Deck 5: Introduction to Hypothesis Testing
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/99
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Introduction to Hypothesis Testing
1
A researcher wants to know if a new type of health insurance works better or worse than a standard form of health insurance. The hypothesis that there will be no difference between the new type of insurance and the old type of insurance is called the:
A)comparison hypothesis
B)research hypothesis
C)null hypothesis
D)functional differential
A)comparison hypothesis
B)research hypothesis
C)null hypothesis
D)functional differential
null hypothesis
2
The logic of hypothesis testing involves figuring out the probability of getting a particular result if:
A)the research hypothesis is true
B)the sampling distribution is accurate
C)the comparison distribution is true
D)the null hypothesis is true
A)the research hypothesis is true
B)the sampling distribution is accurate
C)the comparison distribution is true
D)the null hypothesis is true
the null hypothesis is true
3
For the following question(s): A researcher is interested in a new kind of exercise. This new exercise can be done by anyone because it does not require any equipment, and therefore could be potentially beneficial without cost to the person. The researcher is interested in whether this new exercise will reduce the rate of heart attacks in the people who participate in doing it.
What is the "cutoff on the comparison distribution"?
A)The point at which, assuming the null hypothesis is true, it would be extremely unlikely to get a result this extreme.
B)The point at which, assuming the research hypothesis is true, it would be extremely unlikely to get a result this extreme.
C)The point at which the comparison distribution ends.
D)The point at which you accept the null hypothesis if the result is more extreme.
What is the "cutoff on the comparison distribution"?
A)The point at which, assuming the null hypothesis is true, it would be extremely unlikely to get a result this extreme.
B)The point at which, assuming the research hypothesis is true, it would be extremely unlikely to get a result this extreme.
C)The point at which the comparison distribution ends.
D)The point at which you accept the null hypothesis if the result is more extreme.
The point at which, assuming the null hypothesis is true, it would be extremely unlikely to get a result this extreme.
4
For the following question(s): A researcher is interested in a new kind of exercise. This new exercise can be done by anyone because it does not require any equipment, and therefore could be potentially beneficial without cost to the person. The researcher is interested in whether this new exercise will reduce the rate of heart attacks in the people who participate in doing it.
What is the comparison distribution?
A)The distribution of those who participate in the exercise program.
B)The distribution of those who do not participate in the exercise program.
C)The distribution of those who have heart attacks.
D)The distribution of those who do not have heart attacks.
What is the comparison distribution?
A)The distribution of those who participate in the exercise program.
B)The distribution of those who do not participate in the exercise program.
C)The distribution of those who have heart attacks.
D)The distribution of those who do not have heart attacks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A researcher tests whether there is any difference between how fast people work in the morning versus how fast they work in the evening. What is the NULL hypothesis?
A)People who work in the morning work faster.
B)People who work at night work faster.
C)There is some difference, but which is faster is not predicted.
D)There is no difference in the speed at which people work.
A)People who work in the morning work faster.
B)People who work at night work faster.
C)There is some difference, but which is faster is not predicted.
D)There is no difference in the speed at which people work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A researcher tests effects of a new training program. The hypothesis that this new training program will work better than the old training program is called the:
A)comparison hypothesis
B)research hypothesis
C)null hypothesis
D)there is no special name for this kind of a hypothesis
A)comparison hypothesis
B)research hypothesis
C)null hypothesis
D)there is no special name for this kind of a hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
You want to know if a new employee incentive program really works. How would you test the hypothesis that it does work?
A)Try to disprove the hypothesis that it does work
B)Try to prove the hypothesis that it does work
C)Try to disprove the hypothesis that it does not work
D)Try to prove the hypothesis that it does not work
A)Try to disprove the hypothesis that it does work
B)Try to prove the hypothesis that it does work
C)Try to disprove the hypothesis that it does not work
D)Try to prove the hypothesis that it does not work

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A researcher tests whether a new teaching method is more effective than the old one. What is the RESEARCH hypothesis?
A)The new teaching method is more effective than the old teaching method.
B)The old teaching method is more effective than the new teaching method.
C)There is no difference in effectiveness between the old teaching method and the new teaching method.
D)There is some difference in effectiveness between the old teaching method and the new teaching method, but which is more effective is not predicted.
A)The new teaching method is more effective than the old teaching method.
B)The old teaching method is more effective than the new teaching method.
C)There is no difference in effectiveness between the old teaching method and the new teaching method.
D)There is some difference in effectiveness between the old teaching method and the new teaching method, but which is more effective is not predicted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is a hypothesis?
A)a procedure for using descriptive statistics in research
B)a set of theories about certain facts, relationships, or events
C)a prediction about the results of a research study
D)a way of quantifying the normal curve
A)a procedure for using descriptive statistics in research
B)a set of theories about certain facts, relationships, or events
C)a prediction about the results of a research study
D)a way of quantifying the normal curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Place the five steps of the hypothesis-testing process in the correct order: 1. Determine the characteristics of the comparison distribution.
2) Decide whether to reject the null hypothesis.
3) Restate the question as a research hypothesis and a null hypothesis about the populations.
4) Determine your sample's score on the comparison distribution.
5) Determine the cutoff sample score on the comparison distribution at which the null hypothesis should be rejected.
A)2, 4, 1, 5, 3
B)3, 4, 1, 5, 2
C)1, 3, 5, 4, 2
D)3, 1, 5, 4, 2
2) Decide whether to reject the null hypothesis.
3) Restate the question as a research hypothesis and a null hypothesis about the populations.
4) Determine your sample's score on the comparison distribution.
5) Determine the cutoff sample score on the comparison distribution at which the null hypothesis should be rejected.
A)2, 4, 1, 5, 3
B)3, 4, 1, 5, 2
C)1, 3, 5, 4, 2
D)3, 1, 5, 4, 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
For the following question(s): A researcher is interested in a new kind of exercise. This new exercise can be done by anyone because it does not require any equipment, and therefore could be potentially beneficial without cost to the person. The researcher is interested in whether this new exercise will reduce the rate of heart attacks in the people who participate in doing it.
What is the research hypothesis?
A)People will participate because it does not cost them any money.
B)The exercise will make no difference in the rate of heart attacks.
C)The exercise will reduce the rate of heart attacks.
D)The exercise will increase the rate of heart attacks.
What is the research hypothesis?
A)People will participate because it does not cost them any money.
B)The exercise will make no difference in the rate of heart attacks.
C)The exercise will reduce the rate of heart attacks.
D)The exercise will increase the rate of heart attacks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
For the following question(s): A researcher is interested in a new kind of exercise. This new exercise can be done by anyone because it does not require any equipment, and therefore could be potentially beneficial without cost to the person. The researcher is interested in whether this new exercise will reduce the rate of heart attacks in the people who participate in doing it.
What is the null hypothesis?
A)People will participate because it does not cost them any money.
B)The exercise will make no difference in the rate of heart attacks.
C)The exercise will reduce the rate of heart attacks.
D)The exercise will increase the rate of heart attacks.
What is the null hypothesis?
A)People will participate because it does not cost them any money.
B)The exercise will make no difference in the rate of heart attacks.
C)The exercise will reduce the rate of heart attacks.
D)The exercise will increase the rate of heart attacks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following statements is most accurate about hypothesis testing?
A)It is a central theme in the statistical analysis of virtually all social science research.
B)It is a simple part of statistics that applies to approximately three statistical procedures.
C)It is a fairly uncommon way of using statistics.
D)It is a kind of statistical procedure that is used mainly as part of descriptive statistics.
A)It is a central theme in the statistical analysis of virtually all social science research.
B)It is a simple part of statistics that applies to approximately three statistical procedures.
C)It is a fairly uncommon way of using statistics.
D)It is a kind of statistical procedure that is used mainly as part of descriptive statistics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Another name for the research hypothesis is the:
A)null hypothesis
B)statistical hypothesis
C)void hypothesis
D)alternative hypothesis
A)null hypothesis
B)statistical hypothesis
C)void hypothesis
D)alternative hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A _________________ is a set of principles that attempts to explain one or more facts, relations, or events.
A)curve
B)table
C)theory
D)deviation
A)curve
B)table
C)theory
D)deviation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
You determine the characteristics of the comparison distribution to answer which of the following questions?
A)Given a particular sample value, what is the probability of obtaining that value if the research hypothesis is true?
B)Given a particular sample value, what is the probability of obtaining that value if the null hypothesis is true?
C)Given a particular population value, what is the probability of obtaining that value if the research hypothesis is true?
D)Given a particular population value, what is the probability of obtaining that value if the null hypothesis is false?
A)Given a particular sample value, what is the probability of obtaining that value if the research hypothesis is true?
B)Given a particular sample value, what is the probability of obtaining that value if the null hypothesis is true?
C)Given a particular population value, what is the probability of obtaining that value if the research hypothesis is true?
D)Given a particular population value, what is the probability of obtaining that value if the null hypothesis is false?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What represents the situation in which the null hypothesis is true?
A)the comparison distribution
B)the directional distribution
C)the nondirectional distribution
D)a one-tailed test
A)the comparison distribution
B)the directional distribution
C)the nondirectional distribution
D)a one-tailed test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A theory usually gives rise to various specific _____________ that can be tested in research studies.
A)t tests
B)hypotheses
C)Z scores
D)formulations
A)t tests
B)hypotheses
C)Z scores
D)formulations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A sample is studied to see if it represents a population (called Population 1)that is different from a known population (called Population 2). The comparison distribution is:
A)the same as the distribution of Population 1
B)the same as the distribution of Population 2
C)a rectangular distribution with the same mean and standard deviation as Population 1
D)a rectangular distribution with the same mean and standard deviation as Population 2
A)the same as the distribution of Population 1
B)the same as the distribution of Population 2
C)a rectangular distribution with the same mean and standard deviation as Population 1
D)a rectangular distribution with the same mean and standard deviation as Population 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
How do you set up a hypothesis testing problem?
A)You set it up to test what you predict will happen
B)You set it up to test the opposite of what you predict will happen
C)You set up two problems, one to test what you predict and the other to test the opposite
D)You set up a test that assumes the two populations are different, regardless of whether that is what you predict or not
A)You set it up to test what you predict will happen
B)You set it up to test the opposite of what you predict will happen
C)You set up two problems, one to test what you predict and the other to test the opposite
D)You set up a test that assumes the two populations are different, regardless of whether that is what you predict or not

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Suppose that a researcher wants to know if a new flu drug affects people, either by making them better or worse. Would this be a one-tailed or two-tailed test and why?
A)One-tailed because only one issue is discussed-the drug
B)One-tailed because there is only one interaction, which is between the flu and the drug
C)Two-tailed because there are two variables-whether or not people take the drug and how their flu is affected
D)Two-tailed because there is no predicted direction of the effect of the drug
A)One-tailed because only one issue is discussed-the drug
B)One-tailed because there is only one interaction, which is between the flu and the drug
C)Two-tailed because there are two variables-whether or not people take the drug and how their flu is affected
D)Two-tailed because there is no predicted direction of the effect of the drug

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is a correct argument for using a two-tailed test even if there is a clear basis for predicting a result in a given direction?
A)If the null hypothesis is in fact true, a failure to reject it will give stronger evidence in support of it.
B)One-tailed tests cannot be used in almost any real study involving two groups.
C)If an unexpected result comes out opposite to what is predicted, it does not have to be ignored.
D)A two-tailed test gives you a better chance of getting a significant result.
A)If the null hypothesis is in fact true, a failure to reject it will give stronger evidence in support of it.
B)One-tailed tests cannot be used in almost any real study involving two groups.
C)If an unexpected result comes out opposite to what is predicted, it does not have to be ignored.
D)A two-tailed test gives you a better chance of getting a significant result.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The results of a study are not extreme enough to reject the null hypothesis. What can the researcher conclude with reasonable confidence?
A)Results support the null hypothesis.
B)Results prove that the null hypothesis is true.
C)Results support the research hypothesis.
D)None of the above; the results are inconclusive.
A)Results support the null hypothesis.
B)Results prove that the null hypothesis is true.
C)Results support the research hypothesis.
D)None of the above; the results are inconclusive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Why can a researcher not say that the results PROVE that the research hypothesis is true?
A)Because the results of research studies are based on probabilities
B)Because the results of research studies are generally incorrect
C)Because it is likely that the results will be disproved within a short time
D)All of the above
A)Because the results of research studies are based on probabilities
B)Because the results of research studies are generally incorrect
C)Because it is likely that the results will be disproved within a short time
D)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Based on the results of his study, a researcher rejects the null hypothesis because the probability of obtaining his result if the null hypothesis were true is less than 5%. How would this be symbolized?
A)p = 5%
B)p < .05
C).05 < p
D)p > 5%
A)p = 5%
B)p < .05
C).05 < p
D)p > 5%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The cutoff sample score is also known as the:
A)critical value
B)sampling distribution
C)null value
D)sample Z score
A)critical value
B)sampling distribution
C)null value
D)sample Z score

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If the null hypothesis is rejected, the researcher can conclude that the results:
A)support the research hypothesis
B)prove that the research hypothesis is true
C)were inconclusive
D)support the null hypothesis
A)support the research hypothesis
B)prove that the research hypothesis is true
C)were inconclusive
D)support the null hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A one-tailed test is especially associated with:
A)the research hypothesis
B)the null hypothesis
C)a nondirectional hypothesis
D)a directional hypothesis
A)the research hypothesis
B)the null hypothesis
C)a nondirectional hypothesis
D)a directional hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Suppose the cutoff Z score on the comparison distribution is ±2.31. You could reject the null hypothesis if the sample value's Z score on this distribution was:
A)-2.16
B)-1.41
C)2.16
D)2.83
A)-2.16
B)-1.41
C)2.16
D)2.83

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A researcher reported significant results for a study, noting that ".05 > p." What is NOT standard about this expression?
A)")05" should have been written as "5%"
B)"p" should be Z
C)")05 > p" should have been written "p < .05"
D)nothing is wrong with this expression (it is standard)
A)")05" should have been written as "5%"
B)"p" should be Z
C)")05 > p" should have been written "p < .05"
D)nothing is wrong with this expression (it is standard)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
There is a special complication when using a two-tailed test. The researcher must:
A)multiply the significance percentage by .05
B)divide the significance percentage by .05
C)divide up the significance percentage between the two tails of the distribution
D)divide up the significance percentage by the four quartiles of the distribution
A)multiply the significance percentage by .05
B)divide the significance percentage by .05
C)divide up the significance percentage between the two tails of the distribution
D)divide up the significance percentage by the four quartiles of the distribution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A result is considered statistically significant when a sample value is so extreme that:
A)the research hypothesis is rejected
B)the null hypothesis is accepted
C)the research hypothesis is accepted
D)the null hypothesis is rejected
A)the research hypothesis is rejected
B)the null hypothesis is accepted
C)the research hypothesis is accepted
D)the null hypothesis is rejected

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is the argument for using a one-tailed test when there is a clear basis for predicting a result in a given direction?
A)The underlying mathematics of one-tailed tests are more accurate.
B)If the result is opposite to the prediction, the researcher can still do a two-tailed test later.
C)It is more conservative, in the sense that in using a one-tailed test it is harder to reject the null hypothesis.
D)A particular theory is being tested, and if the results come out opposite to the theory, that adds no more information than if the result simply had not been significant.
A)The underlying mathematics of one-tailed tests are more accurate.
B)If the result is opposite to the prediction, the researcher can still do a two-tailed test later.
C)It is more conservative, in the sense that in using a one-tailed test it is harder to reject the null hypothesis.
D)A particular theory is being tested, and if the results come out opposite to the theory, that adds no more information than if the result simply had not been significant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The cutoff Z score on the comparison distribution is 1.64 and the sample value has a score of 1.32 on the comparison distribution.
A)the null hypothesis cannot be rejected
B)the null hypothesis is rejected
C)the research hypothesis is supported
D)the research hypothesis is rejected
A)the null hypothesis cannot be rejected
B)the null hypothesis is rejected
C)the research hypothesis is supported
D)the research hypothesis is rejected

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is NOT a correct statement of one of the five steps of hypothesis testing?
A)Restate the question as a research hypothesis and a null hypothesis about the populations.
B)Determine the characteristics of the comparison distribution.
C)Determine the cutoff score on the sample distribution at which the research hypothesis should be rejected.
D)Decide whether to reject the null hypothesis.
A)Restate the question as a research hypothesis and a null hypothesis about the populations.
B)Determine the characteristics of the comparison distribution.
C)Determine the cutoff score on the sample distribution at which the research hypothesis should be rejected.
D)Decide whether to reject the null hypothesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What does it mean if a researcher said she rejected the null hypothesis at the .05 level?
A)There was less than a 5% chance that she would have gotten such an extreme result by chance if the null hypothesis were true.
B)There was more than a 5% chance that she would have gotten such an extreme result by chance if the null hypothesis were true.
C)There is a 5% chance that there is a difference between the two populations she is testing if the null hypothesis were true.
D)There is a 95% chance that the research hypothesis is true.
A)There was less than a 5% chance that she would have gotten such an extreme result by chance if the null hypothesis were true.
B)There was more than a 5% chance that she would have gotten such an extreme result by chance if the null hypothesis were true.
C)There is a 5% chance that there is a difference between the two populations she is testing if the null hypothesis were true.
D)There is a 95% chance that the research hypothesis is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
How do you determine whether or not to reject the null hypothesis?
A)If the Z score is less than -1 or greater than +1
B)If the Z score is greater than +2.5
C)Compare the Z score needed to reject the null hypothesis to the actual sample Z score
D)Compare the standard deviation of the sample to the standard deviation of the population
A)If the Z score is less than -1 or greater than +1
B)If the Z score is greater than +2.5
C)Compare the Z score needed to reject the null hypothesis to the actual sample Z score
D)Compare the standard deviation of the sample to the standard deviation of the population

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What are the generally accepted cutoff points (or conventional levels of significance)in hypothesis testing in psychology?
A).001 and .10
B).01 and .05
C).10, .20, and .30
D).05, .25, and .95
A).001 and .10
B).01 and .05
C).10, .20, and .30
D).05, .25, and .95

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is a standard way for the significance level of the result of a hypothesis test to be reported in a research article?
A)p < .01
B)p = .03
C)p < .05
D)all of the above are standard and can be used
A)p < .01
B)p = .03
C)p < .05
D)all of the above are standard and can be used

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A researcher wants to know if a new type of exercise improves peoples' health. Would this be a one-tailed or two-tailed test and why?
A)One-tailed because the study is only interested in whether the exercise increases health
B)One-tailed because the study only looks at the effects of exercise and does not take other factors into account
C)Two-tailed because they will have to study healthy and unhealthy people
D)Two-tailed because there is no predicted direction of difference
A)One-tailed because the study is only interested in whether the exercise increases health
B)One-tailed because the study only looks at the effects of exercise and does not take other factors into account
C)Two-tailed because they will have to study healthy and unhealthy people
D)Two-tailed because there is no predicted direction of difference

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In most behavioral and social science research articles, unless the researcher specifically states that a __________ test was used, it is assumed that it was a __________.
A)two-tailed; one-tailed
B).10 significance test; .25 significance test
C).05 significance test; .01 significance test
D)one-tailed; two-tailed
A)two-tailed; one-tailed
B).10 significance test; .25 significance test
C).05 significance test; .01 significance test
D)one-tailed; two-tailed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In hypothesis testing, if the null hypothesis is rejected, this is taken as support for the __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Decision errors are possible in hypothesis testing because you are making decisions about _______ based on information in ________.
A)distributions; Z tables
B)populations; samples
C)samples; populations
D)distributions; frequency tables
A)distributions; Z tables
B)populations; samples
C)samples; populations
D)distributions; frequency tables

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
__________ is a procedure for deciding whether the outcome of a study (results for a sample)supports a particular theory or practical innovation (which is thought to apply to a population).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Suppose you conduct a study in which you set the significance level cutoff at a lenient probability level, such as 15%. In this case, you would have a 15% chance of making a:
A)Type I error
B)Type II error
C)Type III error
D)computational error
A)Type I error
B)Type II error
C)Type III error
D)computational error

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In hypothesis testing, a statement that there is no difference between populations (or a difference opposite to that predicted)is called the __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
For a two-tailed test at the .05 significance level, the appropriate cutoff Z scores would be:
A)-1.96 and +1.96
B)-2.58 and +2.58
C)-1.64 and +1.64
D)-2.33 and +2.33
A)-1.96 and +1.96
B)-2.58 and +2.58
C)-1.64 and +1.64
D)-2.33 and +2.33

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Complete the table with the correct and incorrect decision-making terms in hypothesis testing: 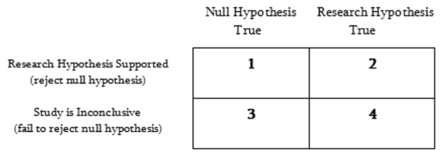
A)1 = Type I error; 2 = correct decision; 3 = Type II error; 4 = computational error
B)1 = correct decision; 2 = Type I error; 3 = Type II error; 4 = correct decision
C)1 = Type I error; 2 = correct decision; 3 = correct decision; 4 = Type II error
D)1 = computational error; 2 = Type I error; 3 = Type II error; 4 = correct decision

A)1 = Type I error; 2 = correct decision; 3 = Type II error; 4 = computational error
B)1 = correct decision; 2 = Type I error; 3 = Type II error; 4 = correct decision
C)1 = Type I error; 2 = correct decision; 3 = correct decision; 4 = Type II error
D)1 = computational error; 2 = Type I error; 3 = Type II error; 4 = correct decision

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The usual rule in statistics is that a study cannot find the null hypothesis to be true-one can only reject or fails to reject the null hypothesis is simply uninformative and such studies tend not to be published. Why is this a problem in the field of psychology and other behavioral sciences?
A)Much work could be avoided if people knew what interventions had not worked.
B)This may lead to ideas being assumed as true just because a few studies found results supporting them (while many more, unreported, had not).
C)Power and effect size considerations are getting ignored.
D)Both A and B are correct.
A)Much work could be avoided if people knew what interventions had not worked.
B)This may lead to ideas being assumed as true just because a few studies found results supporting them (while many more, unreported, had not).
C)Power and effect size considerations are getting ignored.
D)Both A and B are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
When a result is close but does not reach the significance level chosen , if may be reported as a "near significant trend" or as having "approached significance," with, for example,
p < .10. (True or False)
p < .10. (True or False)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Type II errors concern scientists because:
A)it could mean that a good theory or beneficial practice is not used
B)it means that the experiment must be repeated to confirm the positive result
C)rejecting the null hypothesis should only occur when the research hypothesis is true
D)future researchers might build entire theories based on a mistakenly significant result
A)it could mean that a good theory or beneficial practice is not used
B)it means that the experiment must be repeated to confirm the positive result
C)rejecting the null hypothesis should only occur when the research hypothesis is true
D)future researchers might build entire theories based on a mistakenly significant result

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In hypothesis testing, a statement about the predicted relation between populations (often a prediction of difference between population means)is called the __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Failing to reject the null hypothesis when the research hypothesis is true is referred to as:
A)the probability of rejection
B)the error term
C)a Type I error
D)a Type II error
A)the probability of rejection
B)the error term
C)a Type I error
D)a Type II error

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A __________ is a prediction about the results of a research study.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In hypothesis testing, the __________ is the distribution to which you compare the score attained in your actual sample (based on the study results).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A researcher is interested in the effect of going through a terrorist attack on the attitude of police officers about the goodness of people in New York City. After the attack, police may hold more positive attitudes about people (because of various acts of heroism and altruism exhibited by residents)or more negative attitudes because of negative outcomes (looting and dishonesty after the event). What type of hypothesis should the researcher make?
A)directional
B)significant
C)percentile
D)nondirectional
A)directional
B)significant
C)percentile
D)nondirectional

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Conventional levels of significance have been set at 5% and 1% in order to:
A)maximally protect against Type I error
B)maximally protect against Type II error
C)compromise between the risk of a Type I and Type II error
D)none of the above; these levels were set historically in an arbitrary way without regard to issues associated with Type I or Type II error
A)maximally protect against Type I error
B)maximally protect against Type II error
C)compromise between the risk of a Type I and Type II error
D)none of the above; these levels were set historically in an arbitrary way without regard to issues associated with Type I or Type II error

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Setting the significance level cutoff at .10 instead of the more usual .05 increases the likelihood of:
A)a Type I error
B)a Type II error
C)failing to reject the null hypothesis
D)accepting the null hypothesis when, in fact, it is false
A)a Type I error
B)a Type II error
C)failing to reject the null hypothesis
D)accepting the null hypothesis when, in fact, it is false

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A Type I error is the result of:
A)improper measurement techniques on the part of the researcher
B)failing to reject the null hypothesis when, in fact, it is true
C)incorrectly rejecting the null hypothesis
D)incorrectly accepting the null hypothesis
A)improper measurement techniques on the part of the researcher
B)failing to reject the null hypothesis when, in fact, it is true
C)incorrectly rejecting the null hypothesis
D)incorrectly accepting the null hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Setting the significance level at a very extreme cutoff (such as .001)increases the chances of:
A)getting a significant result
B)rejecting the null hypothesis
C)a Type I error
D)a Type II error
A)getting a significant result
B)rejecting the null hypothesis
C)a Type I error
D)a Type II error

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The __________ distribution represents the situation if the null hypothesis is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A study is done with a sample of one person. The general population (Population 2)has a mean of 30 and a standard deviation of 5. The cutoff Z score for significance in this study is a Z of 1.96. The raw score of the sample person is 45. What should you conclude? __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A(n)__________ hypothesis is a research hypothesis predicting that one population will have higher scores than the other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The comparison distribution is based on the distribution of the voting behavior of _________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
For the following question(s): A study tests the prediction that people who spend a great deal of time on the beach have more eye problems than people in general.
The null hypothesis is _________.
The null hypothesis is _________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Most behavioral and social scientists use the ________ significance level, but those wanting to be more conservative commonly use the ________ levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Before conducting a study, a researcher determines the cutoff sample score on the __________ distribution at which the null hypothesis would be rejected if the sample is more extreme than this cutoff score.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
When the null hypothesis is rejected, the results of a study are said to be ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The 1% and 5% levels are the ________ levels of significance in behavioral and social science research.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
________ is a way of saying in symbols that a research result is significant at the .05 level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
For the following question(s): A study tests the prediction that people who spend a great deal of time on the beach have more eye problems than people in general.
Population 1 refers to __________. Population 2 refers to people in general.
Population 1 refers to __________. Population 2 refers to people in general.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If the value of the sample is more extreme than the _________ on the comparison distribution, then the null hypothesis will be rejected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A research hypothesis that does not predict a particular direction of difference between populations is called a(n)________ hypothesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
For the following question(s): A researcher wants to know whether people who listen regularly to radio talk shows are more or less likely to vote in national elections than are people in general.
The ________ is that there is no difference in voting between those who do and do not listen regularly to radio talk shows.
The ________ is that there is no difference in voting between those who do and do not listen regularly to radio talk shows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
In a(n)_________, the region of the comparison distribution in which the null hypothesis would be rejected is all on one side of the distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The researchers would use a(n)_________ -tailed test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If the cutoff represents the most extreme 5% of the comparison distribution, then 5% is called the __________ level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
When testing a directional hypothesis, you use a(n)________ test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
For the following question(s): A study tests the prediction that people who spend a great deal of time on the beach have more eye problems than people in general.
The research hypothesis is __________.
The research hypothesis is __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A study is done with a sample of one person. In the general population (Population 2), Population M = 100 and Population SD = 8. The cutoff Z score for significance in this study is a Z of 1.64. The raw score of the sample is 110. What should you conclude? __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



