Deck 17: Work and the Labor Market
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/38
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Work and the Labor Market
1
What are the four factors that influence the elasticity of market labor demand?
The four factors are:
1. The elasticity of demand for a firm's good.
2. The relative importance of the factor in the production process.
3. The possibility of, and cost of, substitution in production.
4. The degree to which marginal productivity falls with an increase in the factor.
18. How is artificial intelligence likely to influence the labor market?
Artificial intelligence is a technological change that will displace certain types of mental labor that people previously thought was unique to humans, by algorithms. There will still be work for humans on the high end and low end of creativity-designing algorithms on the high end, and doing the mental scut work of filling an algorithm to a particular issue on the less creative end. So it will likely not reduce the total number of jobs, but it will significantly change the nature of the jobs.
1. The elasticity of demand for a firm's good.
2. The relative importance of the factor in the production process.
3. The possibility of, and cost of, substitution in production.
4. The degree to which marginal productivity falls with an increase in the factor.
18. How is artificial intelligence likely to influence the labor market?
Artificial intelligence is a technological change that will displace certain types of mental labor that people previously thought was unique to humans, by algorithms. There will still be work for humans on the high end and low end of creativity-designing algorithms on the high end, and doing the mental scut work of filling an algorithm to a particular issue on the less creative end. So it will likely not reduce the total number of jobs, but it will significantly change the nature of the jobs.
2
Give four examples of the interaction of market, social, and political forces in real-world labor markets.
(Any four of the following are possible.)
1. Even though equilibrium wages differ between professors of English and professors of Economics, they often receive the same salary because certain perceptions of "fairness" require it. These perceptions are a social force.
2. On average, women earn about 85 cents for every $1 earned by men. Market forces can explain about half of this differential. The other half may represent discrimination. In this case a social force.
3. Members of a single group undertake certain types of jobs, perhaps because expertise is more easily shared within a group. This would be a social force.
4. Firms often pay higher than market wages. This may reflect perceptions of fairness and thus a social force or it may be that better paid workers are more efficient and there is a saving in monitoring costs, a market force.
5. It is often seems that there are two categories of jobs: dead-end jobs and jobs with a potential for advancement. The existence of these dual or segmented labor markets probably reflects some form of discrimination, which may be a social or market force.
6. The rate of unemployment among blacks is more than twice as high as the rate among whites. This probably reflects discrimination in labor markets and in other markets as well such as the housing and education markets. This is probably the result of social, political, and market forces.
1. Even though equilibrium wages differ between professors of English and professors of Economics, they often receive the same salary because certain perceptions of "fairness" require it. These perceptions are a social force.
2. On average, women earn about 85 cents for every $1 earned by men. Market forces can explain about half of this differential. The other half may represent discrimination. In this case a social force.
3. Members of a single group undertake certain types of jobs, perhaps because expertise is more easily shared within a group. This would be a social force.
4. Firms often pay higher than market wages. This may reflect perceptions of fairness and thus a social force or it may be that better paid workers are more efficient and there is a saving in monitoring costs, a market force.
5. It is often seems that there are two categories of jobs: dead-end jobs and jobs with a potential for advancement. The existence of these dual or segmented labor markets probably reflects some form of discrimination, which may be a social or market force.
6. The rate of unemployment among blacks is more than twice as high as the rate among whites. This probably reflects discrimination in labor markets and in other markets as well such as the housing and education markets. This is probably the result of social, political, and market forces.
3
A firm notices that wages in another country are lower than it currently pays its employees. What are three reasons why the firm may choose not to relocate?
The text lists five.
1. Differences in worker productivity.
2. Transportation costs.
3. Potential trade restrictions.
4. Compatibility of production techniques with social institutions.
5. The focal point phenomenon.
1. Differences in worker productivity.
2. Transportation costs.
3. Potential trade restrictions.
4. Compatibility of production techniques with social institutions.
5. The focal point phenomenon.
4
Why will an increase in the marginal income tax rate likely lead to a reduction in the number of hours worked? Why will an increase in the marginal income tax rate likely lead to an increase in the number of hours worked.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is a labor market?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Four factors that influence the elasticity of market labor supply are. (1) Individuals' opportunity cost of working, (2) the type of market being discussed, (3) the elasticity of individuals' supply curves, and (4) individuals entering and leaving the labor market. How does each factor affect the elasticity of labor supply?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is Luddite reasoning, and what do most economists find wrong with it?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What government programs, other than income taxes, have a negative incentive effect on individuals' work effort?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What does it mean to say that the demand for labor is a derived demand?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Why is the normal shape of the labor supply curve upward sloping?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What does it mean to say that the demand for labor is a derived demand?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is a monopsony? Why in this case are the marginal factor cost and the supply not the same?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Four factors that influence the elasticity of market labor demand are: (1) the elasticity of demand for a firm's good, (2) the relative importance of the factor in the production process, (3) the possibility of, and cost of, substitution in production, and (4) the degree to which the marginal productivity falls with an increase in the factor. How does each affect market labor demand?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
How do you explain the fact that, over the last century, real wages in the U.S. increased substantially while the average number of hours worked per person fell?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Define a monopsony, and explain why in this case the marginal factor cost and the supply are not the same. What is the relationship between a monopsony and a bilateral monopoly? How is the wage rate determined in a situation of bilateral monopoly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is the income effect and the substitution effect in the context of the supply of labor?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Describe the three types of demand-side discrimination in the labor market and give an example of each. Which of these types of discrimination is the most easily eliminated?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Why would an increase in the marginal income tax rate likely to lead to a reduction in the number of hours worked (all other things held constant)? Why would an increase in the marginal income tax rate might actually lead to an increase in the number of hours worked?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What are four factors that influence the elasticity of market labor supply?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is entrepreneurship?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What are three types of demand-side discrimination in the labor market?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What are efficiency wages? Why do firms pay them?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Demonstrate graphically and explain verbally a monopsony labor market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Demonstrate graphically and explain verbally a bilateral monopoly labor market. What will happen to wages and quantity of labor employed in comparison to a competitive market?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Mangy Mutt Modifiers (3M) grooms dogs. 3M has a fixed capital stock, and uses only one variable input, labor. Additionally, 3M sells its output and buys its labor under competitive market conditions. Using the information provided, answer the questions that follow. 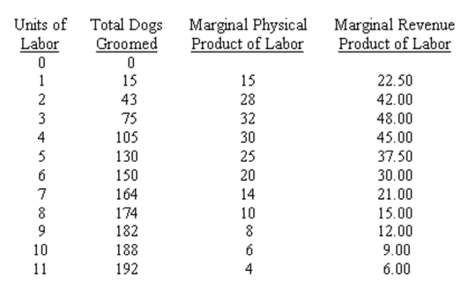 (a) If the competitive wage rate is $15.00 per unit of labor, how many units of labor will 3M hire? Briefly explain your answer.
(a) If the competitive wage rate is $15.00 per unit of labor, how many units of labor will 3M hire? Briefly explain your answer.
(b) Calculate 3M's gross profit at that combination of wages and labor. Assume that there are zero capital costs, so gross profits equal total revenue less labor costs. Show your calculation.
 (a) If the competitive wage rate is $15.00 per unit of labor, how many units of labor will 3M hire? Briefly explain your answer.
(a) If the competitive wage rate is $15.00 per unit of labor, how many units of labor will 3M hire? Briefly explain your answer.(b) Calculate 3M's gross profit at that combination of wages and labor. Assume that there are zero capital costs, so gross profits equal total revenue less labor costs. Show your calculation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the three types of demand-side discrimination discussed in the text is the most easily eliminated?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Suppose that you are unemployed and collecting unemployment insurance benefits of $200 per week, and suppose that your income is tax-free. Your employment counselor calls you and reports that she has found you a job that offers 40 hours of work per week at $12.50 per hour. You do some quick calculations and discover that your after-tax earnings from this job would be $360 per week. If unemployment benefits are cut off as soon as you regain employment, what is the real take-home wage rate from your new job offer? What does that make the tax rate on your earnings? (Hint: the loss of benefits is an implicit tax.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
How is MRP different for a monopolist than for a perfectly competitive firm? In which type of firm will MRP be lower? Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Explain how each of the following events affects the equilibrium wage and the equilibrium quantity of labor (assume all else is constant with each event). Be sure to explain whether demand for or supply of labor has changed.
(1) The price of output a firm produces rises.
(2) A leisure-hour provides greater marginal benefit.
(3) The marginal income tax rate rises.
(4) New immigration laws restrict the hiring of illegal workers.
(5) A reduction in welfare benefits.
(6) The cost of machines falls (labor and machines are substitutes).
(7) Technology makes labor more productive.
(8) The industry becomes more monopolistic.
(9) The price of the product a firm produced falls.
(1) The price of output a firm produces rises.
(2) A leisure-hour provides greater marginal benefit.
(3) The marginal income tax rate rises.
(4) New immigration laws restrict the hiring of illegal workers.
(5) A reduction in welfare benefits.
(6) The cost of machines falls (labor and machines are substitutes).
(7) Technology makes labor more productive.
(8) The industry becomes more monopolistic.
(9) The price of the product a firm produced falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Consider the following labor supply and demand diagram: 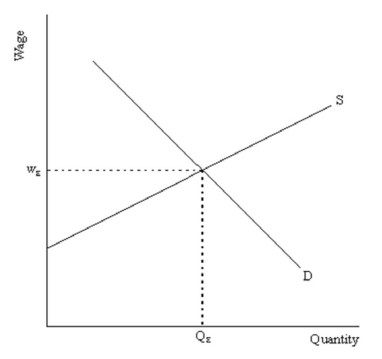 For each of the following situations, explain (and illustrate) what would happen to the market for labor.
For each of the following situations, explain (and illustrate) what would happen to the market for labor.
(a) The firms who are employing these workers experience a big increase in the demand for their products.
(b) Intel develops a new computer chip that is capable of doing the same work as two employees. Assume that workers and computers are substitutes in Intel's production function.
(c) A newly elected U.S. president issues an executive order, restricting all immigration into the U.S.
 For each of the following situations, explain (and illustrate) what would happen to the market for labor.
For each of the following situations, explain (and illustrate) what would happen to the market for labor.(a) The firms who are employing these workers experience a big increase in the demand for their products.
(b) Intel develops a new computer chip that is capable of doing the same work as two employees. Assume that workers and computers are substitutes in Intel's production function.
(c) A newly elected U.S. president issues an executive order, restricting all immigration into the U.S.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Using a supply and demand diagram, demonstrate graphically and explain verbally the following statement: "Existing workers prefer inelastic labor supplies but employers prefer elastic labor supplies."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Suppose you are considering two possible summer jobs. One is with an outdoor painting company as a painter, the other is as a sales associate in an up-scale department store (please assume that you are in this strictly for the money, so ignore whether one job sounds inherently more or less attractive to you personally). Both jobs are union jobs, and both unions are presently negotiating for significant wage increases. You can't afford to get laid off half way through the summer, and the last people hired will be the first laid off if there is a layoff, so you are concerned about the elasticity of demand for labor for both employers. Which would probably be more elastic, and why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What are efficiency wages and comparable worth laws? How does each impact the labor market?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the difference between the marginal revenue product and the value of the marginal product?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
You have been asked to evaluate the pay of English Professors and Economics Professors at a small liberal arts college. The college's personnel department has generated some supply and demand information from similar colleges, which is presented in the diagrams below. 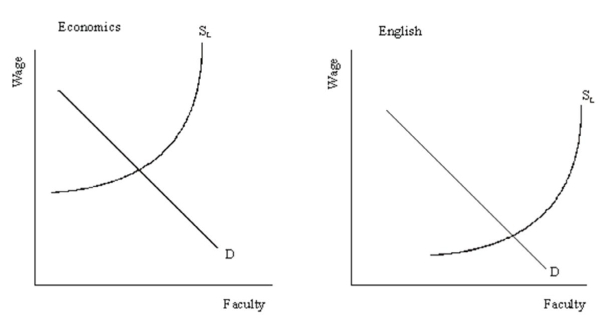 (a) Illustrate a market-based pay scale for each type of professor.
(a) Illustrate a market-based pay scale for each type of professor.
(b) Illustrate a pay scale based upon the principle that "a faculty member is a faculty member: they are all teachers, the only difference is the subject that they teach. They should receive equal pay for equal work."
(c) Describe what difficulty the college might have in its recruiting process if it follows the pay system in (b) rather than that in (a).
 (a) Illustrate a market-based pay scale for each type of professor.
(a) Illustrate a market-based pay scale for each type of professor.(b) Illustrate a pay scale based upon the principle that "a faculty member is a faculty member: they are all teachers, the only difference is the subject that they teach. They should receive equal pay for equal work."
(c) Describe what difficulty the college might have in its recruiting process if it follows the pay system in (b) rather than that in (a).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What is the cost minimization condition?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
List three general principles concerning the factors that influence a firm's demand for labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
You are the owner of an auto body shop. Due to a recent hailstorm you have a twofold increase in the number of cars to repair. What is the short-term impact that this hailstorm will have on your demand for auto body technicians? What will be the results in the market for these technicians with respect to wages and the number employed? What will be the long-term results in the market for these technicians with respect to wages and the number employed? (NOTE: Your answer should include two diagrams.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 38 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



