Deck 17: Managing Our Waste
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/56
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Managing Our Waste
1
Choose the item that best matches each item in the following:
The second-largest component of U.S. municipal solid waste
A)heavy metals
B)yard debris
C)food scraps
D)plastic
E)glass
F)paper
G)radioactive materials
H)pesticide precursors
I)e-waste
The second-largest component of U.S. municipal solid waste
A)heavy metals
B)yard debris
C)food scraps
D)plastic
E)glass
F)paper
G)radioactive materials
H)pesticide precursors
I)e-waste
yard debris
2
Choose the item that best matches each item in the following:
Often the primary contributor to solid waste in developing nations
A)heavy metals
B)yard debris
C)food scraps
D)plastic
E)glass
F)paper
G)radioactive materials
H)pesticide precursors
I)e-waste
Often the primary contributor to solid waste in developing nations
A)heavy metals
B)yard debris
C)food scraps
D)plastic
E)glass
F)paper
G)radioactive materials
H)pesticide precursors
I)e-waste
food scraps
3
The first bottle bills were ________________.
A) designed to cut down on litter
B) designed to provide incentives to industry
C) initiated in the 1990s
D) designed to provide glass for road construction
E) a consequence of landfill regulations
A) designed to cut down on litter
B) designed to provide incentives to industry
C) initiated in the 1990s
D) designed to provide glass for road construction
E) a consequence of landfill regulations
designed to cut down on litter
4
The Fresh Kills Landfill ________________.
A) is the United Statesʹ first landfill conversion project
B) is New Yorkʹs first and only modern sanitary landfill
C) will remain open until late 2020
D) site will be converted into a public park
E) was abandoned in the late 1970s
A) is the United Statesʹ first landfill conversion project
B) is New Yorkʹs first and only modern sanitary landfill
C) will remain open until late 2020
D) site will be converted into a public park
E) was abandoned in the late 1970s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Deep inside landfills, bacteria decompose organic wastes in a low oxygen environment. This anaerobic decomposition results in a mix of gases called landfill gas, which consists of about 50% ________________.
A) methane
B) hydrogen
C) argon
D) carbon monoxide
E) chlorine gas
A) methane
B) hydrogen
C) argon
D) carbon monoxide
E) chlorine gas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
To safeguard against groundwater contamination, sanitary landfills are ________________.
A) lined with cement
B) lined with plastic and clay
C) located on slopes so water runs downhill
D) located on industrial sites where groundwater is not used for drinking or agriculture
E) located in unpopulated areas
A) lined with cement
B) lined with plastic and clay
C) located on slopes so water runs downhill
D) located on industrial sites where groundwater is not used for drinking or agriculture
E) located in unpopulated areas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
________________ is the conversion of organic waste into mulch or humus.
A) Cogeneration
B) Compacting
C) Injecting
D) Reusing
E) Composting
A) Cogeneration
B) Compacting
C) Injecting
D) Reusing
E) Composting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
As of 2008, the average American generates about ________________ pounds of solid waste per day.
A) 4.4
B) 13.7
C) 1.5
D) 9
E) 40
A) 4.4
B) 13.7
C) 1.5
D) 9
E) 40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
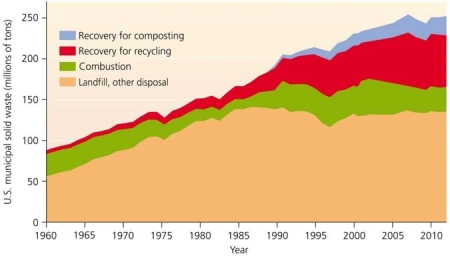 Use the figure above to answer the following question
Use the figure above to answer the following questionThe year __________________ demonstrated the greatest volume of recycling.
A) 1998
B) 2008
C) 1960
D) 1970
E) 1985

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Choose the item that best matches each item in the following:
The largest component of U.S. municipal solid waste
A)heavy metals
B)yard debris
C)food scraps
D)plastic
E)glass
F)paper
G)radioactive materials
H)pesticide precursors
I)e-waste
The largest component of U.S. municipal solid waste
A)heavy metals
B)yard debris
C)food scraps
D)plastic
E)glass
F)paper
G)radioactive materials
H)pesticide precursors
I)e-waste

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
 Use the figure above to answer the following question
Use the figure above to answer the following questionOf the following, the ________________ demonstrated the greatest rate of increase in total municipal solid waste generated.
A) 2000s
B) 1960s
C) 1990s
D) 1970s
E) 1980s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Choose the item that best matches each item in the following:
Waste that has taken up a substantially greater share of the waste stream since 1970
A)heavy metals
B)yard debris
C)food scraps
D)plastic
E)glass
F)paper
G)radioactive materials
H)pesticide precursors
I)e-waste
Waste that has taken up a substantially greater share of the waste stream since 1970
A)heavy metals
B)yard debris
C)food scraps
D)plastic
E)glass
F)paper
G)radioactive materials
H)pesticide precursors
I)e-waste

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
 Use the figure above to answer the following question
Use the figure above to answer the following questionThe amount of waste sent to landfills leveled off around _______________.
A) 1985
B) 1965
C) 1970
D) 1995
E) 2009

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
 Use the figure above to answer the following question
Use the figure above to answer the following questionVolume of waste recovered by composting was insignificant until _______________
A) the late 1980s
B) the early 1960s
C) 1980
D) 2000
E) 2009

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Choose the item that best matches each item in the following:
Include mercury, lead, cadmium, and chromium
A)heavy metals
B)yard debris
C)food scraps
D)plastic
E)glass
F)paper
G)radioactive materials
H)pesticide precursors
I)e-waste
Include mercury, lead, cadmium, and chromium
A)heavy metals
B)yard debris
C)food scraps
D)plastic
E)glass
F)paper
G)radioactive materials
H)pesticide precursors
I)e-waste

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The best solution to the solid waste problem is to ________________.
A) increase the number of WTE facilities
B) subsidize WTE facilities
C) increase the number of oceanic burial sites
D) increase the number of sanitary landfills
E) reduce the amount of material that enters the waste stream
A) increase the number of WTE facilities
B) subsidize WTE facilities
C) increase the number of oceanic burial sites
D) increase the number of sanitary landfills
E) reduce the amount of material that enters the waste stream

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
 Use the figure above to answer the following question
Use the figure above to answer the following questionFrom the 1960s to the present, the trend has been that ____________ over time.
A) more overall waste was produced
B) less waste was recovered for recycling
C) there have been equal ratios of land disposal, combustion, and recovery
D) less waste was sent to landfills
E) less overall waste was produced

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Choose the item that best matches each item in the following:
Most rapidly growing new component of hazardous municipal waste
A)heavy metals
B)yard debris
C)food scraps
D)plastic
E)glass
F)paper
G)radioactive materials
H)pesticide precursors
I)e-waste
Most rapidly growing new component of hazardous municipal waste
A)heavy metals
B)yard debris
C)food scraps
D)plastic
E)glass
F)paper
G)radioactive materials
H)pesticide precursors
I)e-waste

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Of the following, ________________ produce(s) the largest amount of hazardous waste.
A) utilities
B) building demolitions
C) industry
D) agriculture
E) households
A) utilities
B) building demolitions
C) industry
D) agriculture
E) households

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The second step in the recycling loop is ________________.
A) the incineration of paper
B) the purchase by consumers of products made from recycled materials
C) the elimination of number 1 plastics
D) the use of recyclables by industry to manufacture new products
E) the collection and processing of recyclable materials
A) the incineration of paper
B) the purchase by consumers of products made from recycled materials
C) the elimination of number 1 plastics
D) the use of recyclables by industry to manufacture new products
E) the collection and processing of recyclable materials

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Deep-well injection ________________.
A) has been banned as unsafe by the Dept. of the Interior
B) is the EPA-approved method of disposing of low-level radioactive wastes
C) is a pool of strong acids on the land surface used for breaking down e -waste
D) injects mostly liquid hazardous wastes into porous rock isolated by impervious clay deep beneath human water supplies
E) is a method of disposing of hazardous wastes in deep aquifers
A) has been banned as unsafe by the Dept. of the Interior
B) is the EPA-approved method of disposing of low-level radioactive wastes
C) is a pool of strong acids on the land surface used for breaking down e -waste
D) injects mostly liquid hazardous wastes into porous rock isolated by impervious clay deep beneath human water supplies
E) is a method of disposing of hazardous wastes in deep aquifers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
All of the following are considered to define types of hazardous waste except ________________.
A) ignitable
B) inert
C) corrosive
D) reactive
E) toxic
A) ignitable
B) inert
C) corrosive
D) reactive
E) toxic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The EPA is charged with cleaning up brownfields, which are ________________.
A) desert regions used for unsafe nuclear waste disposal
B) urban areas contaminated by acid drainage from mining
C) agricultural lands polluted by acid and heavy metals
D) lands whose reuse or development is complicated by the presence of hazardous materials
E) coastal sea grass beds damaged by industrial dumping
A) desert regions used for unsafe nuclear waste disposal
B) urban areas contaminated by acid drainage from mining
C) agricultural lands polluted by acid and heavy metals
D) lands whose reuse or development is complicated by the presence of hazardous materials
E) coastal sea grass beds damaged by industrial dumping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Of the following, ________________ are classified as hazardous heavy metals.
A) nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium
B) aluminum, iron, silicon
C) carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
D) any non-biodegradable materials
E) lead, mercury, cadmium
A) nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium
B) aluminum, iron, silicon
C) carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
D) any non-biodegradable materials
E) lead, mercury, cadmium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Of the following, ________________ represent criteria for classifying hazardous waste.
A) non-biodegradable and biodegradable
B) ignitable, corrosive, reactive, toxic
C) solid, liquid, gaseous
D) inorganic and organic
E) municipal, industrial and agricultural
A) non-biodegradable and biodegradable
B) ignitable, corrosive, reactive, toxic
C) solid, liquid, gaseous
D) inorganic and organic
E) municipal, industrial and agricultural

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Industrial ecologists ________________.
A) primarily analyze industrial inputs
B) advocate for taxes on green industries
C) favor an economy that moves linearly rather than circularly
D) urge an emphasis on internal manufacturing costs rather than external costs
E) redesign industrial systems to minimize physical inefficiency and maximize economic efficiency
A) primarily analyze industrial inputs
B) advocate for taxes on green industries
C) favor an economy that moves linearly rather than circularly
D) urge an emphasis on internal manufacturing costs rather than external costs
E) redesign industrial systems to minimize physical inefficiency and maximize economic efficiency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The current state of e-wastes is that ________________.
A) the recycling rate has dropped significantly between 1999 and 2010
B) because the EPA has classified e-wastes as toxic, more than 95% are being recycled
C) only because of the actions of charitable organizations, the recycling rate is 5%
D) by EPA mandate, all metals in electronics have been replaced by biodegradable materials
E) although recycling is improved, the rate of e-wastes going into landfills and incinerators is rising
A) the recycling rate has dropped significantly between 1999 and 2010
B) because the EPA has classified e-wastes as toxic, more than 95% are being recycled
C) only because of the actions of charitable organizations, the recycling rate is 5%
D) by EPA mandate, all metals in electronics have been replaced by biodegradable materials
E) although recycling is improved, the rate of e-wastes going into landfills and incinerators is rising

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
RCRA is a U.S. law enacted in the 1970s to ________________.
A) regulate how hazardous waste is handled
B) reduce environmental levels of the 12 most toxic chemicals, called the ʺdirty dozenʺ
C) regulate greenhouse gas emissions from power plants
D) protect endangered species
E) restrict use of off-road vehicles in national parks
A) regulate how hazardous waste is handled
B) reduce environmental levels of the 12 most toxic chemicals, called the ʺdirty dozenʺ
C) regulate greenhouse gas emissions from power plants
D) protect endangered species
E) restrict use of off-road vehicles in national parks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The earthworms, fungi, and bacteria in your compost pile will NOT be happy if you give them ________________.
A) food scraps
B) paper
C) grass clippings
D) plastic
E) autumn leaves
A) food scraps
B) paper
C) grass clippings
D) plastic
E) autumn leaves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In the 2010 Vancouver Winter Olympics, the metals in the winnersʹ medals were ________________.
A) recovered from surface impoundments
B) produced from mining wastes in Vancouver
C) recovered from local MRFs
D) recovered from local landfills
E) made partly from precious metals recovered from recycled e-waste
A) recovered from surface impoundments
B) produced from mining wastes in Vancouver
C) recovered from local MRFs
D) recovered from local landfills
E) made partly from precious metals recovered from recycled e-waste

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Heavy metals ________________.
A) become less hazardous over time as they degrade chemically
B) are unregulated by the U.S. government
C) bioaccumulate in animal tissues
D) become less hazardous after incineration
E) are not harmful unless they are directly ingested
A) become less hazardous over time as they degrade chemically
B) are unregulated by the U.S. government
C) bioaccumulate in animal tissues
D) become less hazardous after incineration
E) are not harmful unless they are directly ingested

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In Edmonton, Alberta, Canada, glass is ________________.
A) melted down to make light bulbs
B) dumped at landfills
C) composted
D) recycled into reflective paint and signs
E) incinerated
A) melted down to make light bulbs
B) dumped at landfills
C) composted
D) recycled into reflective paint and signs
E) incinerated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
E-wastes are a source of ________________.
A) compostable organic compounds
B) acid corrosives
C) radioactive materials
D) heavy and precious metals
E) ignitables
A) compostable organic compounds
B) acid corrosives
C) radioactive materials
D) heavy and precious metals
E) ignitables

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
________________ represent(s) the largest source of unregulated hazardous waste.
A) Households
B) Utilities
C) Farmers
D) Large industry
E) Small businesses
A) Households
B) Utilities
C) Farmers
D) Large industry
E) Small businesses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The Trash Track project ________________.
A) allows cities to charge polluters who dump large volumes of trash
B) measures the volume of various categories of municipal waste in various cities
C) monitors the movement of trash items to improve efficiency of management processes
D) monitors the amount of hazardous items in municipal waste
E) tells managers which items should be recycled
A) allows cities to charge polluters who dump large volumes of trash
B) measures the volume of various categories of municipal waste in various cities
C) monitors the movement of trash items to improve efficiency of management processes
D) monitors the amount of hazardous items in municipal waste
E) tells managers which items should be recycled

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
As of 2014, under the jurisdiction of the EPA, approximately ________________ % of hazardous sites identified under CERCLA as a national priority have been cleaned up.
A) 60
B) 3
C) 40
D) 50
E) 30
A) 60
B) 3
C) 40
D) 50
E) 30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Approximately ________________ % of all U.S. residents are served by curbside recycling programs, and the part of the U.S. waste stream that is recycled is currently about %.
A) 30; 90
B) 40; 50
C) 60; 100
D) 30; 30
E) 50; 25
A) 30; 90
B) 40; 50
C) 60; 100
D) 30; 30
E) 50; 25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Recycling aluminum cans saves ________________% of the energy needed to make the same amount of aluminum from virgin bauxite.
A) 95
B) 50
C) 80
D) 25
E) 70
A) 95
B) 50
C) 80
D) 25
E) 70

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Funding for superfund toxic waste sites ________________.
A) is no longer necessary because by 2010 all sites had been cleaned and restored
B) has become the responsibility of taxpayers since 2004
C) is currently paid by polluting industries
D) has been eased because the costs of cleanup have diminished
E) is a portion of the EPAʹs budget
A) is no longer necessary because by 2010 all sites had been cleaned and restored
B) has become the responsibility of taxpayers since 2004
C) is currently paid by polluting industries
D) has been eased because the costs of cleanup have diminished
E) is a portion of the EPAʹs budget

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Life-cycle analysis ________________.
A) defines how different organisms interact within ecosystems
B) examines the life cycle of products for ecological efficiency
C) examines the cycling of carbon in the environment
D) is the study of statistical changes in the human population
E) is an environmental movement designed to reduce municipal traffic and encourage alternative forms of transport
A) defines how different organisms interact within ecosystems
B) examines the life cycle of products for ecological efficiency
C) examines the cycling of carbon in the environment
D) is the study of statistical changes in the human population
E) is an environmental movement designed to reduce municipal traffic and encourage alternative forms of transport

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Read the following scenario and answer the question below.
The prevalence of ʺthrowaway mentalitiesʺ and increased packaging has amplified the consumption of paper and plastic in our society. Disposable plates, cups, and utensils are convenient, sanitary, and inexpensive. Further packaging also preserves freshness, prevents breakage, protects against tampering, provides information to consumers, and allows shipment of products over long distances. However, paper and plastic do not degrade readily in sanitary landfills.
Garbologist William Rathje found legible newspapers in landfills decades after disposal. Because trees used to make virgin paper and petrochemicals used to make plastics may soon become depleted, source reduction is the best solution to the waste dilemma. Denmark has banned the use of non -refillable beverage containers and McDonaldʹs restaurants in Austria and Sweden have been using biodegradable, compostable cutlery. Recycling has value as well, as long as the recycling loop is closed and people purchase recycled items. Bottle bills and municipal curbside collection provide recycling incentives.
Paper recycling is profitable if waste is properly sorted. All kinds of paper and cardboard are recyclable. Food and paperboard (uncorrugated thin coated board) can contaminate collections, however, reducing their value. After processing, paper and cardboard are used to make paper towels and paperboard for packaging cereal, shoes, and toys. Decapped, washed, and squashed plastic is recycled into carpets, pillows, and new bottles. Although low -density polyethylene, or LDPE (recycling symbol #4), from grocery bags is the most widely used plastic, beverage bottle polyethylene terephthalate, or PETE (symbol #1), and high-density polyethylene, or HDPE (symbol #2), are the most widely recycled plastics.
Containers from toxic substances such as motor oil, pesticides, and solvents are not usually accepted with collected plastic because of contamination. Methods to reuse and recycle polystyrene are in development, although presently, Styrofoam is not collected with other plastics and so it is considered a contaminant as well.
Closing the recycling loop refers to __________.
A) finding ways to recycle all plastics, including polystyrene
B) composting of biodegradable plastic
C) avoiding contamination of plastic and paper collectables during sorting
D) covering landfills once they have outlived their usefulness and converting them to public parks
E) purchasing items made from recycled materials
The prevalence of ʺthrowaway mentalitiesʺ and increased packaging has amplified the consumption of paper and plastic in our society. Disposable plates, cups, and utensils are convenient, sanitary, and inexpensive. Further packaging also preserves freshness, prevents breakage, protects against tampering, provides information to consumers, and allows shipment of products over long distances. However, paper and plastic do not degrade readily in sanitary landfills.
Garbologist William Rathje found legible newspapers in landfills decades after disposal. Because trees used to make virgin paper and petrochemicals used to make plastics may soon become depleted, source reduction is the best solution to the waste dilemma. Denmark has banned the use of non -refillable beverage containers and McDonaldʹs restaurants in Austria and Sweden have been using biodegradable, compostable cutlery. Recycling has value as well, as long as the recycling loop is closed and people purchase recycled items. Bottle bills and municipal curbside collection provide recycling incentives.
Paper recycling is profitable if waste is properly sorted. All kinds of paper and cardboard are recyclable. Food and paperboard (uncorrugated thin coated board) can contaminate collections, however, reducing their value. After processing, paper and cardboard are used to make paper towels and paperboard for packaging cereal, shoes, and toys. Decapped, washed, and squashed plastic is recycled into carpets, pillows, and new bottles. Although low -density polyethylene, or LDPE (recycling symbol #4), from grocery bags is the most widely used plastic, beverage bottle polyethylene terephthalate, or PETE (symbol #1), and high-density polyethylene, or HDPE (symbol #2), are the most widely recycled plastics.
Containers from toxic substances such as motor oil, pesticides, and solvents are not usually accepted with collected plastic because of contamination. Methods to reuse and recycle polystyrene are in development, although presently, Styrofoam is not collected with other plastics and so it is considered a contaminant as well.
Closing the recycling loop refers to __________.
A) finding ways to recycle all plastics, including polystyrene
B) composting of biodegradable plastic
C) avoiding contamination of plastic and paper collectables during sorting
D) covering landfills once they have outlived their usefulness and converting them to public parks
E) purchasing items made from recycled materials

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Read the following scenario and answer the question below.
The prevalence of ʺthrowaway mentalitiesʺ and increased packaging has amplified the consumption of paper and plastic in our society. Disposable plates, cups, and utensils are convenient, sanitary, and inexpensive. Further packaging also preserves freshness, prevents breakage, protects against tampering, provides information to consumers, and allows shipment of products over long distances. However, paper and plastic do not degrade readily in sanitary landfills.
Garbologist William Rathje found legible newspapers in landfills decades after disposal. Because trees used to make virgin paper and petrochemicals used to make plastics may soon become depleted, source reduction is the best solution to the waste dilemma. Denmark has banned the use of non -refillable beverage containers and McDonaldʹs restaurants in Austria and Sweden have been using biodegradable, compostable cutlery. Recycling has value as well, as long as the recycling loop is closed and people purchase recycled items. Bottle bills and municipal curbside collection provide recycling incentives.
Paper recycling is profitable if waste is properly sorted. All kinds of paper and cardboard are recyclable. Food and paperboard (uncorrugated thin coated board) can contaminate collections, however, reducing their value. After processing, paper and cardboard are used to make paper towels and paperboard for packaging cereal, shoes, and toys. Decapped, washed, and squashed plastic is recycled into carpets, pillows, and new bottles. Although low -density polyethylene, or LDPE (recycling symbol #4), from grocery bags is the most widely used plastic, beverage bottle polyethylene terephthalate, or PETE (symbol #1), and high-density polyethylene, or HDPE (symbol #2), are the most widely recycled plastics.
Containers from toxic substances such as motor oil, pesticides, and solvents are not usually accepted with collected plastic because of contamination. Methods to reuse and recycle polystyrene are in development, although presently, Styrofoam is not collected with other plastics and so it is considered a contaminant as well.
__________ are wastepaper contaminants that cannot effectively be recycled.
A) Cereal boxes
B) Office papers
C) Paper shopping bags
D) Corrugated cardboard boxes
E) Newspapers
The prevalence of ʺthrowaway mentalitiesʺ and increased packaging has amplified the consumption of paper and plastic in our society. Disposable plates, cups, and utensils are convenient, sanitary, and inexpensive. Further packaging also preserves freshness, prevents breakage, protects against tampering, provides information to consumers, and allows shipment of products over long distances. However, paper and plastic do not degrade readily in sanitary landfills.
Garbologist William Rathje found legible newspapers in landfills decades after disposal. Because trees used to make virgin paper and petrochemicals used to make plastics may soon become depleted, source reduction is the best solution to the waste dilemma. Denmark has banned the use of non -refillable beverage containers and McDonaldʹs restaurants in Austria and Sweden have been using biodegradable, compostable cutlery. Recycling has value as well, as long as the recycling loop is closed and people purchase recycled items. Bottle bills and municipal curbside collection provide recycling incentives.
Paper recycling is profitable if waste is properly sorted. All kinds of paper and cardboard are recyclable. Food and paperboard (uncorrugated thin coated board) can contaminate collections, however, reducing their value. After processing, paper and cardboard are used to make paper towels and paperboard for packaging cereal, shoes, and toys. Decapped, washed, and squashed plastic is recycled into carpets, pillows, and new bottles. Although low -density polyethylene, or LDPE (recycling symbol #4), from grocery bags is the most widely used plastic, beverage bottle polyethylene terephthalate, or PETE (symbol #1), and high-density polyethylene, or HDPE (symbol #2), are the most widely recycled plastics.
Containers from toxic substances such as motor oil, pesticides, and solvents are not usually accepted with collected plastic because of contamination. Methods to reuse and recycle polystyrene are in development, although presently, Styrofoam is not collected with other plastics and so it is considered a contaminant as well.
__________ are wastepaper contaminants that cannot effectively be recycled.
A) Cereal boxes
B) Office papers
C) Paper shopping bags
D) Corrugated cardboard boxes
E) Newspapers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Read the following scenario and answer the question below.
The prevalence of ʺthrowaway mentalitiesʺ and increased packaging has amplified the consumption of paper and plastic in our society. Disposable plates, cups, and utensils are convenient, sanitary, and inexpensive. Further packaging also preserves freshness, prevents breakage, protects against tampering, provides information to consumers, and allows shipment of products over long distances. However, paper and plastic do not degrade readily in sanitary landfills.
Garbologist William Rathje found legible newspapers in landfills decades after disposal. Because trees used to make virgin paper and petrochemicals used to make plastics may soon become depleted, source reduction is the best solution to the waste dilemma. Denmark has banned the use of non -refillable beverage containers and McDonaldʹs restaurants in Austria and Sweden have been using biodegradable, compostable cutlery. Recycling has value as well, as long as the recycling loop is closed and people purchase recycled items. Bottle bills and municipal curbside collection provide recycling incentives.
Paper recycling is profitable if waste is properly sorted. All kinds of paper and cardboard are recyclable. Food and paperboard (uncorrugated thin coated board) can contaminate collections, however, reducing their value. After processing, paper and cardboard are used to make paper towels and paperboard for packaging cereal, shoes, and toys. Decapped, washed, and squashed plastic is recycled into carpets, pillows, and new bottles. Although low -density polyethylene, or LDPE (recycling symbol #4), from grocery bags is the most widely used plastic, beverage bottle polyethylene terephthalate, or PETE (symbol #1), and high-density polyethylene, or HDPE (symbol #2), are the most widely recycled plastics.
Containers from toxic substances such as motor oil, pesticides, and solvents are not usually accepted with collected plastic because of contamination. Methods to reuse and recycle polystyrene are in development, although presently, Styrofoam is not collected with other plastics and so it is considered a contaminant as well.
Paper and plastic waste share the following characteristics: ____________________.
A) they are both made from petrochemicals
B) their increased consumption leads to increased waste
C) they readily degrade in landfills
D) both are more than 90% recycled in the United States
E) they cannot be incinerated to produce energy
The prevalence of ʺthrowaway mentalitiesʺ and increased packaging has amplified the consumption of paper and plastic in our society. Disposable plates, cups, and utensils are convenient, sanitary, and inexpensive. Further packaging also preserves freshness, prevents breakage, protects against tampering, provides information to consumers, and allows shipment of products over long distances. However, paper and plastic do not degrade readily in sanitary landfills.
Garbologist William Rathje found legible newspapers in landfills decades after disposal. Because trees used to make virgin paper and petrochemicals used to make plastics may soon become depleted, source reduction is the best solution to the waste dilemma. Denmark has banned the use of non -refillable beverage containers and McDonaldʹs restaurants in Austria and Sweden have been using biodegradable, compostable cutlery. Recycling has value as well, as long as the recycling loop is closed and people purchase recycled items. Bottle bills and municipal curbside collection provide recycling incentives.
Paper recycling is profitable if waste is properly sorted. All kinds of paper and cardboard are recyclable. Food and paperboard (uncorrugated thin coated board) can contaminate collections, however, reducing their value. After processing, paper and cardboard are used to make paper towels and paperboard for packaging cereal, shoes, and toys. Decapped, washed, and squashed plastic is recycled into carpets, pillows, and new bottles. Although low -density polyethylene, or LDPE (recycling symbol #4), from grocery bags is the most widely used plastic, beverage bottle polyethylene terephthalate, or PETE (symbol #1), and high-density polyethylene, or HDPE (symbol #2), are the most widely recycled plastics.
Containers from toxic substances such as motor oil, pesticides, and solvents are not usually accepted with collected plastic because of contamination. Methods to reuse and recycle polystyrene are in development, although presently, Styrofoam is not collected with other plastics and so it is considered a contaminant as well.
Paper and plastic waste share the following characteristics: ____________________.
A) they are both made from petrochemicals
B) their increased consumption leads to increased waste
C) they readily degrade in landfills
D) both are more than 90% recycled in the United States
E) they cannot be incinerated to produce energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What are the three basic steps in the recycling loop? What is the step that needs the most attention if the recycling loop is going to work?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
There are three main disposal methods for hazardous waste. One is landfills. Describe how hazardous waste landfills differ from ordinary sanitary landfills. Briefly discuss the other two ways that hazardous waste is contained.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Discuss the benefits and environmental disadvantages of modern-day landfills in the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Briefly describe the three main components of waste management. Which method is preferred?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Describe what environmentalists mean when they say that RCRA deals with waste streams by life cycle analysis (ʺfrom cradle to graveʺ).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Briefly describe the pros and cons of curbside recycling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If reducing waste can increase efficiency, why is the output of industrial waste still so great? What is the application of industrial ecology and life-cycle analysis to these problems?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What are the benefits and drawbacks of incinerating trash? How have these problems been dealt with in most developed countries?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Read the following scenario and answer the question below.
The prevalence of ʺthrowaway mentalitiesʺ and increased packaging has amplified the consumption of paper and plastic in our society. Disposable plates, cups, and utensils are convenient, sanitary, and inexpensive. Further packaging also preserves freshness, prevents breakage, protects against tampering, provides information to consumers, and allows shipment of products over long distances. However, paper and plastic do not degrade readily in sanitary landfills.
Garbologist William Rathje found legible newspapers in landfills decades after disposal. Because trees used to make virgin paper and petrochemicals used to make plastics may soon become depleted, source reduction is the best solution to the waste dilemma. Denmark has banned the use of non -refillable beverage containers and McDonaldʹs restaurants in Austria and Sweden have been using biodegradable, compostable cutlery. Recycling has value as well, as long as the recycling loop is closed and people purchase recycled items. Bottle bills and municipal curbside collection provide recycling incentives.
Paper recycling is profitable if waste is properly sorted. All kinds of paper and cardboard are recyclable. Food and paperboard (uncorrugated thin coated board) can contaminate collections, however, reducing their value. After processing, paper and cardboard are used to make paper towels and paperboard for packaging cereal, shoes, and toys. Decapped, washed, and squashed plastic is recycled into carpets, pillows, and new bottles. Although low -density polyethylene, or LDPE (recycling symbol #4), from grocery bags is the most widely used plastic, beverage bottle polyethylene terephthalate, or PETE (symbol #1), and high-density polyethylene, or HDPE (symbol #2), are the most widely recycled plastics.
Containers from toxic substances such as motor oil, pesticides, and solvents are not usually accepted with collected plastic because of contamination. Methods to reuse and recycle polystyrene are in development, although presently, Styrofoam is not collected with other plastics and so it is considered a contaminant as well.
LDPE is __________.
A) the plastic used to make grocery bags
B) banned in Denmark
C) not currently recycled
D) a toxin found in most plastics
E) the most widely recycled plastic
The prevalence of ʺthrowaway mentalitiesʺ and increased packaging has amplified the consumption of paper and plastic in our society. Disposable plates, cups, and utensils are convenient, sanitary, and inexpensive. Further packaging also preserves freshness, prevents breakage, protects against tampering, provides information to consumers, and allows shipment of products over long distances. However, paper and plastic do not degrade readily in sanitary landfills.
Garbologist William Rathje found legible newspapers in landfills decades after disposal. Because trees used to make virgin paper and petrochemicals used to make plastics may soon become depleted, source reduction is the best solution to the waste dilemma. Denmark has banned the use of non -refillable beverage containers and McDonaldʹs restaurants in Austria and Sweden have been using biodegradable, compostable cutlery. Recycling has value as well, as long as the recycling loop is closed and people purchase recycled items. Bottle bills and municipal curbside collection provide recycling incentives.
Paper recycling is profitable if waste is properly sorted. All kinds of paper and cardboard are recyclable. Food and paperboard (uncorrugated thin coated board) can contaminate collections, however, reducing their value. After processing, paper and cardboard are used to make paper towels and paperboard for packaging cereal, shoes, and toys. Decapped, washed, and squashed plastic is recycled into carpets, pillows, and new bottles. Although low -density polyethylene, or LDPE (recycling symbol #4), from grocery bags is the most widely used plastic, beverage bottle polyethylene terephthalate, or PETE (symbol #1), and high-density polyethylene, or HDPE (symbol #2), are the most widely recycled plastics.
Containers from toxic substances such as motor oil, pesticides, and solvents are not usually accepted with collected plastic because of contamination. Methods to reuse and recycle polystyrene are in development, although presently, Styrofoam is not collected with other plastics and so it is considered a contaminant as well.
LDPE is __________.
A) the plastic used to make grocery bags
B) banned in Denmark
C) not currently recycled
D) a toxin found in most plastics
E) the most widely recycled plastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Describe the advantages of composting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Describe the growing problems in dealing with E-waste.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Read the following scenario and answer the question below.
The prevalence of ʺthrowaway mentalitiesʺ and increased packaging has amplified the consumption of paper and plastic in our society. Disposable plates, cups, and utensils are convenient, sanitary, and inexpensive. Further packaging also preserves freshness, prevents breakage, protects against tampering, provides information to consumers, and allows shipment of products over long distances. However, paper and plastic do not degrade readily in sanitary landfills.
Garbologist William Rathje found legible newspapers in landfills decades after disposal. Because trees used to make virgin paper and petrochemicals used to make plastics may soon become depleted, source reduction is the best solution to the waste dilemma. Denmark has banned the use of non -refillable beverage containers and McDonaldʹs restaurants in Austria and Sweden have been using biodegradable, compostable cutlery. Recycling has value as well, as long as the recycling loop is closed and people purchase recycled items. Bottle bills and municipal curbside collection provide recycling incentives.
Paper recycling is profitable if waste is properly sorted. All kinds of paper and cardboard are recyclable. Food and paperboard (uncorrugated thin coated board) can contaminate collections, however, reducing their value. After processing, paper and cardboard are used to make paper towels and paperboard for packaging cereal, shoes, and toys. Decapped, washed, and squashed plastic is recycled into carpets, pillows, and new bottles. Although low -density polyethylene, or LDPE (recycling symbol #4), from grocery bags is the most widely used plastic, beverage bottle polyethylene terephthalate, or PETE (symbol #1), and high-density polyethylene, or HDPE (symbol #2), are the most widely recycled plastics.
Containers from toxic substances such as motor oil, pesticides, and solvents are not usually accepted with collected plastic because of contamination. Methods to reuse and recycle polystyrene are in development, although presently, Styrofoam is not collected with other plastics and so it is considered a contaminant as well.
Plastic __________.
A) polystyrene is considered a plastic contaminant
B) not made from recyclables is made from renewable raw materials
C) from grocery bags is labeled with recycling symbols #1 and #2
D) from beverage containers is easily recyclable if decapped, washed, and squashed
E) containers from motor oil are recycled with beverage bottles to make new bottles
The prevalence of ʺthrowaway mentalitiesʺ and increased packaging has amplified the consumption of paper and plastic in our society. Disposable plates, cups, and utensils are convenient, sanitary, and inexpensive. Further packaging also preserves freshness, prevents breakage, protects against tampering, provides information to consumers, and allows shipment of products over long distances. However, paper and plastic do not degrade readily in sanitary landfills.
Garbologist William Rathje found legible newspapers in landfills decades after disposal. Because trees used to make virgin paper and petrochemicals used to make plastics may soon become depleted, source reduction is the best solution to the waste dilemma. Denmark has banned the use of non -refillable beverage containers and McDonaldʹs restaurants in Austria and Sweden have been using biodegradable, compostable cutlery. Recycling has value as well, as long as the recycling loop is closed and people purchase recycled items. Bottle bills and municipal curbside collection provide recycling incentives.
Paper recycling is profitable if waste is properly sorted. All kinds of paper and cardboard are recyclable. Food and paperboard (uncorrugated thin coated board) can contaminate collections, however, reducing their value. After processing, paper and cardboard are used to make paper towels and paperboard for packaging cereal, shoes, and toys. Decapped, washed, and squashed plastic is recycled into carpets, pillows, and new bottles. Although low -density polyethylene, or LDPE (recycling symbol #4), from grocery bags is the most widely used plastic, beverage bottle polyethylene terephthalate, or PETE (symbol #1), and high-density polyethylene, or HDPE (symbol #2), are the most widely recycled plastics.
Containers from toxic substances such as motor oil, pesticides, and solvents are not usually accepted with collected plastic because of contamination. Methods to reuse and recycle polystyrene are in development, although presently, Styrofoam is not collected with other plastics and so it is considered a contaminant as well.
Plastic __________.
A) polystyrene is considered a plastic contaminant
B) not made from recyclables is made from renewable raw materials
C) from grocery bags is labeled with recycling symbols #1 and #2
D) from beverage containers is easily recyclable if decapped, washed, and squashed
E) containers from motor oil are recycled with beverage bottles to make new bottles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Read the following scenario and answer the question below.
The prevalence of ʺthrowaway mentalitiesʺ and increased packaging has amplified the consumption of paper and plastic in our society. Disposable plates, cups, and utensils are convenient, sanitary, and inexpensive. Further packaging also preserves freshness, prevents breakage, protects against tampering, provides information to consumers, and allows shipment of products over long distances. However, paper and plastic do not degrade readily in sanitary landfills.
Garbologist William Rathje found legible newspapers in landfills decades after disposal. Because trees used to make virgin paper and petrochemicals used to make plastics may soon become depleted, source reduction is the best solution to the waste dilemma. Denmark has banned the use of non -refillable beverage containers and McDonaldʹs restaurants in Austria and Sweden have been using biodegradable, compostable cutlery. Recycling has value as well, as long as the recycling loop is closed and people purchase recycled items. Bottle bills and municipal curbside collection provide recycling incentives.
Paper recycling is profitable if waste is properly sorted. All kinds of paper and cardboard are recyclable. Food and paperboard (uncorrugated thin coated board) can contaminate collections, however, reducing their value. After processing, paper and cardboard are used to make paper towels and paperboard for packaging cereal, shoes, and toys. Decapped, washed, and squashed plastic is recycled into carpets, pillows, and new bottles. Although low -density polyethylene, or LDPE (recycling symbol #4), from grocery bags is the most widely used plastic, beverage bottle polyethylene terephthalate, or PETE (symbol #1), and high-density polyethylene, or HDPE (symbol #2), are the most widely recycled plastics.
Containers from toxic substances such as motor oil, pesticides, and solvents are not usually accepted with collected plastic because of contamination. Methods to reuse and recycle polystyrene are in development, although presently, Styrofoam is not collected with other plastics and so it is considered a contaminant as well.
The best way to reduce plastic in landfills is to ________________.
A) urge the government to pass more bottle bills
B) buy products produced locally with minimal packaging
C) reuse beverage bottles
D) increase use of recycled items
E) use biodegradable plastic items
The prevalence of ʺthrowaway mentalitiesʺ and increased packaging has amplified the consumption of paper and plastic in our society. Disposable plates, cups, and utensils are convenient, sanitary, and inexpensive. Further packaging also preserves freshness, prevents breakage, protects against tampering, provides information to consumers, and allows shipment of products over long distances. However, paper and plastic do not degrade readily in sanitary landfills.
Garbologist William Rathje found legible newspapers in landfills decades after disposal. Because trees used to make virgin paper and petrochemicals used to make plastics may soon become depleted, source reduction is the best solution to the waste dilemma. Denmark has banned the use of non -refillable beverage containers and McDonaldʹs restaurants in Austria and Sweden have been using biodegradable, compostable cutlery. Recycling has value as well, as long as the recycling loop is closed and people purchase recycled items. Bottle bills and municipal curbside collection provide recycling incentives.
Paper recycling is profitable if waste is properly sorted. All kinds of paper and cardboard are recyclable. Food and paperboard (uncorrugated thin coated board) can contaminate collections, however, reducing their value. After processing, paper and cardboard are used to make paper towels and paperboard for packaging cereal, shoes, and toys. Decapped, washed, and squashed plastic is recycled into carpets, pillows, and new bottles. Although low -density polyethylene, or LDPE (recycling symbol #4), from grocery bags is the most widely used plastic, beverage bottle polyethylene terephthalate, or PETE (symbol #1), and high-density polyethylene, or HDPE (symbol #2), are the most widely recycled plastics.
Containers from toxic substances such as motor oil, pesticides, and solvents are not usually accepted with collected plastic because of contamination. Methods to reuse and recycle polystyrene are in development, although presently, Styrofoam is not collected with other plastics and so it is considered a contaminant as well.
The best way to reduce plastic in landfills is to ________________.
A) urge the government to pass more bottle bills
B) buy products produced locally with minimal packaging
C) reuse beverage bottles
D) increase use of recycled items
E) use biodegradable plastic items

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



