Deck 26: Population Growth and Regulation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/116
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 26: Population Growth and Regulation
1
To determine the number of individuals added to a population during a given time, we multiply the growth rate (r)by the:
A)biotic potential.
B)original population size.
C)environmental resistance.
D)final population size.
E)number of immigrants.
A)biotic potential.
B)original population size.
C)environmental resistance.
D)final population size.
E)number of immigrants.
B
2
The different species within an ecosystem that interact in various ways make up a(n):
A)population.
B)community.
C)trophic level.
D)aggregation.
E)ecotone.
A)population.
B)community.
C)trophic level.
D)aggregation.
E)ecotone.
B
3
A population grows exponentially when:
A)the birth rate and the death rate are equal.
B)the birth rate exceeds the death rate and immigration exceeds emigration.
C)emigration exceeds immigration and the birth rate equals the death rate.
D)the death rate equals the birth rate and immigration is equal to emigration.
E)the carrying capacity is exceeded.
A)the birth rate and the death rate are equal.
B)the birth rate exceeds the death rate and immigration exceeds emigration.
C)emigration exceeds immigration and the birth rate equals the death rate.
D)the death rate equals the birth rate and immigration is equal to emigration.
E)the carrying capacity is exceeded.
B
4
Which species has the highest biotic potential?
A)a fungus that produces thousands of reproductive spores every day
B)a bacteria that divides only once every 3 weeks
C)a rat that produces a litter of 6 pups every 3 months
D)an elephant that produces a single calf every 3 years
E)a lioness that produces 3 cubs once a year
A)a fungus that produces thousands of reproductive spores every day
B)a bacteria that divides only once every 3 weeks
C)a rat that produces a litter of 6 pups every 3 months
D)an elephant that produces a single calf every 3 years
E)a lioness that produces 3 cubs once a year

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Floods and fires are examples of ________, which can dramatically and unpredictably reduce populations.
A)density-dependent factors
B)logistic growth factors
C)biotic factors
D)demographic factors
E)environmental resistance
A)density-dependent factors
B)logistic growth factors
C)biotic factors
D)demographic factors
E)environmental resistance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If a population of 100 birds increases to 120 birds in a year, what is r?
A)0)16
B)0)20
C)1)2
D)2
E)20
A)0)16
B)0)20
C)1)2
D)2
E)20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A population size will remain stable if:
A)the number of births each year is constant and the birth rate is higher than the death rate.
B)the population grows by a fixed percentage of its size each year.
C)the rate of emigration is higher than the rate of immigration.
D)the birth and death rates are equal, as are the rates of emigration and immigration.
E)environmental resistance declines each year.
A)the number of births each year is constant and the birth rate is higher than the death rate.
B)the population grows by a fixed percentage of its size each year.
C)the rate of emigration is higher than the rate of immigration.
D)the birth and death rates are equal, as are the rates of emigration and immigration.
E)environmental resistance declines each year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Environmental resistance is:
A)limits imposed on population growth by only the living environment (such as predators or competitors).
B)limits imposed on population growth by only the nonliving environment.
C)limits imposed on population growth by both the living and nonliving environments.
D)a factor that decreases both death rates and birth rates.
E)a factor that increases both death rates and birth rates.
A)limits imposed on population growth by only the living environment (such as predators or competitors).
B)limits imposed on population growth by only the nonliving environment.
C)limits imposed on population growth by both the living and nonliving environments.
D)a factor that decreases both death rates and birth rates.
E)a factor that increases both death rates and birth rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Exponential growth occurs when:
A)the number of births each year is constant and the birth rate is higher than the death rate.
B)the population grows by a fixed percentage of its size each year.
C)the rate of emigration is higher than the rate of immigration.
D)the biotic potential decreases each year.
E)environmental resistance declines each year.
A)the number of births each year is constant and the birth rate is higher than the death rate.
B)the population grows by a fixed percentage of its size each year.
C)the rate of emigration is higher than the rate of immigration.
D)the biotic potential decreases each year.
E)environmental resistance declines each year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What happened to the forests of Easter Island?
A)They disappeared after humans brought herbivores to the island.
B)They never existed; the island has always been barren.
C)They disappeared as a result of clear-cutting by humans.
D)They have not existed for several million years.
E)They disappeared when humans brought a tree disease to the island.
A)They disappeared after humans brought herbivores to the island.
B)They never existed; the island has always been barren.
C)They disappeared as a result of clear-cutting by humans.
D)They have not existed for several million years.
E)They disappeared when humans brought a tree disease to the island.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Based on the data in the table, this population has a(n)________ growth pattern? 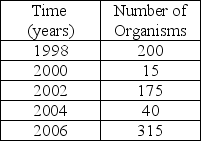
A)exponential
B)boom-and-bust
C)scramble competition
D)J-curve
E)S-curve

A)exponential
B)boom-and-bust
C)scramble competition
D)J-curve
E)S-curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A biologist who investigates how organisms interact with one another and with their nonliving environment is studying:
A)physiology.
B)anatomy.
C)morphology.
D)genetics.
E)ecology.
A)physiology.
B)anatomy.
C)morphology.
D)genetics.
E)ecology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A complex, interrelated network of organisms and the surrounding nonliving environment in a defined area is a(n):
A)community.
B)ecosystem.
C)population.
D)biosphere.
E)biome.
A)community.
B)ecosystem.
C)population.
D)biosphere.
E)biome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which factor does NOT influence the size a population reaches over time?
A)number of individuals migrating
B)number of deaths
C)age of females at reproduction
D)distance traveled by migrants
E)number of births
A)number of individuals migrating
B)number of deaths
C)age of females at reproduction
D)distance traveled by migrants
E)number of births

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
All members of a species that reside within an ecosystem make up a(n):
A)population.
B)community.
C)trophic level.
D)aggregation.
E)ecotone.
A)population.
B)community.
C)trophic level.
D)aggregation.
E)ecotone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When a population has inhabited an area for a long time and the population size has stabilized because of space and food limitations:
A)the carrying capacity of the area has been reached.
B)density dependence is clearly not involved in the population growth.
C)predation decreases.
D)density-independent factors are involved.
E)the environmental resistance declines.
A)the carrying capacity of the area has been reached.
B)density dependence is clearly not involved in the population growth.
C)predation decreases.
D)density-independent factors are involved.
E)the environmental resistance declines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Environmental resistance may limit the size of populations by:
A)increasing both birth and death rates.
B)decreasing both birth and death rates.
C)increasing death rates and/or decreasing birth rates.
D)decreasing death rates and/or increasing birth rates.
E)changing the biotic potential.
A)increasing both birth and death rates.
B)decreasing both birth and death rates.
C)increasing death rates and/or decreasing birth rates.
D)decreasing death rates and/or increasing birth rates.
E)changing the biotic potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An insect population grows exponentially until an early winter freeze kills almost all the insects. The next spring the population grows exponentially again. This type of population growth is called:
A)boom-and-bust cycles.
B)S-curve growth.
C)density-dependent growth.
D)density-independent growth.
E)sustained cycling.
A)boom-and-bust cycles.
B)S-curve growth.
C)density-dependent growth.
D)density-independent growth.
E)sustained cycling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Based on the data in the table, this population has a ________ growth pattern. 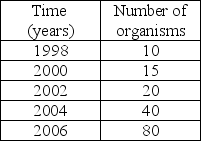
A)replacement-level fertility
B)boom-and-bust
C)scramble competition
D)J-curve
E)S-curve

A)replacement-level fertility
B)boom-and-bust
C)scramble competition
D)J-curve
E)S-curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In a deciduous oak forest in the northeastern United States, one example of a nonliving component of the ecosystem is:
A)nematodes in the soil that feed on plant roots.
B)nematodes in the soil that feed on dead organic matter.
C)sunlight that filters through the canopy.
D)animals such as deer that migrate through the forest but do not eat in the forest.
E)the smaller plants living under the oak trees.
A)nematodes in the soil that feed on plant roots.
B)nematodes in the soil that feed on dead organic matter.
C)sunlight that filters through the canopy.
D)animals such as deer that migrate through the forest but do not eat in the forest.
E)the smaller plants living under the oak trees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A random population distribution:
A)is an advantage in avoiding predators.
B)occurs when resources are evenly spaced.
C)allows predators to hunt more effectively.
D)is rare.
E)is found only in plants.
A)is an advantage in avoiding predators.
B)occurs when resources are evenly spaced.
C)allows predators to hunt more effectively.
D)is rare.
E)is found only in plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Gum bush releases a chemical from its roots that prevents any seeds from germinating in the soil above the roots. This is an example of:
A)social competition.
B)predation.
C)parasitism.
D)contest competition.
E)scramble competition.
A)social competition.
B)predation.
C)parasitism.
D)contest competition.
E)scramble competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Herd animals typically live in a ________ distribution pattern.
A)uniform
B)random
C)clumped
D)J-curve
E)scrambled
A)uniform
B)random
C)clumped
D)J-curve
E)scrambled

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Purple loosestrife was introduced into the Great Lakes region from Europe and sold as a garden flower. It produces thousands of seeds and has no natural predators there. It now clogs acres of wetlands and is considered a(n):
A)density-independent species.
B)density-dependent species.
C)predator.
D)invasive species.
E)replacement-level fertility.
A)density-independent species.
B)density-dependent species.
C)predator.
D)invasive species.
E)replacement-level fertility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In ________ competition, one organism uses social or chemical interactions to limit the access of other individuals to resources.
A)contest
B)scramble
C)interspecific
D)intramural
E)social
A)contest
B)scramble
C)interspecific
D)intramural
E)social

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If a caterpillar eats all the seedlings in your garden, killing all of them, the caterpillar is acting as a:
A)predator.
B)parasite.
C)competitor.
D)density-independent factor.
E)saprophyte.
A)predator.
B)parasite.
C)competitor.
D)density-independent factor.
E)saprophyte.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When mosquitoes are abundant, purple martins flock to the area and feed exclusively on them. When mosquito populations are not large, purple martins are similarly scarce and feed on other insects. This is an example of:
A)density-independent regulation.
B)density-dependent regulation.
C)ecosystem carrying capacity.
D)community carrying capacity.
E)exotic regulation.
A)density-independent regulation.
B)density-dependent regulation.
C)ecosystem carrying capacity.
D)community carrying capacity.
E)exotic regulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If the individuals of a species are very likely to live until old age, that species exhibits a(n)________ survivorship curve.
A)convex
B)constant
C)concave
D)S-shaped
E)declining
A)convex
B)constant
C)concave
D)S-shaped
E)declining

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In areas that have a stable population, the number of children born in a period of time is:
A)increasing.
B)decreasing.
C)approximately equal to the number of adults.
D)higher than the number of adults.
E)lower than the number of adults.
A)increasing.
B)decreasing.
C)approximately equal to the number of adults.
D)higher than the number of adults.
E)lower than the number of adults.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Why do many non-native species, such as a prickly pear cactus brought to Australia from South America, rapidly become abundant when first introduced?
A)The climate in the new site is more favorable than in its native site.
B)Non-native species increase their reproductive rate when introduced.
C)There are fewer predators and parasites capable of attacking the non-native species in the new site.
D)The carrying capacity at the new site is higher than at the native site.
E)Growth changes from an S-curve to a J-curve at the new site.
A)The climate in the new site is more favorable than in its native site.
B)Non-native species increase their reproductive rate when introduced.
C)There are fewer predators and parasites capable of attacking the non-native species in the new site.
D)The carrying capacity at the new site is higher than at the native site.
E)Growth changes from an S-curve to a J-curve at the new site.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Parasites affect their hosts' population sizes in a:
A)density-dependent fashion and usually directly kill the hosts.
B)density-dependent fashion and do not usually directly kill the hosts.
C)density-independent fashion and usually directly kill the hosts.
D)density-independent fashion and do not usually directly kill the hosts.
E)density-dependent fashion and do not affect host death rates.
A)density-dependent fashion and usually directly kill the hosts.
B)density-dependent fashion and do not usually directly kill the hosts.
C)density-independent fashion and usually directly kill the hosts.
D)density-independent fashion and do not usually directly kill the hosts.
E)density-dependent fashion and do not affect host death rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In a population of lemmings, a sudden freeze that caused many of the lemmings to die is an example of a:
A)nonliving and density-independent factor.
B)living and density-dependent factor.
C)nonliving and density-dependent factor.
D)living and density-independent factor.
E)normal boom-and-bust cycle.
A)nonliving and density-independent factor.
B)living and density-dependent factor.
C)nonliving and density-dependent factor.
D)living and density-independent factor.
E)normal boom-and-bust cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If most of the individuals of a species die when they are young, that species exhibits a(n)________ survivorship curve.
A)convex
B)constant
C)concave
D)S-shaped
E)declining
A)convex
B)constant
C)concave
D)S-shaped
E)declining

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, people increased Earth's capacity to support more humans through ________ advances.
A)cultural
B)agricultural
C)industrial-medical
D)social
E)demographic
A)cultural
B)agricultural
C)industrial-medical
D)social
E)demographic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What might cause a uniform population distribution?
A)the need for a group to care for its offspring
B)allelopathy (the release of chemicals by plants to inhibit the growth of other plants nearby)
C)localization of resources
D)the need to find a mate
E)scarce resources
A)the need for a group to care for its offspring
B)allelopathy (the release of chemicals by plants to inhibit the growth of other plants nearby)
C)localization of resources
D)the need to find a mate
E)scarce resources

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Exponential growth occurs:
A)only for a limited time in natural populations.
B)only in laboratory populations.
C)frequently in natural populations.
D)at regular intervals in natural populations.
E)only in theory, never in actual populations.
A)only for a limited time in natural populations.
B)only in laboratory populations.
C)frequently in natural populations.
D)at regular intervals in natural populations.
E)only in theory, never in actual populations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In his 1798 book, An Essay on the Principle of Population, Thomas Malthus stated: "the power of [Earth's human] population [to increase] is indefinitely greater than the power in the earth to produce subsistence for man." He explained that our population increases exponentially while we can increase our food supply only linearly. In modern terminology, what did Malthus mean by "the power in the earth to produce subsistence for man"?
A)biotic potential
B)birth rate
C)carrying capacity
D)environmental resistance
E)growth rate
A)biotic potential
B)birth rate
C)carrying capacity
D)environmental resistance
E)growth rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A population of rabbits introduced into an island grew rapidly for a few years and then the growth slowed down. Why did the population become stable?
A)The carrying capacity was reached.
B)Environmental resistance declined.
C)The rate of immigration declined.
D)The value of r decreased.
E)A bust cycle was about to begin.
A)The carrying capacity was reached.
B)Environmental resistance declined.
C)The rate of immigration declined.
D)The value of r decreased.
E)A bust cycle was about to begin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is an important density-independent factor limiting population size?
A)predation
B)weather
C)environmental resistance
D)competition
E)quantity of food
A)predation
B)weather
C)environmental resistance
D)competition
E)quantity of food

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Some predators feed preferentially on the most abundant prey. This is an example of ________ predation.
A)density-dependent
B)density-independent
C)competitive
D)exponential
E)cyclical
A)density-dependent
B)density-independent
C)competitive
D)exponential
E)cyclical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
During the past 50 years, the amount of cropland per person has:
A)decreased by 90%.
B)decreased by more than half.
C)decreased slightly.
D)stayed about the same.
E)increased slightly.
A)decreased by 90%.
B)decreased by more than half.
C)decreased slightly.
D)stayed about the same.
E)increased slightly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A J-curve is typical of a stable population. True or False?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A forest fire is a density-independent population control factor. True or False?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Invasive species can rapidly disrupt an ecosystem because they have a high biotic potential and face little environmental resistance. True or False?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
According to the equation for population growth rate, if two populations have the same death rates, then the population with r = 2 will increase more rapidly than a population with r = 4. True or False?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Populations that have been relatively undisturbed by man normally grow with no limits set by their environments. True or False?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In countries that have large numbers of children under age 15, the population is:
A)becoming larger.
B)becoming smaller.
C)staying the same.
D)hard to predict.
E)able to expand its carrying capacity.
A)becoming larger.
B)becoming smaller.
C)staying the same.
D)hard to predict.
E)able to expand its carrying capacity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If all the people in the world were to live at the American level in terms of technology, wealth, education, and other factors, the population of the world would have to ________ in order to support them.
A)double
B)reduce by half
C)reduce to a fifth of the current level
D)reduce to less than a tenth of the current level
E)decrease by 90%
A)double
B)reduce by half
C)reduce to a fifth of the current level
D)reduce to less than a tenth of the current level
E)decrease by 90%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The United Nations estimates that by 2050, the world's population may reach over ________ billion and still be growing.
A)7)0
B)9)0
C)12.4
D)15.6
E)20.5
A)7)0
B)9)0
C)12.4
D)15.6
E)20.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In countries where the number of children younger than 15 is approximately equal to the number between ages 15 and 45, the population is:
A)expanding slowly.
B)stable.
C)shrinking slightly.
D)growing exponentially.
E)declining drastically.
A)expanding slowly.
B)stable.
C)shrinking slightly.
D)growing exponentially.
E)declining drastically.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Malthus's prediction that our human population would eventually reach a point where we cannot sustain ourselves did not occur. Why?
A)Dramatic reductions in fertility rates brought an end to population growth before the crisis point was reached.
B)Malthus was wrong; human populations can grow indefinitely
C)Technological advances unforeseen by Malthus increased the carrying capacity to a greater extent and faster than predicted.
D)The two world wars and the AIDS crisis caused such massive mortality that the human population has stabilized.
E)Humans continue to find ways to enhance environmental quality, thus enabling more people to be supported.
A)Dramatic reductions in fertility rates brought an end to population growth before the crisis point was reached.
B)Malthus was wrong; human populations can grow indefinitely
C)Technological advances unforeseen by Malthus increased the carrying capacity to a greater extent and faster than predicted.
D)The two world wars and the AIDS crisis caused such massive mortality that the human population has stabilized.
E)Humans continue to find ways to enhance environmental quality, thus enabling more people to be supported.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
As a developing country passes through the demographic transition,
A)its age structure changes but its growth rate remains unchanged.
B)its birth and death rates decrease simultaneously.
C)its growth rate first falls but later recovers.
D)first its birth rate decreases, followed by its death rate.
E)first its death rate decreases, followed by its birth rate.
A)its age structure changes but its growth rate remains unchanged.
B)its birth and death rates decrease simultaneously.
C)its growth rate first falls but later recovers.
D)first its birth rate decreases, followed by its death rate.
E)first its death rate decreases, followed by its birth rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The growth rate of a population is the difference between the birth rate and the death rate. True or False?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Parasitism is a density-dependent population control. True or False?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
When a new population stabilizes at the carrying capacity, it is described as logistic population growth. True or False?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Interspecific competition is a density-independent factor. True or False?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Developing countries tend to have a(n)________ age structure diagram.
A)rectangular
B)inverted triangle-shaped
C)pyramid-shaped
D)square
E)round
A)rectangular
B)inverted triangle-shaped
C)pyramid-shaped
D)square
E)round

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
An effective parasite is one that kills its host quickly. True or False?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
At present, Earth's human population is:
A)stable.
B)declining.
C)increasing exponentially.
D)increasing at a constant rate.
E)increasing by about 10% per year.
A)stable.
B)declining.
C)increasing exponentially.
D)increasing at a constant rate.
E)increasing by about 10% per year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Americans use about ________ times as much energy as the world average.
A)1)5
B)2
C)5
D)10
E)20
A)1)5
B)2
C)5
D)10
E)20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The amount of land needed to meet a person's resource and waste demands is called an ecological footprint. True or False?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Density-dependent factors become less effective as the population size increases. True or False?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
All the members of a species that live in a specific geographic region form a(n)________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The sum of all factors that limit the ability of a population to grow is known as ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Prey, such as lemmings, may have a density-dependent effect on predator populations, such as those of the snowy owl, by enabling the predator to increase the number of its offspring at high prey densities. True or False?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
All the areas of Earth that support life make up the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In the equation "population growth = r × N," the letter r stands for ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The ________ of a population is the maximum rate at which a population could increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Humans are classified as a late-loss population. True or False?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Increased population densities and increased competition lead to increased emigration. True or False?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Within their territory, pack animals like wolves exhibit a uniform distribution. True or False?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When resources are limited but spread evenly throughout a region, plants are likely to form a uniform distribution pattern. True or False?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Natural populations cannot exceed their carrying capacities. True or False?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The human population currently shows a J-curve growth pattern. True or False?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Deforestation increases the productivity of land. True or False?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In a constant-loss population, an organism has an equal risk of dying at any time during its life span. True or False?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The United States has the lowest replacement-level fertility of the developed countries. True or False?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In a stable population with neither immigration nor emigration, the replacement-level fertility is one child per woman. True or False?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A measure of the ability of a population to grow under ideal circumstances is its ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In a maple forest in the spring, the ground is often covered with young maple seedlings, which compete for light and nutrients. By fall, most of the seedlings have died, leaving only a few survivors. This is an example of ________ competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



