? The unemployment rate is:
A) ((employed - labor force)/employed) x 100.
B) ((labor force - employed)/labor force) x 100.
C) (unemployed/population) x 100.
D) ((employed - unemployed)/labor force) x 100.
A) ((employed - labor force)/employed) x 100.
B) ((labor force - employed)/labor force) x 100.
C) (unemployed/population) x 100.
D) ((employed - unemployed)/labor force) x 100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following individuals can be classified as a marginally attached worker?
A) Bob, stops looking for a job as a 5th grade teacher after looking for a job the last 6 months.
B) Jane was looking for a job but stopped looking because of her inability to find a babysitter for her 2- year- old son.
C) Jane is currently looking for a job and has not found one.
D) A and B are correct.
A) Bob, stops looking for a job as a 5th grade teacher after looking for a job the last 6 months.
B) Jane was looking for a job but stopped looking because of her inability to find a babysitter for her 2- year- old son.
C) Jane is currently looking for a job and has not found one.
D) A and B are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If the economy is experiencing 50 percent inflation per month, then a donut that costs $1.50 today will cost _______ next month.
A) $1.00
B) $2.25
C) $1.75
D) $2.00
A) $1.00
B) $2.25
C) $1.75
D) $2.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In 1999, the U.S. population 16 years old or older was 207.8 million, the number employed was 133.5 million, the number unemployed was 5.9 million, and the labor force was 139.4 million. The labor- force participation rate in 1999 was _______%.
A) 4.2
B) 95.8
C) 67.1
D) 64.2
A) 4.2
B) 95.8
C) 67.1
D) 64.2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is not an example of seasonal unemployment?
A) lost farming jobs during the winter
B) lost accounting jobs after April
C) lost textiles jobs due to a recession
D) lost retail jobs after the Christmas
A) lost farming jobs during the winter
B) lost accounting jobs after April
C) lost textiles jobs due to a recession
D) lost retail jobs after the Christmas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The cost of the basket of goods in Year 1 is $200 and the cost of the basket of goods in Year 2 is $225. If Year 1 is used as the base year, the Year 2 price index is:
A) 112.5.
B) 150.
C) 80.
D) 66.67.
A) 112.5.
B) 150.
C) 80.
D) 66.67.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Based on statistics on unemployment, which group of workers experience the highest unemployment rates?
A) African American, 16- 19 years old
B) women maintaining families
C) unmarried men
D) White, 16- 19 years old
A) African American, 16- 19 years old
B) women maintaining families
C) unmarried men
D) White, 16- 19 years old

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The number of people classified as employed is 220,000 and the number of people classified as unemployed is 30,000. The size of the labor force:
A) equals 300,000.
B) equals 200,000.
C) equals 250,000.
D) cannot be determined from this information.
A) equals 300,000.
B) equals 200,000.
C) equals 250,000.
D) cannot be determined from this information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Suppose an individual works 12 hours per week in a family business and is not looking for other work. Also assume that the individual is not paid for the 12 hours of work. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, this individual would be classified as:
A) not in the labor force.
B) a discouraged worker.
C) employed.
D) none of the above
A) not in the labor force.
B) a discouraged worker.
C) employed.
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17

Refer to Table 6.2. The total number of people employed is:
A) 129.67 million.
B) 73.5 million.
C) 128.92 million.
D) 199.5 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The unemployment rate equals:
A) labor force/population.
B) (labor force - employed)/labor force.
C) unemployed/employed.
D) (employed - unemployed)/labor force.
A) labor force/population.
B) (labor force - employed)/labor force.
C) unemployed/employed.
D) (employed - unemployed)/labor force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
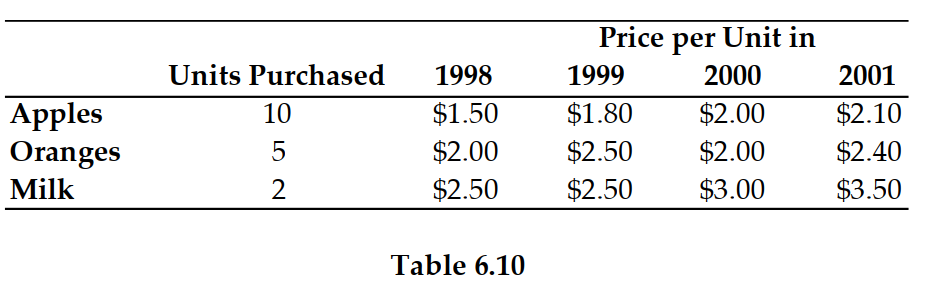
Refer to Table 6.10. Suppose 1999 is the base year. The price index in 1999 is:
A) 10.
B) 100.
C) 1.
D) 1,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
An increase in the number of discouraged workers will cause the:
A) unemployment rate to decrease and the labor force to decrease.
B) unemployment rate to increase and the labor force to increase.
C) unemployment rate to decrease and the labor force to increase.
D) unemployment rate to increase and the labor force to decrease.
A) unemployment rate to decrease and the labor force to decrease.
B) unemployment rate to increase and the labor force to increase.
C) unemployment rate to decrease and the labor force to increase.
D) unemployment rate to increase and the labor force to decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A person who is currently actively looking for a job, but has a job that pays for 5 hours a week only is classified by the BLS as:
A) employed.
B) not in the labor force.
C) unemployed.
D) under 16.
A) employed.
B) not in the labor force.
C) unemployed.
D) under 16.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22

Refer to Table 6.4. The unemployment rate rate equals:
A) 83.5%.
B) 3.1%.
C) 66.6%.
D) 3.7%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the difference between the CPI and the GDP chain index?
A) The CPI includes capital goods but the chain index does not.
B) The CPI basket includes more goods and services than the GDP chain index basket.
C) The CPI includes a fixed basket of goods while the chain index does not.
D) The CPI measures price changes while the GDP chain index measures production changes.
A) The CPI includes capital goods but the chain index does not.
B) The CPI basket includes more goods and services than the GDP chain index basket.
C) The CPI includes a fixed basket of goods while the chain index does not.
D) The CPI measures price changes while the GDP chain index measures production changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
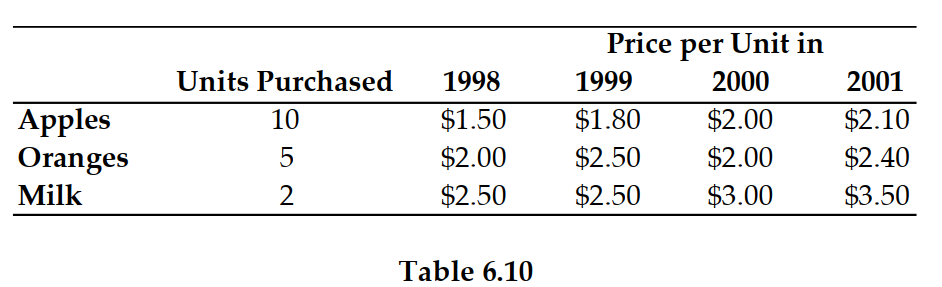
Refer to Table 6.10. If 1999 is the base year, the price index in 2000 is:
A) 89.2.
B) 102.4.
C) 100.9.
D) 101.4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Unanticipated inflation is the difference between:
A) the inflation rate this year and the inflation rate that we want the economy to have this year.
B) the actual observed inflation rate this year and the inflation rate last year.
C) the inflation rate last year and the inflation rate that we want the economy to have last year.
D) the expected inflation rate and the actual observed inflation rate.
A) the inflation rate this year and the inflation rate that we want the economy to have this year.
B) the actual observed inflation rate this year and the inflation rate last year.
C) the inflation rate last year and the inflation rate that we want the economy to have last year.
D) the expected inflation rate and the actual observed inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The labor force participation rate equals:
A) employed / population.
B) (labor force) / (population 16 years or older).
C) population /(labor force).
D) (labor force)/ population.
A) employed / population.
B) (labor force) / (population 16 years or older).
C) population /(labor force).
D) (labor force)/ population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
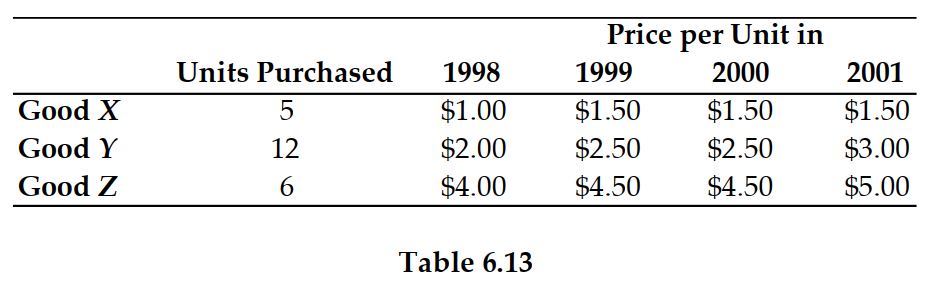
Refer to Table 6.13. If 1999 is the base year, the inflation rate between 1999 and 2000 is:
A) 30.7%.
B) 21.7%.
C) 3.78%.
D) 0.0%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
According to the application, as more individuals avail of disability benefits,
A) the unemployment rate increases because they are not part of the labor force.
B) the unemployment rate decreases because they are not part of the labor force.
C) the unemployment rate decreases because they are now considered employed.
D) the unemployment rate increases because they are now considered unemployed.
A) the unemployment rate increases because they are not part of the labor force.
B) the unemployment rate decreases because they are not part of the labor force.
C) the unemployment rate decreases because they are now considered employed.
D) the unemployment rate increases because they are now considered unemployed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Many economists believe that each year inflation is overestimated by between:
A) 2.5% and 3.5%.
B) 0.5% and 1.5%.
C) 0.1% and 0.5%.
D) 1.5% and 2.5%.
A) 2.5% and 3.5%.
B) 0.5% and 1.5%.
C) 0.1% and 0.5%.
D) 1.5% and 2.5%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
COLA is an acronym that stands for
A) Cost of Living Alone.
B) Cost of Living Adjustment.
C) Cost of Living Annually.
D) Cost of Living Account.
A) Cost of Living Alone.
B) Cost of Living Adjustment.
C) Cost of Living Annually.
D) Cost of Living Account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If the price index in 2000 is 120 and the price index in 2001 is 112, then the rate of inflation between 2000 and 2001 is:
A) - 8.6%.
B) - 8.7%.
C) - 6.6%.
D) - 4.17%.
A) - 8.6%.
B) - 8.7%.
C) - 6.6%.
D) - 4.17%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If 1999 is the base year and the inflation rate between 1999 and 2000 is - 12%, the price index in 2000 must be equal to:
A) 88.
B) - 120.
C) 120.
D) cannot be determined from this information because the base year is not known
A) 88.
B) - 120.
C) 120.
D) cannot be determined from this information because the base year is not known

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A worker who currently is not working, but is not looking for a job is considered as:
A) in the labor force.
B) not in the labor force.
C) unemployed.
D) employed.
A) in the labor force.
B) not in the labor force.
C) unemployed.
D) employed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following is considered a cost of unemployment?
A) severe psychological costs to the job loser
B) higher crime, suicide and divorce rates
C) wasted resources because a worker is not being utilized
D) All of the above are considered costs of unemployment.
A) severe psychological costs to the job loser
B) higher crime, suicide and divorce rates
C) wasted resources because a worker is not being utilized
D) All of the above are considered costs of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following individuals are hurt when the economy experiences unanticipated inflation?
A) savers
B) fixed income earners
C) lenders
D) All of the above are hurt by unanticipated inflation.
A) savers
B) fixed income earners
C) lenders
D) All of the above are hurt by unanticipated inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Deflation is a great economic problem because:
A) prices and wages fall but debts remain the same.
B) prices fall more slowly than wages.
C) lower prices and wages promote unemployment.
D) prices and wages fall but interest rates remain the same.
A) prices and wages fall but debts remain the same.
B) prices fall more slowly than wages.
C) lower prices and wages promote unemployment.
D) prices and wages fall but interest rates remain the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If the U.S. economy experienced a large deflation, what would most likely happen to U.S. banks?
A) U.S. banks would not be affected by the deflation.
B) U.S. banks would experience large profits.
C) U.S. banks will find themselves making more loans.
D) U.S. bank profits would decline as more borrowers default.
A) U.S. banks would not be affected by the deflation.
B) U.S. banks would experience large profits.
C) U.S. banks will find themselves making more loans.
D) U.S. bank profits would decline as more borrowers default.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Recall Application 2, "More Disability, Less Unemployment?" to answer the following questions:
According to the application, the federal Disability Insurance program provides income to:
A) elderly workers who are deemed able to engage in substantial employment.
B) non- elderly workers who are deemed able to engage in substantial employment.
C) non- elderly workers who are deemed unable to engage in substantial employment.
D) elderly workers who are deemed unable to engage in substantial employment.
According to the application, the federal Disability Insurance program provides income to:
A) elderly workers who are deemed able to engage in substantial employment.
B) non- elderly workers who are deemed able to engage in substantial employment.
C) non- elderly workers who are deemed unable to engage in substantial employment.
D) elderly workers who are deemed unable to engage in substantial employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The cost of the basket of goods in 2009 is $550 and the cost of the basket of goods in 2010 is $700. If 2009 is used as the base year, the price index for 2010 is:
A) 127.2.
B) 78.5.
C) 155.
D) 100.
A) 127.2.
B) 78.5.
C) 155.
D) 100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
An auto worker in Ohio who loses her job because the company relocated the plant to another country represents an example of:
A) cyclical unemployment.
B) frictional unemployment.
C) structural unemployment.
D) natural unemployment.
A) cyclical unemployment.
B) frictional unemployment.
C) structural unemployment.
D) natural unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
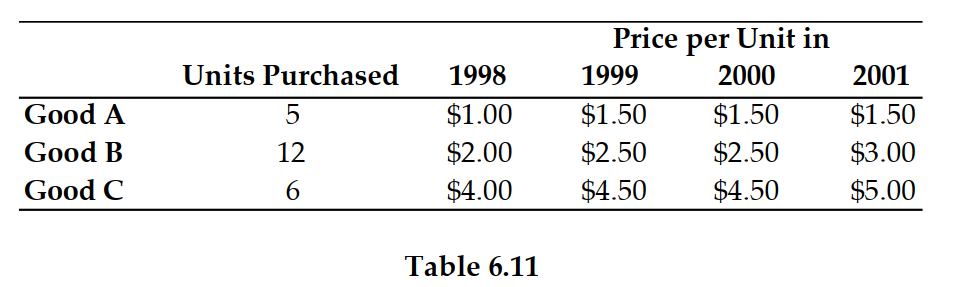
Refer to Table 6.11. If 1999 is the base year, then the inflation rate (i.e., the growth rate of the price index) between 1999 and 2000 is:
A) 17.8 percent.
B) zero percent.
C) 121.7 percent.
D) 2.17 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Suppose the unemployment rate is currently at 5 percent. If the number of unemployed increases by the same number as the number of people unemployed, then:
A) the labor force participation rate will decrease.
B) the unemployment rate will decrease.
C) the unemployment rate will increase.
D) the population growth rate will increase.
A) the labor force participation rate will decrease.
B) the unemployment rate will decrease.
C) the unemployment rate will increase.
D) the population growth rate will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Suppose that the CPI in 1999 was 125.2 and the CPI in 2000 was 139.1. The rate of inflation between 1999 and 2000 was:
A) 13.9%.
B) 11.1%.
C) 12.9%.
D) 14.3%.
A) 13.9%.
B) 11.1%.
C) 12.9%.
D) 14.3%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
When people who were previously looking for jobs stop looking for jobs, they are classified as:
A) employed.
B) in the labor force.
C) unemployed.
D) not in the labor force.
A) employed.
B) in the labor force.
C) unemployed.
D) not in the labor force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Recall Application 2, "More Disability, Less Unemployment?" to answer the following questions:
According to the application, changes in the federal Disability Insurance program:
A) decreased the number of elderly adults receiving benefits from the program.
B) decreased the number of non- elderly adults receiving benefits from the program.
C) increased the number of elderly adults receiving benefits from the program.
D) increased the number of non- elderly adults receiving benefits from the program.
According to the application, changes in the federal Disability Insurance program:
A) decreased the number of elderly adults receiving benefits from the program.
B) decreased the number of non- elderly adults receiving benefits from the program.
C) increased the number of elderly adults receiving benefits from the program.
D) increased the number of non- elderly adults receiving benefits from the program.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The sum of the frictional and structural unemployment rates is thought of as the:
A) cyclical rate of unemployment.
B) natural rate of unemployment.
C) seasonal rate of unemployment.
D) normal rate of unemployment.
A) cyclical rate of unemployment.
B) natural rate of unemployment.
C) seasonal rate of unemployment.
D) normal rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A discouraged worker is:
A) marginally attached.
B) not currently looking for a job.
C) not in the labor force.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) marginally attached.
B) not currently looking for a job.
C) not in the labor force.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
An individual worked for an airline that went out of business because the airline was unable to meet new federal safety standards. While the individual is unemployed, she will be classified as:
A) naturally unemployed.
B) frictionally unemployed.
C) cyclically unemployed.
D) structurally unemployed.
A) naturally unemployed.
B) frictionally unemployed.
C) cyclically unemployed.
D) structurally unemployed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
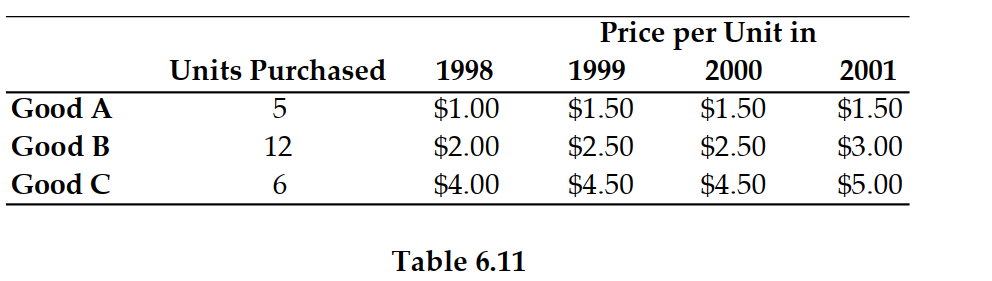
Refer to Table 6.11. If 1999 is the base year, then the inflation (i.e., the growth rate of the price index) between 2000 and 2001 is:
A) about 21 percent.
B) about 14 percent.
C) about 17 percent.
D) about 38 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
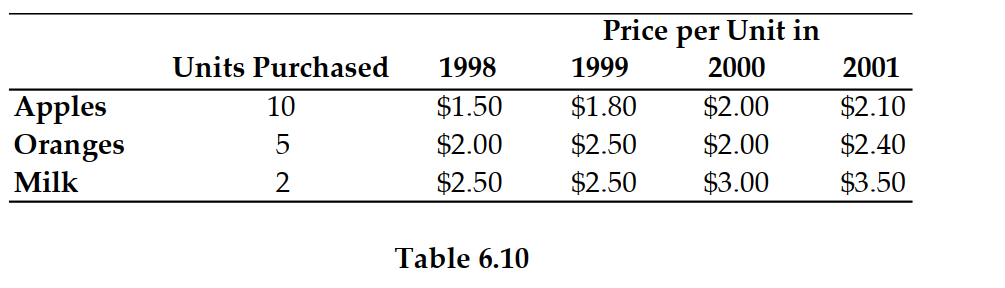
Refer to Table 6.10. If 1999 is the base year, the price index in 2001 is:
A) 120.5.
B) 109.8.
C) 115.2.
D) 112.7.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If the labor force is 250,000 and the total population 16 years of age or older is 300,000, the labor- force participation rate is:
A) 79.5%.
B) 80.9%.
C) 45.4%.
D) 83.3%.
A) 79.5%.
B) 80.9%.
C) 45.4%.
D) 83.3%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If 1999 is the base year and the inflation rate between 1999 and 2000 is 7%, the price index in 2000 must be equal to:
A) 170.
B) 107.
C) 70.
D) cannot be determined from this information because the index in the base year is not given
A) 170.
B) 107.
C) 70.
D) cannot be determined from this information because the index in the base year is not given

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Unanticipated inflation arbitrarily redistributes income because:
A) actual tax revenue decreases and so do government subsidies.
B) medical costs rise faster than health insurance premiums.
C) people forecast relative prices incorrectly and either gain or lose purchasing power.
D) nominal interest rates fall below real interest rates.
A) actual tax revenue decreases and so do government subsidies.
B) medical costs rise faster than health insurance premiums.
C) people forecast relative prices incorrectly and either gain or lose purchasing power.
D) nominal interest rates fall below real interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When the economy's unemployment rate equals the natural rate, which type of unemployment is assumed to be zero?
A) frictional and structural unemployment
B) structural unemployment
C) cyclical unemployment
D) frictional unemployment
A) frictional and structural unemployment
B) structural unemployment
C) cyclical unemployment
D) frictional unemployment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Recall Application 3, "Social Norms, Unemployment ,and Perceived Happiness," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, men suffered _ in well- being when _ were also unemployed.
A) a larger decline; their peers
B) a smaller decline; their peers
C) a smaller increase; their family
D) a larger decline; their family
According to the application, men suffered _ in well- being when _ were also unemployed.
A) a larger decline; their peers
B) a smaller decline; their peers
C) a smaller increase; their family
D) a larger decline; their family

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
NEETS ARE THE NEW DISCOURAGED WORKERS IN JAPAN
Who are the new discouraged workers in Japan?
In Japan, there is growing concern about young people who are not joining the labor force. Young workers who have given up looking for work and often receive support from their parents are known as NEETs—"not in education, employment, or training." Because Japan has an aging population and does not encourage immigration, it is concerned about labor shortages and has focused attention on the NEETs. Many in Japan are concerned over this phenomenon because it potentially signals a change in the strong Japanese work ethic.
However, the number of individuals in this category is quite small, only 2 percent of Japan’s 33 million young people between the ages of 15 and 34. Nonetheless, the fact that the Japanese decided to name this group suggests that it is socially significant to them. In the United States, individuals not seeking work and supported by their parents would be out of the labor force and possibly marginally attached workers.
Labor shortages in Japan increased focus on the NEETs. This labor shortage is caused by:
A) a strong work ethic.
B) a population boom.
C) an aging population.
D) a recession.
Who are the new discouraged workers in Japan?
In Japan, there is growing concern about young people who are not joining the labor force. Young workers who have given up looking for work and often receive support from their parents are known as NEETs—"not in education, employment, or training." Because Japan has an aging population and does not encourage immigration, it is concerned about labor shortages and has focused attention on the NEETs. Many in Japan are concerned over this phenomenon because it potentially signals a change in the strong Japanese work ethic.
However, the number of individuals in this category is quite small, only 2 percent of Japan’s 33 million young people between the ages of 15 and 34. Nonetheless, the fact that the Japanese decided to name this group suggests that it is socially significant to them. In the United States, individuals not seeking work and supported by their parents would be out of the labor force and possibly marginally attached workers.
Labor shortages in Japan increased focus on the NEETs. This labor shortage is caused by:
A) a strong work ethic.
B) a population boom.
C) an aging population.
D) a recession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Suppose that the CPI in Year 1 is 250 and the CPI in Year 2 is 100. The rate of inflation between Year 1 and Year 2 is:
A) 14.28%.
B) 40%.
C) - 150%.
D) - 60%.
A) 14.28%.
B) 40%.
C) - 150%.
D) - 60%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Recall Application 2, "More Disability, Less Unemployment?" to answer the following questions:
According to the application, the changes in the federal Disability Insurance program:
A) made the program's benefits more generous for low- skilled workers.
B) made it easier to enter the program.
C) increased the value of healthcare services.
D) All of the above characterizes the changes in the program.
According to the application, the changes in the federal Disability Insurance program:
A) made the program's benefits more generous for low- skilled workers.
B) made it easier to enter the program.
C) increased the value of healthcare services.
D) All of the above characterizes the changes in the program.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
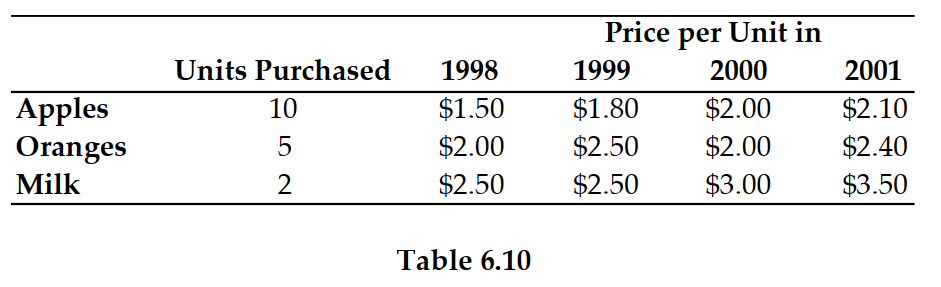
Refer to Table 6.10. If 1999 is the base year, the price index in 1998 is:
A) 103.9.
B) 96.7.
C) 113.8.
D) 84.5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Suppose that the CPI in Year 1 is 150 and the CPI in Year 2 is 200. The rate of inflation between Year 1 and Year 2 is:
A) 33.33%.
B) 50%.
C) 25%.
D) 14.28%.
A) 33.33%.
B) 50%.
C) 25%.
D) 14.28%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A person who leaves the labor force because they could not find a job is called:
A) a dissatisfied worker.
B) a disgruntled worker.
C) a discouraged worker.
D) a disbarred worker.
A) a dissatisfied worker.
B) a disgruntled worker.
C) a discouraged worker.
D) a disbarred worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The largest cost associated with unanticipated inflation is:
A) the menu cost.
B) the distortion of our tax system.
C) the shoe- leather cost.
D) the arbitrary redistribution of income and wealth.
A) the menu cost.
B) the distortion of our tax system.
C) the shoe- leather cost.
D) the arbitrary redistribution of income and wealth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Carla lost her job and immediately started looking for another job. As a result the:
A) unemployment rate remains constant.
B) labor force increases.
C) unemployment rate increases.
D) labor force decreases.
A) unemployment rate remains constant.
B) labor force increases.
C) unemployment rate increases.
D) labor force decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
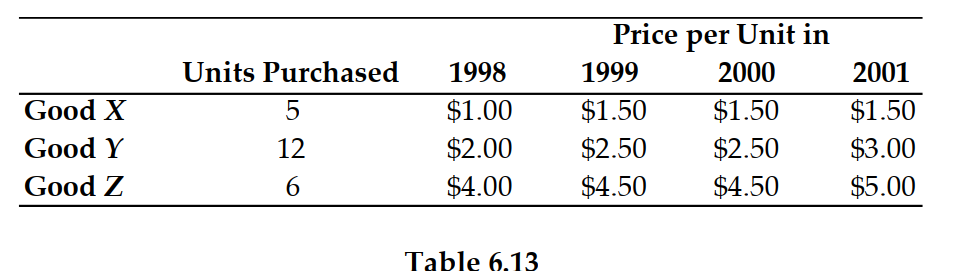
Refer to Table 6.13. If 1999 is the base year, the inflation rate between 1999 and 2001 is:
A) 9%.
B) 114%.
C) 14%.
D) 1.4%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A person who is currently actively looking for a job, but has not found a job is classified by the BLS as:
A) unemployed.
B) under 16.
C) not in the labor force.
D) employed.
A) unemployed.
B) under 16.
C) not in the labor force.
D) employed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
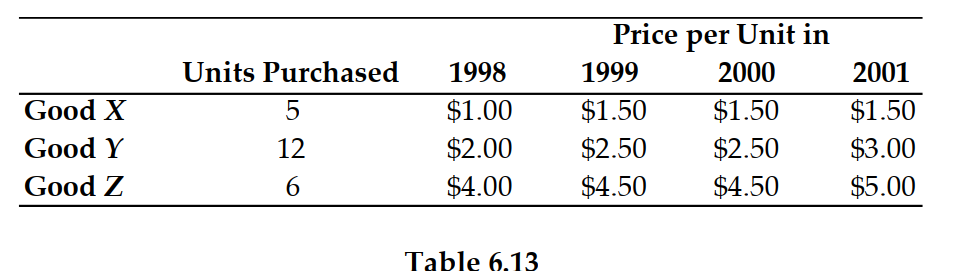
Refer to Table 6.13. If 2000 is the base year, the inflation rate between 1999 and 2001 is:
A) 9%.
B) 114%.
C) 1.4%.
D) 14%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The labor force participation rate is the ratio of the:
A) labor force to the total population 16 years old or older.
B) number employed to total population.
C) number employed to the total population 16 years old or older.
D) labor force to total population.
A) labor force to the total population 16 years old or older.
B) number employed to total population.
C) number employed to the total population 16 years old or older.
D) labor force to total population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If you expect that the inflation rate is 5 percent and the inflation actual inflation rate turned out to be exactly 5 percent, then:
A) the inflation rate was fully anticipated and there is no unanticipated inflation.
B) the inflation rate was fully unanticipated.
C) the anticipated inflation rate equals zero.
D) the anticipated and unanticipated inflation rate equals 5 percent.
A) the inflation rate was fully anticipated and there is no unanticipated inflation.
B) the inflation rate was fully unanticipated.
C) the anticipated inflation rate equals zero.
D) the anticipated and unanticipated inflation rate equals 5 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If the number of unemployed increases by the same number as the number of people in the labor force, then:
A) the unemployment rate will decrease.
B) the population growth rate will increase.
C) the unemployment rate will increase.
D) the labor force participation rate will decrease.
A) the unemployment rate will decrease.
B) the population growth rate will increase.
C) the unemployment rate will increase.
D) the labor force participation rate will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The economy attains full employment when the unemployment rate
A) equals the natural rate of unemployment.
B) is equal to zero.
C) equals to seven percent or higher.
D) equals the structural rate of unemployment.
A) equals the natural rate of unemployment.
B) is equal to zero.
C) equals to seven percent or higher.
D) equals the structural rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Recall Application 3, "Social Norms, Unemployment ,and Perceived Happiness," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, Andrew Clark found that the more an individual was, the aggressive he or she was in looking for a job.
A) in debt; less
B) content; more
C) lazy; less
D) unhappy; more
According to the application, Andrew Clark found that the more an individual was, the aggressive he or she was in looking for a job.
A) in debt; less
B) content; more
C) lazy; less
D) unhappy; more

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
An individual who cannot find a job because his or her job skills have become obsolete is an example of:
A) frictional unemployment.
B) seasonal unemployment.
C) structural unemployment.
D) cyclical unemployment.
A) frictional unemployment.
B) seasonal unemployment.
C) structural unemployment.
D) cyclical unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The natural rate of unemployment is generally thought of as the:
A) sum of the structural unemployment and cyclical unemployment rates.
B) sum of the frictional unemployment and structural unemployment rates.
C) ratio of the frictional unemployment rate to the cyclical unemployment rate.
D) sum of the frictional unemployment and cyclical unemployment rates.
A) sum of the structural unemployment and cyclical unemployment rates.
B) sum of the frictional unemployment and structural unemployment rates.
C) ratio of the frictional unemployment rate to the cyclical unemployment rate.
D) sum of the frictional unemployment and cyclical unemployment rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Suppose that 1999 is the base year and the price index for 2008 is 130. A basket of goods that is valued $450 in 2008 would cost _______ in 1999.
A) $4203
B) $346
C) $320
D) $585
A) $4203
B) $346
C) $320
D) $585

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Discouraged workers are workers who leave the labor force because of:
A) their inability to find jobs.
B) the difficulty of finding transportation.
C) difficulty of finding appropriate childcare.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) their inability to find jobs.
B) the difficulty of finding transportation.
C) difficulty of finding appropriate childcare.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
During the early 1990s, companies started downsizing. One of the results of this downsizing was the permanent reduction in the number of middle management positions. This change in the way businesses operate would have:
A) not affected the natural rate of unemployment.
B) increased the natural rate of unemployment.
C) decreased the natural rate of unemployment.
D) either increased or decreased the natural rate of unemployment.
A) not affected the natural rate of unemployment.
B) increased the natural rate of unemployment.
C) decreased the natural rate of unemployment.
D) either increased or decreased the natural rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The economy is in a recession and the housing market is in a slump. As a result of this, a real estate firm lays off half of its real estate agents. This is an example of:
A) natural unemployment.
B) structural unemployment.
C) cyclical unemployment.
D) frictional unemployment.
A) natural unemployment.
B) structural unemployment.
C) cyclical unemployment.
D) frictional unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The unemployment rate is defined as the ratio of the:
A) number of people unemployed to the total population 16 years old or older.
B) labor force to the total population 16 years old or older.
C) number of people unemployed to total population.
D) none of the above
A) number of people unemployed to the total population 16 years old or older.
B) labor force to the total population 16 years old or older.
C) number of people unemployed to total population.
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79

Refer to Table 6.1. The labor force equals:
A) 14,000.
B) 16,500.
C) 16,000.
D) 13,500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
While one benefit of unemployment insurance is that it can temporarily offset some of the financial costs of losing a job, its downside is that it:
A) increases the incentive for a worker to find a job immediately.
B) increases the incentive for the worker to have a second job.
C) decreases the length of time a worker remains unemployed.
D) increases the length of time a worker remains unemployed.
A) increases the incentive for a worker to find a job immediately.
B) increases the incentive for the worker to have a second job.
C) decreases the length of time a worker remains unemployed.
D) increases the length of time a worker remains unemployed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 206 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



