Deck 9: Ventricular Dysrhythmias
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/50
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Ventricular Dysrhythmias
1
Which of the following rhythms does not necessarily require immediate emergency interventions?
A)Asystole
B)Ventricular fibrillation
C)Premature ventricular complexes
D)Ventricular tachycardia
A)Asystole
B)Ventricular fibrillation
C)Premature ventricular complexes
D)Ventricular tachycardia
Premature ventricular complexes
2
Which of these terms applies specifically to PVCs that occur in varied shapes and forms?
A)Unifocal PVCs
B)Bigeminy PVCs
C)Interpolated PVCs
D)Multifocal PVCs
A)Unifocal PVCs
B)Bigeminy PVCs
C)Interpolated PVCs
D)Multifocal PVCs
Multifocal PVCs
3
What is the inherent rate of the Purkinje network?
A)20 to 40 bpm
B)40 to 60 bpm
C)60 to 100 bpm
D)100 to 150 bpm
A)20 to 40 bpm
B)40 to 60 bpm
C)60 to 100 bpm
D)100 to 150 bpm
20 to 40 bpm
4
Why do ventricular rhythms occur?
A)Because higher pacemaker sites within the heart have failed
B)Because the rate impulses from the SA node are too fast for ventricular response
C)Because a first-degree AV block prevents atrial impulses from reaching the ventricles
D)Because the ventricular impulses are stronger than the atrial impulses
A)Because higher pacemaker sites within the heart have failed
B)Because the rate impulses from the SA node are too fast for ventricular response
C)Because a first-degree AV block prevents atrial impulses from reaching the ventricles
D)Because the ventricular impulses are stronger than the atrial impulses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is the cause of agonal rhythms?
A)Failure of the SA node
B)Failure of all pacemakers of the heart
C)Blocked conduction at the AV node
D)Loose electrode wires
A)Failure of the SA node
B)Failure of all pacemakers of the heart
C)Blocked conduction at the AV node
D)Loose electrode wires

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which ventricular dysrhythmia has a heart rate less than 20 bpm?
A)Agonal rhythm
B)Asystole
C)Idioventricular rhythm
D)Ventricular fibrillation
A)Agonal rhythm
B)Asystole
C)Idioventricular rhythm
D)Ventricular fibrillation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the term for a PVC that occurs on the T wave or during the vulnerable period of the ventricular refractory period?
A)R-on-T PVC
B)Bigeminy
C)Trigeminy
D)T-on-R PVC
A)R-on-T PVC
B)Bigeminy
C)Trigeminy
D)T-on-R PVC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Identify the following rhythm: 
A)Idioventricular rhythm
B)Sinus bradycardia
C)Agonal rhythm
D)Asystole

A)Idioventricular rhythm
B)Sinus bradycardia
C)Agonal rhythm
D)Asystole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which ventricular dysrhythmia has a heart rate between 20 and 40 bpm?
A)Agonal rhythm
B)Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
C)Idioventricular rhythm
D)Asystole
A)Agonal rhythm
B)Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
C)Idioventricular rhythm
D)Asystole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is the term for PVCs that all have a similar shape on a tracing?
A)Coupling
B)R-on-T PVCs.
C)Unifocal PVCs
D)Interpolated PVCs
A)Coupling
B)R-on-T PVCs.
C)Unifocal PVCs
D)Interpolated PVCs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Where are the ventricular pacemaker cells found?
A)At the bundle of His
B)At the AV node
C)At the Purkinje fibers
D)At the SA node
A)At the bundle of His
B)At the AV node
C)At the Purkinje fibers
D)At the SA node

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is the term for PVCs that occur during the normal R-R interval and do not interrupt the normal cycle?
A)Occasional PVCs
B)Interpolated PVCs
C)Frequent PVCs
D)Coupling
A)Occasional PVCs
B)Interpolated PVCs
C)Frequent PVCs
D)Coupling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is an ectopic impulse that occurs early in the cycle and originates from the ventricles?
A)PAC
B)SVT
C)PVC
D)PJC
A)PAC
B)SVT
C)PVC
D)PJC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is the term for two PVCs back to back?
A)Occasional PVCs
B)Frequent PVCs
C)Coupling
D)Bigeminy
A)Occasional PVCs
B)Frequent PVCs
C)Coupling
D)Bigeminy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is it called when more than six PVCs occur per minute?
A)Occasional PVCs
B)Ventricular tachycardia
C)Ventricular fibrillation
D)Frequent PVCs
A)Occasional PVCs
B)Ventricular tachycardia
C)Ventricular fibrillation
D)Frequent PVCs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In all ventricular dysrhythmias, which of the following qualities describes P-P intervals?
A)Biphasic
B)Missing
C)Regular
D)Irregular
A)Biphasic
B)Missing
C)Regular
D)Irregular

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
PVCs can occur because of hypoxic states. What must be done to determine whether hypoxia is causing a patient's PVCs?
A)Draw blood samples to evaluate oxygen saturation.
B)Carefully monitor the heart rate and rhythm.
C)Provide the patient with oxygen.
D)Draw blood samples to evaluate electrolyte levels.
A)Draw blood samples to evaluate oxygen saturation.
B)Carefully monitor the heart rate and rhythm.
C)Provide the patient with oxygen.
D)Draw blood samples to evaluate electrolyte levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements about PVCs is true?
A)PVCs will not lead to ventricular tachycardia.
B)PVCs may be unifocal or multifocal in origin.
C)PVCs can only originate from one site in the ventricles.
D)PVCs never have an effect on the conduction of normal impulses.
A)PVCs will not lead to ventricular tachycardia.
B)PVCs may be unifocal or multifocal in origin.
C)PVCs can only originate from one site in the ventricles.
D)PVCs never have an effect on the conduction of normal impulses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
QRS complexes that measure 0.12 seconds or greater and a heart rate between 20 and 40 bpm indicate that the impulses causing ventricular depolarization are coming from which location?
A)AV node
B)SA node
C)Interatrial pathways
D)Purkinje fibers
A)AV node
B)SA node
C)Interatrial pathways
D)Purkinje fibers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the term for ventricular rhythms that originate in the Purkinje network?
A)Junctional escape rhythms
B)Ventricular escape rhythms
C)Asystole rhythms
D)Agonal rhythms
A)Junctional escape rhythms
B)Ventricular escape rhythms
C)Asystole rhythms
D)Agonal rhythms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
You are recording an ECG; a portion of the tracing is shown here. Your patient is pale and tells you that she is a little dizzy. Which of the following is the least likely reason for the tracing? 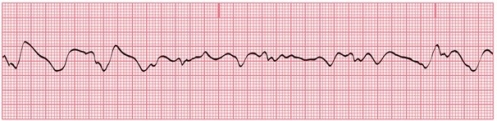
A)Poorly attached or dried-out electrodes
B)Broken lead wires
C)Excessive patient movement
D)Ventricular fibrillation

A)Poorly attached or dried-out electrodes
B)Broken lead wires
C)Excessive patient movement
D)Ventricular fibrillation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which ventricular dysrhythmia is sometimes referred to as "straight-line" or "flat-line"?
A)Agonal
B)Asystole
C)Ventricular fibrillation
D)Sinus bradycardia
A)Agonal
B)Asystole
C)Ventricular fibrillation
D)Sinus bradycardia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What percentage of patients with ventricular tachycardia become unconscious immediately?
A)10%
B)30%
C)50%
D)75%
A)10%
B)30%
C)50%
D)75%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Identify the following rhythm: 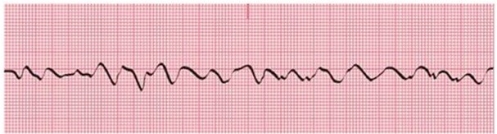
A)Ventricular tachycardia
B)Ventricular fibrillation
C)Asystole
D)SVT

A)Ventricular tachycardia
B)Ventricular fibrillation
C)Asystole
D)SVT

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the primary difference between idioventricular rhythm and accelerated idioventricular rhythm?
A)Heart rate
B)QRS complex
C)P wave
D)R-R interval
A)Heart rate
B)QRS complex
C)P wave
D)R-R interval

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In which ventricular dysrhythmia do the ventricle walls quiver, preventing any movement of blood out of the ventricles and resulting in no cardiac output?
A)Ventricular fibrillation
B)Ventricular flutter
C)Ventricular tachycardia
D)Supraventricular tachycardia
A)Ventricular fibrillation
B)Ventricular flutter
C)Ventricular tachycardia
D)Supraventricular tachycardia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following statements about agonal rhythm and asystole is false?
A)Both rhythms have an absence of P waves.
B)In both rhythms, the patient will be unconscious.
C)Both rhythms are life threatening and require basic and advanced life support.
D)Both rhythms are considered flat-line rhythms.
A)Both rhythms have an absence of P waves.
B)In both rhythms, the patient will be unconscious.
C)Both rhythms are life threatening and require basic and advanced life support.
D)Both rhythms are considered flat-line rhythms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is absent with apnea?
A)Pulse
B)Blood pressure
C)Breathing
D)Electrical activity
A)Pulse
B)Blood pressure
C)Breathing
D)Electrical activity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is a characteristic of the R-R interval in an idioventricular rhythm?
A)It cannot be determined.
B)It is usually irregular due to ectopic beats.
C)It is regular.
D)It depends on the pattern of PVCs.
A)It cannot be determined.
B)It is usually irregular due to ectopic beats.
C)It is regular.
D)It depends on the pattern of PVCs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Identify the following rhythm: 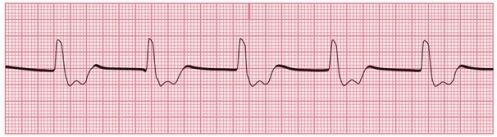
A)Idioventricular rhythm
B)Agonal rhythm
C)Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
D)Ventricular fibrillation

A)Idioventricular rhythm
B)Agonal rhythm
C)Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
D)Ventricular fibrillation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Identify the following rhythm: 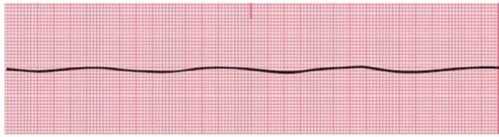
A)Asystole
B)Agonal
C)Ventricular fibrillation
D)Sinus bradycardia

A)Asystole
B)Agonal
C)Ventricular fibrillation
D)Sinus bradycardia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is a characteristic of an idioventricular rhythm?
A)Upright P waves
B)Wide QRS complexes
C)Heart rate of 40 to 100 bpm
D)Constant P-R intervals
A)Upright P waves
B)Wide QRS complexes
C)Heart rate of 40 to 100 bpm
D)Constant P-R intervals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is the typical heart rate with accelerated idioventricular rhythm?
A)Less than 20 bpm
B)20 to 40 bpm
C)40 to 100 bpm
D)100 to 150 bpm
A)Less than 20 bpm
B)20 to 40 bpm
C)40 to 100 bpm
D)100 to 150 bpm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In which ventricular dysrhythmia do three or more PVCs occur in a row with a ventricular rate greater than 100 bpm?
A)SVT
B)Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
C)Ventricular fibrillation
D)Ventricular tachycardia
A)SVT
B)Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
C)Ventricular fibrillation
D)Ventricular tachycardia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following signs and symptoms are characteristic of every patient experiencing ventricular fibrillation?
A)Shortness of breath, hypotension, and bradycardia
B)Talkativeness, hypertension, and tachycardia
C)Unconsciousness, apnea, and no pulse
D)Dizziness, chest pain, and cough
A)Shortness of breath, hypotension, and bradycardia
B)Talkativeness, hypertension, and tachycardia
C)Unconsciousness, apnea, and no pulse
D)Dizziness, chest pain, and cough

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Identify the following rhythm: 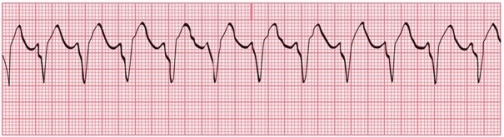
A)SVT
B)Ventricular tachycardia
C)Ventricular fibrillation
D)Accelerated idioventricular rhythm

A)SVT
B)Ventricular tachycardia
C)Ventricular fibrillation
D)Accelerated idioventricular rhythm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is the difference between ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation?
A)Ventricular fibrillation is chaotic in appearance; ventricular tachycardia has an absence of P waves, a heart rate of 40-100 bpm, and a wide and bizarre QRS complex.
B)Ventricular tachycardia has three or more PVCs and a heart rate greater than 100 bpm; ventricular fibrillation has no P wave and an early QRS complex that is wide and bizarre in appearance.
C)Ventricular tachycardia has three or more PVCs and a heart rate greater than 100 bpm; ventricular fibrillation is chaotic electrical activity with only fibrillatory waves.
D)Ventricular fibrillation is chaotic electrical activity with only fibrillatory waves; ventricular tachycardia has an absence of P waves, a heart rate less than 20 bpm, and wide and bizarre QRS complexes.
A)Ventricular fibrillation is chaotic in appearance; ventricular tachycardia has an absence of P waves, a heart rate of 40-100 bpm, and a wide and bizarre QRS complex.
B)Ventricular tachycardia has three or more PVCs and a heart rate greater than 100 bpm; ventricular fibrillation has no P wave and an early QRS complex that is wide and bizarre in appearance.
C)Ventricular tachycardia has three or more PVCs and a heart rate greater than 100 bpm; ventricular fibrillation is chaotic electrical activity with only fibrillatory waves.
D)Ventricular fibrillation is chaotic electrical activity with only fibrillatory waves; ventricular tachycardia has an absence of P waves, a heart rate less than 20 bpm, and wide and bizarre QRS complexes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
How is ventricular fibrillation is typically described?
A)Absence of rhythm
B)Organized rhythm
C)Chaotic rhythm
D)Wide and bizarre rhythm
A)Absence of rhythm
B)Organized rhythm
C)Chaotic rhythm
D)Wide and bizarre rhythm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which factor is least important regarding crash carts?
A)The crash cart must be nearby and ready to go.
B)The crash cart must be well stocked with emergency supplies.
C)The emergency equipment on the crash cart must be functioning properly.
D)A list of currently stocked emergency medications must be present on the cart.
A)The crash cart must be nearby and ready to go.
B)The crash cart must be well stocked with emergency supplies.
C)The emergency equipment on the crash cart must be functioning properly.
D)A list of currently stocked emergency medications must be present on the cart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What symptoms would a patient in asystole exhibit?
A)Difficulty breathing and bradycardia
B)Unconsciousness and apnea
C)Chest pains and palpitations
D)Alert and oriented
A)Difficulty breathing and bradycardia
B)Unconsciousness and apnea
C)Chest pains and palpitations
D)Alert and oriented

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In accelerated idioventricular rhythm, how do the QRS complexes appear?
A)They fall within the normal range of 0.12 to 0.20 seconds due to the heart rate.
B)They cannot be distinguished because the heart rate is too rapid.
C)They have a classic wide and bizarre appearance.
D)They are irregular because of multifocal ventricular impulses.
A)They fall within the normal range of 0.12 to 0.20 seconds due to the heart rate.
B)They cannot be distinguished because the heart rate is too rapid.
C)They have a classic wide and bizarre appearance.
D)They are irregular because of multifocal ventricular impulses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Why can't the atrial rate be determined in idioventricular rhythms?
A)The P waves are buried in the QRS complexes.
B)The wide and bizarre QRS complex masks the P waves.
C)Atrial depolarization is absent.
D)The atrial rate is too irregular to be determined.
A)The P waves are buried in the QRS complexes.
B)The wide and bizarre QRS complex masks the P waves.
C)Atrial depolarization is absent.
D)The atrial rate is too irregular to be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
To rule out fine ventricular fibrillation, asystole must be confirmed in at least how many leads?
A)Two
B)Three
C)Four
D)Five
A)Two
B)Three
C)Four
D)Five

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
When a person's heart rate is less than 60 bpm, how does the heart try to pick up the rate?
A)By activating impulses from multiple foci
B)By generating ventricular escape beats
C)By pumping more oxygen to the body cells
D)By increasing the atrial depolarization rate
A)By activating impulses from multiple foci
B)By generating ventricular escape beats
C)By pumping more oxygen to the body cells
D)By increasing the atrial depolarization rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The patient on which you are about to perform an ECG tells you that she sometimes feels a "thumping" in her chest. Which of the following might you expect to see on the ECG tracing?
A)Ventricular tachycardia
B)Ventricular fibrillation
C)Idioventricular rhythm
D)Premature ventricular complexes
A)Ventricular tachycardia
B)Ventricular fibrillation
C)Idioventricular rhythm
D)Premature ventricular complexes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following rhythms might a patient be able to tolerate without signs of low cardiac output?
A)Ventricular tachycardia
B)Ventricular fibrillation
C)Idioventricular rhythm
D)Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
A)Ventricular tachycardia
B)Ventricular fibrillation
C)Idioventricular rhythm
D)Accelerated idioventricular rhythm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What is the ventricular rate in asystole?
A)40 to 60 bpm
B)20 to 40 bpm
C)10 to 20 bpm
D)0 (the heart is not beating)
A)40 to 60 bpm
B)20 to 40 bpm
C)10 to 20 bpm
D)0 (the heart is not beating)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In which ventricular dysrhythmia are the ventricles essentially in a continuous contraction-relaxation pattern with no period of delay between depolarizations?
A)Ventricular tachycardia
B)Ventricular fibrillation
C)Idioventricular rhythm
D)Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
A)Ventricular tachycardia
B)Ventricular fibrillation
C)Idioventricular rhythm
D)Accelerated idioventricular rhythm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
You have been asked to perform an ECG on a hospital patient who was admitted to the cardiac care unit this morning. When you review the ECG tracing from the emergency department before the patient was admitted, you notice that the patient had an idioventricular rhythm. As you prepare to enter the patient's room, you will not be surprised to find the patient in what state?
A)Alert and oriented
B)Unconscious
C)Combative
D)Hypertensive
A)Alert and oriented
B)Unconscious
C)Combative
D)Hypertensive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
An accident victim is being treated in the emergency department. A friend who was present at the time of the accident is in the patient's cubicle when the patient's ECG monitor sounds an alarm and shows a flat-line pattern. The patient's friend becomes frantic. What should you do?
A)Tell the patient's friend to get out of the way so the medical team can work.
B)Calmly escort the patient's friend out of the immediate area.
C)Ask the patient's friend to begin CPR while you get the emergency cart.
D)Tell the patient's friend to go to the desk and ask that the physician be notified.
A)Tell the patient's friend to get out of the way so the medical team can work.
B)Calmly escort the patient's friend out of the immediate area.
C)Ask the patient's friend to begin CPR while you get the emergency cart.
D)Tell the patient's friend to go to the desk and ask that the physician be notified.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



