Deck 16: The Dynamics of Inflation and Unemployment
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/186
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: The Dynamics of Inflation and Unemployment
1
Economists believe that Alan Greenspan's credibility in his determination to fight inflation has helped the U.S.:
A) raised the unemployment rate in 2003.
B) reduce inflation in the 1990s.
C) caused the financial crisis in 2008.
D) increased inflation in the 2000s.
A) raised the unemployment rate in 2003.
B) reduce inflation in the 1990s.
C) caused the financial crisis in 2008.
D) increased inflation in the 2000s.
reduce inflation in the 1990s.
2
If Bob feels better off after getting a 5 percent nominal wage increase even though the price level also went up by 5 percent. In this scenario, Bob falls victim to:
A) money illusion.
B) nominal confusion.
C) purchasing power craziness.
D) money hallucination.
A) money illusion.
B) nominal confusion.
C) purchasing power craziness.
D) money hallucination.
money illusion.
3
If the quantity equation holds, then a country operating under a gold standard will experience deflation:
A) when the supply of gold decreases.
B) when people find other non- monetary uses for gold
C) when it buys more goods from another country using gold.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) when the supply of gold decreases.
B) when people find other non- monetary uses for gold
C) when it buys more goods from another country using gold.
D) All of the above are correct.
All of the above are correct.
4
If nominal GDP is $700 billion and the money supply is $100 billion, the velocity of money is:
A) 7.0.
B) 3.0.
C) 0.7.
D) 3.5.
A) 7.0.
B) 3.0.
C) 0.7.
D) 3.5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
According to the quantity equation, a reduction in the velocity of money, all else fixed, will tend to cause:
A) a reduction in the money supply.
B) an increase in nominal GDP.
C) a reduction in nominal GDP.
D) an increase in the money supply.
A) a reduction in the money supply.
B) an increase in nominal GDP.
C) a reduction in nominal GDP.
D) an increase in the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
During 1989, prices were increasing by approximately 302,200% a year in Argentina. This is an example of a:
A) moderate inflation.
B) deflation.
C) hyperinflation.
D) disinflation.
A) moderate inflation.
B) deflation.
C) hyperinflation.
D) disinflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
People are said to have rational expectations if they:
A) assume that this year's inflation rate will be equal to the average inflation rate over the past 10 years.
B) use all available information in forming their expectations.
C) merely guess at the inflation rate.
D) assume that this year's inflation rate will be the same as last year's inflation rate.
A) assume that this year's inflation rate will be equal to the average inflation rate over the past 10 years.
B) use all available information in forming their expectations.
C) merely guess at the inflation rate.
D) assume that this year's inflation rate will be the same as last year's inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
According to the growth version of the quantity equation, if the money supply increases by 10 percent while velocity stays constant and real GDP increased by 12 percent, then:
A) the economy experienced hyperinflation.
B) the economy experienced a recession.
C) the economy experienced a deflation.
D) the unemployment rate increased by 2 percent.
A) the economy experienced hyperinflation.
B) the economy experienced a recession.
C) the economy experienced a deflation.
D) the unemployment rate increased by 2 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
According to the growth version of the quantity equation, if the money supply increases by 10 percent while velocity stays constant and real GDP increased by 2 percent, then the price level:
A) increased by 12 percent.
B) increased by 8 percent.
C) decreased by 8 percent.
D) decreased by 12 percent.
A) increased by 12 percent.
B) increased by 8 percent.
C) decreased by 8 percent.
D) decreased by 12 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If the expectations Phillips curve holds true, then the unemployment rate varies with the:
A) unanticipated inflation rate.
B) long- run growth rate of real GDP.
C) anticipated inflation rate.
D) money supply.
A) unanticipated inflation rate.
B) long- run growth rate of real GDP.
C) anticipated inflation rate.
D) money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Jim's nominal wage increased by 1%, and the prices of goods that Jim buys increased by 4%. Jim's real wage has:
A) remained constant.
B) increased.
C) decreased.
D) changed by 5%, but the direction of the change is ambiguous.
A) remained constant.
B) increased.
C) decreased.
D) changed by 5%, but the direction of the change is ambiguous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When people form expectations about future inflation based on last period's inflation rate, it is said that expectations are formed:
A) analytically.
B) using the rule of Law.
C) using a rule of thumb.
D) rationally.
A) analytically.
B) using the rule of Law.
C) using a rule of thumb.
D) rationally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Recall Application 2, "Increased Political Independence for the Bank of England Lowered Inflation Expectations," to
answer the following questions:
According to the application, independence from political influence reinforces central bank credibility because:
A) it allows the central bank to aim for zero inflation.
B) it makes central banks more believable in their commitment to fighting inflation.
C) it increases the central bank's capability to stabilize real GDP.
D) all of the above
answer the following questions:
According to the application, independence from political influence reinforces central bank credibility because:
A) it allows the central bank to aim for zero inflation.
B) it makes central banks more believable in their commitment to fighting inflation.
C) it increases the central bank's capability to stabilize real GDP.
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The Phillips curve depicts the relationship between:
A) money supply and interest rate.
B) inflation and unemployment.
C) output and the price level.
D) aggregate demand and aggregate expenditures.
A) money supply and interest rate.
B) inflation and unemployment.
C) output and the price level.
D) aggregate demand and aggregate expenditures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Hyperinflation is an inflation rate that exceeds:
A) 50 percent inflation per day.
B) 50 percent inflation per month.
C) 50 percent deflation per week.
D) 50 percent inflation per year.
A) 50 percent inflation per day.
B) 50 percent inflation per month.
C) 50 percent deflation per week.
D) 50 percent inflation per year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If the actual unemployment rate is above the natural rate, we would expect that:
A) the inflation rate is increasing.
B) the inflation rate is zero.
C) the inflation rate is constant.
D) the inflation rate is decreasing.
A) the inflation rate is increasing.
B) the inflation rate is zero.
C) the inflation rate is constant.
D) the inflation rate is decreasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
After World War II, prices were increasing by 19,800% a month in Hungary. This is an example of a/an:
A) hyperdeflation.
B) hyperinflation.
C) unexpected deflation.
D) disinflation.
A) hyperdeflation.
B) hyperinflation.
C) unexpected deflation.
D) disinflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Recall Application 2, "Increased Political Independence for the Bank of England Lowered Inflation Expectations," to
answer the following questions:
According to the application, if the bonds that were not adjusted for inflation and the inflation adjusted bonds had the same yield after the Bank of England's announced its increased political independence, then:
A) people expect that the Bank of England's independence has no effect on inflation.
B) people expect that the Bank of England's independence will allow inflation equal to the current bond yield.
C) people expect that the Bank of England's independence will result in zero inflation.
D) people expect that the Bank of England's independence will result in the elimination of inflation adjusted bonds.
answer the following questions:
According to the application, if the bonds that were not adjusted for inflation and the inflation adjusted bonds had the same yield after the Bank of England's announced its increased political independence, then:
A) people expect that the Bank of England's independence has no effect on inflation.
B) people expect that the Bank of England's independence will allow inflation equal to the current bond yield.
C) people expect that the Bank of England's independence will result in zero inflation.
D) people expect that the Bank of England's independence will result in the elimination of inflation adjusted bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If the money supply is currently $100 million and the government prints another $300 million to finance the budget deficit, then we should expect:
A) a 200 percent inflation rate.
B) a 3 percent inflation rate.
C) a 200 million percent inflation rate
D) a 300 percent inflation rate.
A) a 200 percent inflation rate.
B) a 3 percent inflation rate.
C) a 200 million percent inflation rate
D) a 300 percent inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The heads of central banks are typically very conservative about inflation because:
A) they can influence expectations of inflation and those, in turn, influence actual behavior.
B) they can influence rational expectations and those, in turn, influence irrational expectations.
C) they can influence the budget deficit and, in turn, promote hyperinflation.
D) they can influence expectations of government spending and those, in turn, influence nominal wages.
A) they can influence expectations of inflation and those, in turn, influence actual behavior.
B) they can influence rational expectations and those, in turn, influence irrational expectations.
C) they can influence the budget deficit and, in turn, promote hyperinflation.
D) they can influence expectations of government spending and those, in turn, influence nominal wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If labor union leaders are successful in demanding a wage increase, then their actions will cause:
A) AD to decrease.
B) the AS to increase.
C) AS to decrease.
D) AD to increase.
A) AD to decrease.
B) the AS to increase.
C) AS to decrease.
D) AD to increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Suppose that the government collects $500 in taxes and borrows $1000 from the public. If the government prints $200 in new money to finance its budget deficit, how much is the government spending?
A) $1200
B) $1500
C) $700
D) $1700
A) $1200
B) $1500
C) $700
D) $1700

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Recall Application 3, "Hyperinflation in Zimbabwe," to answer the following questions:
An 8 million percent annual increase in the price level implies that if the price of a basket of goods in June 2007 was $100, then in June 2008, the price of the same basket of goods would be:
A) $800 million.
B) $100.
C) $80,000.
D) $8 million.
An 8 million percent annual increase in the price level implies that if the price of a basket of goods in June 2007 was $100, then in June 2008, the price of the same basket of goods would be:
A) $800 million.
B) $100.
C) $80,000.
D) $8 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Inflation in the long run is positively correlated with:
A) nominal wages and nominal interest rates.
B) neither nominal wages nor nominal interest rates.
C) nominal interest rates, but not nominal wages.
D) nominal wage growth, but not nominal interest rates.
A) nominal wages and nominal interest rates.
B) neither nominal wages nor nominal interest rates.
C) nominal interest rates, but not nominal wages.
D) nominal wage growth, but not nominal interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
When the Fed randomly increases the money supply at a lower rate than what is expected by the public,:
A) the demand for money will accelerate.
B) interest rates go up.
C) investment goes down.
D) the public will immediately lower their inflation expectations.
A) the demand for money will accelerate.
B) interest rates go up.
C) investment goes down.
D) the public will immediately lower their inflation expectations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
One of the main insights of monetarism is that:
A) the government can effectively manage aggregate demand by using its spending and taxing powers.
B) inflation can continue indefinitely without the cooperation of the central bank.
C) sustained inflation is a monetary phenomenon.
D) velocity is unstable and subject to wide fluctuations.
A) the government can effectively manage aggregate demand by using its spending and taxing powers.
B) inflation can continue indefinitely without the cooperation of the central bank.
C) sustained inflation is a monetary phenomenon.
D) velocity is unstable and subject to wide fluctuations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The quantity equation is derived from:
A) the definition of economics.
B) the definition of real GDP.
C) the definition of money.
D) the definition of velocity.
A) the definition of economics.
B) the definition of real GDP.
C) the definition of money.
D) the definition of velocity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A policy that reduces the natural rate of unemployment:
A) shifts the expectations Phillips curve left.
B) makes the long- run Phillips curve horizontal.
C) shifts the expectations Phillips curve right.
D) has no effect on the expectations Phillips curve.
A) shifts the expectations Phillips curve left.
B) makes the long- run Phillips curve horizontal.
C) shifts the expectations Phillips curve right.
D) has no effect on the expectations Phillips curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If firms have rational expectations and if they set prices and wages on this basis, then:
A) there are likely to be unexploited profit opportunities for extended periods.
B) they will perceive their prices have risen relative to other prices, and this leads them to produce more output.
C) they will still not know the demand curve for their output and the supply curve of labor that they face.
D) on average, prices and wages will be set at levels that ensure equilibrium in the goods and labor markets.
A) there are likely to be unexploited profit opportunities for extended periods.
B) they will perceive their prices have risen relative to other prices, and this leads them to produce more output.
C) they will still not know the demand curve for their output and the supply curve of labor that they face.
D) on average, prices and wages will be set at levels that ensure equilibrium in the goods and labor markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If the quantity equation holds, then a country operating under a gold standard will experience inflation:
A) during a gold rush similar to California's gold rush in 1849.
B) when it buys more goods from another country using gold.
C) when the price of gold increases.
D) when people find other non- monetary uses for gold.
A) during a gold rush similar to California's gold rush in 1849.
B) when it buys more goods from another country using gold.
C) when the price of gold increases.
D) when people find other non- monetary uses for gold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Recall Application 1, "Shifts in the Natural Rate of Unemployment" to answer the following questions:
According to the application, the Beveridge Curve depicts:
A) the positive relationship between the unemployment rate and the number of job vacancies.
B) the positive relationship between the unemployment rate and the inflation rate.
C) the negative relationship between the unemployment rate and the number of job vacancies.
D) the negative relationship between the unemployment rate and the GDP.
According to the application, the Beveridge Curve depicts:
A) the positive relationship between the unemployment rate and the number of job vacancies.
B) the positive relationship between the unemployment rate and the inflation rate.
C) the negative relationship between the unemployment rate and the number of job vacancies.
D) the negative relationship between the unemployment rate and the GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Recall Application 1, "Shifts in the Natural Rate of Unemployment" to answer the following questions:
According to the application, William Dickens estimated that the natural rate of unemployment in 1970 was:
A) 6 percent.
B) 4 percent.
C) 7 percent.
D) 5 percent.
According to the application, William Dickens estimated that the natural rate of unemployment in 1970 was:
A) 6 percent.
B) 4 percent.
C) 7 percent.
D) 5 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The group of economists who emphasize the role that the money supply plays in determining nominal income and inflation are called:
A) Keynesians.
B) classicals.
C) inflationists.
D) monetarists.
A) Keynesians.
B) classicals.
C) inflationists.
D) monetarists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The velocity of money is calculated as the ratio of:
A) real GDP to the money supply.
B) the overall price level to the money supply.
C) nominal GDP to the overall price level.
D) nominal GDP to the money supply.
A) real GDP to the money supply.
B) the overall price level to the money supply.
C) nominal GDP to the overall price level.
D) nominal GDP to the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If the quantity equation holds, then a country operating under a gold standard will experience _______ when its residents discover large gold deposits underground.
A) deflation
B) disinflation
C) inflation
D) All of the above are correct.
A) deflation
B) disinflation
C) inflation
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If prices increase by 4 percent and wages increase by 8 percent, the:
A) nominal wage has not changed.
B) real wage has increased.
C) real wage has not changed.
D) nominal wage has increased by 4 percent.
A) nominal wage has not changed.
B) real wage has increased.
C) real wage has not changed.
D) nominal wage has increased by 4 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The expectations Phillips curve shows the inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment when:
A) the unemployment rate is above the natural rate.
B) the economy experiences no inflation.
C) we take into account expectations of inflation.
D) the economy experiences high inflation.
A) the unemployment rate is above the natural rate.
B) the economy experiences no inflation.
C) we take into account expectations of inflation.
D) the economy experiences high inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Economists argue that central banks that are credible in their fight against inflation can more easily:
A) lower inflation without creating extra unemployment.
B) lead the economy into a depression.
C) buy bonds.
D) increase the money supply.
A) lower inflation without creating extra unemployment.
B) lead the economy into a depression.
C) buy bonds.
D) increase the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If the government prints a $500 bill and it takes the government $2.50 to print the bill, then the seignorage that the government collects is:
A) $2.50.
B) $500.
C) $502.50.
D) $497.50.
A) $2.50.
B) $500.
C) $502.50.
D) $497.50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following will shift the natural rate of unemployment?
A) changes in the state of the economy
B) changes in labor productivity
C) changes in the age structure of the labor force
D) all of the above
A) changes in the state of the economy
B) changes in labor productivity
C) changes in the age structure of the labor force
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
After experiencing about 4 percent inflation the last 10 years, Americans start to believe that the inflation for this year is also 4 percent. This belief regarding the future path of inflation based on previous inflation is called:
A) intuitions of inflation.
B) expectations of inflation.
C) rational expectations.
D) a self fulfilling prophecy.
A) intuitions of inflation.
B) expectations of inflation.
C) rational expectations.
D) a self fulfilling prophecy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Recall Application 2, "Increased Political Independence for the Bank of England Lowered Inflation Expectations," to
answer the following questions:
According to the application, the study by Mark Spiegel concluded that inflation expectations decreased after the Bank of England announced political independence because:
A) the difference between the nominal GDP growth rate and real GDP growth rate decreased.
B) the difference in the interest rates of inflation adjusted bonds and non- inflation adjusted bonds decreased.
C) the difference in the interest rates of inflation adjusted bonds and non- inflation adjusted bonds increased.
D) the difference between nominal and real GDP decreased.
answer the following questions:
According to the application, the study by Mark Spiegel concluded that inflation expectations decreased after the Bank of England announced political independence because:
A) the difference between the nominal GDP growth rate and real GDP growth rate decreased.
B) the difference in the interest rates of inflation adjusted bonds and non- inflation adjusted bonds decreased.
C) the difference in the interest rates of inflation adjusted bonds and non- inflation adjusted bonds increased.
D) the difference between nominal and real GDP decreased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The theory of rational expectations suggests that the forecasts made using the rational expectations model:
A) consistently underestimate the actual rate of inflation in the future.
B) are correct on average.
C) consistently overestimate the actual rate of inflation in the future.
D) are always correct.
A) consistently underestimate the actual rate of inflation in the future.
B) are correct on average.
C) consistently overestimate the actual rate of inflation in the future.
D) are always correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
According to the growth version of the quantity equation, a 4% increase in the money supply (holding velocity constant) causes a 2% increase in prices only if:
A) nominal GDP increases by 2 percent.
B) real GDP increases by 2 percent.
C) real GDP decreases by 2 percent.
D) nominal GDP decreases by 2 percent.
A) nominal GDP increases by 2 percent.
B) real GDP increases by 2 percent.
C) real GDP decreases by 2 percent.
D) nominal GDP decreases by 2 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In the long run, a decrease in the growth rate of the money supply will cause
A) nominal interest rates to decrease and decrease the real interest rate.
B) nominal interest rates to increase and will increase the real interest rate.
C) nominal interest rates to increase and will not affect the real interest rate.
D) nominal interest rates to decrease and will not affect the real interest rate.
A) nominal interest rates to decrease and decrease the real interest rate.
B) nominal interest rates to increase and will increase the real interest rate.
C) nominal interest rates to increase and will not affect the real interest rate.
D) nominal interest rates to decrease and will not affect the real interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
According to the growth version of the quantity equation, if the money supply doubles while all else stays constant, then:
A) real GDP doubles.
B) the inflation rate doubles.
C) the interest rates doubles.
D) nominal GDP doubles.
A) real GDP doubles.
B) the inflation rate doubles.
C) the interest rates doubles.
D) nominal GDP doubles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Recall Application 3, "Hyperinflation in Zimbabwe," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, which of the following contributed to the hyperinflation in Zimbabwe:
A) the bribing of soldiers and supporters using newly minted currency.
B) Mugabe's policies to intervene militarily in African conflicts.
C) decline in tax revenues and export revenues.
D) All of the above contributed to the hyperinflation.
According to the application, which of the following contributed to the hyperinflation in Zimbabwe:
A) the bribing of soldiers and supporters using newly minted currency.
B) Mugabe's policies to intervene militarily in African conflicts.
C) decline in tax revenues and export revenues.
D) All of the above contributed to the hyperinflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following economists was responsible for developing the theory of rational expectations?
A) John Keynes
B) Milton Friedman
C) Robert Barro
D) Robert Lucas
A) John Keynes
B) Milton Friedman
C) Robert Barro
D) Robert Lucas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
When Bob incorrectly believed that his real wage went up when his nominal wages increased because he failed to factor in the effects of inflation, then economists say that he is a victim of:
A) the discouraged worker effect.
B) inflation injustice.
C) unemployment.
D) money illusion.
A) the discouraged worker effect.
B) inflation injustice.
C) unemployment.
D) money illusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following did not contribute to higher inflation in the late 1970s?
A) expansionary monetary policies used to lower the unemployment rates below the natural rate
B) Paul Volcker becomes the Fed Chairman
C) an oil shock in 1979
D) expansionary fiscal policies used to lower the unemployment rates below the natural rate
A) expansionary monetary policies used to lower the unemployment rates below the natural rate
B) Paul Volcker becomes the Fed Chairman
C) an oil shock in 1979
D) expansionary fiscal policies used to lower the unemployment rates below the natural rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Recall Application 3, "Hyperinflation in Zimbabwe," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, if the US$12 lunch equals 1.1 trillion Zimbabwean dollars, then how many Zimbabwean dollars does it take to buy a US dollar?
A) about 917 billion
B) about 91.7 billion
C) about 917 million
D) about 9.17 billion
According to the application, if the US$12 lunch equals 1.1 trillion Zimbabwean dollars, then how many Zimbabwean dollars does it take to buy a US dollar?
A) about 917 billion
B) about 91.7 billion
C) about 917 million
D) about 9.17 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If the price level increases from 120 to 320 in one month, the inflation rate for that month equals:
A) 267 percent.
B) 2.67 percent.
C) 8%.
D) 67 percent.
A) 267 percent.
B) 2.67 percent.
C) 8%.
D) 67 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following is an example of a nominal wage?
A) $12 per hour
B) €120 million per year
C) $2400 per month
D) All of the above are examples of nominal wages.
A) $12 per hour
B) €120 million per year
C) $2400 per month
D) All of the above are examples of nominal wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Recall Application 2, "Increased Political Independence for the Bank of England Lowered Inflation Expectations," to
answer the following questions:
According to the application, the way to measure inflation expectations in England was to compare:
A) nominal GDP growth rates and real GDP growth rates.
B) interest rates of inflation adjusted mutual funds and non- inflation adjusted mutual funds.
C) interest rates of inflation adjusted stock prices and non- inflation adjusted stock prices.
D) interest rates of inflation adjusted bonds and non- inflation adjusted bonds.
answer the following questions:
According to the application, the way to measure inflation expectations in England was to compare:
A) nominal GDP growth rates and real GDP growth rates.
B) interest rates of inflation adjusted mutual funds and non- inflation adjusted mutual funds.
C) interest rates of inflation adjusted stock prices and non- inflation adjusted stock prices.
D) interest rates of inflation adjusted bonds and non- inflation adjusted bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A decrease in inflationary expectations that causes a decrease in the growth rate of firms' prices shifts the:
A) aggregate supply curve to the left.
B) aggregate supply curve to the right.
C) aggregate demand curve to the right.
D) aggregate demand curve to the left.
A) aggregate supply curve to the left.
B) aggregate supply curve to the right.
C) aggregate demand curve to the right.
D) aggregate demand curve to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If expectations regarding inflation change, an expansionary fiscal policy causes:
A) the short- run Phillips curve to shift.
B) a movement along the short- run Phillips curve.
C) the long- run Phillips curve to shift.
D) the short- run Phillips curve to remain constant.
A) the short- run Phillips curve to shift.
B) a movement along the short- run Phillips curve.
C) the long- run Phillips curve to shift.
D) the short- run Phillips curve to remain constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If prices increase by 8 percent and wages increase by 6 percent, the:
A) real wage has increased.
B) real wage has fallen.
C) nominal wage has fallen.
D) real wage has not changed.
A) real wage has increased.
B) real wage has fallen.
C) nominal wage has fallen.
D) real wage has not changed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Bridget wants to make an 8% real return on a loan that she is planning to make, and the expected inflation rate during the period of the loan is 10%. She should charge an interest rate of:
A) 18%.
B) - 2%.
C) 8%.
D) 2%.
A) 18%.
B) - 2%.
C) 8%.
D) 2%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
An increase in the money supply, holding all else constant will cause:
A) an increase in the velocity of money.
B) no change to the velocity of GDP.
C) an increase in the velocity of GDP.
D) a decrease in the velocity of money.
A) an increase in the velocity of money.
B) no change to the velocity of GDP.
C) an increase in the velocity of GDP.
D) a decrease in the velocity of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following contributed to the rise in the natural rate of unemployment in Europe?
A) generous benefits to the unemployed
B) restrictions on employers that made it more difficult to fire workers.
C) the average incomes of Europeans increased during the 1990s.
D) A and B are correct.
A) generous benefits to the unemployed
B) restrictions on employers that made it more difficult to fire workers.
C) the average incomes of Europeans increased during the 1990s.
D) A and B are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following were policies implemented by Paul Volcker in response to inflationary pressure in the 1980s?
A) Increase the money supply and interest rates.
B) Tighten money supply to raise interest rates.
C) Increase tax rates to slow down the economy.
D) Increase government spending to lower the unemployment rates.
A) Increase the money supply and interest rates.
B) Tighten money supply to raise interest rates.
C) Increase tax rates to slow down the economy.
D) Increase government spending to lower the unemployment rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Recall Application 3, "Hyperinflation in Zimbabwe," to answer the following questions:
According to the application, the price level in June 2008 was _______ percent higher than the year before.
A) 8 million
B) 4,000
C) 50 trillion
D) 300,000
According to the application, the price level in June 2008 was _______ percent higher than the year before.
A) 8 million
B) 4,000
C) 50 trillion
D) 300,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If labor union leaders believe that the Fed is more inclined to fight inflation than unemployment, then they are more likely to:
A) be reluctant in demanding a wage hike.
B) demand an increase in the number of work days for the same wage.
C) demand a wage hike.
D) demand a wage decrease.
A) be reluctant in demanding a wage hike.
B) demand an increase in the number of work days for the same wage.
C) demand a wage hike.
D) demand a wage decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
To end hyperinflation, the government must first:
A) eliminate tax collection.
B) eliminate the use of money.
C) eliminate the budget deficits.
D) be replaced.
A) eliminate tax collection.
B) eliminate the use of money.
C) eliminate the budget deficits.
D) be replaced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The growth version of the quantity equation can be expressed as:
A) growth rate of money - growth rate of velocity = inflation - real GDP growth.
B) growth rate of money + growth rate of velocity = inflation - real GDP growth.
C) growth rate of money X growth rate of velocity = inflation X real GDP growth.
D) growth rate of money + growth rate of velocity = inflation + real GDP growth.
A) growth rate of money - growth rate of velocity = inflation - real GDP growth.
B) growth rate of money + growth rate of velocity = inflation - real GDP growth.
C) growth rate of money X growth rate of velocity = inflation X real GDP growth.
D) growth rate of money + growth rate of velocity = inflation + real GDP growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If firms have rational expectations and if they set prices and wages on this basis, then prices and wages:
A) will always be above market- clearing levels.
B) will always be at market- clearing levels.
C) will, on average, be set at market- clearing levels.
D) will never be set at market- clearing levels.
A) will always be above market- clearing levels.
B) will always be at market- clearing levels.
C) will, on average, be set at market- clearing levels.
D) will never be set at market- clearing levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If the actual unemployment rate is below the natural rate, we would expect that:
A) the inflation rate is decreasing.
B) the inflation rate is constant.
C) the inflation rate is zero.
D) the inflation rate is increasing.
A) the inflation rate is decreasing.
B) the inflation rate is constant.
C) the inflation rate is zero.
D) the inflation rate is increasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The revenue raised by the government from printing money is called:
A) treasury bills.
B) federal funds.
C) taxes.
D) seignorage.
A) treasury bills.
B) federal funds.
C) taxes.
D) seignorage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
INFLATION-INDEXED BONDS IN THE UNITED STATES
Are there bonds that can protect your investments from inflation?
In 1997, the U.S. Department of the Treasury created a new financial instrument called the Treasury Inflation-Protected
Security, or TIPS. The key feature of TIPS is that the payments to investors adjust automatically to compensate for the actual
changes in the Consumer Price Index. Therefore, TIPS provide protection to investors from inflation.
Like other government bonds, TIPS make interest payments every six months and a payment of the original principal when
the bond matures. However, unlike other Treasury bonds, these payments are automatically adjusted for changes in inflation.
Despite their obvious attractions, the market for TIPS is still rather small. As of 2005, there were about $200 billion in TIPS
outstanding, compared to a total volume of about $4 trillion ($4,000 billion) total Treasury obligations. Because TIPS
compensate for actual inflation, the interest rate on these bonds differs from conventional bonds by the expected inflation
rate. By comparing the interest rates on TIPS to other government bonds of similar maturity, economists can estimate the
public’s expectations of inflation.
SOURCE: Simon Kwan, "Inflation Expectations: How the Market Speaks," Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco Economic
Letter, October 7, 2005.
According to the application, the difference between the interest rates on TIPS and the interest rates on non- inflation indexed securities represents:
A) the public's expectation of inflation in today.
B) the government's expectation of inflation in the future.
C) the public's expectation of inflation in the future.
D) the Fed's expectation of inflation in the today.
Are there bonds that can protect your investments from inflation?
In 1997, the U.S. Department of the Treasury created a new financial instrument called the Treasury Inflation-Protected
Security, or TIPS. The key feature of TIPS is that the payments to investors adjust automatically to compensate for the actual
changes in the Consumer Price Index. Therefore, TIPS provide protection to investors from inflation.
Like other government bonds, TIPS make interest payments every six months and a payment of the original principal when
the bond matures. However, unlike other Treasury bonds, these payments are automatically adjusted for changes in inflation.
Despite their obvious attractions, the market for TIPS is still rather small. As of 2005, there were about $200 billion in TIPS
outstanding, compared to a total volume of about $4 trillion ($4,000 billion) total Treasury obligations. Because TIPS
compensate for actual inflation, the interest rate on these bonds differs from conventional bonds by the expected inflation
rate. By comparing the interest rates on TIPS to other government bonds of similar maturity, economists can estimate the
public’s expectations of inflation.
SOURCE: Simon Kwan, "Inflation Expectations: How the Market Speaks," Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco Economic
Letter, October 7, 2005.
According to the application, the difference between the interest rates on TIPS and the interest rates on non- inflation indexed securities represents:
A) the public's expectation of inflation in today.
B) the government's expectation of inflation in the future.
C) the public's expectation of inflation in the future.
D) the Fed's expectation of inflation in the today.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Suppose that the money supply is $150 billion and nominal GDP is $600 billion. The velocity of money is:
A) 2.
B) 4.
C) 3.
D) 5.
A) 2.
B) 4.
C) 3.
D) 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
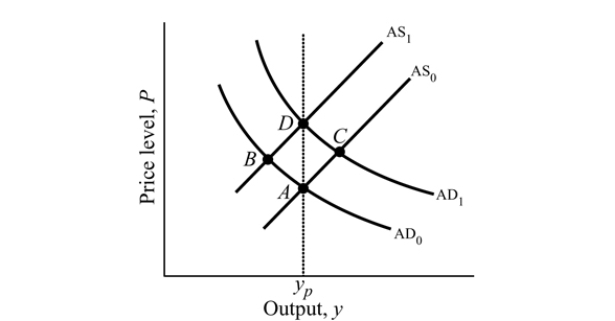 Figure 16.1
Figure 16.1Refer to Figure 16.1 to answer this question. Suppose the economy is initially at Point A. If labor leaders successfully negotiate a wage increase, then the economy will move to point:
A) B.
B) C.
C) D.
D) A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
INFLATION-INDEXED BONDS IN THE UNITED STATES
Are there bonds that can protect your investments from inflation?
In 1997, the U.S. Department of the Treasury created a new financial instrument called the Treasury Inflation-Protected
Security, or TIPS. The key feature of TIPS is that the payments to investors adjust automatically to compensate for the actual
changes in the Consumer Price Index. Therefore, TIPS provide protection to investors from inflation.
Like other government bonds, TIPS make interest payments every six months and a payment of the original principal when
the bond matures. However, unlike other Treasury bonds, these payments are automatically adjusted for changes in inflation.
Despite their obvious attractions, the market for TIPS is still rather small. As of 2005, there were about $200 billion in TIPS
outstanding, compared to a total volume of about $4 trillion ($4,000 billion) total Treasury obligations. Because TIPS
compensate for actual inflation, the interest rate on these bonds differs from conventional bonds by the expected inflation
rate. By comparing the interest rates on TIPS to other government bonds of similar maturity, economists can estimate the
public’s expectations of inflation.
SOURCE: Simon Kwan, "Inflation Expectations: How the Market Speaks," Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco Economic
Letter, October 7, 2005.
According to the application, if the interest rates on TIPS are higher than the interest rates on non- inflation indexed securities, then:
A) the public expects a deflation in the future.
B) the public expects stagflation in the future.
C) the public expects hyperinflation in the future.
D) the public expects inflation in the future.
Are there bonds that can protect your investments from inflation?
In 1997, the U.S. Department of the Treasury created a new financial instrument called the Treasury Inflation-Protected
Security, or TIPS. The key feature of TIPS is that the payments to investors adjust automatically to compensate for the actual
changes in the Consumer Price Index. Therefore, TIPS provide protection to investors from inflation.
Like other government bonds, TIPS make interest payments every six months and a payment of the original principal when
the bond matures. However, unlike other Treasury bonds, these payments are automatically adjusted for changes in inflation.
Despite their obvious attractions, the market for TIPS is still rather small. As of 2005, there were about $200 billion in TIPS
outstanding, compared to a total volume of about $4 trillion ($4,000 billion) total Treasury obligations. Because TIPS
compensate for actual inflation, the interest rate on these bonds differs from conventional bonds by the expected inflation
rate. By comparing the interest rates on TIPS to other government bonds of similar maturity, economists can estimate the
public’s expectations of inflation.
SOURCE: Simon Kwan, "Inflation Expectations: How the Market Speaks," Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco Economic
Letter, October 7, 2005.
According to the application, if the interest rates on TIPS are higher than the interest rates on non- inflation indexed securities, then:
A) the public expects a deflation in the future.
B) the public expects stagflation in the future.
C) the public expects hyperinflation in the future.
D) the public expects inflation in the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If labor union leaders believe that the Fed is more inclined to fight unemployment than keep inflation in check, then they are more likely to:
A) demand a wage decrease.
B) demand a wage hike.
C) demand an increase in the number of work days for the same wage.
D) not demand a wage hike.
A) demand a wage decrease.
B) demand a wage hike.
C) demand an increase in the number of work days for the same wage.
D) not demand a wage hike.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In an effort to improve the central bank's credibility in fighting inflation, the central bank in New Zealand:
A) has been releasing incorrect information about the true inflation that the economy has been experiencing.
B) has been operating under a law that specifies that its only goal is to maintain stable prices.
C) has been running advertisements on the television pledging their credibility.
D) no longer issues currency and uses the Australian dollar to conduct open market operations.
A) has been releasing incorrect information about the true inflation that the economy has been experiencing.
B) has been operating under a law that specifies that its only goal is to maintain stable prices.
C) has been running advertisements on the television pledging their credibility.
D) no longer issues currency and uses the Australian dollar to conduct open market operations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
According to the growth version of the quantity equation, a 4% increase in the money supply, holding velocity constant, causes a 4% increase in:
A) nominal GDP.
B) output.
C) employment.
D) real GDP.
A) nominal GDP.
B) output.
C) employment.
D) real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
An increase in inflationary expectations that causes an increase in the growth rate of firms' prices shifts the:
A) aggregate demand curve to the right.
B) aggregate supply curve to the left.
C) aggregate demand curve to the left.
D) aggregate supply curve to the right.
A) aggregate demand curve to the right.
B) aggregate supply curve to the left.
C) aggregate demand curve to the left.
D) aggregate supply curve to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Hyperinflation causes inefficiency in the economy because:
A) people spend all their time working.
B) people spend all their time hunting for jobs.
C) people spend none of their time hunting for bargains.
D) people spend all their time hunting for bargains.
A) people spend all their time working.
B) people spend all their time hunting for jobs.
C) people spend none of their time hunting for bargains.
D) people spend all their time hunting for bargains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Political scientists and economists argue that truly autonomous central banks that are subject to minimal political influence are more likely to be:
A) less credible in their fight against inflation.
B) more credible in their attempts in reviving a troubled economy.
C) more credible in their fight against inflation.
D) less credible in their fight against unemployment.
A) less credible in their fight against inflation.
B) more credible in their attempts in reviving a troubled economy.
C) more credible in their fight against inflation.
D) less credible in their fight against unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following contributed to the increase in the unemployment rate in 1983?
A) The Fed actively tried to increase inflation via contractionary policies.
B) The Fed actively tried to make the US dollar depreciate via contractionary policies.
C) The Fed actively tried to reduce inflation via contractionary policies.
D) The Fed actively tried to make the US dollar appreciate via contractionary policies.
A) The Fed actively tried to increase inflation via contractionary policies.
B) The Fed actively tried to make the US dollar depreciate via contractionary policies.
C) The Fed actively tried to reduce inflation via contractionary policies.
D) The Fed actively tried to make the US dollar appreciate via contractionary policies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
You want to make a 5% real return on a loan that you are planning to make, and the expected inflation rate during the period of the loan is 6%. You should charge a nominal interest rate of:
A) - 11%.
B) - 1%.
C) 1%.
D) 11%.
A) - 11%.
B) - 1%.
C) 1%.
D) 11%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



