Deck 8: Cellular Respiration
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/49
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Cellular Respiration
1
The electron transport chain and chemiosmosis produce ________ ATP from each NADH and ________ ATP from each FADH2 entering the system.
A)4; 2
B)3; 2
C)2; 4
D)2; 3
A)4; 2
B)3; 2
C)2; 4
D)2; 3
B
2
During glycolysis ________ carbons will enter the pathway and ________ carbons will leave in the form of pyruvates.
A)6; 6
B)6; 3
C)3; 6
D)12; 6
E)oxaloacetate
A)6; 6
B)6; 3
C)3; 6
D)12; 6
E)oxaloacetate
A
3
The majority of the carbon dioxide we exhale is produced in
A)glycolysis.
B)the electron transport system.
C)lactate fermentation.
D)the citric acid cycle.
A)glycolysis.
B)the electron transport system.
C)lactate fermentation.
D)the citric acid cycle.
D
4
Glycolysis occurs before fermentation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
One turn of the citric acid cycle produces
A)2 NADH,FADH2,and 2 ATP.
B)3 NADH,1 FADH2,and 1 ATP.
C)1 NADH,3 FADH2,and 2 ATP.
D)3 NADH,2 FADH2,and 1 ATP.
E)3 NADH,1 FADH2,and 2 ATP.
A)2 NADH,FADH2,and 2 ATP.
B)3 NADH,1 FADH2,and 1 ATP.
C)1 NADH,3 FADH2,and 2 ATP.
D)3 NADH,2 FADH2,and 1 ATP.
E)3 NADH,1 FADH2,and 2 ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The preparatory reaction converts
A)glucose into pyruvates.
B)pyruvates into glucose.
C)pyruvates into acetyl CoA and carbon dioxide.
D)pyruvates into acetyl CoA and water.
E)acetyl CoA into pyruvates and carbon dioxide.
A)glucose into pyruvates.
B)pyruvates into glucose.
C)pyruvates into acetyl CoA and carbon dioxide.
D)pyruvates into acetyl CoA and water.
E)acetyl CoA into pyruvates and carbon dioxide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Glycolysis occurs before the preparatory reaction and the citric acid cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The first phase of cellular respiration is
A)the citric acid cycle.
B)glycolysis.
C)the electron transport system.
D)fermentation.
E)the preparatory reaction.
A)the citric acid cycle.
B)glycolysis.
C)the electron transport system.
D)fermentation.
E)the preparatory reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Glycolysis is a catabolic process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Glycolysis will yield a net of 2 ATP only during aerobic respiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Glycolysis produces 1 pyruvate and 3 NADH coenzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Degradative reactions
A)cause death.
B)can drive anabolic reactions.
C)tend to be endergonic.
D)include the buildup of products such as complex proteins and nucleic acids.
E)All of the choices are true.
A)cause death.
B)can drive anabolic reactions.
C)tend to be endergonic.
D)include the buildup of products such as complex proteins and nucleic acids.
E)All of the choices are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which process reduces molecular oxygen to water?
A)the citric acid cycle
B)glycolysis
C)the electron transport system
D)fermentation
E)the preparatory reaction
A)the citric acid cycle
B)glycolysis
C)the electron transport system
D)fermentation
E)the preparatory reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Acetyl CoA is produced from
A)pyruvate and CoA.
B)citric acid and CoA.
C)ATP and pyruvate.
D)CO2 and pyruvate.
E)citric acid and CO2.
A)pyruvate and CoA.
B)citric acid and CoA.
C)ATP and pyruvate.
D)CO2 and pyruvate.
E)citric acid and CO2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Complete oxidative breakdown of glucose results in ________ ATP molecules.
A)2
B)4
C)32
D)36
E)39
A)2
B)4
C)32
D)36
E)39

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Aerobic cellular respiration yields about ________ of the energy of glucose in ATP molecules.
A)2%
B)15%
C)28%
D)39%
A)2%
B)15%
C)28%
D)39%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The first reaction in the citric acid cycle binds which of the following molecules together?
A)carbon dioxide to a four-carbon (C4)molecule.
B)carbon dioxide to a five-carbon (C5)molecule.
C)acetyl CoA to a C5 molecule.
D)acetyl CoA to a C4 molecule.
A)carbon dioxide to a four-carbon (C4)molecule.
B)carbon dioxide to a five-carbon (C5)molecule.
C)acetyl CoA to a C5 molecule.
D)acetyl CoA to a C4 molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of these processes occurs in the cytosol?
A)the citric acid cycle
B)glycolysis
C)the electron transport system
D)the preparatory reaction
A)the citric acid cycle
B)glycolysis
C)the electron transport system
D)the preparatory reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which process produces both NADH and FADH2?
A)the citric acid cycle
B)glycolysis
C)the electron transport system
D)fermentation
E)the preparatory reaction
A)the citric acid cycle
B)glycolysis
C)the electron transport system
D)fermentation
E)the preparatory reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which process produces alcohol or lactate?
A)the citric acid cycle
B)glycolysis
C)the electron transport system
D)fermentation
E)the preparatory reaction
A)the citric acid cycle
B)glycolysis
C)the electron transport system
D)fermentation
E)the preparatory reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Adult humans cannot synthesize ________ out of the ________ common amino acids.
A)eleven; twenty
B)nine; eleven
C)nine; twenty
D)any; twenty
E)half; all
A)eleven; twenty
B)nine; eleven
C)nine; twenty
D)any; twenty
E)half; all

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The most important contribution of the citric acid cycle to cellular respiration is
A)production of large quantities of ATP.
B)creation of proton gradients.
C)reduction of glucose and corresponding oxidation of carbon dioxide.
D)oxidation of metabolite molecules and the corresponding reduction of coenzymes.
E)release of CO2.
A)production of large quantities of ATP.
B)creation of proton gradients.
C)reduction of glucose and corresponding oxidation of carbon dioxide.
D)oxidation of metabolite molecules and the corresponding reduction of coenzymes.
E)release of CO2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The correct sequence for aerobic metabolic breakdown of glucose is
A)glycolysis-preparatory reaction-citric acid cycle-electron transport system.
B)preparatory reaction-glycolysis-electron transport-citric acid cycle.
C)electron transport system-citric acid cycle-preparatory reaction-glycolysis.
D)None of the choices are correct.
A)glycolysis-preparatory reaction-citric acid cycle-electron transport system.
B)preparatory reaction-glycolysis-electron transport-citric acid cycle.
C)electron transport system-citric acid cycle-preparatory reaction-glycolysis.
D)None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Aerobic respiration involves oxidation - reduction and the movement of electrons from one molecule to another.Study the figure to identify A and B as either oxidation or reduction. 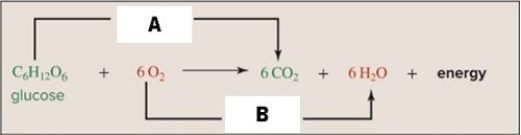


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Identify "A." 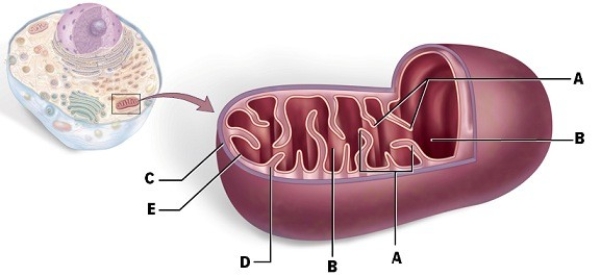
A)grana
B)matrix
C)cristae
D)intermembrane space
E)outer membrane

A)grana
B)matrix
C)cristae
D)intermembrane space
E)outer membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Identify "E." 
A)inner membrane
B)matrix
C)cristae
D)intermembrane space
E)outer membrane

A)inner membrane
B)matrix
C)cristae
D)intermembrane space
E)outer membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Why is it beneficial for pyruvate to be reduced via fermentation when oxygen is not available?
A)The organism can survive short spells of anaerobic conditions and maintain growth and reproduction.
B)The fermentation reaction regenerates NAD+,which is required for the first step in the energy-harvesting phase of glycolysis.
C)Fermentation can provide a rapid burst of ATP.
D)All of the choices are advantages.
E)None of the choices is an advantage.
A)The organism can survive short spells of anaerobic conditions and maintain growth and reproduction.
B)The fermentation reaction regenerates NAD+,which is required for the first step in the energy-harvesting phase of glycolysis.
C)Fermentation can provide a rapid burst of ATP.
D)All of the choices are advantages.
E)None of the choices is an advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Compared with other components found in a plant cell such as the cell membrane,the chloroplasts or the nucleus,the mitochondria would be the only one that would
A)form an electrochemical gradient across a membrane.
B)use significant amounts of oxygen to produce ATP.
C)use a chemiosmotic complex to produce ATP.
D)produce ATP via glycolysis.
E)release protons (H+).
A)form an electrochemical gradient across a membrane.
B)use significant amounts of oxygen to produce ATP.
C)use a chemiosmotic complex to produce ATP.
D)produce ATP via glycolysis.
E)release protons (H+).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The amino acids we cannot synthesize are called ________ because we ________.
A)unnecessary; therefore,do not need them
B)limiting; must include them in our diet
C)anabolic; must use alternative amino acids
D)essential; must include them in our diet
E)superfluous; must survive without them
A)unnecessary; therefore,do not need them
B)limiting; must include them in our diet
C)anabolic; must use alternative amino acids
D)essential; must include them in our diet
E)superfluous; must survive without them

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Some desert beetles can live without ever drinking liquid water.They survive on "metabolic water," which
A)is water obtained from eating other organisms.
B)is water absorbed directly from the atmosphere.
C)is water formed during the electron transport chain.
D)is water formed during glycolysis.
E)is water that was stored in the beetle's tissue during its larval stage.
A)is water obtained from eating other organisms.
B)is water absorbed directly from the atmosphere.
C)is water formed during the electron transport chain.
D)is water formed during glycolysis.
E)is water that was stored in the beetle's tissue during its larval stage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Identify "C." 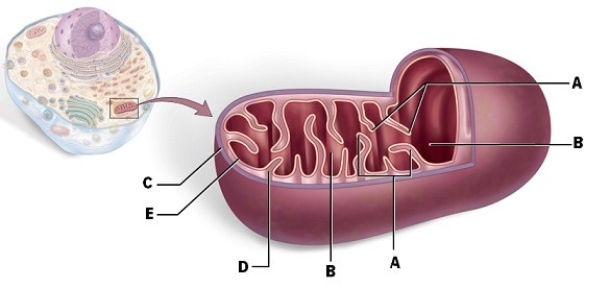
A)inner membrane
B)matrix
C)cristae
D)intermembrane space
E)outer membrane

A)inner membrane
B)matrix
C)cristae
D)intermembrane space
E)outer membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The final electron acceptor in glycolysis is oxygen and this step will occur within the matrix of the mitochondria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Normally our body will run aerobic respiration in order to produce the required amount of ATP to sustain life.When we run out of oxygen we will shift over to anaerobic respiration.What is the value of anaerobic respiration to our system?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What would happen to the process in this figure if oxygen was not available? 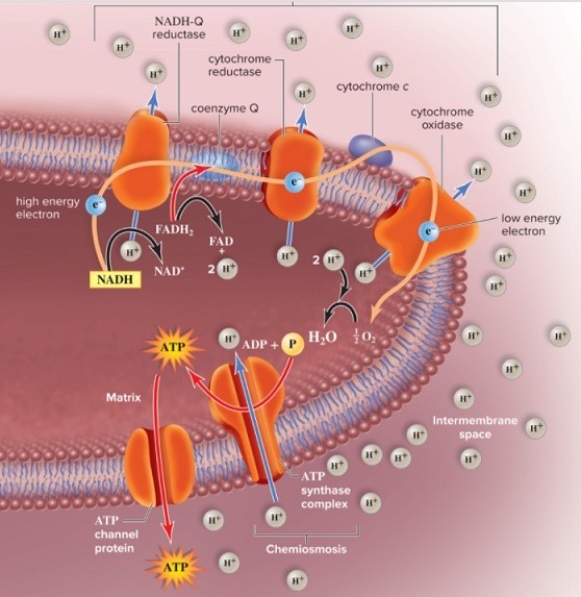


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Identify "B." 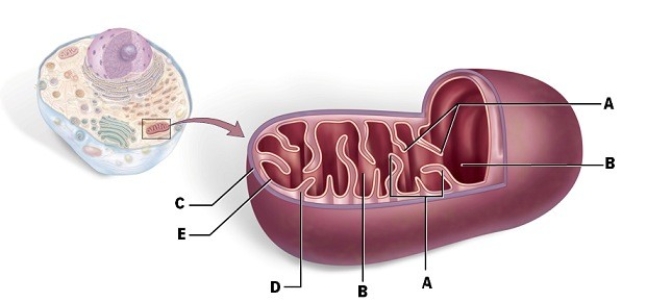
A)inner membrane
B)matrix
C)cristae
D)intermembrane space
E)outer membrane

A)inner membrane
B)matrix
C)cristae
D)intermembrane space
E)outer membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The membrane protein _____ will catalyze the reaction ADP + P ATP as H+ flow down a gradient from the intermembrane space into the matrix.
A)the sodium-potassium pump
B)ATP synthase
C)cholesterol
D)NADH-Q reductase
A)the sodium-potassium pump
B)ATP synthase
C)cholesterol
D)NADH-Q reductase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Identify "D." 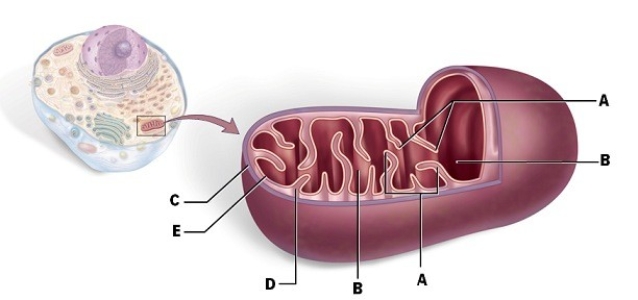
A)inner membrane
B)matrix
C)cristae
D)intermembrane space
E)outer membrane

A)inner membrane
B)matrix
C)cristae
D)intermembrane space
E)outer membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Some bacteria are strict aerobes and others are strict anaerobes.Some bacteria,however,are facultative anaerobes and can live with or without oxygen.If given the choice of using oxygen or not,which pathway should a facultative anaerobe perform?
A)Use oxygen since aerobic metabolism provides more ATP per molecule of carbohydrate than anaerobic metabolism.
B)Avoid using oxygen since anaerobic metabolism provides more ATP per molecule of carbohydrate than aerobic metabolism.
C)It doesn't matter; both processes will produce the same results.
A)Use oxygen since aerobic metabolism provides more ATP per molecule of carbohydrate than anaerobic metabolism.
B)Avoid using oxygen since anaerobic metabolism provides more ATP per molecule of carbohydrate than aerobic metabolism.
C)It doesn't matter; both processes will produce the same results.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
For fatty acids to enter the citric acid cycle of aerobic respiration,the fatty acids must be
A)deaminated.
B)combined with glycerol.
C)combined with ATP.
D)converted to acetyl groups.
E)converted into five-carbon sugars.
A)deaminated.
B)combined with glycerol.
C)combined with ATP.
D)converted to acetyl groups.
E)converted into five-carbon sugars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Study the figure to match the substrates with the corresponding pathway. 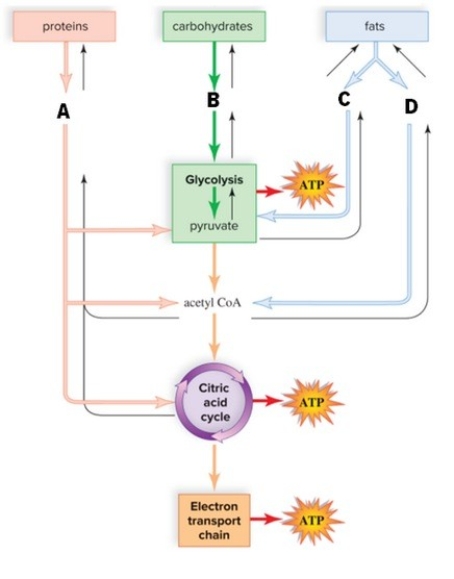
A)A is glycerol; B is amino acids; C is glucose; D is fatty acids
B)A is glucose; B is fatty acids; C is glycerol; D is amino acids
C)A is amino acids; B is fatty acids; C is glucose; D is glycerol
D)A is amino acids; B is glucose; C is glycerol; D is fatty acids

A)A is glycerol; B is amino acids; C is glucose; D is fatty acids
B)A is glucose; B is fatty acids; C is glycerol; D is amino acids
C)A is amino acids; B is fatty acids; C is glucose; D is glycerol
D)A is amino acids; B is glucose; C is glycerol; D is fatty acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Chloroplasts are capable of performing photosynthesis which is the most common anabolic process on the planet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following coenzymes will accept two electrons and two hydrogen ions during the oxidation of glucose?
A)FAD
B)NAD+
C)FADH
D)NADH
A)FAD
B)NAD+
C)FADH
D)NADH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What is the correct summary for the energy investment vs.energy harvesting steps of glycolysis?
A)2 ATP are invested and 4 ATP are harvested to produce a net gain of 2 ATP.
B)4 ATP are invested and 6 ATP are harvested to produce a net gain of 2 ATP.
C)No ATP are invested and 2 ATP are harvested to produce a net gain of 2 ATP.
D)2 ATP are invested and no ATP are harvested to produce a net loss of 2 ATP.
A)2 ATP are invested and 4 ATP are harvested to produce a net gain of 2 ATP.
B)4 ATP are invested and 6 ATP are harvested to produce a net gain of 2 ATP.
C)No ATP are invested and 2 ATP are harvested to produce a net gain of 2 ATP.
D)2 ATP are invested and no ATP are harvested to produce a net loss of 2 ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Fermentation follows glycolysis in some cells when oxygen is not available.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The breakdown of glucose in cellular respiration is a catabolic reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which statement is correct about the input and output of carbon during glycolysis?
A)There is an input of 6 carbons (glucose)and an output of 6 carbons (2 pyruvates).
B)There is an input of 6 carbons (2 pyruvates)and an output of 6 carbons (1 glucose).
C)There is an input of 6 carbons (glucose)and an output of 6 carbons (6 CO2).
D)There is an input of 6 carbons (glucose)and an output of 3 carbons (pyruvate).
A)There is an input of 6 carbons (glucose)and an output of 6 carbons (2 pyruvates).
B)There is an input of 6 carbons (2 pyruvates)and an output of 6 carbons (1 glucose).
C)There is an input of 6 carbons (glucose)and an output of 6 carbons (6 CO2).
D)There is an input of 6 carbons (glucose)and an output of 3 carbons (pyruvate).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
During the preparatory reaction of aerobic respiration what happens to the carbon molecules?
A)The carbon molecules are broken down from a 3-carbon to a 2-carbon acetyl group and a 1-carbon CO2 is released.
B)The carbon molecules are broken down from a 4-carbon to a 3-carbon acetyl group and a 2-carbon CO2 is released.
C)The carbon molecules are converted from a 2-carbon to a 3-carbon acetyl group and a 1-carbon CO2 is consumed.
D)The carbon molecules are broken down from a 3-carbon to a 1-carbon acetyl group and two 1-carbon CO2 are released.
A)The carbon molecules are broken down from a 3-carbon to a 2-carbon acetyl group and a 1-carbon CO2 is released.
B)The carbon molecules are broken down from a 4-carbon to a 3-carbon acetyl group and a 2-carbon CO2 is released.
C)The carbon molecules are converted from a 2-carbon to a 3-carbon acetyl group and a 1-carbon CO2 is consumed.
D)The carbon molecules are broken down from a 3-carbon to a 1-carbon acetyl group and two 1-carbon CO2 are released.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Fermentation is the process that produces bubbles of carbon dioxide that makes bread dough rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Each molecule of NADH produced in the mitochondria provides enough energy to form two ATP molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



