Deck 18: International Trade and Public Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/226
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: International Trade and Public Policy
1
The consumption possibilities curve shows the combinations of goods that can be:
A) produced by a nation before trading begins.
B) produced by a nation after trade begins.
C) consumed by a nation after trading begins.
D) consumed by a nation before trade begins.
A) produced by a nation before trading begins.
B) produced by a nation after trade begins.
C) consumed by a nation after trading begins.
D) consumed by a nation before trade begins.
consumed by a nation after trading begins.
2
Which of the following groups of countries are members of NAFTA?
A) The U.S.A., Japan, and Mexico
B) The U.S.A., Canada, and Mexico
C) The U.S.A., France, and Germany
D) Japan, Canada, and Mexico
A) The U.S.A., Japan, and Mexico
B) The U.S.A., Canada, and Mexico
C) The U.S.A., France, and Germany
D) Japan, Canada, and Mexico
The U.S.A., Canada, and Mexico
3
Which of the following situations will arise in the domestic market following the imposition of an import quota?
A) imports decrease, domestic production increases, prices increase
B) imports decrease, domestic production decreases, prices increase
C) imports increase, domestic production decreases, prices decrease
D) imports decrease, domestic production increases, prices decrease
A) imports decrease, domestic production increases, prices increase
B) imports decrease, domestic production decreases, prices increase
C) imports increase, domestic production decreases, prices decrease
D) imports decrease, domestic production increases, prices decrease
imports decrease, domestic production increases, prices increase
4
Which of the following situations will arise in the domestic market following the removal of an import quota?
A) imports increase, domestic production increases, prices increase
B) imports decrease, domestic production increases, prices decrease
C) imports decrease, domestic production decreases, prices increase
D) imports increase, domestic production decreases, prices decrease
A) imports increase, domestic production increases, prices increase
B) imports decrease, domestic production increases, prices decrease
C) imports decrease, domestic production decreases, prices increase
D) imports increase, domestic production decreases, prices decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
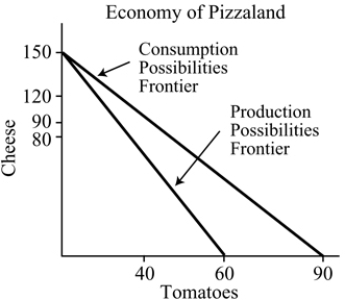 Figure 18.2
Figure 18.2Refer to Figure 18.2. The opportunity cost of producing cheese in Pizzaland is:
A) 2.5 tomatoes.
B) 0.6 tomatoes.
C) 0.4 tomato.
D) 1.67 tomatoes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The terms of trade is the:
A) rate at which two goods will be exchanged.
B) the end point of a consumption possibilities curve.
C) exchange rate for two nations.
D) opportunity costs of production.
A) rate at which two goods will be exchanged.
B) the end point of a consumption possibilities curve.
C) exchange rate for two nations.
D) opportunity costs of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Suppose nation A produces only two goods, apples and oranges . If nation A produces only apples, it can make 12 apples per day. If nation A produces only oranges, it can make 36 oranges per day. If the country has a constant production trade- off between apples and oranges, then the opportunity cost of one orange in nation A is:
A) 3 apples.
B) 0.33 apples.
C) 12 apples.
D) 36 apples.
A) 3 apples.
B) 0.33 apples.
C) 12 apples.
D) 36 apples.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When is an import ban the same as an import quota?
A) when the good under the import ban is taxed
B) when the quota is zero
C) never
D) when all the goods under the quota is taxed
A) when the good under the import ban is taxed
B) when the quota is zero
C) never
D) when all the goods under the quota is taxed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following organizations has over 149 member nations and oversees the General Agreement on Trade and Tariffs?
A) European Union
B) World Trade Organization
C) North American Free Trade Agreement
D) Asian Pacific Economic Cooperation
A) European Union
B) World Trade Organization
C) North American Free Trade Agreement
D) Asian Pacific Economic Cooperation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Under current WTO rules, a country can adopt:
A) only WTO- approved environmental standards.
B) any environmental standard it chooses, even if it discriminates against foreign producers.
C) only the same environmental standards as its immediate geographic neighbors.
D) any environmental standard it chooses as long as it does not discriminate against foreign producers.
A) only WTO- approved environmental standards.
B) any environmental standard it chooses, even if it discriminates against foreign producers.
C) only the same environmental standards as its immediate geographic neighbors.
D) any environmental standard it chooses as long as it does not discriminate against foreign producers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following trade policies will prevent a foreign supplier to sell even one unit of the good in the domestic market?
A) import quota
B) voluntary export restraint
C) import tariffs
D) import ban
A) import quota
B) voluntary export restraint
C) import tariffs
D) import ban

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
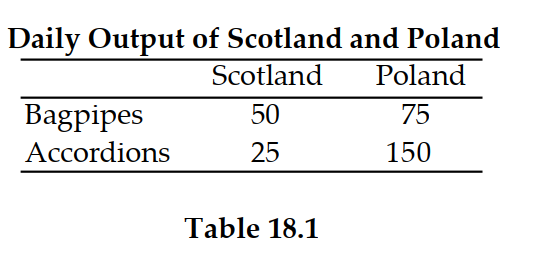
Refer to Table 18.1. Scotland has a comparative advantage in:
A) accordions.
B) bagpipes.
C) both accordions and bagpipes.
D) neither accordions nor bagpipes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following benefits from a quota or VER?
A) the government
B) domestic producers
C) consumers
D) all of the above
A) the government
B) domestic producers
C) consumers
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following trade policies raises prices for domestic consumers?
A) voluntary export restraints
B) tariffs
C) import quotas
D) all of the above
A) voluntary export restraints
B) tariffs
C) import quotas
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
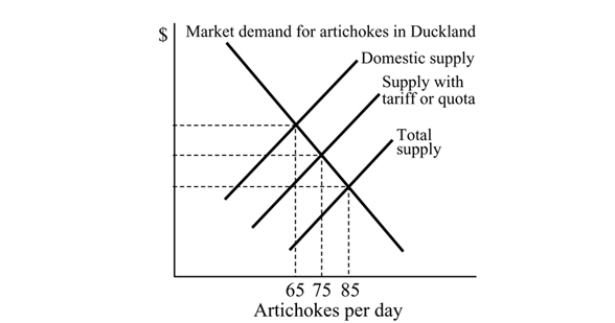 Figure 18.4
Figure 18.4Refer to Figure 18.4. With free trade, what is the equilibrium quantity of artichokes in Duckland?
A) 75
B) 65
C) 85
D) 30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
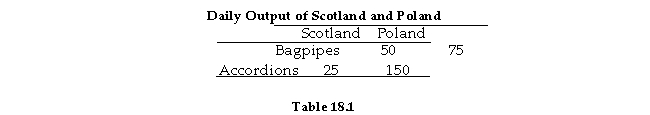
Refer to Table 18.1. If Poland produces 50 bagpipes, how many accordions can they produce for the rest of the day?
A) 75
B) 50
C) 125
D) 25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
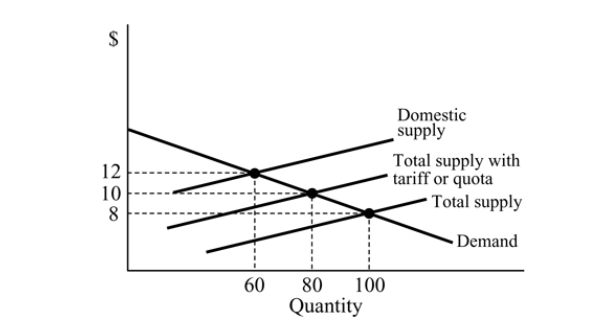 Figure 18.3
Figure 18.3Refer to Figure 18.3. With an import ban, the equilibrium quantity is:
A) 80.
B) 100.
C) 40.
D) 60.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Recall Application 4, "Trade, Consumption and Inequality," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, living standards have not become more unequal because:
A) the prices of goods and services that low income groups have paid have risen slower than the prices of goods and services that high income groups have paid.
B) the prices of goods and services that low income groups have paid have been dropping while the prices of goods and services that high income groups have not.
C) the prices of goods and services that low income groups have paid have risen faster than the prices of goods and services that high income groups have paid.
D) the prices of goods and services that low income groups have paid have risen while the prices of goods and services that high income groups have not.
According to the application, living standards have not become more unequal because:
A) the prices of goods and services that low income groups have paid have risen slower than the prices of goods and services that high income groups have paid.
B) the prices of goods and services that low income groups have paid have been dropping while the prices of goods and services that high income groups have not.
C) the prices of goods and services that low income groups have paid have risen faster than the prices of goods and services that high income groups have paid.
D) the prices of goods and services that low income groups have paid have risen while the prices of goods and services that high income groups have not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A voluntary export restraint is a trade policy by which a nation agrees to limit its:
A) exports of a good in order to avoid more restrictive trade policies.
B) imports of a good.
C) imports of a good, but only under the threat of more restrictive trade policies.
D) exports of a good in order to increase employment.
A) exports of a good in order to avoid more restrictive trade policies.
B) imports of a good.
C) imports of a good, but only under the threat of more restrictive trade policies.
D) exports of a good in order to increase employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20

Refer to Table 18.2. The opportunity cost of stereos in the U.S. is:
A) 4 tractors.
B) 2 tractors.
C) 1/4 tractor.
D) 1/2 tractor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Recall Application 3, "Are They Really Dumping?" to answer the following questions:
Based on what you learned from the application, can a firm who exports to the U.S. be charged with dumping even though the price they sell at home is lower?
A) No.
B) Yes, because the "constructed value" estimated by the department of Commerce can overstate the price that the firm charges at home.
C) Yes, because the firm that brings forward the charges can supply overstated figures data to the Department of Commerce.
D) B and C are correct.
Based on what you learned from the application, can a firm who exports to the U.S. be charged with dumping even though the price they sell at home is lower?
A) No.
B) Yes, because the "constructed value" estimated by the department of Commerce can overstate the price that the firm charges at home.
C) Yes, because the firm that brings forward the charges can supply overstated figures data to the Department of Commerce.
D) B and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Suppose France produces only two goods, airplanes and grapes. If France has a comparative advantage in grapes, a move toward free trade will:
A) benefit grape workers, harm airplane workers, but harm the nation as a whole.
B) harm grape workers, harm airplane workers, but benefit the nation as a whole.
C) harm grape workers, benefit airplane workers, but benefit the nation as a whole.
D) benefit grape workers, harm airplane workers, but benefit the nation as a whole.
A) benefit grape workers, harm airplane workers, but harm the nation as a whole.
B) harm grape workers, harm airplane workers, but benefit the nation as a whole.
C) harm grape workers, benefit airplane workers, but benefit the nation as a whole.
D) benefit grape workers, harm airplane workers, but benefit the nation as a whole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Suppose the United States produces only two goods, grapes and tractors. If the United States has a comparative advantage in tractors, a move toward free trade will:
A) benefit tractor workers, harm grape workers, but harm the nation as a whole.
B) harm tractor workers, benefit grape workers, but benefit the nation as a whole.
C) benefit tractor workers, harm grape workers, but benefit the nation as a whole.
D) harm tractor workers, harm grape workers, but benefit the nation as a whole.
A) benefit tractor workers, harm grape workers, but harm the nation as a whole.
B) harm tractor workers, benefit grape workers, but benefit the nation as a whole.
C) benefit tractor workers, harm grape workers, but benefit the nation as a whole.
D) harm tractor workers, harm grape workers, but benefit the nation as a whole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Recall Application 4, "Trade, Consumption and Inequality," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, examples of non- durable goods include:
A) massages.
B) televisions.
C) toys.
D) cars.
According to the application, examples of non- durable goods include:
A) massages.
B) televisions.
C) toys.
D) cars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The increase in the U.S trade deficit with Mexico after NAFTA went into effect was most likely the result of:
A) predatory dumping by U.S. companies.
B) the devaluation of the peso.
C) predatory dumping by Mexican companies.
D) the appreciation of the peso.
A) predatory dumping by U.S. companies.
B) the devaluation of the peso.
C) predatory dumping by Mexican companies.
D) the appreciation of the peso.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If France can produce grapes at a higher opportunity cost than any other nation, France is said to have a(n) _______ in the production of grapes.
A) comparative advantage
B) absolute advantage
C) comparative disadvantage
D) autarky
A) comparative advantage
B) absolute advantage
C) comparative disadvantage
D) autarky

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
 Figure 18.1
Figure 18.1Refer to Figure 18.1. Duckland has a comparative advantage in the production of:
A) sunglasses.
B) umbrellas.
C) both umbrellas and sunglasses.
D) neither umbrellas nor sunglasses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Autarky refers to:
A) the equilibrium a nation reaches after trade begins.
B) a nation in the Middle East.
C) a situation in which there is no trade.
D) a situation in which nations trade goods and services.
A) the equilibrium a nation reaches after trade begins.
B) a nation in the Middle East.
C) a situation in which there is no trade.
D) a situation in which nations trade goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
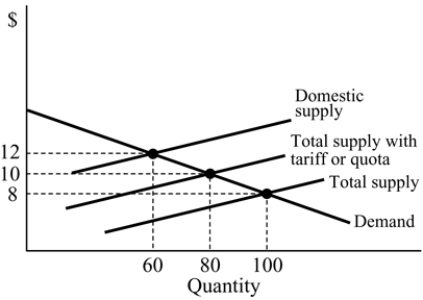 Figure 18.3
Figure 18.3Refer to Figure 18.3. With free trade, the equilibrium price is:
A) $10.
B) $12.
C) $8.
D) $0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
For a nation to have a comparative advantage in a good it must have:
A) more resources.
B) better resources.
C) a straight- line production possibilities curve.
D) a lower opportunity cost of producing that good.
A) more resources.
B) better resources.
C) a straight- line production possibilities curve.
D) a lower opportunity cost of producing that good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A tariff is a:
A) limit on the amount a good that can be imported.
B) voluntary reduction of exports.
C) tax on a domestically produced goods.
D) tax on an imported good.
A) limit on the amount a good that can be imported.
B) voluntary reduction of exports.
C) tax on a domestically produced goods.
D) tax on an imported good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Suppose there are only 2 nations A and B, and only two goods, x and y. If nation A produces only x, it can make 20x per day. If nation A produces only y, it can make 15y per day. If nation B produces only x, it can make 15x per day. If nation B produces only y, it can make 15y per day. After trade begins nation _______ will specialize in the production of x and nation _______ will specialize in the production of y.
A) A; A
B) B; A
C) A; B
D) B; B
A) A; A
B) B; A
C) A; B
D) B; B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
As a whole, nations are better off after trade and specialization because:
A) nations experience an outward shift of their production possibilities curve.
B) nations can consume along their production possibilities curve, which is above of their consumption possibilities curve.
C) nations can consume along their consumption possibilities curve, which is above of their production possibilities curve.
D) nations can consume along their consumption possibilities curve, which is below of their production possibilities curve.
A) nations experience an outward shift of their production possibilities curve.
B) nations can consume along their production possibilities curve, which is above of their consumption possibilities curve.
C) nations can consume along their consumption possibilities curve, which is above of their production possibilities curve.
D) nations can consume along their consumption possibilities curve, which is below of their production possibilities curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If France can produce grapes at a lower opportunity cost than any other nation, France is said to have a(n)_______ in the production of grapes.
A) autarky
B) comparative disadvantage
C) comparative advantage
D) absolute advantage
A) autarky
B) comparative disadvantage
C) comparative advantage
D) absolute advantage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
As punishment to Europe for refusing to remove their ban on U.S. and Canadian hormone- treated beef, the WTO allowed the U.S. and Canada:
A) to ban all goods and services imported from Europe.
B) impose retaliatory tariffs on a wide range of European products.
C) impose retaliatory quotas on a wide range of European products.
D) to ban only European beef from entering their countries.
A) to ban all goods and services imported from Europe.
B) impose retaliatory tariffs on a wide range of European products.
C) impose retaliatory quotas on a wide range of European products.
D) to ban only European beef from entering their countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
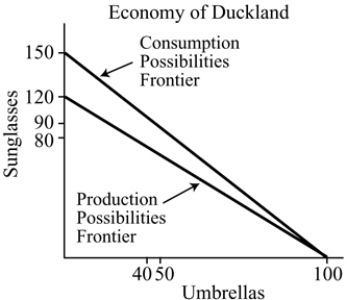 Figure 18.1
Figure 18.1Refer to Figure 18.1. In autarky, the maximum amount of umbrellas that Duckland can produce is:
A) 40.
B) 50.
C) 100.
D) 150.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The difficulty with enforcing anti- dumping laws is that predatory pricing is difficult to determine if the lower price is due to:
A) firm generosity.
B) higher costs.
C) economies of scale.
D) price discrimination.
A) firm generosity.
B) higher costs.
C) economies of scale.
D) price discrimination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What are some of the reasons why people protest against free trade?
A) Trading with other countries, as opposed to self- sufficiency, diminishes our independence and sovereignty.
B) Trading with other countries causes us to lose our cultural identity.
C) People believe that trade can cause income inequality.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) Trading with other countries, as opposed to self- sufficiency, diminishes our independence and sovereignty.
B) Trading with other countries causes us to lose our cultural identity.
C) People believe that trade can cause income inequality.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Suppose the US imposes a ban on imported steel from China because the Chinese steel was made with factories that pollute the environment. If China complains to the WTO regarding the US ban, the WTO will side with:
A) China, because the pollution in China does not harm the US directly.
B) the US, because a country can determine what goods can and cannot enter its borders.
C) the US, because US factories have to comply with US environmental standards.
D) China, because the WTO is in favor of industries that generate pollution.
A) China, because the pollution in China does not harm the US directly.
B) the US, because a country can determine what goods can and cannot enter its borders.
C) the US, because US factories have to comply with US environmental standards.
D) China, because the WTO is in favor of industries that generate pollution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In 2002, President Bush imposed a tariff on imported steel in order to protect domestic steel producers. What was the reason why the tariff ended?
A) the threat of a possible recession in the U.S.
B) the decrease in demand for steel by US industries
C) the threat of retaliatory tariffs by Europe
D) the improved profitability of domestic steel firms
A) the threat of a possible recession in the U.S.
B) the decrease in demand for steel by US industries
C) the threat of retaliatory tariffs by Europe
D) the improved profitability of domestic steel firms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Recall Application 1, "The Impact of Tariffs on the Poor," to answer the following questions:
After reading the application, we can conclude that U.S. tariffs hurt poor consumer's the disproportionately because:
A) U.S. tariffs fall heaviest on labor intensive goods.
B) U.S. tariffs are on goods like apparel items that poor consumers spend a larger fraction of income on.
C) U.S. tariffs fall heaviest on the lowest price goods in a category.
D) all of the above
After reading the application, we can conclude that U.S. tariffs hurt poor consumer's the disproportionately because:
A) U.S. tariffs fall heaviest on labor intensive goods.
B) U.S. tariffs are on goods like apparel items that poor consumers spend a larger fraction of income on.
C) U.S. tariffs fall heaviest on the lowest price goods in a category.
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
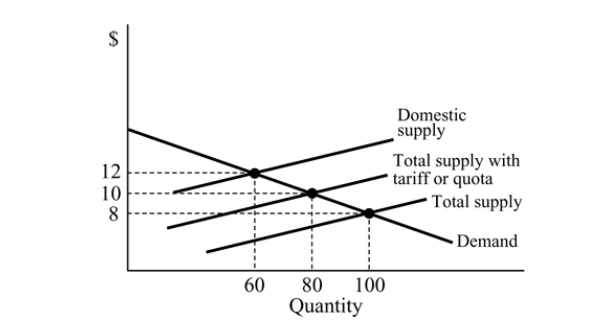 Figure 18.3
Figure 18.3Refer to Figure 18.3. With an import ban, the equilibrium price is:
A) $8.
B) $0.
C) $12.
D) $10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The combinations of goods a nation can consume after trade and specialization begin are illustrated by the _______ curve.
A) supply
B) demand
C) consumption possibilities
D) production possibilities
A) supply
B) demand
C) consumption possibilities
D) production possibilities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A tax on an imported good is known as a(n):
A) voluntary export restraint.
B) import quota.
C) import ban.
D) tariff.
A) voluntary export restraint.
B) import quota.
C) import ban.
D) tariff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If Nation A can produce shirts at a lower opportunity cost than any other nation, Nation A is said to have a(n) _______ in the production of shirts.
A) comparative advantage
B) comparative disadvantage
C) absolute advantage
D) autarky
A) comparative advantage
B) comparative disadvantage
C) absolute advantage
D) autarky

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Voluntary Export Restraints (VERs):
A) are legal under the WTO rules.
B) have the same effect as an import quota.
C) violate the spirit of international trade agreements.
D) all of the above
A) are legal under the WTO rules.
B) have the same effect as an import quota.
C) violate the spirit of international trade agreements.
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
An import quota:
A) increases the amount of a good imported, thus increasing prices.
B) increases the amount of a good imported, thus decreasing prices.
C) limits the amount of a good that can be imported, thus decreasing prices.
D) limits the amount of a good that can be imported, thus increasing prices.
A) increases the amount of a good imported, thus increasing prices.
B) increases the amount of a good imported, thus decreasing prices.
C) limits the amount of a good that can be imported, thus decreasing prices.
D) limits the amount of a good that can be imported, thus increasing prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48

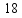
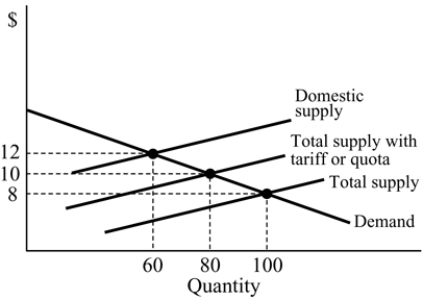 Figure 18.3
Figure 18.3Refer to Figure 18.3. With a tariff or quota, the equilibrium quantity is:
A) 60.
B) 80.
C) 40.
D) 100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Recall Application 3, "Are They Really Dumping?" to answer the following questions:
According to the application, how many cases of dumping in 1995- 1998 used the actual price in the foreign market to make a determination if a dumping occurred?
A) 4 out of 141
B) 137 out of 141
C) all 141 out of 141
D) none of the 141
According to the application, how many cases of dumping in 1995- 1998 used the actual price in the foreign market to make a determination if a dumping occurred?
A) 4 out of 141
B) 137 out of 141
C) all 141 out of 141
D) none of the 141

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50

Refer to Table 18.2. The opportunity cost of tractors in Japan is:
A) 2 stereos.
B) 4 stereos.
C) 1/4 stereo.
D) 1/2 stereo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following trade agreements provides for the development of a single market among its members?
A) European Union
B) World Trade Organization
C) Asian Pacific Economic Cooperation
D) North American Free Trade Agreement
A) European Union
B) World Trade Organization
C) Asian Pacific Economic Cooperation
D) North American Free Trade Agreement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A nation can produce anywhere _______ its production possibilities curve.
A) on
B) outside
C) inside
D) both A and C
A) on
B) outside
C) inside
D) both A and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
An import ban results in:
A) a decrease in the supply of the product.
B) a decrease in the quantity of the product bought and sold.
C) an increase in the product's price.
D) all of the above
A) a decrease in the supply of the product.
B) a decrease in the quantity of the product bought and sold.
C) an increase in the product's price.
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Refer to Table 18.1. If Scotland produces 10 bagpipes, how many accordions can they produce for the rest of the day?
A) 15
B) 20
C) 25
D) 40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
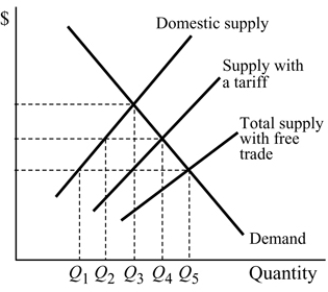 Figure 18.5
Figure 18.5In Figure 18.5, compared to free trade, the tariff causes domestic production of the good to:
A) increase by Q5- Q4.
B) decrease by Q5- Q4.
C) increase by Q2- Q1.
D) decrease by Q2- Q1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
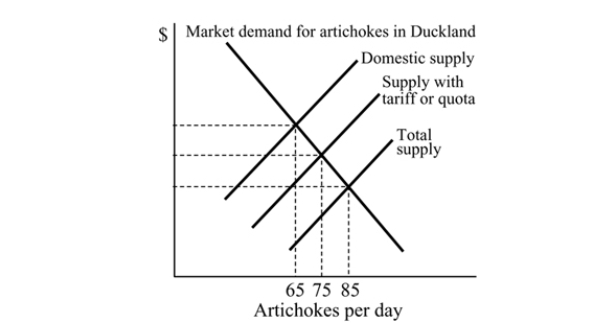 Figure 18.4
Figure 18.4Refer to Figure 18.4. With free trade, how many artichokes are produced domestically in Duckland?
A) 0
B) 65
C) 30
D) 75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
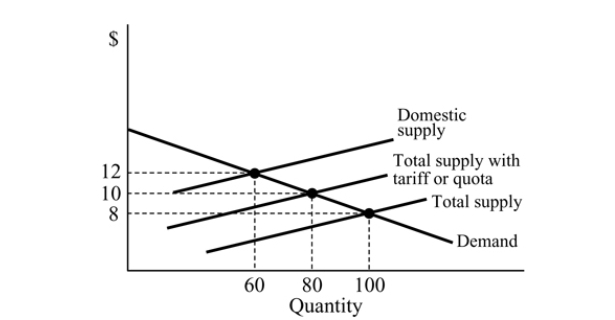 Figure 18.3
Figure 18.3Refer to Figure 18.3. With an import ban, domestic production is:
A) 80.
B) 0.
C) 60.
D) 100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58

Refer to Table 18.2. Possible terms of trade between the U.S. and Japan are:
A) 1 tractor for 3 stereos.
B) 1 tractor for 1/3 stereo.
C) 1 stereo for 1/3 tractor.
D) 1 stereo for 8 tractors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
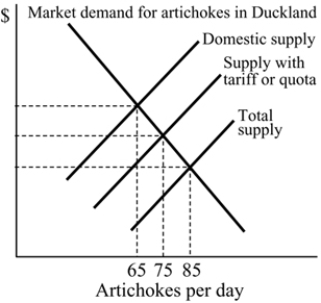 Figure 18.4
Figure 18.4Refer to Figure 18.4. With an import ban, how many artichokes are produced domestically in Duckland?
A) 30
B) 85
C) 75
D) 65

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The example of the VCRs from Korea illustrates dumping due to:
A) predatory pricing.
B) price discrimination.
C) avoidance of environmental laws.
D) retaliatory trade practices.
A) predatory pricing.
B) price discrimination.
C) avoidance of environmental laws.
D) retaliatory trade practices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The WTO and GATT promote trade by:
A) reducing tariffs.
B) setting the prices of goods sold internationally.
C) directing trade.
D) all of the above
A) reducing tariffs.
B) setting the prices of goods sold internationally.
C) directing trade.
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
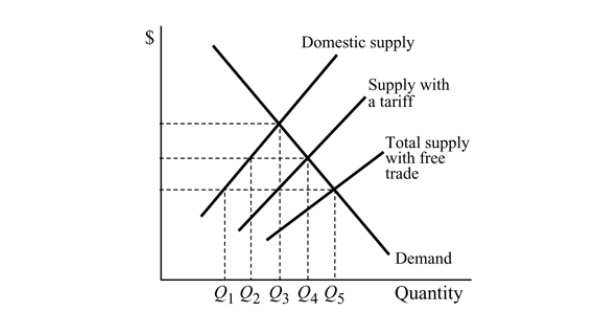 Figure 18.5
Figure 18.5For the good in Figure 18.5 ,with the tariff, the people in the country will produce:
A) Q1.
B) Q5.
C) Q2.
D) Q4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Recall Application 1, "The Impact of Tariffs on the Poor," to answer the following questions:
Because U.S. tariffs are higher on textiles, footwear and apparel items, U.S. tariffs fall relatively most heavily on:
A) the government.
B) the rich.
C) the middle class.
D) the poor.
Because U.S. tariffs are higher on textiles, footwear and apparel items, U.S. tariffs fall relatively most heavily on:
A) the government.
B) the rich.
C) the middle class.
D) the poor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Recall Application 3, "Are They Really Dumping?" to answer the following questions:
Based on what you learned from the application, how will the "constructed value" method used by the Department of Commerce affect the number of cases that it will deem as dumping?
A) The Department of Commerce will identify fewer cases of dumping into the U.S.
B) The Department of Commerce will identify more cases of dumping into the U.S.
C) The Department of Commerce will identify all cases brought in front of them as "not dumping."
D) The Department of Commerce will correctly identify all cases as "dumping."
Based on what you learned from the application, how will the "constructed value" method used by the Department of Commerce affect the number of cases that it will deem as dumping?
A) The Department of Commerce will identify fewer cases of dumping into the U.S.
B) The Department of Commerce will identify more cases of dumping into the U.S.
C) The Department of Commerce will identify all cases brought in front of them as "not dumping."
D) The Department of Commerce will correctly identify all cases as "dumping."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
During the 1980s, firms from _______ were accused of dumping VCRs in Europe.
A) Taiwan
B) Mexico
C) Japan
D) Korea
A) Taiwan
B) Mexico
C) Japan
D) Korea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Voluntary export restraints:
A) violate the spirit of international trade agreements.
B) have the same effect as an import ban.
C) are illegal under the WTO rules.
D) all of the above
A) violate the spirit of international trade agreements.
B) have the same effect as an import ban.
C) are illegal under the WTO rules.
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
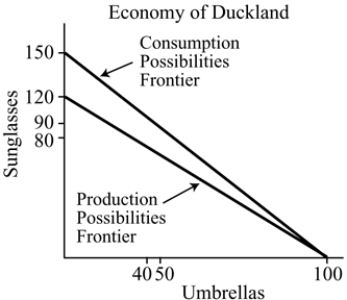 Figure 18.1
Figure 18.1Refer to Figure 18.1. In autarky, the maximum amount of sunglasses that Duckland can produce is:
A) 150.
B) 100.
C) 120.
D) 90.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The phenomenon that occurs when an infant industry becomes better and more efficient as it produces more of a good is called:
A) learning to walk.
B) learning by doing.
C) crawling then walking.
D) comparative advantage.
A) learning to walk.
B) learning by doing.
C) crawling then walking.
D) comparative advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
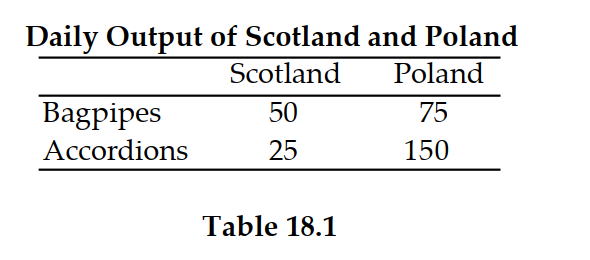
Refer to Table 18.1. The opportunity cost of a bagpipe in Poland is:
A) 1/3 accordion.
B) 1/2 accordion.
C) 6 accordions.
D) 2 accordions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
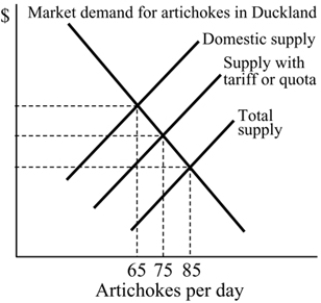 Figure 18.4
Figure 18.4Refer to Figure 18.4. With a tariff or quota, what is the equilibrium quantity of artichokes in Duckland?
A) 85
B) 30
C) 75
D) 65

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Suppose nation A produces only two goods, apples and oranges . If nation A produces only apples, it can make 20 apples per day. If nation A produces only oranges, it can make 15 oranges per day. If the country has a constant production trade- off between apples and oranges, then the opportunity cost of one apple in nation A is:
A) 1.33 oranges.
B) 20 oranges.
C) 15 oranges.
D) .75 oranges.
A) 1.33 oranges.
B) 20 oranges.
C) 15 oranges.
D) .75 oranges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
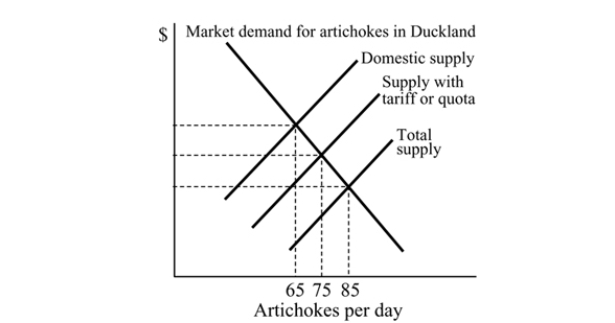 Figure 18.4
Figure 18.4Refer to Figure 18.4. With a tariff or quota, what is the equilibrium price of artichokes in Duckland?
A) $4
B) $5
C) $2
D) $3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following situations will arise in the domestic market following the imposition of a voluntary export restraint?
A) imports decrease, domestic production increases, prices increase
B) imports decrease, domestic production increases, prices decrease
C) imports increase, domestic production increases, prices increase
D) imports increase, domestic production decreases, prices decrease
A) imports decrease, domestic production increases, prices increase
B) imports decrease, domestic production increases, prices decrease
C) imports increase, domestic production increases, prices increase
D) imports increase, domestic production decreases, prices decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
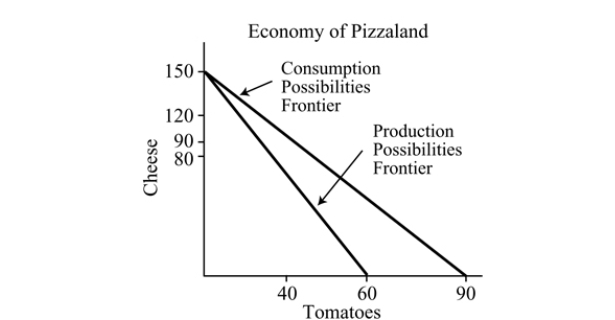 Figure 18.2
Figure 18.2Refer to Figure 18.2. In autarky, the maximum amount of cheese that Pizzaland can produce is:
A) 120.
B) 90.
C) 80.
D) 150.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Recall Application 2, "Protection for Candle Makers," to answer the following questions:
In the application, the French economist Bastiat petitioned for protection of French candle makers from unfair competition from:
A) imported whale oil lamps.
B) the sun.
C) electric lights.
D) foreign candle makers.
In the application, the French economist Bastiat petitioned for protection of French candle makers from unfair competition from:
A) imported whale oil lamps.
B) the sun.
C) electric lights.
D) foreign candle makers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
_______ occurs when a firm cuts prices below production costs in a deliberate attempt to drive competitors out of business.
A) Deliberate dumping.
B) Price discrimination
C) Predatory pricing
D) Voracious dumping
A) Deliberate dumping.
B) Price discrimination
C) Predatory pricing
D) Voracious dumping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
According to the infant industry argument for trade protectionism:
A) tariffs imposed to aid new industries should never be removed.
B) new industries are capable of competing with established rivals.
C) trade barriers must be used to protect domestic workers.
D) new industries need to be shielded in the early stages of learning by doing.
A) tariffs imposed to aid new industries should never be removed.
B) new industries are capable of competing with established rivals.
C) trade barriers must be used to protect domestic workers.
D) new industries need to be shielded in the early stages of learning by doing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A possible reason to impose a protectionist policy such as a tariff is to:
A) slow domestic production.
B) increase the welfare of domestic consumers.
C) aid other nations in developing their own industries.
D) protect domestic workers from foreign competition.
A) slow domestic production.
B) increase the welfare of domestic consumers.
C) aid other nations in developing their own industries.
D) protect domestic workers from foreign competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
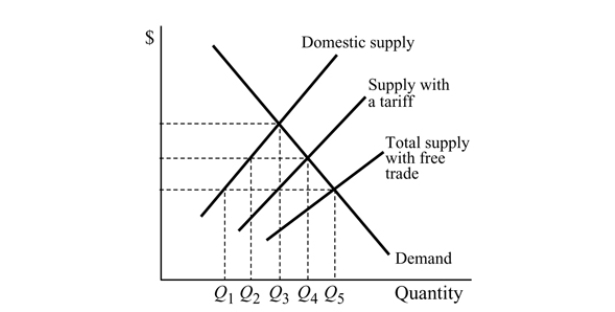 Figure 18.5
Figure 18.5For the good in Figure 18.5, with free trade, the people in the country will buy:
A) Q4.
B) Q3.
C) Q5.
D) Q2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The production possibilities curve represents the set of all:
A) nonlinear forms of production in the economy.
B) combinations of goods and services that can be used in the production of other goods and services.
C) factors of production that can be used to manufacture goods and services.
D) feasible combinations of goods given that a nation's resources are fully employed.
A) nonlinear forms of production in the economy.
B) combinations of goods and services that can be used in the production of other goods and services.
C) factors of production that can be used to manufacture goods and services.
D) feasible combinations of goods given that a nation's resources are fully employed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 226 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



