Deck 21: Structural Stagnation and Globalization
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/22
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: Structural Stagnation and Globalization
1
Explain graphically and with words the effect of expansionary fiscal policy in the globalized AS/AD model. 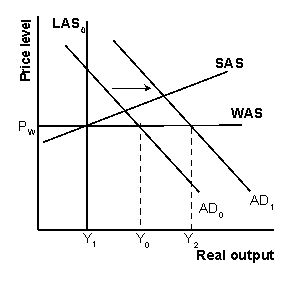

In the graph shown, the quantity of aggregate demand at PW is Y0.Domestic producers supply Y1, creating a trade deficit of Y0- Y1.Expansionary fiscal policy shifts the AD curve out to the right to AD1.Aggregate quantity demanded rises to Y2 and the trade deficit rises to Y2- Y1.
2
What is meant by import-led stagnation?
An import-led stagnation is slow growth caused by the structural problems accompanying globalization.According to the structural stagnation hypothesis, the U.S.trade deficit has a significant impact on employment-at $30,000 a job, a $550 billion trade deficit translates into more than 2 million fewer jobs for the United States than if there was no trade deficit and everything else was identical.Simply put, the trade deficit translates into higher unemployment and lower potential output until these displaced workers find new jobs in different fields that are competitive in the globalized economy.
3
Explain how globalization can limit a country's potential output.
A world price for goods below the U.S.price of goods enables U.S.consumers to consume more than they had previously.But it also makes it harder for U.S.producers to sell their goods, which means that, due to structural reasons, international competitive forces put a limit on domestic potential output.If potential output were determined only by the physical existence of workers and factories, potential output would not have fallen.But according to the structural stagnation hypothesis, potential output depends on more than physical productive capacity; it depends on the wages, technology, and global competitive conditions, and when trade deficits are possible, globalization can reduce the amount a high-wage developed country can competitively produce.
4
What would tariffs do to unemployment caused by globalization? Why do most economists not favor using tariffs?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What does a fall in the exchange rate do to a country's potential output and long run aggregate supply?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
How does the world supply curve change if a country's inflation is lower than the world's inflation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Explain the role that globalization and technological change play in the structural stagnation hypothesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Why does fiscal policy in the globalized AS/AD model have a different effect than fiscal policy in the standard AS/AD model?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Why is it often empirically difficult to differentiate a structural stagnation from a standard recession?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
As India and China move up the value added chain, how will the effect of globalization likely change on US workers?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
How does the existence of a nontradable sector change the implications of the globalized AS/AD model?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What adjustment forces would one have expected to resolve structural stagnation in the globalized AS/AD model? Why didn't they occur in the recent U.S.case?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What do almost all the "solutions" to the structural stagnation problem have in common?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
According to the text, how does structural stagnation differ from secular stagnation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Why are deficits of less concern when used to fight a standard recession than when they are used to fight structural stagnation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
State the structural stagnation hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Distinguish between a normal business cycle and structural stagnation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What are three ways in which a country might deal with a structural stagnation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Would you be more likely to advise expansionary fiscal policy in a structural stagnation or in a standard recession? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Would a person in a developed country be better off in an industry producing commodities or an industry producing specialized goods when globalization is occurring?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Explain using the AS/AD model how a positive resource shock can help solve a structural stagnation problem? 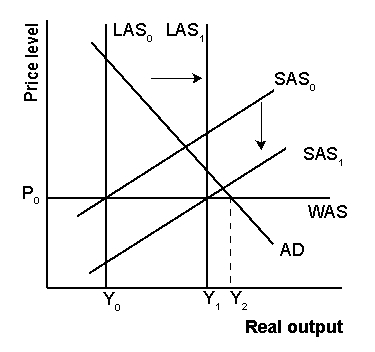


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Demonstrate what would happen to a country's trade deficit if the value of a country's exchange rate fell.Assume the economy begins with LAS, SAS and WAS0. 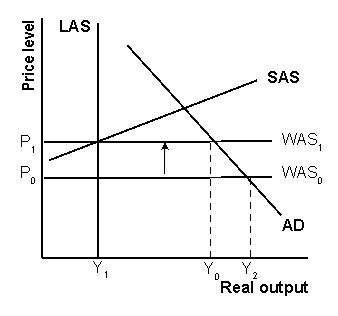


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



