Deck 12: Decisions About Production, Products, and Location
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/175
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Decisions About Production, Products, and Location
1
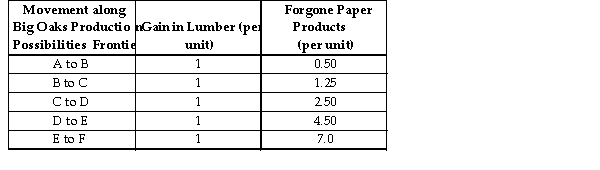 Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.
Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.Refer to the table above. If the profit for each unit of paper product is $3.00 and the profit for each unit of lumber is $13.50, what is the marginal benefit for each unit of lumber produced?
A)$13.50
B)$10.50
C)$3.00
D)$16.50
A
2
 Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.
Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.Refer to the table above. If the profit for each unit of paper product is $3.00 and the profit for each unit of lumber is $13.50, the profit- maximizing quantity of lumber and paper products is located between which to points on Big Oaks' production possibilities frontier?
A)B and C
B)D and E
C)E and F
D)C and D
B
3
 Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.
Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.Refer to the table above. Suppose the profit for each unit of paper product is $2.00 and the profit for each unit of lumber is $5 and Big Oaks is producing the profit- maximizing quantity of lumber and paper products. If the profit from each unit of paper product increases from $2 to $3 and the profit for each unit of lumber does not change, to maximize profit, Big Oaks should produce a proportion of paper products and produce units of paper products and lumber.
A)greater; more
B)smaller; less
C)greater; less
D)smaller; more
A
4
 Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.
Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.Refer to the table above. If the profit for each unit of paper product is $2 and the profit for each unit of lumber is $5, what is Big Oaks' marginal cost of producing between points B and C on their production possibilities frontier?
A)$6.25
B)$2.50
C)$1.25
D)$5.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
 Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.
Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.Refer to the table above. If the profit for each unit of paper product is $2 and the profit for each unit of lumber is $5, what is Big Oaks' marginal cost of producing between points D and E on their production possibilities frontier?
A)$4.50
B)$22.50
C)$10.50
D)$9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
 Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.
Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.Refer to the table above. Suppose the profit for each unit of paper product is $3.00 and the profit for each unit of lumber is $13.50 and Big Oaks is producing the profit- maximizing quantity of lumber and paper products. If the profit from each unit of lumber increases from $13.50 to $15.00 and the profit for each unit of paper products does not change, to maximize profit, Big Oaks should produce a proportion of lumber and produce units of paper products and lumber.
A)greater; more
B)smaller; less
C)smaller; more
D)greater; less

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
 Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.
Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.Refer to the table above. If the profit for each unit of paper product is $3.00 and the profit for each unit of lumber is $13.50, what is Big Oaks' marginal cost of producing between points B and C on their production possibilities frontier?
A)$1.25
B)$7.50
C)$5.75
D)$3.75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
 Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.
Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.Refer to the table above. If the profit for each unit of paper product is $3.00 and the profit for each unit of lumber is $13.50, what is the marginal benefit for each unit of paper products produced?
A)$10.50
B)$13.50
C)$16.50
D)$3.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
 Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.
Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.Refer to the table above. Suppose the profit for each unit of paper product is $3.00 and the profit for each unit of lumber is $13.50 and Big Oaks is producing the profit- maximizing quantity of lumber and paper products. If the profit from each unit of paper product increases from $3.00 to $4.00 and the profit for each unit of lumber does not change, to maximize profit, Big Oaks should produce a proportion of paper products and produce _ units of paper products and lumber.
A)greater; less
B)smaller; more
C)smaller; less
D)greater; more

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Suppose Bright Orange is large firm that grows and harvests oranges. Each orange yields 2 ounces of orange juice and exactly one orange peel. The market for oranges is perfectly competitive and Bright Orange sells the orange juice to juice distributors and the orange peels to fragrance companies. At a quantity of 500,000 oranges, juice distributors will pay $0.05 per ounce of orange juice and fragrance companies will pay $0.10 per orange peel. At the quantity of 500,000 oranges, what is the market equilibrium price of an orange?
A)$0.20
B)$0.05
C)$0.15
D)$0.10
A)$0.20
B)$0.05
C)$0.15
D)$0.10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
 Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.
Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.Refer to the table above. If the profit for each unit of paper product is $3.00 and the profit for each unit of lumber is $13.50, what is Big Oaks' marginal cost of producing between points C and D on their production possibilities frontier?
A)$3.75
B)$9.25
C)$7.50
D)$2.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A firm is producing a joint product, Product A and Product B, with variable proportions. At its current production levels, the marginal benefit of producing Product A is $3 and the marginal cost is $2 and the marginal benefit of producing Product B is $4 and the marginal cost is $5. To maximize profits, the managers of the firm should produce of Product A and of Product B.
A)less; less
B)less; more
C)more; more
D)more; less
A)less; less
B)less; more
C)more; more
D)more; less

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Suppose Bright Orange is large firm that grows and harvests oranges. Each orange yields 2 ounces of orange juice and exactly one orange peel. Bright Orange sells the orange juice to juice distributors and the orange peels to fragrance companies. If the market for oranges is perfectly competitive, Bright Orange will determine its profit- maximizing output level based on _.
A)the market price of an orange peel
B)the market price of two ounces of orange juice
C)the market price of an orange
D)the market price of an ounce of orange juice
A)the market price of an orange peel
B)the market price of two ounces of orange juice
C)the market price of an orange
D)the market price of an ounce of orange juice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Suppose Bright Orange is large firm that grows and harvests oranges. Each orange yields 2 ounces of orange juice and exactly one orange peel. The market for oranges is perfectly competitive and Bright Orange sells the orange juice to juice distributors and the orange peels to fragrance companies. At a quantity of 400,000 oranges, juice distributors will pay $0.04 per ounce of orange juice and fragrance companies will pay $0.15 per orange peel. At the quantity of 400,000 oranges, what is the market equilibrium price of an orange?
A)$0.23
B)$0.19
C)$0.25
D)$0.11
A)$0.23
B)$0.19
C)$0.25
D)$0.11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
 Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.
Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.Refer to the table above. If the profit for each unit of paper product is $2 and the profit for each unit of lumber is $5, the profit- maximizing quantity of lumber and paper products is located between which to points on Big Oaks' production possibilities frontier?
A)C and D
B)A and B
C)B and C
D)D and E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
 Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.
Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.Refer to the table above. If the profit for each unit of paper product is $2 and the profit for each unit of lumber is $5, what is the marginal benefit for each unit of lumber produced?
A)$3
B)$2
C)$5
D)$7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Suppose Bright Orange is large firm that grows and harvests oranges. Each orange yields 2 ounces of orange juice and exactly one orange peel. Bright Orange sells the orange juice to juice distributors and the orange peels to fragrance companies. The market demand for Bright Orange's oranges is equal to _ _.
A)the demand for orange peels only
B)the demand for orange juice plus the demand for orange peels
C)the difference between the demand for orange peels and orange juice
D)the demand for orange juice only
A)the demand for orange peels only
B)the demand for orange juice plus the demand for orange peels
C)the difference between the demand for orange peels and orange juice
D)the demand for orange juice only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
 Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.
Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.Refer to the table above. If the profit for each unit of paper product is $2 and the profit for each unit of lumber is $5, what is the marginal benefit for each unit of paper products produced?
A)$3
B)$7
C)$2
D)$5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Joint production is production that results in the simultaneous production of .
A)two or more outputs
B)exactly three outputs
C)exactly two outputs
D)exactly one output
A)two or more outputs
B)exactly three outputs
C)exactly two outputs
D)exactly one output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
 Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.
Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amo paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable prop The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.Refer to the table above. Suppose the profit for each unit of paper product is $2 and the profit for each unit of lumber is $5 and Big Oaks is producing the profit- maximizing quantity of lumber and paper products. If the profit from each unit of lumber increases from $5 to $6 and the profit for each unit of paper products does not change, to maximize profit, Big Oaks should produce a proportion of lumber and produce _ units of paper products and lumber.
A)smaller; less
B)greater; more
C)smaller; more
D)greater; less

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
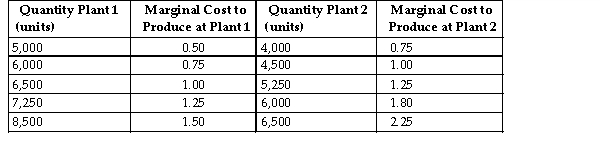 Crunchy Fruits makes dried fruit snacks. Crunchy Fruits has a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The table abo summarizes the marginal cost of production at the individual plants and the corresponding quantity produced at the individual plants.
Crunchy Fruits makes dried fruit snacks. Crunchy Fruits has a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The table abo summarizes the marginal cost of production at the individual plants and the corresponding quantity produced at the individual plants.Refer to the table above. What is Crunchy Fruits total marginal cost to produce 11,750 units?
A)$3.25
B)$2.25
C)$1.25
D)$2.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
 Crunchy Fruits makes dried fruit snacks. Crunchy Fruits has a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The table abo summarizes the marginal cost of production at the individual plants and the corresponding quantity produced at the individual plants.
Crunchy Fruits makes dried fruit snacks. Crunchy Fruits has a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The table abo summarizes the marginal cost of production at the individual plants and the corresponding quantity produced at the individual plants.Refer to the table above. What is Crunchy Fruits total marginal cost to produce 15,000 units?
A)$3.75
B)$3.25
C)$4.50
D)$2.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If a firm is producing a joint product and the price of one of the products increases, the marginal benefit of producing more of that product increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Because the decision involves the production of two goods, marginal analysis cannot be used to determine the profit- maximizing proportions of jointly produced products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
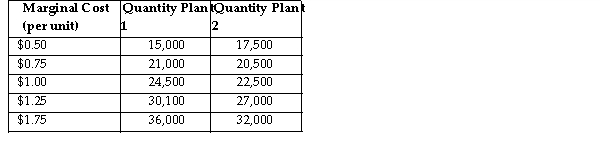 Sweet Grams makes graham cracker snack packages. Sweet Grams is a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The a table summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in the separate plants. Assume Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm.
Sweet Grams makes graham cracker snack packages. Sweet Grams is a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The a table summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in the separate plants. Assume Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm.Refer to the table above. If Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm and the market price $1.00 per unit, what is the profit- maximizing quantity for Sweet Grams to produce at Plant 1?
A)22,500
B)27,000
C)32,000
D)24,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A firm is producing a joint product, Product A and Product B, with variable proportions. At its current production levels, the marginal benefit of producing Product A is $4 and the marginal cost is $2 and the marginal benefit of producing Product B is $4 and the marginal cost is $6. To maximize profits, the managers of the firm should produce of Product A and of Product B.
A)less; more
B)more; more
C)more; less
D)less; less
A)less; more
B)more; more
C)more; less
D)less; less

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If a firm is producing a joint product with variable proportions, if the price of one of the joint products changes, to maximize profits, managers must adjust both the total production of the jointly produced product and the products' proportions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
 Crunchy Fruits makes dried fruit snacks. Crunchy Fruits has a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The table abo summarizes the marginal cost of production at the individual plants and the corresponding quantity produced at the individual plants.
Crunchy Fruits makes dried fruit snacks. Crunchy Fruits has a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The table abo summarizes the marginal cost of production at the individual plants and the corresponding quantity produced at the individual plants.Refer to the table above. What is Crunchy Fruits total marginal cost to produce 13,250 units?
A)$1.25
B)$1.80
C)$3.00
D)$3.05

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
 Crunchy Fruits makes dried fruit snacks. Crunchy Fruits has a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The table abo summarizes the marginal cost of production at the individual plants and the corresponding quantity produced at the individual plants.
Crunchy Fruits makes dried fruit snacks. Crunchy Fruits has a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The table abo summarizes the marginal cost of production at the individual plants and the corresponding quantity produced at the individual plants.Refer to the table above. What is Crunchy Fruits total marginal cost to produce 9,000 units?
A)$0.50
B)$1.25
C)$2.25
D)$0.75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A firm is producing a joint product, Product A and Product B, with variable proportions. At its current production levels, the marginal benefit of producing Product A is $12 and the marginal cost is $15 and the marginal benefit of producing Product B is $10 and the marginal cost is $6. To maximize profits, the managers of the firm should produce of Product A and of Product B.
A)less; more
B)more; more
C)more; less
D)less; less
A)less; more
B)more; more
C)more; less
D)less; less

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
 Sweet Grams makes graham cracker snack packages. Sweet Grams is a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The a table summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in the separate plants. Assume Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm.
Sweet Grams makes graham cracker snack packages. Sweet Grams is a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The a table summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in the separate plants. Assume Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm.Refer to the table above. If Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm and the market price $1.25 per unit, what is the profit- maximizing total quantity for Sweet Grams to produce?
A)68,000
B)57,100
C)30,100
D)27,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
 Crunchy Fruits makes dried fruit snacks. Crunchy Fruits has a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The table abo summarizes the marginal cost of production at the individual plants and the corresponding quantity produced at the individual plants.
Crunchy Fruits makes dried fruit snacks. Crunchy Fruits has a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The table abo summarizes the marginal cost of production at the individual plants and the corresponding quantity produced at the individual plants.Refer to the table above. What is Crunchy Fruits total marginal cost to produce 10,500 units?
A)$1.75
B)$.075
C)$1.00
D)$2.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A firm is producing a joint product, Product A and Product B, with variable proportions. At its current production levels, the marginal benefit of producing Product A is $8 and the marginal cost is $12 and the marginal benefit of producing Product B is $8 and the marginal cost is $2. To maximize profits, the managers of the firm should produce of Product A and of Product B.
A)more; more
B)less; less
C)less; more
D)more; less
A)more; more
B)less; less
C)less; more
D)more; less

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If a multi- plant firm has three plants and uses each of the plants to produce its product, the marginal cost to produce the firm's product is equal to .
A)the sum of the average fixed costs from each of the three plants
B)the plant with the highest marginal cost
C)the sum of the marginal costs from each of the three plants
D)the plant with the lowest marginal cost
A)the sum of the average fixed costs from each of the three plants
B)the plant with the highest marginal cost
C)the sum of the marginal costs from each of the three plants
D)the plant with the lowest marginal cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A firm is producing a joint product, Product A and Product B, with variable proportions. At its current production levels, the marginal benefit of producing Product A is $2 and the marginal cost is $4 and the marginal benefit of producing Product B is $5 and the marginal cost is $3. To maximize profits, the managers of the firm should produce of Product A and of Product B.
A)more; more
B)more; less
C)less; less
D)less; more
A)more; more
B)more; less
C)less; less
D)less; more

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A firm is producing a joint product, Product A and Product B, with variable proportions. At its current production levels, the marginal benefit of producing Product A is $10 and the marginal cost is $8 and the marginal benefit of producing Product B is $2 and the marginal cost is $6. To maximize profits, the managers of the firm should produce of Product A and of Product B.
A)more; less
B)less; more
C)less; less
D)more; more
A)more; less
B)less; more
C)less; less
D)more; more

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
 Sweet Grams makes graham cracker snack packages. Sweet Grams is a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The a table summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in the separate plants. Assume Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm.
Sweet Grams makes graham cracker snack packages. Sweet Grams is a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The a table summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in the separate plants. Assume Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm.Refer to the table above. If Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm and the market price $1.25 per unit, what is the profit- maximizing quantity for Sweet Grams to produce at Plant 2?
A)27,000
B)30,100
C)22,500
D)32,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
 Sweet Grams makes graham cracker snack packages. Sweet Grams is a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The a table summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in the separate plants. Assume Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm.
Sweet Grams makes graham cracker snack packages. Sweet Grams is a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The a table summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in the separate plants. Assume Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm.Refer to the table above. If Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm and the market price $1.25 per unit, what is the profit- maximizing quantity for Sweet Grams to produce at Plant 1?
A)36,000
B)24,500
C)30,100
D)27,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When making output decisions, managers of firms producing a joint product with fixed proportions need to pay attention to the separate prices of the joint goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If a firm is producing a joint product with variable proportions, producing more of one product means producing more of the other product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
 Sweet Grams makes graham cracker snack packages. Sweet Grams is a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The a table summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in the separate plants. Assume Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm.
Sweet Grams makes graham cracker snack packages. Sweet Grams is a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The a table summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in the separate plants. Assume Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm.Refer to the table above. If Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm and the market price $1.75 per unit, what is the profit- maximizing total quantity for Sweet Grams to produce?
A)75,000
B)58,500
C)68,000
D)65,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A multi- plant firm has three plants and, at its current production levels, the marginal cost of production at each of the three plants is $3. If the firm is perfectly competitive and the market price of its product is $9, which of the following is true?
A)The firm should decrease output at each of the plants to maximize profit.
B)The firm should exactly triple output in each of the plants to maximize profit.
C)The firm is producing the profit- maximizing total output.
D)The firm should increase output at each of the plants to maximize profit.
A)The firm should decrease output at each of the plants to maximize profit.
B)The firm should exactly triple output in each of the plants to maximize profit.
C)The firm is producing the profit- maximizing total output.
D)The firm should increase output at each of the plants to maximize profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
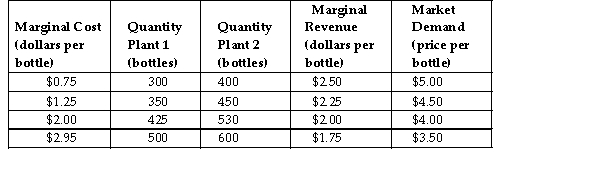 Just Juice produces whole fruit juice that it sells in single bottles. Just Juice is a multi- plant firm with market power. The abov summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in Just Juice's two plants with the corresponding marginal revenue (dollars per bottle)and market demand (price per bottle).
Just Juice produces whole fruit juice that it sells in single bottles. Just Juice is a multi- plant firm with market power. The abov summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in Just Juice's two plants with the corresponding marginal revenue (dollars per bottle)and market demand (price per bottle).Refer to the table above. If Just Juice is producing the profit- maximizing total quantity, what is the profit - maximizing price for Just Juice to charge per bottle?
A)$4.00
B)$3.50
C)$2.00
D)$4.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A multi- plant firm has three plants and, at its current production levels, the marginal cost of production at each of the three plants is $2.00. If the firm is perfectly competitive and the market price of its product is $5, which of the following is true?
A)The firm is producing the profit- maximizing total output.
B)The firm should exactly triple output in each of the plants to maximize profit.
C)The firm is not producing the profit- maximizing total output.
D)The firm should increase output at each of the plants to maximize profit.
A)The firm is producing the profit- maximizing total output.
B)The firm should exactly triple output in each of the plants to maximize profit.
C)The firm is not producing the profit- maximizing total output.
D)The firm should increase output at each of the plants to maximize profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If the market price for multi- plant, perfectly competitive firm is $5, to maximize its profits, the firm should set the overall marginal cost of production to exceed $5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If the market price for multi- plant, perfectly competitive firm is $4, to maximize its profits, the firm should set the overall marginal cost of production equal to $4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Regardless if a multi- plant firm is perfectly competitive or has market power, to maximize profits, managers need to set the overall marginal cost from producing in each of their plants equal to the marginal revenue to find the profit- maximizing total quantity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
 Sweet Grams makes graham cracker snack packages. Sweet Grams is a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The a table summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in the separate plants. Assume Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm.
Sweet Grams makes graham cracker snack packages. Sweet Grams is a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The a table summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in the separate plants. Assume Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm.Refer to the table above. If Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm and the market price $1.75 per unit, what is the profit- maximizing quantity for Sweet Grams to produce at Plant 1?
A)32,500
B)36,000
C)32,000
D)30,100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A multi- plant firm is a firm with more than one demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
 Sweet Grams makes graham cracker snack packages. Sweet Grams is a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The a table summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in the separate plants. Assume Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm.
Sweet Grams makes graham cracker snack packages. Sweet Grams is a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The a table summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in the separate plants. Assume Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm.Refer to the table above. If Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm and the market price $1.00 per unit, what is the profit- maximizing total quantity for Sweet Grams to produce?
A)47,000
B)22,500
C)52,000
D)24,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A multi- plant firm has three plants and, at its current production levels, the marginal cost of production at each of the three plants is $2. If the firm is perfectly competitive and the market price of its product is $6, which of the following is true?
A)The firm should decrease output at each of the plants to maximize profit.
B)The firm should increase output at each of the plants to maximize profit.
C)The firm is producing the profit- maximizing total output.
D)The firm should exactly triple output in each of the plants to maximize profit.
A)The firm should decrease output at each of the plants to maximize profit.
B)The firm should increase output at each of the plants to maximize profit.
C)The firm is producing the profit- maximizing total output.
D)The firm should exactly triple output in each of the plants to maximize profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
 Sweet Grams makes graham cracker snack packages. Sweet Grams is a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The a table summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in the separate plants. Assume Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm.
Sweet Grams makes graham cracker snack packages. Sweet Grams is a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The a table summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in the separate plants. Assume Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm.Refer to the table above. If Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm and the market price $1.75 per unit, what is the profit- maximizing quantity for Sweet Grams to produce at Plant 2?
A)36,000
B)27,000
C)32,000
D)32,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
 Just Juice produces whole fruit juice that it sells in single bottles. Just Juice is a multi- plant firm with market power. The abov summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in Just Juice's two plants with the corresponding marginal revenue (dollars per bottle)and market demand (price per bottle).
Just Juice produces whole fruit juice that it sells in single bottles. Just Juice is a multi- plant firm with market power. The abov summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in Just Juice's two plants with the corresponding marginal revenue (dollars per bottle)and market demand (price per bottle).Refer to the table above. What is the profit- maximizing total quantity for Just Juice to produce?
A)1,100
B)530
C)850
D)955

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A multi- plant firm has three plants. At its current production levels, the marginal cost of production is $1.50 at plant 1, $1.50 at plant 2, and $1.50 at plant 3. The firm's overall marginal cost of production is _.
A)$7.50
B)$1.50
C)$4.50
D)$3.00
A)$7.50
B)$1.50
C)$4.50
D)$3.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
 Just Juice produces whole fruit juice that it sells in single bottles. Just Juice is a multi- plant firm with market power. The abov summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in Just Juice's two plants with the corresponding marginal revenue (dollars per bottle)and market demand (price per bottle).
Just Juice produces whole fruit juice that it sells in single bottles. Just Juice is a multi- plant firm with market power. The abov summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in Just Juice's two plants with the corresponding marginal revenue (dollars per bottle)and market demand (price per bottle).Refer to the table above. What is the profit- maximizing quantity for Just Juice to produce at Plant 2?
A)530
B)425
C)450
D)600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If a multi- plant firm with market power is maximizing its profits, the price it charges per unit of its product will _ its .
A)equal; overall marginal cost
B)exceed; demand
C)exceed; overall marginal cost
D)equal; overall average cost
A)equal; overall marginal cost
B)exceed; demand
C)exceed; overall marginal cost
D)equal; overall average cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A multi- plant firm has three plants. At its current production levels, the marginal cost of production is $2 at plant 1, $2.25 at plant 2, and $2.10 at plant 3. The firm's overall marginal cost of production is .
A)$4.25
B)$6.35
C)$7.20
D)$2.25
A)$4.25
B)$6.35
C)$7.20
D)$2.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
 Sweet Grams makes graham cracker snack packages. Sweet Grams is a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The a table summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in the separate plants. Assume Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm.
Sweet Grams makes graham cracker snack packages. Sweet Grams is a multi- plant firm with two production facilities. The a table summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in the separate plants. Assume Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm.Refer to the table above. If Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm and the market price $1.00 per unit, what is the profit- maximizing quantity for Sweet Grams to produce at Plant 2?
A)24,000
B)20,500
C)22,500
D)27,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
 Just Juice produces whole fruit juice that it sells in single bottles. Just Juice is a multi- plant firm with market power. The abov summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in Just Juice's two plants with the corresponding marginal revenue (dollars per bottle)and market demand (price per bottle).
Just Juice produces whole fruit juice that it sells in single bottles. Just Juice is a multi- plant firm with market power. The abov summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in Just Juice's two plants with the corresponding marginal revenue (dollars per bottle)and market demand (price per bottle).Refer to the table above. What is the profit- maximizing quantity for Just Juice to produce at Plant 1?
A)425
B)350
C)530
D)500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If a multi- plant firm has market power, to maximize profit, it should set a price that exceeds its overall marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
View Your World, a high- end window manufacturer, directly pays all of the transaction costs. The managers of View Your World are considering the profit- maximizing location for their plant. If locating the plant closer to its customers saves $15,000 in transportation costs of its windows to its customers, but causes an additional $11,500 in input transportation costs, View Your World locate its plant closer to its customers as the marginal benefit is than the marginal cost.
A)should not; more
B)should; less
C)should not; less
D)should; greater
A)should not; more
B)should; less
C)should not; less
D)should; greater

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
All of the following location characteristics can result in higher worker salaries except which one?
A)poor climate
B)low cost of living
C)unpleasant work conditions
D)long commute time
A)poor climate
B)low cost of living
C)unpleasant work conditions
D)long commute time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If View Your World, a high- end window manufacturer, directly pays all of the transaction costs, the total cost to produce its windows includes all of the following except which one?
A)the cost of transporting the product to its customers
B)the cost of transporting the inputs to make the windows to the plants
C)the cost to add another production plant
D)the cost of producing the windows
A)the cost of transporting the product to its customers
B)the cost of transporting the inputs to make the windows to the plants
C)the cost to add another production plant
D)the cost of producing the windows

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If a firm with two large plants installs a large, custom built packing machine in each of its plants, the custom packing machine is an example of .
A)specialized capital
B)a compensating wage differential
C)geographic variation
D)managerial diseconomies
A)specialized capital
B)a compensating wage differential
C)geographic variation
D)managerial diseconomies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
All of the following are true regarding managerial diseconomies except which one?
A)They affect a firm's total profit.
B)They cause an increase in a firm's total profit.
C)They can increase as a firm expands its scope of operations.
D)They can increase as a firm adds more plants.
A)They affect a firm's total profit.
B)They cause an increase in a firm's total profit.
C)They can increase as a firm expands its scope of operations.
D)They can increase as a firm adds more plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Happy Cows is a dairy farm that is currently earning $50,000 in economic profit. The managers of Happy Cows are considering adding a second dairy farm, which will generate an additional $10,000 in economic profit. It is economically sound for the managers of Happy Cows to add the second farm if, after accounting for the managerial diseconomies, the first farm's economic profits exceed .
A)$20,000
B)$40,000
C)$10,000
D)$30,000
A)$20,000
B)$40,000
C)$10,000
D)$30,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Happy Cows is a dairy farm that is currently earning $20,000 in economic profit. The managers of Happy Cows are considering adding a second dairy farm; however, the managerial diseconomies from adding the second farm cause Happy Cows current farm's economic profit to fall to $15,000. It is economically sound for Happy Cows to add the second farm if _ .
A)the second farm's economic profit exceeds $5,000
B)the second farm's economic profit is at least $4,800
C)the second farm's economic profit is less than $5,000
D)the second farm's economic profit is at least $4,000
A)the second farm's economic profit exceeds $5,000
B)the second farm's economic profit is at least $4,800
C)the second farm's economic profit is less than $5,000
D)the second farm's economic profit is at least $4,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Happy Cows is a dairy farm that is currently earning $75,000 in economic profit. The managers of Happy Cows are considering adding a second dairy farm, which will generate an additional $30,000 in economic profit. It is economically sound for the managers of Happy Cows to add the second farm if, after accounting for the managerial diseconomies, the first farm's economic profits exceed .
A)$35,000
B)$30,000
C)$25,000
D)$45,000
A)$35,000
B)$30,000
C)$25,000
D)$45,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A plant is located at the cost- minimizing location when the marginal benefit of moving closer to the inputs is the marginal cost.
A)exactly double
B)greater than
C)equal to
D)less than
A)exactly double
B)greater than
C)equal to
D)less than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
All of the following location characteristics can result in higher worker salaries except which one?
A)high cost of living
B)short commute time
C)poor climate
D)unpleasant work conditions
A)high cost of living
B)short commute time
C)poor climate
D)unpleasant work conditions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
View Your World, a high- end window manufacturer, directly pays all of the transaction costs. The managers of View Your World are considering the profit- maximizing location for their plant. If locating the plant closer to its customers saves $10,000 in transportation costs of its windows to its customers, but causes an additional $7,500 in input transportation costs, View Your World locate its plant closer to its customers as the marginal benefit is than the marginal cost.
A)should not; more
B)should; greater
C)should not; less
D)should; less
A)should not; more
B)should; greater
C)should not; less
D)should; less

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If a firm pays all transportation costs and it is very costly to transport the inputs, but relatively inexpensive to transport the final product, the cost- minimizing location for the plant will be closer to the and farther away from the .
A)customers; inputs
B)customers; distributors
C)distributors; customers
D)inputs; customers
A)customers; inputs
B)customers; distributors
C)distributors; customers
D)inputs; customers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If a firm with two large plants installs a large, custom built assembly line in each of its plants, the custom assembly line is an example of .
A)managerial diseconomies
B)geographic variation
C)a compensating wage differential
D)specialized capital
A)managerial diseconomies
B)geographic variation
C)a compensating wage differential
D)specialized capital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Compared to a firm that has many small plants, a firm with a few large plants is likely to have all of the following except which one?
A)fewer inputs
B)greater managerial diseconomies
C)greater availability of specialized capital
D)less managerial diseconomies
A)fewer inputs
B)greater managerial diseconomies
C)greater availability of specialized capital
D)less managerial diseconomies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Happy Cows is a dairy farm that is currently earning $100,000 in economic profit. The managers of Happy Cows are considering adding a second dairy farm, which will generate an additional $40,000 in economic profit. It is economically sound for the managers of Happy Cows to add the second farm if, after accounting for the managerial diseconomies, the first farm's economic profits exceed .
A)$60,000
B)$10,000
C)$40,000
D)$30,000
A)$60,000
B)$10,000
C)$40,000
D)$30,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Happy Cows is a dairy farm that is currently earning $5,000 in economic profit. The managers of Happy Cows are considering adding a second dairy farm; however, the managerial diseconomies from adding the second farm cause Happy Cows current farm's economic profit to fall to $3,000. It is economically sound for Happy Cows to add the second farm if .
A)the second farm's economic profit is at least $1,750
B)the second farm's economic profit is less than $2,000
C)the second farm's economic profit is at least $1,500
D)the second farm's economic profit exceeds $2,000
A)the second farm's economic profit is at least $1,750
B)the second farm's economic profit is less than $2,000
C)the second farm's economic profit is at least $1,500
D)the second farm's economic profit exceeds $2,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If a firm has two plants, one located in desirable Scenic Springs and the other located in the undesirable Swamp Lands, the workers in Scenic Springs will be paid _ than the workers in Swamp Land and the difference in wages is referred to as a .
A)more; worker equity payment
B)less; worker equity payment
C)less; compensating wage differential
D)more; compensating wage differential
A)more; worker equity payment
B)less; worker equity payment
C)less; compensating wage differential
D)more; compensating wage differential

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
View Your World, a high- end window manufacturer, directly pays all of the transaction costs. The managers of View Your World are considering the profit- maximizing location for their plant. If locating the plant closer to its customers saves $7,000 in transportation costs of its windows to its customers, but causes an additional $7,500 in input transportation costs, View Your World locate its plant closer to its customers as the marginal benefit is than the marginal cost.
A)should not; more
B)should; less
C)should not; less
D)should; greater
A)should not; more
B)should; less
C)should not; less
D)should; greater

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
All of the following location characteristics can result in lower worker salaries except which one?
A)great climate
B)low cost of living
C)short commute time
D)unpleasant work conditions
A)great climate
B)low cost of living
C)short commute time
D)unpleasant work conditions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A firm has two plants, one located in desirable Scenic Springs and the other located in the undesirable Swamp Lands. If the workers in Scenic Springs are paid $50,000 a year and the workers in Swamp Land are paid $60,000, which of the following is true?
A)The $60,000 salary is a compensating wage differential.
B)The $60,000 salary is a worker equity payment.
C)The $10,000 difference in salaries is the compensating wage differential.
D)The $10,000 difference in salaries is the worker equity payment.
A)The $60,000 salary is a compensating wage differential.
B)The $60,000 salary is a worker equity payment.
C)The $10,000 difference in salaries is the compensating wage differential.
D)The $10,000 difference in salaries is the worker equity payment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



