Deck 19: The World of International Finance
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/189
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: The World of International Finance
1
Recall Application 3, "A Downside to the Euro," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, how did countries like Spain and Greece benefit from being members of the Euro- zone?
A) By using the euro, Spanish and Greek exporters can sell their goods to other countries without an exchange rate premium.
B) By using the euro, investors would be assured that Spain and Greece would pursue inflationary policies.
C) By using the euro, Spain and Greece now have full control of monetary policy.
D) By using the euro, investors would no longer fear that Spain and Greece would pursue inflationary policies.
According to the application, how did countries like Spain and Greece benefit from being members of the Euro- zone?
A) By using the euro, Spanish and Greek exporters can sell their goods to other countries without an exchange rate premium.
B) By using the euro, investors would be assured that Spain and Greece would pursue inflationary policies.
C) By using the euro, Spain and Greece now have full control of monetary policy.
D) By using the euro, investors would no longer fear that Spain and Greece would pursue inflationary policies.
By using the euro, investors would no longer fear that Spain and Greece would pursue inflationary policies.
2
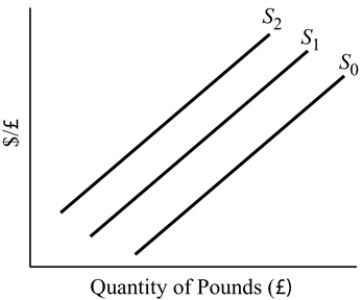 Figure 19.4
Figure 19.4Refer to Figure 19.4. Which of the following will shift the supply of pounds from S1 to S0?
A) a decrease in the British price level
B) a decrease in British income
C) an increase in the British price level
D) an increase in U.S. income
an increase in the British price level
3
According to purchasing power parity, if it takes five times as many Russian rubles to buy a basket of goods in Russia as it takes U.S. dollars to buy a basket of goods in the United States, then:
A) the equilibrium exchange rate should be five rubles per dollar.
B) there is a lower rate of inflation in Russia than in the United States.
C) the equilibrium exchange rate should be one ruble per five dollars.
D) the law of one price no longer holds.
A) the equilibrium exchange rate should be five rubles per dollar.
B) there is a lower rate of inflation in Russia than in the United States.
C) the equilibrium exchange rate should be one ruble per five dollars.
D) the law of one price no longer holds.
the equilibrium exchange rate should be five rubles per dollar.
4
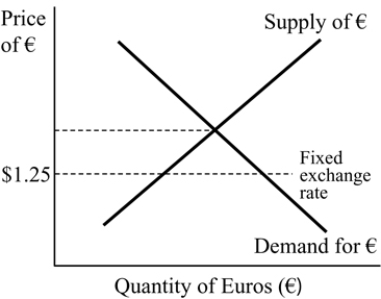 Figure 19.5
Figure 19.5From Figure 19.5 above, suppose the U.S. is currently fixing its exchange rate at $1.25 per euro. If the U.S. wants to attain equilibrium in the foreign exchange market, it must:
A) devalue its currency.
B) abandon the U.S. dollar in favor of the euro.
C) keep the exchange rate unchanged.
D) revalue its currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The system of accounts that measures transactions of goods, services, income, and financial assets between domestic households, businesses, and governments and residents of the rest of the world during a specific time period is called the:
A) current account.
B) exchange rate.
C) balance of payments.
D) financial account.
A) current account.
B) exchange rate.
C) balance of payments.
D) financial account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The trade deficit in Mexico did not cause a problem prior to 1994 because:
A) oil prices were high and Mexico was a net exporter of oil.
B) Mexicans abroad remitted huge sums of foreign currencies back to Mexico.
C) foreign investors willingly traded their foreign currencies for Mexican pesos to buy Mexican securities.
D) the Mexican peso was pegged to the U.S. dollar.
A) oil prices were high and Mexico was a net exporter of oil.
B) Mexicans abroad remitted huge sums of foreign currencies back to Mexico.
C) foreign investors willingly traded their foreign currencies for Mexican pesos to buy Mexican securities.
D) the Mexican peso was pegged to the U.S. dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
All other things equal, an appreciation of the U.S. real exchange rate causes:
A) a decrease in imports and an increase in exports.
B) an increase in imports and an increase in exports.
C) an increase in imports and a decrease in exports.
D) a decrease in imports and a decrease in exports.
A) a decrease in imports and an increase in exports.
B) an increase in imports and an increase in exports.
C) an increase in imports and a decrease in exports.
D) a decrease in imports and a decrease in exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Under a flexible exchange rate system, the exchange rate between two currencies is determined by:
A) the demand and supply of both countries' currencies.
B) the Bretton Woods agreement.
C) the governments of both countries.
D) the International Monetary Fund.
A) the demand and supply of both countries' currencies.
B) the Bretton Woods agreement.
C) the governments of both countries.
D) the International Monetary Fund.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The theory of international exchange that holds that exchange rates are set so that the price of similar goods in different countries is the same as:
A) price- feedback.
B) trade- feedback.
C) purchasing power parity.
D) the J- curve theory.
A) price- feedback.
B) trade- feedback.
C) purchasing power parity.
D) the J- curve theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Recall Application 1, "The Chinese Yuan and Big Macs," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, the dollar price of a Big Mac in the US is higher than the dollar price of the Big Mac in:
A) Switzerland.
B) China.
C) Mexico.
D) both B and C are correct.
According to the application, the dollar price of a Big Mac in the US is higher than the dollar price of the Big Mac in:
A) Switzerland.
B) China.
C) Mexico.
D) both B and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Those who supply _______ are holders of pounds seeking to exchange them for .
A) pounds; dollars
B) both pounds and dollars; dollars
C) pounds; pounds
D) dollars; pounds
A) pounds; dollars
B) both pounds and dollars; dollars
C) pounds; pounds
D) dollars; pounds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
One benefit of flexible exchange rates is that flexible exchange rates are
A) making international transactions easier and cheaper.
B) under the full control of the government.
C) changing as the price levels and interest rates between countries change.
D) very volatile.
A) making international transactions easier and cheaper.
B) under the full control of the government.
C) changing as the price levels and interest rates between countries change.
D) very volatile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
_______ is the situation where the central bank buys or sells foreign currencies to affect the country's exchange rate.
A) Capital flight
B) Foreign exchange market intervention
C) Expansionary monetary policy
D) Revaluation
A) Capital flight
B) Foreign exchange market intervention
C) Expansionary monetary policy
D) Revaluation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If the income from investments by Americans abroad is less than the income from investments by non- Americans in the U.S. , then net income from abroad is:
A) zero.
B) decreasing.
C) positive.
D) negative.
A) zero.
B) decreasing.
C) positive.
D) negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
All other things equal, an appreciation of the U.S. real exchange rate causes consumers to buy _______domestic goods and _______ foreign goods.
A) fewer; more
B) more; more
C) fewer; fewer
D) more; fewer
A) fewer; more
B) more; more
C) fewer; fewer
D) more; fewer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The real exchange rate is the:
A) price of another currency minus the inflation rate.
B) rate at which an individual can trade the currency of one country for another.
C) rate at which domestic goods are traded for foreign goods.
D) the price of another currency.
A) price of another currency minus the inflation rate.
B) rate at which an individual can trade the currency of one country for another.
C) rate at which domestic goods are traded for foreign goods.
D) the price of another currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A U.S. individual buys shares in a Swiss company. This transaction will be entered as:
A) a negative in the U.S. current account.
B) a negative in the U.S. financial account.
C) a positive in the U.S. current account.
D) a positive in the U.S. capital account.
A) a negative in the U.S. current account.
B) a negative in the U.S. financial account.
C) a positive in the U.S. current account.
D) a positive in the U.S. capital account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If U.S. interest rates fall relative to British interest rates:
A) the demand for the pound decreases and the dollar depreciates.
B) the demand for the pound increases and the dollar appreciates.
C) the demand for the pound decreases and the dollar appreciates.
D) the demand for the pound increases and the dollar depreciates.
A) the demand for the pound decreases and the dollar depreciates.
B) the demand for the pound increases and the dollar appreciates.
C) the demand for the pound decreases and the dollar appreciates.
D) the demand for the pound increases and the dollar depreciates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The Bretton Woods exchange rate system was
A) a floating exchange rate system.
B) a single currency system.
C) a fixed exchange rate system.
D) both a fixed and a flexible exchange rate system.
A) a floating exchange rate system.
B) a single currency system.
C) a fixed exchange rate system.
D) both a fixed and a flexible exchange rate system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
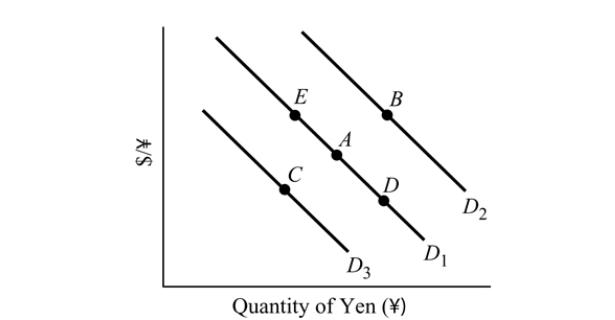 Figure 19.3
Figure 19.3Refer to Figure 19.3. The market equilibrium for yen is currently at Point A. An increase in income in the U.S. causes a movement to Point _______.
A) E
B) C
C) B
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
More German companies start to invest in the United States. This will lead to a(n):
A) increase in the supply of dollars and a decrease in the demand for euros.
B) decrease in the demand for dollars and an increase in the demand for euros.
C) increase in the demand for dollars and a decrease in the supply of euros.
D) increase in the demand for dollars and an increase in the supply of euros.
A) increase in the supply of dollars and a decrease in the demand for euros.
B) decrease in the demand for dollars and an increase in the demand for euros.
C) increase in the demand for dollars and a decrease in the supply of euros.
D) increase in the demand for dollars and an increase in the supply of euros.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In 1971, most countries, including the United States:
A) adopted a new system of fixed exchange rates.
B) returned to the gold standard.
C) gave up trying to fix exchange rates formally and began allowing them to be determined essentially by supply and demand.
D) adopted a single, internationally accepted currency whose use is limited to international transactions.
A) adopted a new system of fixed exchange rates.
B) returned to the gold standard.
C) gave up trying to fix exchange rates formally and began allowing them to be determined essentially by supply and demand.
D) adopted a single, internationally accepted currency whose use is limited to international transactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The real exchange rate between the U.S. and Japan is expressed as:
A) the number of baskets of U.S. goods that you can buy with a yen.
B) the amount of dollars you can buy with a Japanese yen.
C) the number of baskets of Japanese goods that you can buy with a basket of goods in the U.S.
D) the number of baskets of Japanese goods that you can buy with a U.S. dollar.
A) the number of baskets of U.S. goods that you can buy with a yen.
B) the amount of dollars you can buy with a Japanese yen.
C) the number of baskets of Japanese goods that you can buy with a basket of goods in the U.S.
D) the number of baskets of Japanese goods that you can buy with a U.S. dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is not included in the current account?
A) statistical discrepancy
B) investment income from abroad
C) exports of goods
D) export of services
A) statistical discrepancy
B) investment income from abroad
C) exports of goods
D) export of services

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Recall Application 1, "The Chinese Yuan and Big Macs," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, the dollar price of a Big Mac in the US is lower than the dollar price of the Big Mac in:
A) the United Kingdom.
B) China.
C) Switzerland.
D) Mexico.
According to the application, the dollar price of a Big Mac in the US is lower than the dollar price of the Big Mac in:
A) the United Kingdom.
B) China.
C) Switzerland.
D) Mexico.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A high rate of inflation in one country relative to another puts pressure on the exchange rate between the two countries, and there is a general tendency for the:
A) currency of the high- inflation country to depreciate.
B) currency of the high- inflation country to appreciate.
C) currency of the low- inflation country to depreciate.
D) none of the above
A) currency of the high- inflation country to depreciate.
B) currency of the high- inflation country to appreciate.
C) currency of the low- inflation country to depreciate.
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Recall Application 3, "A Downside to the Euro," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, what caused the increase in wage rates in Greece?
A) An export boom pushed the unemployment rate well below the natural rate.
B) The government instituted a new minimum wage law, raising minimum wages 50 percent.
C) Greece pursue expansionary monetary policies immediately after joining the Euro- zone.
D) An investment boom financed a wide range of projects in the country, increasing the demand for workers.
According to the application, what caused the increase in wage rates in Greece?
A) An export boom pushed the unemployment rate well below the natural rate.
B) The government instituted a new minimum wage law, raising minimum wages 50 percent.
C) Greece pursue expansionary monetary policies immediately after joining the Euro- zone.
D) An investment boom financed a wide range of projects in the country, increasing the demand for workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is not included in the U.S. financial account?
A) change in U.S. government assets held abroad
B) change in foreign private assets held in the United States
C) Mexico's debt to the U.S. that was forgiven
D) change in private U.S. assets held abroad
A) change in U.S. government assets held abroad
B) change in foreign private assets held in the United States
C) Mexico's debt to the U.S. that was forgiven
D) change in private U.S. assets held abroad

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When a country experiences a balance of payments surplus in a fixed exchange rate system, it usually _______ the currency to reduce exports.
A) tries to hold constant the value of
B) abandons
C) allows the revaluation of
D) allows the devaluation of
A) tries to hold constant the value of
B) abandons
C) allows the revaluation of
D) allows the devaluation of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In 1986, the U.S. net international investment position was $136 billion. This means that in 1986:
A) the U.S. was a net lender.
B) foreign governments made $136 billion in investments in the US.
C) the U.S. government made $136 billion in investments abroad.
D) the U.S. was a net borrower.
A) the U.S. was a net lender.
B) foreign governments made $136 billion in investments in the US.
C) the U.S. government made $136 billion in investments abroad.
D) the U.S. was a net borrower.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
One drawback of a fixed exchange rate is that it:
A) requires the coordination of economic policies between countries.
B) makes international transactions more expensive.
C) requires previous authorization of the IMF in order to be altered.
D) makes international transactions less efficient.
A) requires the coordination of economic policies between countries.
B) makes international transactions more expensive.
C) requires previous authorization of the IMF in order to be altered.
D) makes international transactions less efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
With a fixed exchange rate system, the balance of payments of a country:
A) is always negative.
B) always equals zero.
C) is always positive.
D) can be zero, positive or negative.
A) is always negative.
B) always equals zero.
C) is always positive.
D) can be zero, positive or negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The sum of the current account + the capital account + the financial account equals:
A) net international investment.
B) statistical discrepancy.
C) zero.
D) the balance of payments.
A) net international investment.
B) statistical discrepancy.
C) zero.
D) the balance of payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Under the Bretton Woods system, which country directly pegged its currency to gold?
A) Germany
B) the UK
C) the U.S.
D) Japan
A) Germany
B) the UK
C) the U.S.
D) Japan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What was the U.S. response to the Mexican currency crisis of 1994?
A) The U.S., along with other international agencies , arranged for Mexico to borrow dollars with an extended repayment period.
B) The U.S. converted the Mexican peso into US dollars to shield itself from the currency crisis.
C) The U.S. did not do anything, and allowed the Mexican economy to collapse.
D) The U.S. bought a lot of Mexican- made goods to increase Mexico's net exports.
A) The U.S., along with other international agencies , arranged for Mexico to borrow dollars with an extended repayment period.
B) The U.S. converted the Mexican peso into US dollars to shield itself from the currency crisis.
C) The U.S. did not do anything, and allowed the Mexican economy to collapse.
D) The U.S. bought a lot of Mexican- made goods to increase Mexico's net exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following exacerbated the problems caused by the trade deficit in Mexico prior to 1994?
A) the government and firms began to borrow in U.S. dollars instead of Mexican pesos.
B) political turmoil forced foreign investors to pull out their investments in the country.
C) the Mexican government did not undertake steps to slow down the growth rate of prices in Mexico.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) the government and firms began to borrow in U.S. dollars instead of Mexican pesos.
B) political turmoil forced foreign investors to pull out their investments in the country.
C) the Mexican government did not undertake steps to slow down the growth rate of prices in Mexico.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
An increase in the U.S. interest rate relative to the British interest rate will cause a(n):
A) increase in demand for dollars and an increase in the demand for British pounds.
B) decrease in demand for dollars and an increase in the supply of British pounds.
C) increase in demand for dollars and a reduction in the supply of British pounds.
D) increase in demand for dollars and an increase in the supply of British pounds.
A) increase in demand for dollars and an increase in the demand for British pounds.
B) decrease in demand for dollars and an increase in the supply of British pounds.
C) increase in demand for dollars and a reduction in the supply of British pounds.
D) increase in demand for dollars and an increase in the supply of British pounds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Suppose that a laptop computer costs 840 British pounds in the United Kingdom and $1,400 in the United States. If the nominal exchange rate is 0.6 pounds per U.S. dollar, then the real exchange rate is:
A) 1 British laptop computer per U.S. laptop computer.
B) 3/5 British laptop computer per U.S. laptop computer.
C) 5/3 British laptop computer per U.S. laptop computer.
D) none of the above
A) 1 British laptop computer per U.S. laptop computer.
B) 3/5 British laptop computer per U.S. laptop computer.
C) 5/3 British laptop computer per U.S. laptop computer.
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following increases the price of the dollar relative to the Mexican peso?
A) an increase in the supply of dollars
B) an increase in the demand for dollars
C) a decrease in the supply of pesos
D) an increase in the demand for pesos
A) an increase in the supply of dollars
B) an increase in the demand for dollars
C) a decrease in the supply of pesos
D) an increase in the demand for pesos

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
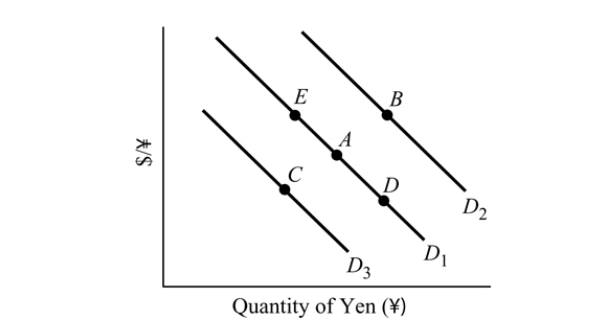 Figure 19.3
Figure 19.3Refer to Figure 19.3. The market for yen is currently at Point A. An increase in the U.S. interest rates causes the equilibrium to move to point _______ and the U.S. dollar will _______.
A) C; appreciate
B) B; depreciate
C) D; appreciate
D) A; appreciate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
An increase in U.S. exports to Russia _______ the demand for U.S. dollars and _______ the supply of Russian rubles.
A) decreases; increases
B) increases; decreases
C) decreases; decreases
D) increases; increases
A) decreases; increases
B) increases; decreases
C) decreases; decreases
D) increases; increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Recall Application 4, "The Argentine Financial Crisis," to answer the question below:
The Argentine economy suffered a depression after the financial crisis in 2002 because:
A) imports increased.
B) the freeze in bank accounts caused a sharp increase in wealth.
C) the freeze in bank accounts caused a sharp decrease in wealth.
D) imports decreased.
The Argentine economy suffered a depression after the financial crisis in 2002 because:
A) imports increased.
B) the freeze in bank accounts caused a sharp increase in wealth.
C) the freeze in bank accounts caused a sharp decrease in wealth.
D) imports decreased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Since reaching a high in July 2008, the price of oil has been fluctuating at lower prices worldwide. Based on the argument provided in the Application, how will this drop in the price of oil affect the amount of international investment made by Russia.
A) It will experience unpredictable increases and decreases.
B) It will probably increase.
C) It will probably decrease.
D) It will probably stay the same.
A) It will experience unpredictable increases and decreases.
B) It will probably increase.
C) It will probably decrease.
D) It will probably stay the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The Mexican financial crisis of 1994 did not develop into a generalized financial collapse thanks to:
A) a large revaluation of the Mexican peso.
B) massive lending of dollars to Mexico.
C) the creation of the euro.
D) the coordination of Mexican monetary policy with the Fed.
A) a large revaluation of the Mexican peso.
B) massive lending of dollars to Mexico.
C) the creation of the euro.
D) the coordination of Mexican monetary policy with the Fed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Recall Application 2, "World Savings and the U.S. Current Account Deficits," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, the U.S. can continue having current account deficits only because:
A) other countries choose to buy U.S. patents.
B) other countries choose to sell foreign patents.
C) other countries choose to purchase U.S. assets.
D) other countries choose to sell foreign assets.
According to the application, the U.S. can continue having current account deficits only because:
A) other countries choose to buy U.S. patents.
B) other countries choose to sell foreign patents.
C) other countries choose to purchase U.S. assets.
D) other countries choose to sell foreign assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Recall Application 1, "The Chinese Yuan and Big Macs," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, because the actual dollar- yuan exchange rate was 6.8 yuan per U.S. dollar and the predicted purchasing power exchange rate (using the Big Mac) in China is 3.49 yuan, then:
A) the dollar is undervalued and the Big Mac is overvalued.
B) the dollar is undervalued.
C) the Big Mac is overvalued.
D) the yuan is undervalued.
According to the application, because the actual dollar- yuan exchange rate was 6.8 yuan per U.S. dollar and the predicted purchasing power exchange rate (using the Big Mac) in China is 3.49 yuan, then:
A) the dollar is undervalued and the Big Mac is overvalued.
B) the dollar is undervalued.
C) the Big Mac is overvalued.
D) the yuan is undervalued.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The real exchange rate is the:
A) the price of U.S. goods and services relative to foreign goods and services.
B) price of foreign goods relative to U.S. dollars.
C) the price of U.S. goods and services relative to other U.S. goods and services.
D) price of domestic goods relative to foreign currencies.
A) the price of U.S. goods and services relative to foreign goods and services.
B) price of foreign goods relative to U.S. dollars.
C) the price of U.S. goods and services relative to other U.S. goods and services.
D) price of domestic goods relative to foreign currencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The law of one price indicates that the:
A) prices will adjust so that the price of similar goods in different countries is the same.
B) exchange rate will always exceed 1.
C) exchange rate will always equal 1.
D) interest rate on domestic and foreign bonds must be the same.
A) prices will adjust so that the price of similar goods in different countries is the same.
B) exchange rate will always exceed 1.
C) exchange rate will always equal 1.
D) interest rate on domestic and foreign bonds must be the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Suppose a pound of dry roasted coffee beans cost $3 in the United States and 6 pounds in England. The law of one price would predict that the exchange rate in the long- run is:
A) $1 = 2 pounds.
B) 1 pound = $4.
C) $1 = 3 pounds.
D) $1 = 1/2 pound.
A) $1 = 2 pounds.
B) 1 pound = $4.
C) $1 = 3 pounds.
D) $1 = 1/2 pound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In the supply and demand for U.S. dollars in Europe, who is a demander in that market?
A) Americans who want to invest in Europe
B) Americans who want to bring their investments back to the U.S.
C) Europeans who want to invest in the U.S.
D) B and C only
A) Americans who want to invest in Europe
B) Americans who want to bring their investments back to the U.S.
C) Europeans who want to invest in the U.S.
D) B and C only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In 1986, the U.S. net international investment position was $136 billion. This means that the amount of:
A) U.S. holdings of foreign assets was less than the foreign holdings of U.S. assets by $136 billion.
B) U.S. holdings of foreign assets exceeded the foreign holdings of U.S. assets by $136 billion.
C) the foreign holdings of U.S. assets was $136 billion.
D) U.S. holdings of foreign assets was $136 billion.
A) U.S. holdings of foreign assets was less than the foreign holdings of U.S. assets by $136 billion.
B) U.S. holdings of foreign assets exceeded the foreign holdings of U.S. assets by $136 billion.
C) the foreign holdings of U.S. assets was $136 billion.
D) U.S. holdings of foreign assets was $136 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
When the demand of a country's currency exceeds the supply of the currency at the current exchange rate, the country experiences:
A) a balance of payments surplus.
B) a capital account surplus.
C) a capital account deficit.
D) a balance of payments deficit.
A) a balance of payments surplus.
B) a capital account surplus.
C) a capital account deficit.
D) a balance of payments deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The balance of payments is divided into three major accounts, the:
A) current account, capital account and the cash account.
B) financial account, payments account and the capital account.
C) current account, payments account and the cash account.
D) current account, financial account and the capital account.
A) current account, capital account and the cash account.
B) financial account, payments account and the capital account.
C) current account, payments account and the cash account.
D) current account, financial account and the capital account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is not included in the financial account?
A) change in U.S. government assets held abroad
B) income received on investments
C) change in foreign assets held in the United States
D) change in private U.S. assets held abroad
A) change in U.S. government assets held abroad
B) income received on investments
C) change in foreign assets held in the United States
D) change in private U.S. assets held abroad

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following is not included in the U.S. current account?
A) exports of services
B) net investment income
C) change in private U.S. assets held abroad
D) imports of goods
A) exports of services
B) net investment income
C) change in private U.S. assets held abroad
D) imports of goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
An increase in British demand for U.S. goods and services is likely to:
A) not change the quantity of pounds supplied but increase the quantity of pounds demanded.
B) increase the quantity of pounds supplied.
C) increase the quantity of pounds demanded.
D) decrease the quantity of pounds supplied and not change the quantity of pounds demanded.
A) not change the quantity of pounds supplied but increase the quantity of pounds demanded.
B) increase the quantity of pounds supplied.
C) increase the quantity of pounds demanded.
D) decrease the quantity of pounds supplied and not change the quantity of pounds demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
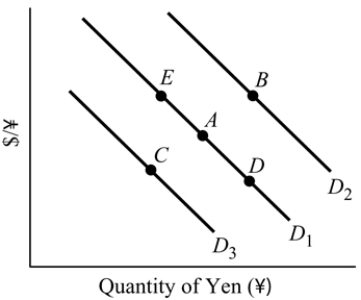 Figure 19.1
Figure 19.1Refer to Figure 19.1. The yen is currently at Point A. An appreciation of the U.S. dollar causes a movement to Point _______.
A) D
B) E
C) B
D) C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following is in the capital account?
A) statistical discrepancy
B) net investment income
C) net exports
D) net purchases of foreign assets
A) statistical discrepancy
B) net investment income
C) net exports
D) net purchases of foreign assets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Recall Application 1, "The Chinese Yuan and Big Macs," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, the predicted purchasing power exchange rate in China is 3.49 yuan. This implies that:
A) the cost of a Big Mac in China is 3.49 yuan.
B) if the exchange rate is 3.49 yuan for one US dollar, then the Big Mac in both countries would cost the same.
C) the US dollar should be worth 3.49 yuan more than the current exchange rate.
D) the US dollar should be worth 3.49 yuan less than the current exchange rate.
According to the application, the predicted purchasing power exchange rate in China is 3.49 yuan. This implies that:
A) the cost of a Big Mac in China is 3.49 yuan.
B) if the exchange rate is 3.49 yuan for one US dollar, then the Big Mac in both countries would cost the same.
C) the US dollar should be worth 3.49 yuan more than the current exchange rate.
D) the US dollar should be worth 3.49 yuan less than the current exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
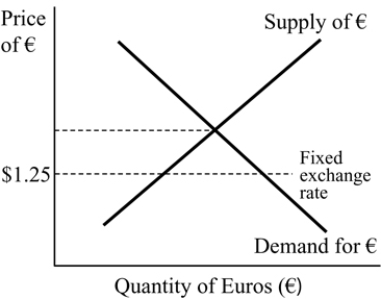 Figure 19.5
Figure 19.5From Figure 19.5 above, if the U.S. fixes the exchange rate at $1.25 per euro, then the U.S experiences:
A) capital account surplus.
B) capital account deficit.
C) a balance of payments deficit.
D) a balance of payments surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A balance of payments surplus occurs when a country experiences a _______ that is not matched by additional purchases of _______ by the private sector.
A) current account surplus; foreign assets
B) current account surplus; government issued debt
C) financial account surplus; foreign assets
D) capital account surplus; home made goods and services
A) current account surplus; foreign assets
B) current account surplus; government issued debt
C) financial account surplus; foreign assets
D) capital account surplus; home made goods and services

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A U.S. firm buys the copyrights of Beatles songs, formerly held by a British company. This transaction is recorded as:
A) negative in the U.S. current account.
B) positive in the U.S. capital account.
C) negative in the U.S. capital account.
D) positive in the U.S. current account.
A) negative in the U.S. current account.
B) positive in the U.S. capital account.
C) negative in the U.S. capital account.
D) positive in the U.S. current account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If an American firm Citigroup earns profits while operating a business in London, then the value of the profit is entered as a _______ in the U.S. _______ account.
A) negative; financial account
B) negative capital account
C) negative; current account
D) positive; current account
A) negative; financial account
B) negative capital account
C) negative; current account
D) positive; current account

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
An Italian citizen buys a U.S. bond. This transaction will be entered as:
A) a negative in the U.S. current account.
B) a positive in the U.S. current account.
C) a positive in the U.S. financial account.
D) a positive in the U.S. capital account.
A) a negative in the U.S. current account.
B) a positive in the U.S. current account.
C) a positive in the U.S. financial account.
D) a positive in the U.S. capital account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following is not included in the U.S. financial account?
A) change in foreign private assets held in the United States
B) exports of U.S. made goods to Japan
C) change in foreign government assets held in the United States
D) change in private U.S. assets held abroad
A) change in foreign private assets held in the United States
B) exports of U.S. made goods to Japan
C) change in foreign government assets held in the United States
D) change in private U.S. assets held abroad

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Net international investment position measures:
A) the imbalance between the amount of foreign assets sold to domestic residents and the quantity of foreign goods and services purchased by domestic residents.
B) foreign holdings of domestic assets.
C) the imbalance between the amount of domestic assets held by foreigners and the amount of foreign assets held by domestic residents.
D) the imbalance between the amount of domestic assets held by foreigners and the quantity of domestic goods and services purchased by foreigners.
A) the imbalance between the amount of foreign assets sold to domestic residents and the quantity of foreign goods and services purchased by domestic residents.
B) foreign holdings of domestic assets.
C) the imbalance between the amount of domestic assets held by foreigners and the amount of foreign assets held by domestic residents.
D) the imbalance between the amount of domestic assets held by foreigners and the quantity of domestic goods and services purchased by foreigners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following is an item in the U.S. current account?
A) net investment income
B) the change in foreign private assets held in the United States
C) the change in foreign government assets held in the United States
D) the change in private U.S. assets held abroad
A) net investment income
B) the change in foreign private assets held in the United States
C) the change in foreign government assets held in the United States
D) the change in private U.S. assets held abroad

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A U.S. firm builds a factory in South Africa. This will be entered as a:
A) positive in the U.S. current account.
B) negative in the U.S. financial account.
C) positive in the U.S. financial account.
D) negative in the U.S. current account.
A) positive in the U.S. current account.
B) negative in the U.S. financial account.
C) positive in the U.S. financial account.
D) negative in the U.S. current account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Under the Bretton Woods exchange rate system, each country's exchange rate was pegged to
A) gold.
B) the U.S. dollar.
C) the British pound.
D) the Japanese Yen
A) gold.
B) the U.S. dollar.
C) the British pound.
D) the Japanese Yen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If it takes more U.S. dollars to get a euro, then:
A) the U.S. dollar appreciates and the euro depreciates.
B) the U.S. dollar and the euro depreciates.
C) the U.S. dollar depreciates and the euro appreciates.
D) the U.S. dollar and the euro appreciates.
A) the U.S. dollar appreciates and the euro depreciates.
B) the U.S. dollar and the euro depreciates.
C) the U.S. dollar depreciates and the euro appreciates.
D) the U.S. dollar and the euro appreciates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The U.S. real exchange rate appreciates when:
A) the number of dollars you need to buy a basket of foreign goods increase.
B) the number of dollars you need to buy a basket of foreign goods decrease.
C) a foreign basket of goods can exchange for more baskets of goods from the US.
D) a US basket of goods can exchange for more baskets of goods from other countries.
A) the number of dollars you need to buy a basket of foreign goods increase.
B) the number of dollars you need to buy a basket of foreign goods decrease.
C) a foreign basket of goods can exchange for more baskets of goods from the US.
D) a US basket of goods can exchange for more baskets of goods from other countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Suppose that a bushel of wheat costs $3 in the U.S. and 20 pesos in Mexico. If the nominal exchange rate is 10 pesos per dollar, the real exchange rate is:
A) 3/2 bushels of Mexican wheat per bushel of U.S. wheat.
B) 2/3 bushels of Mexican wheat per bushel of U.S. wheat.
C) $2 per bushel of Mexican wheat.
D) $1.50 per bushel of Mexican wheat.
A) 3/2 bushels of Mexican wheat per bushel of U.S. wheat.
B) 2/3 bushels of Mexican wheat per bushel of U.S. wheat.
C) $2 per bushel of Mexican wheat.
D) $1.50 per bushel of Mexican wheat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If BMW (a German company) earns profits while operating a business in the United States, then the value of the profit is entered as a _______ in the U.S. _______ account.
A) negative; financial account
B) negative capital account
C) positive; current account
D) negative; current account
A) negative; financial account
B) negative capital account
C) positive; current account
D) negative; current account

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Recall Application 3, "A Downside to the Euro," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, how was Greece harmed from being a member of the Euro- zone?
A) By using the euro, investment in Greece was more expensive.
B) By using the euro, Greece could not devalue its currency to solve its financial crisis.
C) By using the euro, Greece would have to allow its currency to appreciate in order to prevent a financial crisis.
D) By using the euro, investors feared Greece could easily pursue expansionary monetary policies.
According to the application, how was Greece harmed from being a member of the Euro- zone?
A) By using the euro, investment in Greece was more expensive.
B) By using the euro, Greece could not devalue its currency to solve its financial crisis.
C) By using the euro, Greece would have to allow its currency to appreciate in order to prevent a financial crisis.
D) By using the euro, investors feared Greece could easily pursue expansionary monetary policies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following is not included in the U.S. current account?
A) net investment income
B) exports of services
C) imports of goods
D) change in foreign private assets held in the United States
A) net investment income
B) exports of services
C) imports of goods
D) change in foreign private assets held in the United States

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
An index that reflects the average of real exchange rates of the U.S. and its major trading partners is called:
A) a multinational real exchange rate.
B) a multilateral exchange rate.
C) an average nominal exchange rate.
D) none of the above
A) a multinational real exchange rate.
B) a multilateral exchange rate.
C) an average nominal exchange rate.
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Recall Application 4, "The Argentine Financial Crisis," to answer the question below:
According to the application, the exchange rate system that Argentina had between the 1980s and 2002 was a:
A) floating exchange rate with the Brazilian real.
B) fixed exchange rate with the U.S. dollar.
C) fixed exchange rate with the Mexican peso.
D) floating exchange rate with the British pound.
According to the application, the exchange rate system that Argentina had between the 1980s and 2002 was a:
A) floating exchange rate with the Brazilian real.
B) fixed exchange rate with the U.S. dollar.
C) fixed exchange rate with the Mexican peso.
D) floating exchange rate with the British pound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Net international investment position refers to:
A) foreign holdings of domestic assets minus domestic holdings of foreign assets.
B) domestic holdings of foreign assets minus the purchase of foreign goods and services by domestic residents.
C) domestic holdings of foreign assets minus foreign holdings of domestic assets.
D) foreign holdings of domestic assets minus the purchase of domestic goods and services by foreigners.
A) foreign holdings of domestic assets minus domestic holdings of foreign assets.
B) domestic holdings of foreign assets minus the purchase of foreign goods and services by domestic residents.
C) domestic holdings of foreign assets minus foreign holdings of domestic assets.
D) foreign holdings of domestic assets minus the purchase of domestic goods and services by foreigners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
If the U.S. sends food aid to Zimbabwe to help the thousands who are dying from hunger, then the value of the aid is included in the _______ component of _______.
A) net income from abroad; financial account
B) net transfer payments; current account
C) net income from abroad; capital account
D) net exports; current account
A) net income from abroad; financial account
B) net transfer payments; current account
C) net income from abroad; capital account
D) net exports; current account

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following units of measurement would be appropriate for a real exchange rate?
A) 10 percent per year
B) 3 bushels of Mexican corn per bushel of U.S. corn
C) 150 yen per U.S. dollar
D) 1 Mexican T- shirt per $5
A) 10 percent per year
B) 3 bushels of Mexican corn per bushel of U.S. corn
C) 150 yen per U.S. dollar
D) 1 Mexican T- shirt per $5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



