Deck 14: Energy Generation in Mitochondria and Chloroplasts
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Premises:
Responses:
True
False
True
False
True
False
True
False
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Premises:
Responses:
False
True
False
True
False
True
False
True
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Premises:
Responses:
False
True
False
True
False
True
False
True
Question
Match between columns
Premises:
Responses:
False
True
False
True
False
True
False
True
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Premises:
Responses:
True
False
True
False
True
False
True
False
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/72
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Energy Generation in Mitochondria and Chloroplasts
1
Which of the following components of the electron-transport chain does NOT act as a proton pump?
A)NADH dehydrogenase
B)cytochrome c
C)cytochrome c reductase
D)cytochrome c oxidase
A)NADH dehydrogenase
B)cytochrome c
C)cytochrome c reductase
D)cytochrome c oxidase
B
2
Which of the following statements describes the mitochondrial matrix?
A)It is permeable to molecules with molecular mass as high as 5000 daltons.
B)It contains transporters for ATP molecules.
C)It contains proteins that are released during apoptosis.
D)It contains enzymes required for the oxidation of fatty acids.
A)It is permeable to molecules with molecular mass as high as 5000 daltons.
B)It contains transporters for ATP molecules.
C)It contains proteins that are released during apoptosis.
D)It contains enzymes required for the oxidation of fatty acids.
D
3
Which of the following is NOT part of the process known as "oxidative phosphorylation"?
A)Molecular oxygen serves as a final electron acceptor.
B)FADH2 and NADH become oxidized as they transfer a pair of electrons to the electron-transport chain.
C)The electron carriers in the electron-transport chain toggle between reduced and oxidized states as electrons are passed along.
D)ATP molecules are produced in the cytosol as glucose is converted into pyruvate.
A)Molecular oxygen serves as a final electron acceptor.
B)FADH2 and NADH become oxidized as they transfer a pair of electrons to the electron-transport chain.
C)The electron carriers in the electron-transport chain toggle between reduced and oxidized states as electrons are passed along.
D)ATP molecules are produced in the cytosol as glucose is converted into pyruvate.
D
4
Electron transport is coupled to ATP synthesis in mitochondria, in chloroplasts, and in the thermophilic bacterium Methanococcus.Which of the following is likely to affect the coupling of electron transport to ATP synthesis in ALL of these systems?
A)a potent inhibitor of cytochrome c oxidase
B)the removal of oxygen
C)the absence of light
D)an ADP analog that inhibits ATP synthase
A)a potent inhibitor of cytochrome c oxidase
B)the removal of oxygen
C)the absence of light
D)an ADP analog that inhibits ATP synthase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
NADH contains a high-energy bond that, when cleaved, donates a pair of electrons to the electron-transport chain.What are the immediate products of this bond cleavage?
A)NAD+ + OH−
B)NAD+ + H−
C)NAD− + H+
D)NAD + H
A)NAD+ + OH−
B)NAD+ + H−
C)NAD− + H+
D)NAD + H

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
During Stage 2 of oxidative phosphorylation, ATP synthesis is powered by movement of __________ ions through the __________.
A)H+; H+ pump
B)OH-; porin complex
C)H+; ATP synthase
D)elections; electron-transport chain
A)H+; H+ pump
B)OH-; porin complex
C)H+; ATP synthase
D)elections; electron-transport chain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Osmosis describes the movement of water across a biological membrane and down its concentration gradient.In chemiosmosis, useful energy is harnessed by the cell from the movement of __________ across the inner mitochondrial membrane into the matrix __________ a concentration gradient.
A)ATP, against
B)protons, down
C)electrons, down
D)ADP, against
A)ATP, against
B)protons, down
C)electrons, down
D)ADP, against

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following statements about mitochondrial division is TRUE?
A)Mitochondria divide in synchrony with the cell.
B)The rate of mitochondrial division is the same in all cell types.
C)Mitochondrial division is mechanistically similar to prokaryotic cell division.
D)Mitochondria cannot divide and produce energy for the cell at the same time.
A)Mitochondria divide in synchrony with the cell.
B)The rate of mitochondrial division is the same in all cell types.
C)Mitochondrial division is mechanistically similar to prokaryotic cell division.
D)Mitochondria cannot divide and produce energy for the cell at the same time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is the final result of the electron transfers in Stage 1 of the membrane-based processes that drive ATP synthesis in mitochondria?
A)OH− is oxidized to O2
B)pyruvate is oxidized to CO2
C)O2 is reduced to H2O
D)H− is converted to H2
A)OH− is oxidized to O2
B)pyruvate is oxidized to CO2
C)O2 is reduced to H2O
D)H− is converted to H2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following statements describes the mitochondrial intermembrane space?
A)It is permeable to molecules with molecular mass as high as 5000 daltons.
B)It contains transporters for ATP molecules.
C)It contains proteins that are released during apoptosis.
D)It contains enzymes required for the oxidation of fatty acids.
A)It is permeable to molecules with molecular mass as high as 5000 daltons.
B)It contains transporters for ATP molecules.
C)It contains proteins that are released during apoptosis.
D)It contains enzymes required for the oxidation of fatty acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A)The NADH dehydrogenase complex does not pump protons across the membrane.
B)The pH in the mitochondrial matrix is higher than the pH in the intermembrane space.
C)The proton concentration gradient and the membrane potential across the inner mitochondrial membrane tend to work against each other in driving protons from the intermembrane space into the matrix.
D)The difference in proton concentration across the inner mitochondrial membrane has a much larger effect than the membrane potential on the total proton-motive force.
A)The NADH dehydrogenase complex does not pump protons across the membrane.
B)The pH in the mitochondrial matrix is higher than the pH in the intermembrane space.
C)The proton concentration gradient and the membrane potential across the inner mitochondrial membrane tend to work against each other in driving protons from the intermembrane space into the matrix.
D)The difference in proton concentration across the inner mitochondrial membrane has a much larger effect than the membrane potential on the total proton-motive force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following statements describes the phosphorylation event that occurs during the process known as "oxidative phosphorylation"?
A)A phosphate group is added to ADP.
B)ATP is hydrolyzed in order to add phosphate groups to protein substrates.
C)A phosphate group is added to molecular oxygen.
D)Inorganic phosphate is transported into the mitochondrial matrix, increasing the local phosphate concentration.
A)A phosphate group is added to ADP.
B)ATP is hydrolyzed in order to add phosphate groups to protein substrates.
C)A phosphate group is added to molecular oxygen.
D)Inorganic phosphate is transported into the mitochondrial matrix, increasing the local phosphate concentration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following statements describes the mitochondrial outer membrane?
A)It is permeable to molecules with molecular mass as high as 5000 daltons.
B)It contains transporters for ATP molecules.
C)It contains proteins that are released during apoptosis.
D)It contains enzymes required for the oxidation of fatty acids.
A)It is permeable to molecules with molecular mass as high as 5000 daltons.
B)It contains transporters for ATP molecules.
C)It contains proteins that are released during apoptosis.
D)It contains enzymes required for the oxidation of fatty acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The mitochondrial ATP synthase consists of several different protein subunits.Which subunit binds to ADP + Pi and catalyzes the synthesis of ATP as a result of a conformational change?
A)transmembrane H+ carrier
B)F1 ATPase head
C)peripheral stalk
D)central stalk
A)transmembrane H+ carrier
B)F1 ATPase head
C)peripheral stalk
D)central stalk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is the source of protons that are pumped out of the mitochondrial matrix in Stage 1 of oxidative phosphorylation?
A)NADH
B)H2O
C)FADH
D)H2S
A)NADH
B)H2O
C)FADH
D)H2S

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which component of the electron-transport chain is required to combine the pair of electrons with molecular oxygen?
A)cytochrome c
B)cytochrome b-c1 complex
C)ubiquinone
D)cytochrome c oxidase
A)cytochrome c
B)cytochrome b-c1 complex
C)ubiquinone
D)cytochrome c oxidase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Bongkrekic acid is an antibiotic that inhibits the ATP/ADP transport protein in the inner mitochondrial membrane.Which of the following will allow electron transport to occur in mitochondria treated with bongkrekic acid?
A)placing the mitochondria in anaerobic conditions
B)adding FADH2
C)making the inner membrane permeable to protons
D)inhibiting the ATP synthase
A)placing the mitochondria in anaerobic conditions
B)adding FADH2
C)making the inner membrane permeable to protons
D)inhibiting the ATP synthase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The overall relationship that links bond-forming reactions to membrane transport processes in the mitochondria is called
A)chemiosmotic coupling.
B)proton pumping.
C)electron transfer.
D)ATP synthesis.
A)chemiosmotic coupling.
B)proton pumping.
C)electron transfer.
D)ATP synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following statements describes the mitochondrial inner membrane?
A)It is permeable to molecules with molecular mass as high as 5000 daltons.
B)It contains transporters for ATP molecules.
C)It contains proteins that are released during apoptosis.
D)It contains enzymes required for the oxidation of fatty acids.
A)It is permeable to molecules with molecular mass as high as 5000 daltons.
B)It contains transporters for ATP molecules.
C)It contains proteins that are released during apoptosis.
D)It contains enzymes required for the oxidation of fatty acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Modern eukaryotes depend on mitochondria to generate most of the cell's ATP.How many molecules of ATP can a single molecule of glucose generate?
A)30
B)2
C)20
D)36
A)30
B)2
C)20
D)36

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Cytochrome c oxidase is an enzyme complex that uses metal ions to help coordinate the transfer of four electrons to O2.Which metal atoms are found in the active site of this complex?
A)two iron atoms
B)one iron atom and one copper atom
C)one iron atom and one zinc atom
D)one zinc atom and one copper atom
A)two iron atoms
B)one iron atom and one copper atom
C)one iron atom and one zinc atom
D)one zinc atom and one copper atom

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A)Ubiquinone is a small, hydrophobic protein containing a metal group that acts as an electron carrier.
B)A 2Fe2S iron-sulfur center carries one electron, whereas a 4Fe4S iron-sulfur center carries two electrons.
C)Iron-sulfur centers generally have a higher redox potential than do cytochromes.
D)Mitochondrial electron carriers with the highest redox potential generally contain copper ions and/or heme groups.
A)Ubiquinone is a small, hydrophobic protein containing a metal group that acts as an electron carrier.
B)A 2Fe2S iron-sulfur center carries one electron, whereas a 4Fe4S iron-sulfur center carries two electrons.
C)Iron-sulfur centers generally have a higher redox potential than do cytochromes.
D)Mitochondrial electron carriers with the highest redox potential generally contain copper ions and/or heme groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The relationship of free-energy change (ΔG) to the concentrations of reactants and products is important because it predicts the direction of spontaneous chemical reactions.In the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi), the standard free-energy change (ΔG°) is −7.3 kcal/mole.The free-energy change depends on concentrations according to the following equation:
ΔG = ΔG° + 1.42 log10 ([ADP] [Pi]/[ATP])
In a resting muscle, the concentrations of ATP, ADP, and Pi are approximately 0.005 M, 0.001 M, and 0.010 M, respectively.What is the ΔG for ATP hydrolysis in resting muscle?
A)−11.1 kcal/mole
B)−8.72 kcal/mole
C)6.01 kcal/mole
D)−5.88 kcal/mole
ΔG = ΔG° + 1.42 log10 ([ADP] [Pi]/[ATP])
In a resting muscle, the concentrations of ATP, ADP, and Pi are approximately 0.005 M, 0.001 M, and 0.010 M, respectively.What is the ΔG for ATP hydrolysis in resting muscle?
A)−11.1 kcal/mole
B)−8.72 kcal/mole
C)6.01 kcal/mole
D)−5.88 kcal/mole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The relationship of free-energy change (ΔG) to the concentrations of reactants and products is important because it predicts the direction of spontaneous chemical reactions.In the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi), the standard free-energy change (ΔG°) is −7.3 kcal/mole.The free-energy change depends on concentrations according to the following equation:
ΔG = ΔG° + 1.42 log10 ([ADP] [Pi]/[ATP])
In a resting muscle, the concentrations of ATP, ADP, and Pi are approximately 0.005 M, 0.001 M, and 0.010 M, respectively.What is the ΔG for ATP synthesis in resting muscle?
A)−6.01 kcal/mole
B)5.88 kcal/mole
C)8.72 kcal/mole
D)11.1 kcal/mole
ΔG = ΔG° + 1.42 log10 ([ADP] [Pi]/[ATP])
In a resting muscle, the concentrations of ATP, ADP, and Pi are approximately 0.005 M, 0.001 M, and 0.010 M, respectively.What is the ΔG for ATP synthesis in resting muscle?
A)−6.01 kcal/mole
B)5.88 kcal/mole
C)8.72 kcal/mole
D)11.1 kcal/mole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In the electron-transport chain in chloroplasts, __________-energy electrons are taken from __________.
A)high; H2O.
B)low; H2O.
C)high; NADPH.
D)low; NADPH.
A)high; H2O.
B)low; H2O.
C)high; NADPH.
D)low; NADPH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Stage 2 of photosynthesis, sometimes referred to as the dark reactions, involves the reduction of CO2 to produce organic compounds such as sucrose.What cofactor is the electron donor for carbon fixation?
A)H2O
B)NADH
C)FADH2
D)NADPH
A)H2O
B)NADH
C)FADH2
D)NADPH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which ratio of NADH to NAD+ in solution will generate the largest positive redox potential?
A)1:10
B)10:1
C)1:1
D)5:1
A)1:10
B)10:1
C)1:1
D)5:1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If you shine light on chloroplasts and measure the rate of photosynthesis as a function of light intensity, you get a curve that reaches a plateau at a fixed rate of photosynthesis, x, as shown in Figure 14-41. 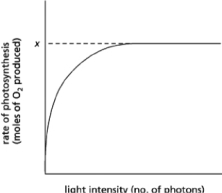 Figure 14-41
Figure 14-41
Which of the following conditions will increase the value of x?
A)increasing the number of chlorophyll molecules in the antenna complexes
B)increasing the number of reaction centers
C)adding a powerful oxidizing agent
D)decreasing the wavelength of light used
 Figure 14-41
Figure 14-41Which of the following conditions will increase the value of x?
A)increasing the number of chlorophyll molecules in the antenna complexes
B)increasing the number of reaction centers
C)adding a powerful oxidizing agent
D)decreasing the wavelength of light used

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Ubiquinone is one of two mobile electron carriers in the electron-transport chain.Where does the additional pair of electrons reside in the reduced ubiquinone molecule?
A)The electrons are added directly to the aromatic ring.
B)The electrons are added to each of two ketone oxygens on the aromatic ring.
C)The electrons are added to the hydrocarbon tail, which hides them inside the membrane bilayer.
D)Both electrons, and one proton, are added to a single ketone oxygen bound to the aromatic ring.
A)The electrons are added directly to the aromatic ring.
B)The electrons are added to each of two ketone oxygens on the aromatic ring.
C)The electrons are added to the hydrocarbon tail, which hides them inside the membrane bilayer.
D)Both electrons, and one proton, are added to a single ketone oxygen bound to the aromatic ring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Photosynthesis is a process that takes place in chloroplasts and uses light energy to generate high-energy electrons, which are passed along an electron-transport chain.Where are the proteins of the electron-transport chain located in chloroplasts?
A)thylakoid space
B)stroma
C)inner membrane
D)thylakoid membrane
A)thylakoid space
B)stroma
C)inner membrane
D)thylakoid membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following statements about "redox potential" is TRUE?
A)Redox potential is a measure of a molecule's capacity to strip electrons from oxygen.
B)For molecules that have a strong tendency to pass along their electrons, the standard redox potential is negative.
C)The transfer of electrons from cytochrome c oxidase to oxygen has a negative redox potential.
D)A molecule's redox potential is a measure of the molecule's capacity to pass along electrons to oxygen.
A)Redox potential is a measure of a molecule's capacity to strip electrons from oxygen.
B)For molecules that have a strong tendency to pass along their electrons, the standard redox potential is negative.
C)The transfer of electrons from cytochrome c oxidase to oxygen has a negative redox potential.
D)A molecule's redox potential is a measure of the molecule's capacity to pass along electrons to oxygen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The ATP synthase found in chloroplasts is structurally similar to the ATP synthase in mitochondria.Given that ATP is being synthesized in the stroma, where will the F0 portion of the ATP synthase be located?
A)thylakoid space
B)stroma
C)inner membrane
D)thylakoid membrane
A)thylakoid space
B)stroma
C)inner membrane
D)thylakoid membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is not an electron carrier that participates in the electron-transport chain?
A)cytochrome
B)quinone
C)rhodopsin
D)copper ion
A)cytochrome
B)quinone
C)rhodopsin
D)copper ion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The relationship of free-energy change (ΔG) to the concentrations of reactants and products is important because it predicts the direction of spontaneous chemical reactions.Consider, for example, the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi).The standard free-energy change (ΔG°) for this reaction is −7.3 kcal/mole.The free-energy change depends on concentrations according to the following equation:
ΔG = ΔG° + 1.42 log10 ([ADP] [Pi]/[ATP])
In a resting muscle, the concentrations of ATP, ADP, and Pi are approximately 0.005 M, 0.001 M, and 0.010 M, respectively.At [Pi] = 0.010 M, what will be the ratio of [ATP] to [ADP] at equilibrium?
A)1.38 × 106
B)1
C)7.2 × 10−8
D)5.14
ΔG = ΔG° + 1.42 log10 ([ADP] [Pi]/[ATP])
In a resting muscle, the concentrations of ATP, ADP, and Pi are approximately 0.005 M, 0.001 M, and 0.010 M, respectively.At [Pi] = 0.010 M, what will be the ratio of [ATP] to [ADP] at equilibrium?
A)1.38 × 106
B)1
C)7.2 × 10−8
D)5.14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In stage 1 of photosynthesis, a proton gradient is generated and ATP is synthesized.Where do protons become concentrated in the chloroplast?
A)thylakoid space
B)stroma
C)inner membrane
D)thylakoid membrane
A)thylakoid space
B)stroma
C)inner membrane
D)thylakoid membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following statements about cytochrome c is TRUE?
A)Cytochrome c shuttles electrons between the NADH dehydrogenase complex and cytochrome c reductase complex.
B)When cytochrome c becomes reduced, two cysteines (sulfur-containing amino acids) become covalently bound to a heme group.
C)The pair of electrons accepted by cytochrome c are added to the porphyrin ring of the bound heme group.
D)Cytochrome c is the last protein in the electron-transport chain, passing its electrons directly to molecular oxygen, a process that reduces O2 to H2O.
A)Cytochrome c shuttles electrons between the NADH dehydrogenase complex and cytochrome c reductase complex.
B)When cytochrome c becomes reduced, two cysteines (sulfur-containing amino acids) become covalently bound to a heme group.
C)The pair of electrons accepted by cytochrome c are added to the porphyrin ring of the bound heme group.
D)Cytochrome c is the last protein in the electron-transport chain, passing its electrons directly to molecular oxygen, a process that reduces O2 to H2O.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
NADH and FADH2 carry high-energy electrons that are used to power the production of ATP in the mitochondria.These cofactors are generated during glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the fatty acid oxidation cycle.Which molecule below can produce the most ATP? Explain your answer.
A)NADH from glycolysis
B)FADH2 from the fatty acid cycle
C)NADH from the citric acid cycle
D)FADH2 from the citric acid cycle
A)NADH from glycolysis
B)FADH2 from the fatty acid cycle
C)NADH from the citric acid cycle
D)FADH2 from the citric acid cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Experimental evidence supporting the chemiosmotic hypothesis was gathered by using artificial vesicles containing a protein that can pump protons in one direction across the vesicle membrane to create a proton gradient.Which protein was used to generate the gradient in a highly controlled manner?
A)cytochrome c oxidase
B)NADH dehydrogenase
C)cytochrome c
D)bacteriorhodopsin
A)cytochrome c oxidase
B)NADH dehydrogenase
C)cytochrome c
D)bacteriorhodopsin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A)Only compounds with negative redox potentials can donate electrons to other compounds under standard conditions.
B)Compounds that donate one electron have higher redox potentials than those compounds that donate two electrons.
C)The ΔE0′ of a redox pair does not depend on the concentration of each member of the pair.
D)The free-energy change, ΔG, for an electron-transfer reaction does not depend on the concentration of each member of a redox pair.
A)Only compounds with negative redox potentials can donate electrons to other compounds under standard conditions.
B)Compounds that donate one electron have higher redox potentials than those compounds that donate two electrons.
C)The ΔE0′ of a redox pair does not depend on the concentration of each member of the pair.
D)The free-energy change, ΔG, for an electron-transfer reaction does not depend on the concentration of each member of a redox pair.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The photosystems in chloroplasts contain hundreds of chlorophyll molecules, most of which are part of
A)plastoquinone.
B)the antenna complex.
C)the reaction center.
D)the ferredoxin complex.
A)plastoquinone.
B)the antenna complex.
C)the reaction center.
D)the ferredoxin complex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following statements about the possible fates of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is FALSE?
A)It can be exported from the chloroplast to the cytosol for conversion into sucrose.
B)It can be used to make starch, which is stored inside the stroma of the chloroplast.
C)It can be used as a precursor for fatty acid synthesis and stored as fat droplets in the stroma.
D)It can be transported into the thylakoid space for use as a secondary electron acceptor downstream of the electron-transport chain.
A)It can be exported from the chloroplast to the cytosol for conversion into sucrose.
B)It can be used to make starch, which is stored inside the stroma of the chloroplast.
C)It can be used as a precursor for fatty acid synthesis and stored as fat droplets in the stroma.
D)It can be transported into the thylakoid space for use as a secondary electron acceptor downstream of the electron-transport chain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Some bacteria can live both aerobically and anaerobically.How does the ATP synthase in the plasma membrane of the bacterium help such bacteria to keep functioning in the absence of oxygen?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The citric acid cycle generates NADH and FADH2, which are then used in the process of oxidative phosphorylation to make ATP.The reactions in the citric acid cycle do not utilize oxygen.Yet the citric acid cycle stops almost immediately when O2 is removed.Explain this observation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Below is a list of breakthroughs in energy metabolism in living systems.Which is the correct order in which they are thought to have evolved?
A)H2O-splitting enzyme activity
B)light-dependent transfer of electrons from H2S to NADPH
C)the consumption of fermentable organic acids
D)oxygen-dependent ATP synthesis
A)A, C, D, B
B)C, A, B, D
C)B, C, A, D
D)C, B, A, D
A)H2O-splitting enzyme activity
B)light-dependent transfer of electrons from H2S to NADPH
C)the consumption of fermentable organic acids
D)oxygen-dependent ATP synthesis
A)A, C, D, B
B)C, A, B, D
C)B, C, A, D
D)C, B, A, D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If you add a compound to illuminated chloroplasts that inhibits the NADP+ reductase, NADPH generation ceases, as expected.However, ferredoxin does not accumulate in the reduced form because it is able to donate its electrons not only to NADP+ (via NADP+ reductase) but also back to the cytochrome b6-f complex.Thus, in the presence of the compound, a "cyclic" form of photosynthesis occurs in which electrons flow in a circle from ferredoxin, to the cytochrome b6-f complex, to plastocyanin, to photosystem I, to ferredoxin.What will happen if you now also inhibit photosystem II?
A)Less ATP will be generated per photon absorbed.
B)ATP synthesis will cease.
C)Plastoquinone will accumulate in the oxidized form.
D)Plastocyanin will accumulate in the oxidized form.
A)Less ATP will be generated per photon absorbed.
B)ATP synthesis will cease.
C)Plastoquinone will accumulate in the oxidized form.
D)Plastocyanin will accumulate in the oxidized form.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the phylogenetic trees in Figure 14-47 is the most accurate? Explain your answer.Note: the mitochondria and chloroplasts are from maize, but they are treated as independent "organisms" for the purposes of this question. (a)
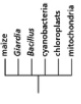
(c)
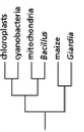
(e)
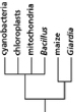
(b)
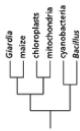
(d)
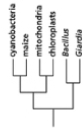 Figure 14-47
Figure 14-47
A)Tree (a)
B)Tree (b)
C)Tree (c)
D)Tree (d)
E)Tree (e)

(c)

(e)

(b)

(d)
 Figure 14-47
Figure 14-47A)Tree (a)
B)Tree (b)
C)Tree (c)
D)Tree (d)
E)Tree (e)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
For each of the following sentences, fill in the blanks with the best word or phrase selected from the list below.Not all words or phrases will be used; each word or phrase should be used only once.
acetyl groups glucose NADPH
carbon dioxide NAD+ oxidative phosphorylation
chemiosmosis NADH oxygen
fatty acids NADP+ pyruvate
Mitochondria can use both __________ and __________ directly as fuel.__________ produced in the citric acid cycle donates electrons to the electron-transport chain.The citric acid cycle oxidizes __________ and produces __________ as a waste product.__________ acts as the final electron acceptor in the electron-transport chain.The synthesis of ATP in mitochondria is also known as __________.
acetyl groups glucose NADPH
carbon dioxide NAD+ oxidative phosphorylation
chemiosmosis NADH oxygen
fatty acids NADP+ pyruvate
Mitochondria can use both __________ and __________ directly as fuel.__________ produced in the citric acid cycle donates electrons to the electron-transport chain.The citric acid cycle oxidizes __________ and produces __________ as a waste product.__________ acts as the final electron acceptor in the electron-transport chain.The synthesis of ATP in mitochondria is also known as __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Match between columns
Premises:
Responses:
True
False
True
False
True
False
True
False

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Based upon what you know about metabolism, explain how electrons are stripped from food molecules and used to drive the electron-transport chain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The enzyme ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase (Rubisco) normally adds carbon dioxide to ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate.However, it will also catalyze a competing reaction in which O2 is added to ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate to form 3-phosphoglycerate and phosphoglycolate.Assume that phosphoglycolate is a compound that cannot be used in any further reactions.If O2 and CO2 have the same affinity for Rubisco, which of the following is the lowest ratio of CO2 to O2 at which a net synthesis of sugar can occur?
A)1:3
B)1:2
C)3:1
D)2:1
A)1:3
B)1:2
C)3:1
D)2:1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Mitochondrial structure and the reaction products generated inside the matrix are critical for generating stores of energy.Answer the following questions based on what you know about mitochondrial structure and processes.
A.The gradients used to generate ATP are maintained across the inner mitochondrial membrane.Why don't we observe a similar gradient generation across the outer mitochondrial membrane?
B.The proton-motive force created by the electrochemical proton gradient is the source of free energy utilized in ATP formation.Describe the two components contributing to the total proton-motive force.
A.The gradients used to generate ATP are maintained across the inner mitochondrial membrane.Why don't we observe a similar gradient generation across the outer mitochondrial membrane?
B.The proton-motive force created by the electrochemical proton gradient is the source of free energy utilized in ATP formation.Describe the two components contributing to the total proton-motive force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Name the mitochondrial localization of each of the following macromolecules.
A.porin proteins
B.mitochondrial chromosome
C.citric acid cycle enzymes
D.electron-transport chain proteins
E.ATP synthase
F.pyruvate transporter
A.porin proteins
B.mitochondrial chromosome
C.citric acid cycle enzymes
D.electron-transport chain proteins
E.ATP synthase
F.pyruvate transporter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Describe the steps by which the F0 portion of the ATP synthase harnesses the proton-motive force to help synthesize ATP.What would you expect to observe if the proton gradient were reversed? Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Match between columns
Premises:
Responses:
False
True
False
True
False
True
False
True

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Oxidative phosphorylation, as it occurs in modern eukaryotes, is a complex process that probably arose in simple stages in primitive bacteria.Which mechanism is proposed to have arisen first as this complex system evolved?
A)electron transfers coupled to a proton pump
B)the reaction of oxygen with an ancestor of cytochrome c oxidase
C)ATP-driven proton pumps
D)the generation of ATP from the energy of a proton gradient
A)electron transfers coupled to a proton pump
B)the reaction of oxygen with an ancestor of cytochrome c oxidase
C)ATP-driven proton pumps
D)the generation of ATP from the energy of a proton gradient

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What are the major molecules that need to be transported into and out of the mitochondrion to keep the citric acid cycle, electron-transport chain, and ATP synthesis going?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
For each of the following sentences, fill in the blanks with the best word or phrase selected from the list below.Not all words or phrases will be used; each word or phrase should be used only once.
cytochrome b-c1 complex oxidation second
cytochrome c oxidation-reduction the
cytochrome c oxidase phosphorylation third
first plastoquinone uniquinone
NADH dehydrogenase reduction
NADH donates electrons to the __________ of the three respiratory enzyme complexes in the mitochondrial electron-transport-chain.__________ is a small protein that acts as a mobile electron carrier in the respiratory chain.__________ transfers electrons to oxygen.Electron transfer in the chain occurs in a series of __________ reactions.The first mobile electron carrier in the respiratory chain is __________.
cytochrome b-c1 complex oxidation second
cytochrome c oxidation-reduction the
cytochrome c oxidase phosphorylation third
first plastoquinone uniquinone
NADH dehydrogenase reduction
NADH donates electrons to the __________ of the three respiratory enzyme complexes in the mitochondrial electron-transport-chain.__________ is a small protein that acts as a mobile electron carrier in the respiratory chain.__________ transfers electrons to oxygen.Electron transfer in the chain occurs in a series of __________ reactions.The first mobile electron carrier in the respiratory chain is __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Explain how the diffusion of ubiquinone in three dimensions is restricted in order to ensure its proximity to the other enzyme complexes for the rapid transfer of electrons?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Match between columns
Premises:
Responses:
False
True
False
True
False
True
False
True

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Match between columns
Premises:
Responses:
False
True
False
True
False
True
False
True

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Explain how scientists used artificial vesicles to prove that the generation of ATP by the ATP synthase was not powered by a single high-energy intermediate but rather by a proton gradient.Be sure to describe the two experiments that were negative controls (no ATP generated), the positive control (ATP generated as expected), and a fourth experiment proving that the gradient is the required energy source.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Compare and contrast the process of reducing N2 to NH3 in Methanococcus jannaschii to the reduction of O2 to H20 in the mitochondrial matrix.What inferences can you draw with respect to the early evolution of energy-generating systems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Use the terms provided below to fill in the blanks.Not all words or phrases will be used; each word or phrase may be used more than once.
benzene longer porphyrin
blue orange red
electrons photons shorter
heme
Photons from sunlight that are in the __________ wavelength range are preferentially absorbed by chlorophyll molecules to raise the energy levels of electrons in the __________ ring.The __________ reflected are lower in energy, which is indicated in the ________, green wavelengths detected by the human eye.
benzene longer porphyrin
blue orange red
electrons photons shorter
heme
Photons from sunlight that are in the __________ wavelength range are preferentially absorbed by chlorophyll molecules to raise the energy levels of electrons in the __________ ring.The __________ reflected are lower in energy, which is indicated in the ________, green wavelengths detected by the human eye.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Match between columns
Premises:
Responses:
True
False
True
False
True
False
True
False

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In 1925, David Keilin used a simple spectroscope to observe the characteristic absorption bands of the cytochromes that participate in the electron-transport chain in mitochondria.A spectroscope passes a very bright light through the sample of interest and then through a prism to display the spectrum from red to blue.If molecules in the sample absorb light of particular wavelengths, dark bands will interrupt the colors of the rainbow.His key discovery was that the absorption bands disappeared when oxygen was introduced and then reappeared when the samples became anoxic.Subsequent findings demonstrated that different cytochromes absorb light of different frequencies.When light of a characteristic wavelength shines on a mitochondrial sample, the amount of light absorbed is proportional to the amount of a particular cytochrome present in its reduced form.Thus, spectrophotometric methods can be used to measure how the amounts of reduced cytochromes change over time in response to various treatments.If isolated mitochondria are incubated with a source of electrons such as succinate, but without oxygen, electrons enter the respiratory chain, reducing each of the electron carriers almost completely.When oxygen is then introduced, the carriers oxidize at different rates, as can be seen from the decline in the amount of reduced cytochrome (see Figure 14-27).Note that cytochromes a1 and a3 cannot be distinguished and thus are listed as cytochrome (a1 + a3).How does this result allow you to order the electron carriers in the respiratory chain? What is their order? 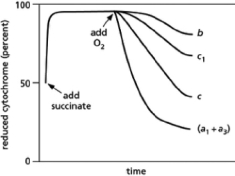
Figure 14-27

Figure 14-27

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Porphyrin ring molecules are critical both for oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria and for photosynthesis in chloroplasts.Compare and contrast the role of this type of molecule in each process and explain the roles of O2 and H2O in each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
For each of the following sentences, choose one of the options enclosed in square brackets to make a correct statement.
An electron bound to a molecule with low affinity for electrons is a [high/low]-energy electron.Transfer of an electron from a molecule with low affinity to one with higher affinity has a [positive/negative] ΔG° and is thus [favorable/unfavorable] under standard conditions.If the reduced form of a redox pair is a strong electron donor with a [high/low] affinity for electrons, it is easily oxidized; the oxidized member of such a redox pair is a [weak/strong] electron acceptor.
An electron bound to a molecule with low affinity for electrons is a [high/low]-energy electron.Transfer of an electron from a molecule with low affinity to one with higher affinity has a [positive/negative] ΔG° and is thus [favorable/unfavorable] under standard conditions.If the reduced form of a redox pair is a strong electron donor with a [high/low] affinity for electrons, it is easily oxidized; the oxidized member of such a redox pair is a [weak/strong] electron acceptor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The respiratory chain is relatively inaccessible in the experimental manipulation of intact mitochondria.After disrupting mitochondria with ultrasound, however, it is possible to isolate functional submitochondrial particles, which consist of broken cristae that have resealed inside-out into small, closed vesicles.In these vesicles, the components that originally faced the matrix are now exposed to the surrounding medium.
A.How might such an arrangement aid in the study of electron transport and ATP synthesis?
B.Consider an anaerobic preparation of such submitochondrial particles.If a small amount of oxygen is added, do you predict that the preparation will consume oxygen in respiration reactions? Will the medium outside the particles become more acidic or more basic? What, if anything, will change if the flow of protons through ATP synthase is blocked by an inhibitor? Explain your answer.
A.How might such an arrangement aid in the study of electron transport and ATP synthesis?
B.Consider an anaerobic preparation of such submitochondrial particles.If a small amount of oxygen is added, do you predict that the preparation will consume oxygen in respiration reactions? Will the medium outside the particles become more acidic or more basic? What, if anything, will change if the flow of protons through ATP synthase is blocked by an inhibitor? Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
For each of the following sentences, fill in the blanks with the best word or phrase selected from the list below.Not all words or phrases will be used; each word or phrase should be used only once.
3-phosphoglycerate NADPH starch
ATP pyruvate sucrose
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate ribose 1,5-bisphosphate
NADH ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate
In the carbon-fixation process in chloroplasts, carbon dioxide is initially added to the sugar __________.The final product of carbon fixation in chloroplasts is the three-carbon compound __________.This is converted into __________ (which can be used directly by the mitochondria), into __________ (which is exported to other cells), and into __________ (which is stored in the stroma).The carbon-fixation cycle requires energy in the form of __________ and reducing power in the form of __________.
3-phosphoglycerate NADPH starch
ATP pyruvate sucrose
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate ribose 1,5-bisphosphate
NADH ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate
In the carbon-fixation process in chloroplasts, carbon dioxide is initially added to the sugar __________.The final product of carbon fixation in chloroplasts is the three-carbon compound __________.This is converted into __________ (which can be used directly by the mitochondria), into __________ (which is exported to other cells), and into __________ (which is stored in the stroma).The carbon-fixation cycle requires energy in the form of __________ and reducing power in the form of __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Human infants have a much larger portion of brown adipose tissue than adult humans.It was found that the mitochondria in brown adipocytes (brown fat cells) have a novel protein in the inner mitochondrial membrane.This protein, called the uncoupling protein (UCP), was found to transport protons from the intermembrane space into the matrix.
A.What is the impact of UCP on oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria of brown fat?
B.Propose an explanation for the higher proportion of brown fat cells in infants compared to adults.
A.What is the impact of UCP on oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria of brown fat?
B.Propose an explanation for the higher proportion of brown fat cells in infants compared to adults.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Describe how a standard flashlight battery can convert energy into useful work and explain how this is similar to the energy conversions in the mitochondria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Consider a redox reaction between molecules A and B.Molecule A has a redox potential of −100 mV and molecule B has a redox potential of +100 mV.For the transfer of electrons from A to B, is the ΔG° positive or negative or zero? Under what conditions will the reverse reaction, transfer of electrons from B to A, occur?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



