Deck 8: Heart Block Dysrhythmias
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/50
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Heart Block Dysrhythmias
1
Which of the following heart block dysrhythmias is identified by a progressively longer PR interval pattern after each blocked QRS complex?
A)First-degree heart block
B)Second-degree heart block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree heart block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree heart block
A)First-degree heart block
B)Second-degree heart block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree heart block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree heart block
Second-degree heart block, Mobitz type I
2
Which heart block dysrhythmia is known as classical heart block?
A)First-degree heart block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree AV block
A)First-degree heart block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree AV block
Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
3
Which of the following is characteristic of an ECG tracing for a second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I?
A)The PR intervals get progressively shorter.
B)Not all of the P waves are followed by a QRS complex.
C)The P waves are inverted.
D)Both the atrial rate and the ventricular rate are regular.
A)The PR intervals get progressively shorter.
B)Not all of the P waves are followed by a QRS complex.
C)The P waves are inverted.
D)Both the atrial rate and the ventricular rate are regular.
Not all of the P waves are followed by a QRS complex.
4
Which heart blocks are the only blocks with an irregular ventricular response?
A)First-degree heart blocks
B)Second-degree heart blocks
C)Third-degree heart blocks
D)Bundle branch blocks
A)First-degree heart blocks
B)Second-degree heart blocks
C)Third-degree heart blocks
D)Bundle branch blocks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What causes a heart block dysrhythmia?
A)The ectopic focus originates above the ventricles.
B)The electrical current has difficulty traveling down the normal conduction pathway.
C)The rhythm originates at the AV junctional tissue, producing retrograde depolarization.
D)An ectopic beat originates in the right or left atrium, resulting in abnormal conduction.
A)The ectopic focus originates above the ventricles.
B)The electrical current has difficulty traveling down the normal conduction pathway.
C)The rhythm originates at the AV junctional tissue, producing retrograde depolarization.
D)An ectopic beat originates in the right or left atrium, resulting in abnormal conduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which heart block rhythm has a constant PR interval that measures greater than 0.20 seconds?
A)First-degree AV block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree AV block
A)First-degree AV block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree AV block

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the heart rate range for first-degree heart block?
A)20 to 40 bpm
B)40 to 60 bpm
C)60 to 100 bpm
D)100 to 150 bpm
A)20 to 40 bpm
B)40 to 60 bpm
C)60 to 100 bpm
D)100 to 150 bpm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
You have performed an ECG on a 34-year-old woman who appears to be in good general health. A portion of the ECG tracing is shown here. Which type of heart block does this patient have? 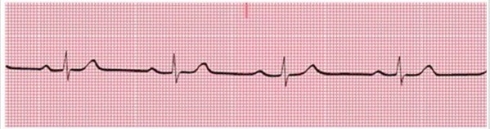
A)First-degree AV block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree AV block

A)First-degree AV block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree AV block

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In first-degree heart block, the electrical current is delayed or blocked along normal conduction pathways ________.
A)Below the AV junction
B)In the ventricles
C)At or above the AV junction
D)Above the SA node
A)Below the AV junction
B)In the ventricles
C)At or above the AV junction
D)Above the SA node

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is a characteristic of P-P intervals in all heart block dysrhythmias?
A)Regular
B)Irregular
C)Absent
D)Unidentifiable
A)Regular
B)Irregular
C)Absent
D)Unidentifiable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Who was the first to discover a type of second-degree heart block?
A)Dr. Karel Frederik Wenckebach
B)Sir Thomas Lewis
C)Willem Einthoven
D)Dr. Woldemar Mobitz
A)Dr. Karel Frederik Wenckebach
B)Sir Thomas Lewis
C)Willem Einthoven
D)Dr. Woldemar Mobitz

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Identify the following rhythm: 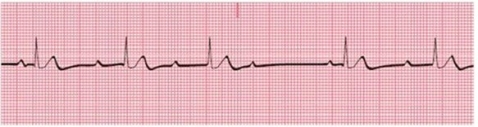
A)First-degree heart block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree AV block

A)First-degree heart block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree AV block

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What symptoms would you observe in a patient with first-degree AV block?
A)The patient would experience extreme fatigue and weakness.
B)The patient would have normal cardiac output and no symptoms.
C)The patient would have a rapid pulse and shortness of breath.
D)The patient would be unconscious.
A)The patient would experience extreme fatigue and weakness.
B)The patient would have normal cardiac output and no symptoms.
C)The patient would have a rapid pulse and shortness of breath.
D)The patient would be unconscious.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is the term for the observation guidelines used to assess the blood supply to the vital organs of the body to maintain normal function?
A)Cardiac output parameters
B)Cardiac cycle
C)Output display
D)Systemic circulation parameters
A)Cardiac output parameters
B)Cardiac cycle
C)Output display
D)Systemic circulation parameters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is characteristic of an ECG tracing for a second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II?
A)The P waves are all the same.
B)A QRS complex follows each P wave.
C)The pacemaker site is in the AV junction.
D)The ventricular rate is less than 40 bpm.
A)The P waves are all the same.
B)A QRS complex follows each P wave.
C)The pacemaker site is in the AV junction.
D)The ventricular rate is less than 40 bpm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Frequent nonconducted QRS complexes are likely to cause signs of ________.
A)High cardiac output
B)Low cardiac output
C)Hypertension
D)Edema
A)High cardiac output
B)Low cardiac output
C)Hypertension
D)Edema

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What type of impulse occurs too soon after the preceding impulse and causes a period when no other impulses can occur in the ventricles?
A)Loss of capture
B)Atrial kick
C)Blocked or nonconducted impulse
D)Inhibited impulse
A)Loss of capture
B)Atrial kick
C)Blocked or nonconducted impulse
D)Inhibited impulse

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which heart block dysrhythmia has regular P-P and R-R intervals that both occur at the same rate?
A)First-degree heart block
B)Second-degree heart block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree heart block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree heart block
A)First-degree heart block
B)Second-degree heart block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree heart block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree heart block

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following heart block dysrhythmias is identified by missing QRS complexes and a consistent PR interval measurement?
A)First-degree heart block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree AV block
A)First-degree heart block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree AV block

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What typically causes second-degree heart block, Mobitz type I?
A)Loss of atrial kick
B)Myocardial infarction
C)Pericarditis
D)Inflammation around the AV node
A)Loss of atrial kick
B)Myocardial infarction
C)Pericarditis
D)Inflammation around the AV node

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
After you report a second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II, to a licensed practitioner, what should you prepare for?
A)A code blue situation and application of a temporary pacemaker
B)A nuclear exercise stress test
C)An ambulatory monitor and an echocardiogram
D)An angiogram and laboratory tests
A)A code blue situation and application of a temporary pacemaker
B)A nuclear exercise stress test
C)An ambulatory monitor and an echocardiogram
D)An angiogram and laboratory tests

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What indicates whether the heart block is low (in the bundle of His)or higher (near the AV junction)?
A)The ventricular rate and QRS configurations
B)The P wave configuration and the PR interval
C)The atrial rate and the P wave configuration
D)The QRS configuration and the P waves
A)The ventricular rate and QRS configurations
B)The P wave configuration and the PR interval
C)The atrial rate and the P wave configuration
D)The QRS configuration and the P waves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In which type of heart block are all of the impulses eventually conducted to the ventricles?
A)First-degree AV block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree AV block
A)First-degree AV block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree AV block

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
How do you distinguish between second-degree AV blocks, Mobitz type I or Mobitz type II?
A)In Mobitz type II, the PR intervals are constant.
B)The ventricular rate is greater than 60 bpm with Mobitz type II.
C)In Mobitz type II, the P waves appear to march right through the QRS complexes.
D)In Mobitz type II, there appears to be a pattern to the irregularity.
A)In Mobitz type II, the PR intervals are constant.
B)The ventricular rate is greater than 60 bpm with Mobitz type II.
C)In Mobitz type II, the P waves appear to march right through the QRS complexes.
D)In Mobitz type II, there appears to be a pattern to the irregularity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In which heart block dysrhythmia would a patient probably be unconscious and require immediate medical intervention?
A)First-degree heart block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree AV block
A)First-degree heart block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree AV block

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is characteristic of an ECG tracing for a first-degree heart block?
A)The PR intervals are greater than 0.20 seconds in duration.
B)The P waves are inverted.
C)Not all of the P waves are followed by QRS complexes.
D)The underlying rhythm is slow.
A)The PR intervals are greater than 0.20 seconds in duration.
B)The P waves are inverted.
C)Not all of the P waves are followed by QRS complexes.
D)The underlying rhythm is slow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
How does first-degree heart block affect a patient's cardiac output?
A)It lowers the cardiac output.
B)It raises the cardiac output.
C)The cardiac output depends on the ventricular response.
D)There is no effect on the cardiac output.
A)It lowers the cardiac output.
B)It raises the cardiac output.
C)The cardiac output depends on the ventricular response.
D)There is no effect on the cardiac output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In third-degree AV block, if the impulse causing ventricular depolarization is coming from the AV junction, what will the heart rate be?
A)20 to 40 bpm
B)40 to 60 bpm
C)60 to 100 bpm
D)100 to 150 bpm
A)20 to 40 bpm
B)40 to 60 bpm
C)60 to 100 bpm
D)100 to 150 bpm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following heart block dysrhythmias is identified by regular P-P and R-R intervals that are firing at two distinctly different rates, causing variable PR intervals?
A)First-degree heart block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)First-degree AV block
D)Third-degree AV block
A)First-degree heart block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)First-degree AV block
D)Third-degree AV block

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In which heart block dysrhythmia are all electrical impulses originating above the ventricles blocked and prevented from reaching the ventricles?
A)Left bundle branch block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree AV block
A)Left bundle branch block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree AV block

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which heart block dysrhythmia is known as complete heart block (CHB)?
A)First-degree heart block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree AV block
A)First-degree heart block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree AV block

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Identify the following rhythm: 
A)First-degree heart block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree AV block

A)First-degree heart block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree AV block

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
You have performed an ECG on a patient at the walk-in clinic where you work. The ECG tracing shows that the patient is in third-degree block. What is your first responsibility to this patient?
A)Observe the patient for symptoms of low cardiac output.
B)Report any signs and symptoms to a licensed practitioner.
C)Initiate emergency procedures if needed.
D)Mount and identify the rhythm strips for documentation.
A)Observe the patient for symptoms of low cardiac output.
B)Report any signs and symptoms to a licensed practitioner.
C)Initiate emergency procedures if needed.
D)Mount and identify the rhythm strips for documentation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which type of heart block tends to progress quickly to third-degree AV block or complete heart block?
A)First-degree heart block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Bundle branch block
A)First-degree heart block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Bundle branch block

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
QRS complexes that measure 0.12 seconds or greater and have a heart rate between 20 and 40 bpm indicate that the impulses causing ventricular depolarization are coming from the ________.
A)SA node
B)AV node
C)Purkinje fibers
D)Interatrial pathways
A)SA node
B)AV node
C)Purkinje fibers
D)Interatrial pathways

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What is the term for the condition in which the atria and ventricles are electrically separated from one another?
A)Atrial kick
B)AV dissociation
C)Automaticity
D)Asystole
A)Atrial kick
B)AV dissociation
C)Automaticity
D)Asystole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following rhythms has a constant PR interval for all conducted beats?
A)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
C)Third-degree AV block
D)All of the answers are correct
A)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
C)Third-degree AV block
D)All of the answers are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
When would you use the mnemonic "Lengthen, lengthen, drop equals Wenckebach"?
A)To differentiate second-degree heart block from third-degree heart block
B)To differentiate first-degree heart block from left bundle branch block
C)To differentiate second-degree Mobitz type I heart block from Mobitz type II heart block
D)To differentiate first-degree heart block from third-degree heart block
A)To differentiate second-degree heart block from third-degree heart block
B)To differentiate first-degree heart block from left bundle branch block
C)To differentiate second-degree Mobitz type I heart block from Mobitz type II heart block
D)To differentiate first-degree heart block from third-degree heart block

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which heart block dysrhythmia is highly unstable and considered a critical condition?
A)First-degree heart block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Bundle branch block
A)First-degree heart block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Bundle branch block

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following statements about second-degree heart block, Mobitz type I, is correct?
A)It is an unstable condition that can quickly lead to complete heart block.
B)It is usually a temporary condition that resolves itself.
C)It is difficult to control using medication.
D)It requires immediate emergency measures.
A)It is an unstable condition that can quickly lead to complete heart block.
B)It is usually a temporary condition that resolves itself.
C)It is difficult to control using medication.
D)It requires immediate emergency measures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which statement best describes the morphology of the P waves in second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II?
A)The P waves are normal in size and shape, and the number of P waves equals the number of QRS complexes.
B)The P waves are normal in size and shape, and there is at least one P wave for every QRS complex.
C)The P waves are inverted, and the number of P waves equals the number of QRS complexes.
D)The P waves are normal in size and shape, and there is no association between the P waves and the QRS complexes.
A)The P waves are normal in size and shape, and the number of P waves equals the number of QRS complexes.
B)The P waves are normal in size and shape, and there is at least one P wave for every QRS complex.
C)The P waves are inverted, and the number of P waves equals the number of QRS complexes.
D)The P waves are normal in size and shape, and there is no association between the P waves and the QRS complexes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
When the ECG tracing shows that a patient has a Wenckebach heart block, which of the following would the licensed practitioner be most likely to order?
A)Immediate cardioversion to prevent a third-degree heart block
B)Further observation for signs of decreasing cardiac output
C)An MRI to determine further details on the patient's condition
D)A temporary pacemaker to prevent low cardiac output
A)Immediate cardioversion to prevent a third-degree heart block
B)Further observation for signs of decreasing cardiac output
C)An MRI to determine further details on the patient's condition
D)A temporary pacemaker to prevent low cardiac output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In first-degree atrioventricular block, how does the PR interval appear on an ECG tracing?
A)It is prolonged and measures more than 0.20 seconds.
B)It becomes progressively longer until a QRS complex is dropped.
C)It is irregular because of nonconducted impulses.
D)It is usually within normal limits.
A)It is prolonged and measures more than 0.20 seconds.
B)It becomes progressively longer until a QRS complex is dropped.
C)It is irregular because of nonconducted impulses.
D)It is usually within normal limits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which type of AV block is sometimes reported with a ratio of P waves to QRS complexes?
A)First-degree heart block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree AV block
A)First-degree heart block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree AV block

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which two types of heart block have a constant PR interval?
A)First-degree and second-degree type Mobitz I
B)First degree and second degree Mobitz type II
C)Second-degree Mobitz type I and third degree
D)Second-degree Mobitz type II and third degree
A)First-degree and second-degree type Mobitz I
B)First degree and second degree Mobitz type II
C)Second-degree Mobitz type I and third degree
D)Second-degree Mobitz type II and third degree

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which two types of heart block result in a variable PR interval?
A)First-degree and second-degree Mobitz type I
B)Second-degree Mobitz type I and second-degree Mobitz type II
C)Second-degree Mobitz type I and third degree
D)Second-degree Mobitz type II and third degree
A)First-degree and second-degree Mobitz type I
B)Second-degree Mobitz type I and second-degree Mobitz type II
C)Second-degree Mobitz type I and third degree
D)Second-degree Mobitz type II and third degree

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
When might a patient with second-degree block, Mobitz type II, exhibit symptoms of decreased cardiac output?
A)When the rate of ventricular contractions decreases below 40 bpm
B)When the rate of atrial contractions decreases below 60 bpm
C)When the rate of ventricular contractions increases above 60 bpm
D)When the rate of atrial contractions increases above 80 bpm
A)When the rate of ventricular contractions decreases below 40 bpm
B)When the rate of atrial contractions decreases below 60 bpm
C)When the rate of ventricular contractions increases above 60 bpm
D)When the rate of atrial contractions increases above 80 bpm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
You have performed an ECG on a patient in the critical care unit at the hospital. A portion of the ECG tracing is shown below. What type of heart block does this patient have? 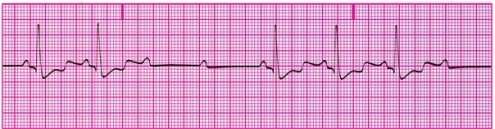
A)First-degree heart block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree AV block

A)First-degree heart block
B)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type I
C)Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
D)Third-degree AV block

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The degree of blockage in heart block rhythms depends on which of the following?
A)The patient's age and physical condition
B)The number of electrical impulses generated
C)The affected area and the cause of the delay or blockage
D)The ventricular heart rate
A)The patient's age and physical condition
B)The number of electrical impulses generated
C)The affected area and the cause of the delay or blockage
D)The ventricular heart rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
You have been asked to perform an ECG on a patient in the emergency department. The patient is pale, and while you are performing the ECG, he loses consciousness. A portion of the ECG tracing is shown below. After noting the patient's condition, what should you do? 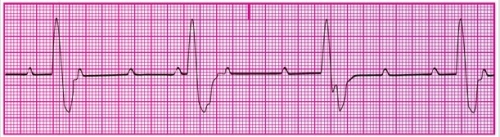
A)Notify the licensed practitioner immediately.
B)Document the rhythm and place it in the patient's chart.
C)Reassure the patient's spouse that this is not a serious problem.
D)Re-perform the ECG to double-check your findings.

A)Notify the licensed practitioner immediately.
B)Document the rhythm and place it in the patient's chart.
C)Reassure the patient's spouse that this is not a serious problem.
D)Re-perform the ECG to double-check your findings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



