Deck 18: International Trade Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/18
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: International Trade Policy
1
What is the WTO? What is the GATT? How are they related?
WTO stands for World Trade Organization.GATT stands for General Agreement on Trade and Tariffs.Both are treaties concerning free trade that have been signed by many nations throughout the world.Note the WTO has replaced the GATT as the operating arrangement/agreement for international trade throughout much of the world.The WTO differs from GATT in that it has greater enforcement powers.
Problems and Applications
Problems and Applications
2
What are trade adjustment assistance programs? Describe the arguments for and against them.
Trade adjustment assistance programs are programs designed to compensate losers for reductions in trade restrictions.The argument in favor of these programs is that since trade makes most members of society better off, by compensating those who are hurt by trade it is likely to minimize any political pressure to maintain trade restrictions.The main argument against these programs is that there is an incentive for abuse: once government money is available to compensate victims, many people find ways to get themselves classified as victims even if they are not hurt by the reduction in the trade restrictions.
3
How are tariffs and quotas similar? How are they different? Explain verbally and demonstrate graphically.
Tariffs and quotas are similar in that they both reduce the amount of the item consumed (QR < QE) and cause the price to increase (PR > PE).They differ in that the additional revenue generated (filled areas in the diagrams) goes to different places.When a quota is imposed the additional revenue goes to the firms supplying the product (the shaded area).When a tariff is imposed the additional revenue goes to the government of the country imposing the tariff (the shaded area). 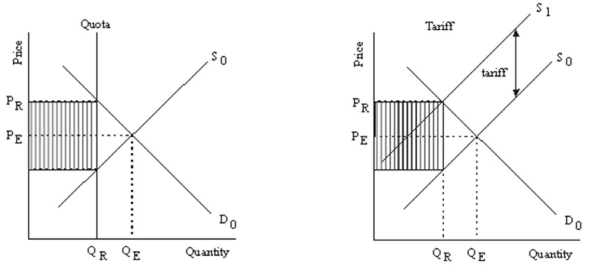

4
What are the six main methods used by governments to restrict trade?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What are strategic trade policies, and when can they become a problem?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Consider the following supply and demand diagram shown for a small domestic country.Note that at the world free-trade price of P* illustrated in the diagram, there are imports of Q1 - Q0. 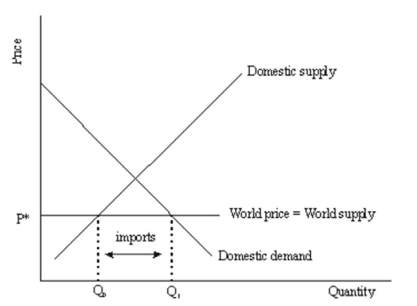 If a government wanted more tariff revenue, given the same tariff, t, would it desire elastic or inelastic demand of the imported good? Explain.Be sure to illustrate your explanation with an appropriate diagram.
If a government wanted more tariff revenue, given the same tariff, t, would it desire elastic or inelastic demand of the imported good? Explain.Be sure to illustrate your explanation with an appropriate diagram.
 If a government wanted more tariff revenue, given the same tariff, t, would it desire elastic or inelastic demand of the imported good? Explain.Be sure to illustrate your explanation with an appropriate diagram.
If a government wanted more tariff revenue, given the same tariff, t, would it desire elastic or inelastic demand of the imported good? Explain.Be sure to illustrate your explanation with an appropriate diagram.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the major reason why developing countries often impose tariffs on imports rather than quotas?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
With what countries or regions does the United States trade the most?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What role do appeals to national security play in arguments to justify trade restrictions? What forms do these restrictions take?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
You are an influential CEO of a company like Wal-Mart, who imports foreign made clothing.The government wants to restrict the quantity of the product that your company imports.Should you use your political influence to lobby the Congress to impose a tariff on the product or a quota? Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
President Trump instituted tariffs on many goods coming into the U.S.in 2018.What was most economists' view of those tariffs?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Define the term "the trade balance." Does the United States have a trade balance that is in deficit or surplus? Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What has happened to the size of international trade (relative to US GDP) since the late 1920's? With what countries or regions does the United States trade the most?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Define tariffs and quotas, and explain the similarities and differences between them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What are the benefits of being a debtor nation? What are the costs?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What does it mean for a country to be a debtor nation? What has to happen for a country to change from a debtor nation to a creditor nation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
How can learning by doing and economies of scale play a role in deciding to impose trade restrictions? What name do we give to the argument for trade restrictions that is based on learning by doing and economies of scale?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Why are trade restrictions less likely to be imposed during a booming economy than during a recession?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 18 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



