Deck 17: Part A: International Trade
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/40
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Part A: International Trade
1
Answer the next three questions on the basis of the following production possibilities data for Francia and Galacia.All data are in tons. 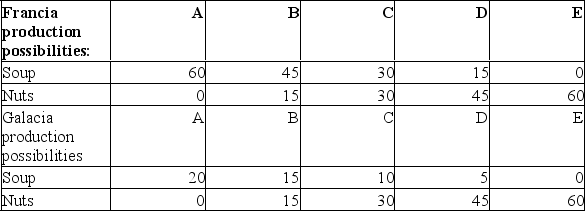 (a) If trade occurs between Francia and Galacia, which nation should export what product? Why?(b) What are the limits of the terms of trade between Francia and Galacia?(c) Assume that prior to specialization and trade, Francia and Galacia chose production possibility "C." Now each specializes according to comparative advantage.What will be the resulting gains from trade? Explain your answer.
(a) If trade occurs between Francia and Galacia, which nation should export what product? Why?(b) What are the limits of the terms of trade between Francia and Galacia?(c) Assume that prior to specialization and trade, Francia and Galacia chose production possibility "C." Now each specializes according to comparative advantage.What will be the resulting gains from trade? Explain your answer.
 (a) If trade occurs between Francia and Galacia, which nation should export what product? Why?(b) What are the limits of the terms of trade between Francia and Galacia?(c) Assume that prior to specialization and trade, Francia and Galacia chose production possibility "C." Now each specializes according to comparative advantage.What will be the resulting gains from trade? Explain your answer.
(a) If trade occurs between Francia and Galacia, which nation should export what product? Why?(b) What are the limits of the terms of trade between Francia and Galacia?(c) Assume that prior to specialization and trade, Francia and Galacia chose production possibility "C." Now each specializes according to comparative advantage.What will be the resulting gains from trade? Explain your answer.(a) Francia should export soup and Galacia should export nuts.Francia is the low cost producer of soup.The opportunity cost of 1 unit of soup is 1 unit of nuts.For Galacia the opportunity cost of 1 unit of soup is 3 units of nuts.Galacia is the low cost producer of nuts.The opportunity cost for Galacia to produce nuts is 1/3 unit of soup.The opportunity cost of nuts for Francia is 1 unit of nuts for 1 unit of soup.(b) The limits are from 1 ton of soup for 1 ton of nuts up to 1 ton of soup for 3 tons of nuts.(c) Before specialization, Francia produced 30 tons and Galacia 10 tons of soup for a total of 40 tons.After specialization and trade, Francia produces 60 tons of soup for a gain of 20 tons of output.Before specialization, Francia produced 30 tons and Galacia 30 tons of nuts.After specialization and trade, Galacia will produce 60 tons of nuts.Total output of this product did not change.
2
How does relaxing the assumption of constant costs affect the comparative advantage argument for trade?
In the simplified analysis of comparative advantage, opportunity costs are assumed to be constant.In other words, the production possibilities curves of nations are linear.The more realistic representation is nations with increasing costs and concave-to-the-origin production possibilities curves.This change, however, does not affect the general conclusion of comparative advantage.To improve efficiency in the allocation of resources, nations must still specialize in the areas of their comparative advantage.The specialization, however, is not complete.While nations increase their production of goods in which they have a comparative advantage, they do not completely eliminate production of other products.
3
Which is more effective in blocking imports, a tariff or a quota?
Generally, an import quota, especially if it is set low, is more effective in blocking the entry of imports into a nation.The reason is that once the import quota has been met, no more goods can be imported into the nation.With a tariff, it is still possible to import goods into a nation, so long as people are willing to pay the tariff on the imported good.Of course the precise answer depends on how low the quota is and how high the tariff is on the product.
4
What are Canada's top four exports and imports?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Answer the next three questions on the basis of the following production possibilities data for Narnia and Somosa.All figures are in thousands of units. 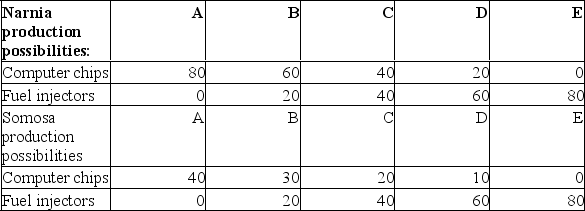 (a) If trade occurs between Narnia and Somosa, which nation should export what product? Why?(b) What are the limits of the terms of trade between Narnia and Somosa?(c) Assume that prior to specialization and trade, Narnia and Somosa chose production possibility "C." Now each specializes according to comparative advantage.What will be the resulting gains from trade? Explain your answer.
(a) If trade occurs between Narnia and Somosa, which nation should export what product? Why?(b) What are the limits of the terms of trade between Narnia and Somosa?(c) Assume that prior to specialization and trade, Narnia and Somosa chose production possibility "C." Now each specializes according to comparative advantage.What will be the resulting gains from trade? Explain your answer.
 (a) If trade occurs between Narnia and Somosa, which nation should export what product? Why?(b) What are the limits of the terms of trade between Narnia and Somosa?(c) Assume that prior to specialization and trade, Narnia and Somosa chose production possibility "C." Now each specializes according to comparative advantage.What will be the resulting gains from trade? Explain your answer.
(a) If trade occurs between Narnia and Somosa, which nation should export what product? Why?(b) What are the limits of the terms of trade between Narnia and Somosa?(c) Assume that prior to specialization and trade, Narnia and Somosa chose production possibility "C." Now each specializes according to comparative advantage.What will be the resulting gains from trade? Explain your answer.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The following table shows the domestic quantity demanded (QD) and quantity supplied (QS) of soybeans in Canada and Brazil at various prices (in Canadian dollars). 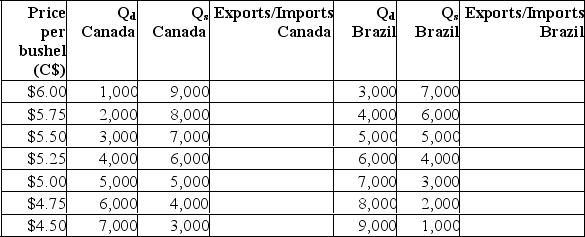 (a) Complete the above table by indicating the size of exports or imports for each country at each price.(b) Suppose Canada and Brazil are closed economies.What is the domestic price of soybeans in Canada? What is the domestic price of soybeans in Brazil?(c) Suppose Canada and Brazil are the only countries in a two-nation world.What is the world price of soybeans? Is Canada an exporter or an importer at the world price? Is Brazil an exporter or an importer at the world price?
(a) Complete the above table by indicating the size of exports or imports for each country at each price.(b) Suppose Canada and Brazil are closed economies.What is the domestic price of soybeans in Canada? What is the domestic price of soybeans in Brazil?(c) Suppose Canada and Brazil are the only countries in a two-nation world.What is the world price of soybeans? Is Canada an exporter or an importer at the world price? Is Brazil an exporter or an importer at the world price?
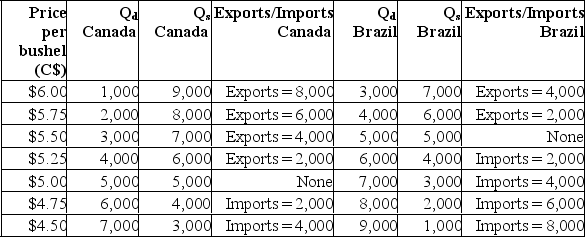
 (a) Complete the above table by indicating the size of exports or imports for each country at each price.(b) Suppose Canada and Brazil are closed economies.What is the domestic price of soybeans in Canada? What is the domestic price of soybeans in Brazil?(c) Suppose Canada and Brazil are the only countries in a two-nation world.What is the world price of soybeans? Is Canada an exporter or an importer at the world price? Is Brazil an exporter or an importer at the world price?
(a) Complete the above table by indicating the size of exports or imports for each country at each price.(b) Suppose Canada and Brazil are closed economies.What is the domestic price of soybeans in Canada? What is the domestic price of soybeans in Brazil?(c) Suppose Canada and Brazil are the only countries in a two-nation world.What is the world price of soybeans? Is Canada an exporter or an importer at the world price? Is Brazil an exporter or an importer at the world price?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Given the data in the graph below, which nation should specialize in steel production and which nation in wheat production? Why? 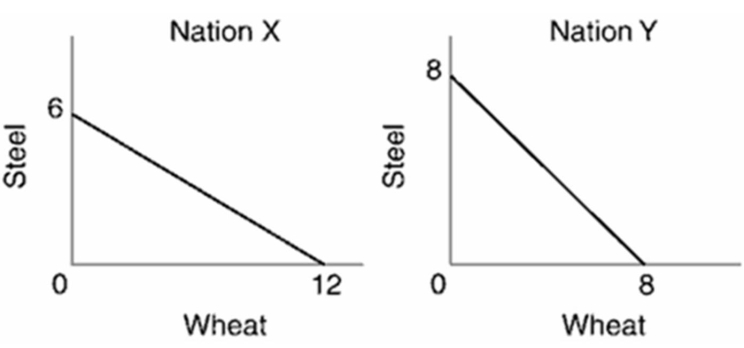


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
"The international flow of goods helps compensate for the international immobility of resources." Analyze and explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Cite three important reasons why nations trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
How important is international trade for Canada?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
How can supply and demand analysis be used to explain the equilibrium price and quantity of exports and imports for aluminum when there is trade between two nations (e.g., the United States and Canada)?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In 2016, what were the top five exporting nations (measured in dollars)?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The table below shows the maximum amounts of food and clothing that two nations, A and B, can produce.Draw the production possibilities curve for A and B using the below graphs.Assume constant costs. 
 (a) What is the cost ratio for the two products?(b) If each nation specializes according to comparative advantage, who should produce and trade each product? Why?(c) What will be the range for the terms of trade? If the terms are set at 1 food = 2 clothing, show how the trading possibilities lines will change in the graph.Explain.
(a) What is the cost ratio for the two products?(b) If each nation specializes according to comparative advantage, who should produce and trade each product? Why?(c) What will be the range for the terms of trade? If the terms are set at 1 food = 2 clothing, show how the trading possibilities lines will change in the graph.Explain.

 (a) What is the cost ratio for the two products?(b) If each nation specializes according to comparative advantage, who should produce and trade each product? Why?(c) What will be the range for the terms of trade? If the terms are set at 1 food = 2 clothing, show how the trading possibilities lines will change in the graph.Explain.
(a) What is the cost ratio for the two products?(b) If each nation specializes according to comparative advantage, who should produce and trade each product? Why?(c) What will be the range for the terms of trade? If the terms are set at 1 food = 2 clothing, show how the trading possibilities lines will change in the graph.Explain.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Answer the following questions regarding international trade:(a) What is the common myth regarding the benefits from international trade?(b) What is the associated implication arising from this myth?(c) What is the true benefit from international trade?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The following table shows the domestic quantity demanded (QD) and quantity supplied (QS) of soybeans in Canada and Brazil at various prices (in Canadian dollars). 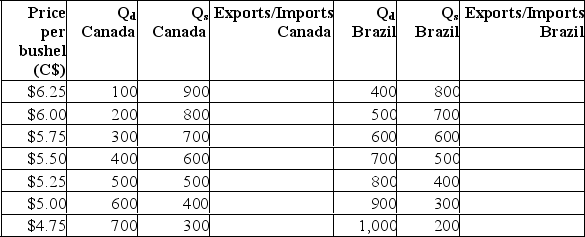 (a) Complete the above table by indicating the size of exports or imports for each country at each price.(b) Suppose Canada and Brazil are closed economies.What is the domestic price of soybeans in Canada? What is the domestic price of soybeans in Brazil?(c) Suppose Canada and Brazil are the only countries in a two-nation world.What is the world price of soybeans? Is Canada an exporter or an importer at the world price? Is Brazil an exporter or an importer at the world price?
(a) Complete the above table by indicating the size of exports or imports for each country at each price.(b) Suppose Canada and Brazil are closed economies.What is the domestic price of soybeans in Canada? What is the domestic price of soybeans in Brazil?(c) Suppose Canada and Brazil are the only countries in a two-nation world.What is the world price of soybeans? Is Canada an exporter or an importer at the world price? Is Brazil an exporter or an importer at the world price?
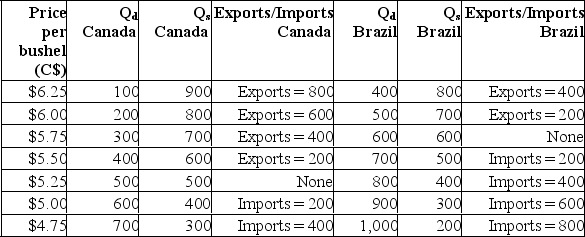
 (a) Complete the above table by indicating the size of exports or imports for each country at each price.(b) Suppose Canada and Brazil are closed economies.What is the domestic price of soybeans in Canada? What is the domestic price of soybeans in Brazil?(c) Suppose Canada and Brazil are the only countries in a two-nation world.What is the world price of soybeans? Is Canada an exporter or an importer at the world price? Is Brazil an exporter or an importer at the world price?
(a) Complete the above table by indicating the size of exports or imports for each country at each price.(b) Suppose Canada and Brazil are closed economies.What is the domestic price of soybeans in Canada? What is the domestic price of soybeans in Brazil?(c) Suppose Canada and Brazil are the only countries in a two-nation world.What is the world price of soybeans? Is Canada an exporter or an importer at the world price? Is Brazil an exporter or an importer at the world price?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Suppose that by devoting all of its resources to the production of X, nation L can produce 40 X.By devoting all of its resources to Y it can produce 20 Y.Comparable figures for nation M are 15 X and 15 Y.According to the principle of comparative advantage, which nation will specialize in which product? What are the limits to the terms of trade?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What are the economic benefits of free trade?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Why has international trade grown rapidly since World War II?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In what ways are national economies linked?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Identify the four basic types of trade barriers and describe each of them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
How do protectionist policies affect consumers, workers, producers, and the government? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What are the net costs of tariffs and quotas on consumption and income distribution?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Evaluate the argument: "Restricting imports from other nations will save Canadian jobs."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The next three questions refer to the information in the following table. 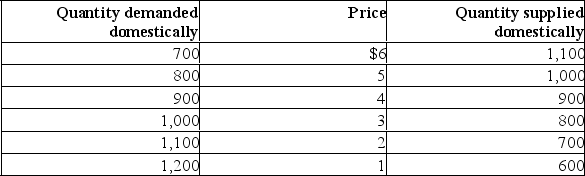 (a) What would price and quantity be if the market were closed to international trade? What would the domestic and foreign quantity supplied be if it were open to international trade and the world price was $2?(b) If the world price was $2 and a tariff of $1 were placed on the product, what would be the total revenues going to domestic producers, foreign producers (after-tax), and the government? Explain.(c) Given a world price of $2, what would be the difference in the total revenue received by foreign producers with a $1 per unit tariff compared with a quota of 200 units?
(a) What would price and quantity be if the market were closed to international trade? What would the domestic and foreign quantity supplied be if it were open to international trade and the world price was $2?(b) If the world price was $2 and a tariff of $1 were placed on the product, what would be the total revenues going to domestic producers, foreign producers (after-tax), and the government? Explain.(c) Given a world price of $2, what would be the difference in the total revenue received by foreign producers with a $1 per unit tariff compared with a quota of 200 units?
 (a) What would price and quantity be if the market were closed to international trade? What would the domestic and foreign quantity supplied be if it were open to international trade and the world price was $2?(b) If the world price was $2 and a tariff of $1 were placed on the product, what would be the total revenues going to domestic producers, foreign producers (after-tax), and the government? Explain.(c) Given a world price of $2, what would be the difference in the total revenue received by foreign producers with a $1 per unit tariff compared with a quota of 200 units?
(a) What would price and quantity be if the market were closed to international trade? What would the domestic and foreign quantity supplied be if it were open to international trade and the world price was $2?(b) If the world price was $2 and a tariff of $1 were placed on the product, what would be the total revenues going to domestic producers, foreign producers (after-tax), and the government? Explain.(c) Given a world price of $2, what would be the difference in the total revenue received by foreign producers with a $1 per unit tariff compared with a quota of 200 units?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Evaluate the validity of the argument that a new industry in a nation needs protection from foreign competition if it is to prosper.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What are the benefits of having a common currency such as the Euro?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Explain and evaluate the validity of the self-sufficiency argument for trade protection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Why might trade barriers be a highly ineffective technique for increasing domestic employment?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Explain the myth behind why buying Canadian and how this does or does not improve the Canadian economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Evaluate this argument for a trade barrier: "Canada needs protection from cheap foreign labour."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Critique the argument that trade protection is needed to protect Canadian jobs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the problem associated with the importing of goods by high-income nations from low-income nations? Explain how consumer organisations in high-income nations have tried to circumvent this problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is the problem with protecting industries in Canada from the dumping of foreign products on the domestic market?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
How can Canada compete successfully with relatively low-wage nations such as India and China?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The next three questions refer to the information in the following table.  (a) What would price and quantity be if the market were closed to international trade? What would the domestic and foreign quantity supplied be if it were open to international trade and the world price was $4?(b) If the world price was $4 and a tariff of $2 were placed on the product, what would be the total revenues going to domestic producers, foreign producers (after-tax), and the government? Explain.(c) Given a world price of $4, what would be the difference in the total revenue received by foreign producers with a $2 per unit tariff compared with a quota of 20,000 units?
(a) What would price and quantity be if the market were closed to international trade? What would the domestic and foreign quantity supplied be if it were open to international trade and the world price was $4?(b) If the world price was $4 and a tariff of $2 were placed on the product, what would be the total revenues going to domestic producers, foreign producers (after-tax), and the government? Explain.(c) Given a world price of $4, what would be the difference in the total revenue received by foreign producers with a $2 per unit tariff compared with a quota of 20,000 units?
 (a) What would price and quantity be if the market were closed to international trade? What would the domestic and foreign quantity supplied be if it were open to international trade and the world price was $4?(b) If the world price was $4 and a tariff of $2 were placed on the product, what would be the total revenues going to domestic producers, foreign producers (after-tax), and the government? Explain.(c) Given a world price of $4, what would be the difference in the total revenue received by foreign producers with a $2 per unit tariff compared with a quota of 20,000 units?
(a) What would price and quantity be if the market were closed to international trade? What would the domestic and foreign quantity supplied be if it were open to international trade and the world price was $4?(b) If the world price was $4 and a tariff of $2 were placed on the product, what would be the total revenues going to domestic producers, foreign producers (after-tax), and the government? Explain.(c) Given a world price of $4, what would be the difference in the total revenue received by foreign producers with a $2 per unit tariff compared with a quota of 20,000 units?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Of all the reason for protests against the WTO, which are most substantive?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What are the similarities and differences in the economic effects of tariffs and quotas?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What are the limitations to the diversification for stability argument for trade protection?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Evaluate the statement: "Tariffs and quotas are needed to protect Canadian products from dumping."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Who gains and who loses from a protective tariff? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



