Deck 9: Aggregate Demand and Supply
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/284
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Aggregate Demand and Supply
1
Which of the following would most likely cause aggregate demand to decrease?
A) The price of lumber increases.
B) There is a new housing boom.
C) Government reduces regulations on businesses.
D) Income taxes rise to reduce the deficit.
A) The price of lumber increases.
B) There is a new housing boom.
C) Government reduces regulations on businesses.
D) Income taxes rise to reduce the deficit.
D
2
If a country increases the amount of goods it imports but its exports remain unchanged:
A) AD shifts right.
B) AD shifts left.
C) AD would not shift.
D) AD would shift but in a random direction.
A) AD shifts right.
B) AD shifts left.
C) AD would not shift.
D) AD would shift but in a random direction.
B
3
The collapse of home values in 2008 led to _____ in Americans' consumption and _____ in their saving rates.
A) a decrease; a decrease
B) a decrease; an increase
C) an increase; a decrease
D) an increase; an increase
A) a decrease; a decrease
B) a decrease; an increase
C) an increase; a decrease
D) an increase; an increase
B
4
Price stickiness refers to:
A) when prices are slow to adjust to economic shocks.
B) when prices of goods and services respond to the stock market.
C) when firms raise their prices as soon as they hear bad news.
D) when prices are controlled by government regulations.
A) when prices are slow to adjust to economic shocks.
B) when prices of goods and services respond to the stock market.
C) when firms raise their prices as soon as they hear bad news.
D) when prices are controlled by government regulations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If AD shifts right as the economy booms, and then SRAS shifts left, what happens to inflation?
A) It increases.
B) It decreases.
C) It stays the same,
D) It falls to zero.
A) It increases.
B) It decreases.
C) It stays the same,
D) It falls to zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The "wealth effect" refers to the fact that when aggregate price levels rise:
A) exports decline.
B) firms cut back on their investments.
C) the real value of savings accounts, bonds, and cash declines.
D) interest rates tend to rise.
A) exports decline.
B) firms cut back on their investments.
C) the real value of savings accounts, bonds, and cash declines.
D) interest rates tend to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If mergers between firms increase throughout the economy, what would happen to the SRAS curve?
A) SRAS shifts left.
B) SRAS shifts right.
C) SRAS would not change.
D) SRAS would disappear.
A) SRAS shifts left.
B) SRAS shifts right.
C) SRAS would not change.
D) SRAS would disappear.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following factors would most likely shift the SRAS curve to the right?
A) an increase in industrial regulations to improve worker safety
B) an increase in the use of truck panels and tails to improve fuel efficiency
C) the federal government's ending its subsidy program on hybrid car production
D) improved consumer expectations in the economy
A) an increase in industrial regulations to improve worker safety
B) an increase in the use of truck panels and tails to improve fuel efficiency
C) the federal government's ending its subsidy program on hybrid car production
D) improved consumer expectations in the economy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following would NOT shift the AD curve?
A) The economy improves and people start spending more.
B) Interest rates rise, which reduces investment spending.
C) An increase in market power occurs in the airline industry.
D) The federal budget is reduced to tackle the deficit problem.
A) The economy improves and people start spending more.
B) Interest rates rise, which reduces investment spending.
C) An increase in market power occurs in the airline industry.
D) The federal budget is reduced to tackle the deficit problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
According to John Maynard Keynes, what determines employment and income?
A) aggregate supply
B) government spending alone
C) aggregate expenditures
D) wages, prices, and interest rates
A) aggregate supply
B) government spending alone
C) aggregate expenditures
D) wages, prices, and interest rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
According to Keynes, what determines the level of employment and income?
A) aggregate expenditures
B) aggregate savings
C) government spending
D) aggregate supply
A) aggregate expenditures
B) aggregate savings
C) government spending
D) aggregate supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If the economy is above long-run equilibrium output, what will happen in the long run if SRAS adjusts?
A) Prices rise and output increases.
B) Prices rise and output decreases.
C) Prices fall and output increases.
D) Prices fall and output decreases.
A) Prices rise and output increases.
B) Prices rise and output decreases.
C) Prices fall and output increases.
D) Prices fall and output decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In the Keynesian model, the price level is _____; in the aggregate demand and supply model, the price level is _____.
A) fixed; fixed
B) flexible; flexible
C) flexible; fixed
D) fixed; flexible
A) fixed; fixed
B) flexible; flexible
C) flexible; fixed
D) fixed; flexible

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Who recognized the need to develop tools to analyze the macroeconomy as a whole?
A) Adam Smith
B) Karl Marx
C) John Maynard Keynes
D) Milton Friedman
A) Adam Smith
B) Karl Marx
C) John Maynard Keynes
D) Milton Friedman

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If business expectations become less favorable, what will likely happen to the AD curve?
A) AD shifts left.
B) AD shifts right.
C) AD does not shift.
D) AD decreases to zero.
A) AD shifts left.
B) AD shifts right.
C) AD does not shift.
D) AD decreases to zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In an AD/AS model, if the economy is below its long-run output, what will happen in the long run if the markets are left alone?
A) AD will shift left.
B) AD will shift right.
C) SRAS will shift left.
D) SRAS will shift right.
A) AD will shift left.
B) AD will shift right.
C) SRAS will shift left.
D) SRAS will shift right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A temporary rise in the price of agricultural crops due to a drought is likely to cause a(n):
A) increase in the long-run aggregate supply.
B) decrease in the long-run aggregate supply.
C) increase in the short-run aggregate supply.
D) decrease in the short-run aggregate supply.
A) increase in the long-run aggregate supply.
B) decrease in the long-run aggregate supply.
C) increase in the short-run aggregate supply.
D) decrease in the short-run aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following curves is vertical?
A) aggregate demand
B) short-run aggregate supply
C) long-run aggregate supply
D) aggregate expenditures line
A) aggregate demand
B) short-run aggregate supply
C) long-run aggregate supply
D) aggregate expenditures line

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the spending multiplier if the marginal propensity to consume is 0.60?
A) 1.67
B) 2.5
C) 4.0
D) 6.67
A) 1.67
B) 2.5
C) 4.0
D) 6.67

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In a depressed economy with a MPC of 0.75, what effect will a $100 increase in government spending have on equilibrium GDP?
A) It will reduce it by $250.
B) It will raise it by $250.
C) It will raise it by $400.
D) It will raise it by $750.
A) It will reduce it by $250.
B) It will raise it by $250.
C) It will raise it by $400.
D) It will raise it by $750.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The _____ effect is a reason for the negative slope of the aggregate demand curve.
A) income
B) substitution
C) interest rate
D) multiplier
A) income
B) substitution
C) interest rate
D) multiplier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The difference between the Keynesian model and the aggregate demand/aggregate supply (AD/AS) model is that the:
A) Keynesian model assumes that prices are constant.
B) AD/AS model assumes that prices are constant.
C) Keynesian model assumes full employment.
D) AD/AS model assumes that equilibrium always occurs at less than full employment.
A) Keynesian model assumes that prices are constant.
B) AD/AS model assumes that prices are constant.
C) Keynesian model assumes full employment.
D) AD/AS model assumes that equilibrium always occurs at less than full employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A(n) _____ in government spending, a _____ domestic currency, and _____ interest rates will shift a country's aggregate demand to the left.
A) decrease; stronger; higher
B) increase; weaker; higher
C) increase; stronger; lower
D) decrease; weaker; lower
A) decrease; stronger; higher
B) increase; weaker; higher
C) increase; stronger; lower
D) decrease; weaker; lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A falling aggregate price level _____ demand for a country's exports and therefore _____ output demanded.
A) increases; increases
B) increases; reduces
C) reduces; increases
D) reduces; reduces
A) increases; increases
B) increases; reduces
C) reduces; increases
D) reduces; reduces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Increased consumer confidence will shift the aggregate demand curve to the _____ and _____ output demanded.
A) left; decrease
B) left; increase
C) right; increase
D) right; decrease
A) left; decrease
B) left; increase
C) right; increase
D) right; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The output of all the goods and services demanded in an economy at various price levels is called:
A) the quantity-price locus.
B) aggregate demand.
C) economic production.
D) the price-output curve.
A) the quantity-price locus.
B) aggregate demand.
C) economic production.
D) the price-output curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following events causes an increase in aggregate demand?
A) decreasing wealth
B) falling interest rates
C) decrease in government spending
D) rising imports
A) decreasing wealth
B) falling interest rates
C) decrease in government spending
D) rising imports

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The aggregate demand curve displays:
A) real GDP demanded at various price levels.
B) nominal GDP versus real GDP.
C) GDP demanded at various investment levels.
D) the business cycle.
A) real GDP demanded at various price levels.
B) nominal GDP versus real GDP.
C) GDP demanded at various investment levels.
D) the business cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
_____ are components of consumer spending that affect aggregate demand.
A) Expected rates of return on investment
B) Taxes
C) Exchange rate changes
D) Government spending programs
A) Expected rates of return on investment
B) Taxes
C) Exchange rate changes
D) Government spending programs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Increased taxes will shift the aggregate demand curve to the _____ and _____ output demanded.
A) left; decrease
B) left; increase
C) right; increase
D) right; decrease
A) left; decrease
B) left; increase
C) right; increase
D) right; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The collapse of home values in 2008 led to _____ in Americans' saving rates, shifting aggregate demand to the _____.
A) a decrease; left
B) a decrease; right
C) an increase; left
D) an increase; right
A) a decrease; left
B) a decrease; right
C) an increase; left
D) an increase; right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A stronger dollar will shift the U.S. aggregate demand curve to the _____ and _____ output demanded.
A) left; decrease
B) left; increase
C) right; increase
D) right; decrease
A) left; decrease
B) left; increase
C) right; increase
D) right; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following events causes a decrease in aggregate demand?
A) improving consumer confidence
B) increase in taxes
C) decrease in interest rates
D) increase in government spending
A) improving consumer confidence
B) increase in taxes
C) decrease in interest rates
D) increase in government spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The curve that shows how much GDP is demanded at various price levels is called:
A) the aggregate expenditures schedule.
B) the consumption line.
C) aggregate demand.
D) aggregate supply.
A) the aggregate expenditures schedule.
B) the consumption line.
C) aggregate demand.
D) aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is NOT a reason the aggregate demand curve is negatively sloped?
A) income effect
B) wealth effect
C) impact on exports
D) interest rate effects
A) income effect
B) wealth effect
C) impact on exports
D) interest rate effects

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following items is NOT a determinant of aggregate demand?
A) consumption
B) investment
C) government saving
D) government spending
A) consumption
B) investment
C) government saving
D) government spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The aggregate demand curve slopes _____ and has _____ on the vertical axis.
A) downward; output
B) downward; the price level
C) upward; output
D) upward; the price level
A) downward; output
B) downward; the price level
C) upward; output
D) upward; the price level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Decreased interest rates will shift the aggregate demand curve to the _____ and _____ output demanded.
A) left; decrease
B) left; increase
C) right; increase
D) right; decrease
A) left; decrease
B) left; increase
C) right; increase
D) right; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A rising aggregate price level _____ an economy's interest rates and therefore _____ output demanded.
A) increases; increases
B) increases; reduces
C) reduces; increases
D) reduces; reduces
A) increases; increases
B) increases; reduces
C) reduces; increases
D) reduces; reduces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Because of the wealth effect, a rising aggregate price level _____ the purchasing power of wealth and therefore _____ output demanded.
A) increases; increases
B) increases; reduces
C) reduces; increases
D) reduces; reduces
A) increases; increases
B) increases; reduces
C) reduces; increases
D) reduces; reduces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When the price of a given product declines, the consumer's spendable income rises because it takes less income to purchase the same quantity. This is called the:
A) net export effect.
B) income effect.
C) substitution effect.
D) interest effect.
A) net export effect.
B) income effect.
C) substitution effect.
D) interest effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
One reason the amount of real output demanded declines when the aggregate price level rises is the resulting reduction in household wealth, called the:
A) income effect.
B) substitution effect.
C) wealth effect.
D) interest rate effect.
A) income effect.
B) substitution effect.
C) wealth effect.
D) interest rate effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
_____ is the output of goods and services demanded at different price levels.
A) Aggregate expenditure
B) Aggregate demand
C) Aggregate spending
D) Aggregate supply
A) Aggregate expenditure
B) Aggregate demand
C) Aggregate spending
D) Aggregate supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
As the aggregate price level declines:
A) there is a movement down along the aggregate demand curve.
B) the aggregate demand curve shifts to the left.
C) there is a movement up along the aggregate demand curve.
D) the aggregate demand curve shifts to the right.
A) there is a movement down along the aggregate demand curve.
B) the aggregate demand curve shifts to the left.
C) there is a movement up along the aggregate demand curve.
D) the aggregate demand curve shifts to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
At high domestic price levels compared to other countries, Americans:
A) sell more exported goods.
B) buy more imported goods.
C) buy the same amount of foreign goods.
D) try to buy American-made goods.
A) sell more exported goods.
B) buy more imported goods.
C) buy the same amount of foreign goods.
D) try to buy American-made goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following would NOT cause a shift in the aggregate demand curve?
A) a change in consumption spending
B) a change in the price level
C) a change in investment
D) a change in net exports
A) a change in consumption spending
B) a change in the price level
C) a change in investment
D) a change in net exports

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
When government spending rises:
A) aggregate demand rises.
B) aggregate demand falls.
C) the aggregate price level falls.
D) it crowds out net exports.
A) aggregate demand rises.
B) aggregate demand falls.
C) the aggregate price level falls.
D) it crowds out net exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If the U.S. aggregate price level rises:
A) U.S. imports rise.
B) the aggregate demand curve shifts to the left.
C) the aggregate demand curve shifts to the right.
D) business investment increases.
A) U.S. imports rise.
B) the aggregate demand curve shifts to the left.
C) the aggregate demand curve shifts to the right.
D) business investment increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following events will NOT cause a rightward shift of the aggregate demand curve?
A) Consumers expect an economic contraction will soon occur.
B) A decrease in interest rates leads to an increase in investment.
C) The dollar depreciates.
D) The government decides to spend more money on goods.
A) Consumers expect an economic contraction will soon occur.
B) A decrease in interest rates leads to an increase in investment.
C) The dollar depreciates.
D) The government decides to spend more money on goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following partly explains why the aggregate demand curve is negatively sloped?
A) When the price of cars manufactured in the United States increases, people buy more cars manufactured abroad.
B) When the price of cars manufactured abroad increases, people buy fewer cars manufactured in the United States.
C) When the interest rate increases, people borrow more money.
D) When the interest rate decreases, people borrow less money.
A) When the price of cars manufactured in the United States increases, people buy more cars manufactured abroad.
B) When the price of cars manufactured abroad increases, people buy fewer cars manufactured in the United States.
C) When the interest rate increases, people borrow more money.
D) When the interest rate decreases, people borrow less money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
When the price of a product falls, causing consumers to purchase more of that product and less of other products, this is known as the:
A) income effect.
B) substitution effect.
C) wealth effect.
D) interest rate effect.
A) income effect.
B) substitution effect.
C) wealth effect.
D) interest rate effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In the aggregate demand/aggregate supply (AD/AS) model, the vertical axis is labeled:
A) aggregate price level.
B) consumption.
C) GDP.
D) consumption plus investment plus government spending.
A) aggregate price level.
B) consumption.
C) GDP.
D) consumption plus investment plus government spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
An increase in net export spending will result in a(n):
A) increase in aggregate demand.
B) increase in aggregate supply.
C) decrease in aggregate supply.
D) decrease in aggregate demand.
A) increase in aggregate demand.
B) increase in aggregate supply.
C) decrease in aggregate supply.
D) decrease in aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following best illustrates the wealth effect?
A) Jacob saved $25,000, which he put in the stock market. The market suddenly did very well, and though Jacob is not yet aware of it, his stock portfolio value rose to $36,000.
B) Simon felt he needed at least $800,000 to retire comfortably. He increased his savings to build up his wealth.
C) The Jones family has $50,000 in a bank. Prices in the market rose dramatically, diminishing their purchasing power by $50,000.
D) Margaret had her savings in Treasury bonds. She thought that stocks might offer her a better opportunity to increase her wealth, so she sold her bonds to buy stocks.
A) Jacob saved $25,000, which he put in the stock market. The market suddenly did very well, and though Jacob is not yet aware of it, his stock portfolio value rose to $36,000.
B) Simon felt he needed at least $800,000 to retire comfortably. He increased his savings to build up his wealth.
C) The Jones family has $50,000 in a bank. Prices in the market rose dramatically, diminishing their purchasing power by $50,000.
D) Margaret had her savings in Treasury bonds. She thought that stocks might offer her a better opportunity to increase her wealth, so she sold her bonds to buy stocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following would NOT cause a shift in the aggregate demand curve?
A) a stock market crash
B) a reduction in raw material prices
C) a decrease in real interest rates
D) an increase in the expected rate of inflation
A) a stock market crash
B) a reduction in raw material prices
C) a decrease in real interest rates
D) an increase in the expected rate of inflation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If the U.S. aggregate price level falls:
A) the purchasing power of wealth declines.
B) net exports rise.
C) interest rates go up.
D) the aggregate demand curve shifts to the right.
A) the purchasing power of wealth declines.
B) net exports rise.
C) interest rates go up.
D) the aggregate demand curve shifts to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A change in _____ will cause a change in the quantity demanded of real GDP.
A) consumer spending
B) investment
C) the price level
D) imports
A) consumer spending
B) investment
C) the price level
D) imports

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The Potbelly Pothole Company is undertaking some investments in its plant. Suppose interest rates fall and new technologies increase the return on its investment. What is likely to happen?
A) The company's demand for investments will fall.
B) There will be no change in the company's demand for investments.
C) The company's demand for investments will first fall as interest rates fall and then rise as technology improves.
D) The company's demand for investments will rise.
A) The company's demand for investments will fall.
B) There will be no change in the company's demand for investments.
C) The company's demand for investments will first fall as interest rates fall and then rise as technology improves.
D) The company's demand for investments will rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
(Figure: Aggregate Demand Shift) 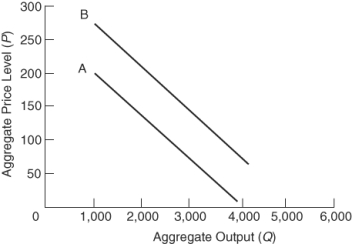 Which of the following may be an explanation for the shift in aggregate demand from line A to line B?
Which of the following may be an explanation for the shift in aggregate demand from line A to line B?
A) Prices fall and increase real wealth.
B) Consumer confidence declines and consumption spending falls.
C) Goods and services become less competitive and exports fall.
D) Interest rates fall and boost investments.
 Which of the following may be an explanation for the shift in aggregate demand from line A to line B?
Which of the following may be an explanation for the shift in aggregate demand from line A to line B?A) Prices fall and increase real wealth.
B) Consumer confidence declines and consumption spending falls.
C) Goods and services become less competitive and exports fall.
D) Interest rates fall and boost investments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The aggregate demand curve:
A) is upward sloping because a higher price level is necessary to make production profitable as production costs rise.
B) is downward sloping because production costs decline as real GDP increases.
C) shows the amount of expenditures required to induce the production of each possible level of real GDP.
D) shows the amount of real GDP that will be demanded at each possible price level.
A) is upward sloping because a higher price level is necessary to make production profitable as production costs rise.
B) is downward sloping because production costs decline as real GDP increases.
C) shows the amount of expenditures required to induce the production of each possible level of real GDP.
D) shows the amount of real GDP that will be demanded at each possible price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Other things equal, when the U.S. aggregate price level falls, U.S. exports _____ and U.S. imports _____.
A) fall; rise
B) fall; fall
C) rise; fall
D) rise; rise
A) fall; rise
B) fall; fall
C) rise; fall
D) rise; rise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
(Figure: Predicting Aggregate Demand Shifts) Which of the following would shift the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2? 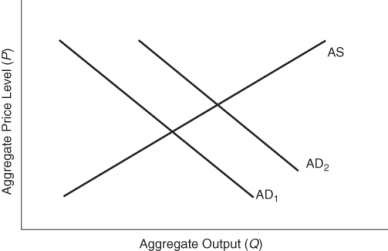
A) a tax increase
B) a decrease in interest rates
C) a decrease in government purchases
D) a worsening of consumer expectations about the future

A) a tax increase
B) a decrease in interest rates
C) a decrease in government purchases
D) a worsening of consumer expectations about the future

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If the U.S. aggregate price level rises:
A) net exports will also rise.
B) interest rates will decline.
C) the aggregate demand curve will shift to the left.
D) the purchasing power of wealth will decrease.
A) net exports will also rise.
B) interest rates will decline.
C) the aggregate demand curve will shift to the left.
D) the purchasing power of wealth will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following events will NOT cause the aggregate demand curve to shift?
A) Businesses are optimistic about the economy, investing heavily in new equipment.
B) Consumers' wealth declines because of a drop in the stock market.
C) A rise in the aggregate price level causes a decline in exports.
D) Governments increase spending on national security in the wake of terrorist attacks.
A) Businesses are optimistic about the economy, investing heavily in new equipment.
B) Consumers' wealth declines because of a drop in the stock market.
C) A rise in the aggregate price level causes a decline in exports.
D) Governments increase spending on national security in the wake of terrorist attacks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
(Figure: Aggregate Demand Shift) 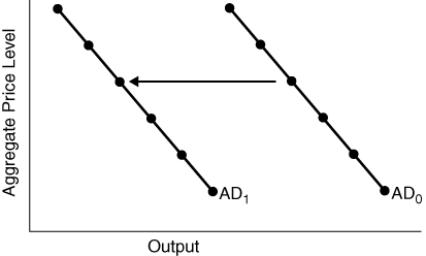 The shift in aggregate demand depicted may be due to a(n):
The shift in aggregate demand depicted may be due to a(n):
A) increase in consumer confidence.
B) decrease in interest rates.
C) increase in income taxes.
D) increase in exports.
 The shift in aggregate demand depicted may be due to a(n):
The shift in aggregate demand depicted may be due to a(n):A) increase in consumer confidence.
B) decrease in interest rates.
C) increase in income taxes.
D) increase in exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
High family debt:
A) reduces the tendency to consume.
B) encourages the tendency to spend.
C) is illegal.
D) is a prime predictor of impending inflation.
A) reduces the tendency to consume.
B) encourages the tendency to spend.
C) is illegal.
D) is a prime predictor of impending inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
_____ taxes and _____ interest rates in the United States, along with _____ incomes in other countries, will shift the U. S. aggregate demand curve to the right.
A) Decreasing; rising; rising
B) Increasing; falling; rising
C) Decreasing; falling; rising
D) Decreasing; falling; falling
A) Decreasing; rising; rising
B) Increasing; falling; rising
C) Decreasing; falling; rising
D) Decreasing; falling; falling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
_____ in wealth and _____ in government spending, along with a(n) _____ of the dollar, will shift the U.S. aggregate demand curve to the left.
A) Decreases; increases; appreciation
B) Increases; decreases; appreciation
C) Decreases; decreases; depreciation
D) Decreases; decreases; appreciation
A) Decreases; increases; appreciation
B) Increases; decreases; appreciation
C) Decreases; decreases; depreciation
D) Decreases; decreases; appreciation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Consumption would decrease and the aggregate demand curve would shift to the:
A) right if taxes increased.
B) right if taxes decreased.
C) left if taxes increased.
D) left if taxes decreased.
A) right if taxes increased.
B) right if taxes decreased.
C) left if taxes increased.
D) left if taxes decreased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following factors will cause the aggregate demand curve to shift to the left?
A) a rise in consumer confidence
B) a fall in excess capacity at businesses
C) an increase in foreign income
D) the appreciation of the dollar
A) a rise in consumer confidence
B) a fall in excess capacity at businesses
C) an increase in foreign income
D) the appreciation of the dollar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following factors is NOT a component of aggregate demand?
A) consumption
B) investment
C) income
D) net exports
A) consumption
B) investment
C) income
D) net exports

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Consumer spending is NOT affected by:
A) wealth.
B) consumer confidence.
C) taxes.
D) inventories.
A) wealth.
B) consumer confidence.
C) taxes.
D) inventories.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If the pound sterling appreciates against the U.S. dollar, England buys _____ U.S. goods, causing the U.S. aggregate demand curve to shift to the _____.
A) more; right
B) more; left
C) fewer; left
D) fewer; right
A) more; right
B) more; left
C) fewer; left
D) fewer; right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Suppose the government raises income taxes, so consumers have less take-home pay. This policy action will cause a(n):
A) increase in aggregate demand.
B) decrease in aggregate demand.
C) increase in short-run aggregate supply.
D) decrease in short-run aggregate supply.
A) increase in aggregate demand.
B) decrease in aggregate demand.
C) increase in short-run aggregate supply.
D) decrease in short-run aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If both consumers and businesses are pessimistic about the future of the economy:
A) there is a movement up along the aggregate demand curve.
B) the aggregate demand curve shifts to the left.
C) there is a movement down along the aggregate demand curve.
D) the aggregate demand curve shifts to the right.
A) there is a movement up along the aggregate demand curve.
B) the aggregate demand curve shifts to the left.
C) there is a movement down along the aggregate demand curve.
D) the aggregate demand curve shifts to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
An increase in the incomes of the countries that purchase U.S.-made products will cause a(n) _____ in the _____ U.S.-made products.
A) decrease; aggregate demand for
B) increase; short-run aggregate supply of
C) increase; aggregate demand for
D) decrease; short-run aggregate supply of
A) decrease; aggregate demand for
B) increase; short-run aggregate supply of
C) increase; aggregate demand for
D) decrease; short-run aggregate supply of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following events will shift the aggregate demand curve to the right?
A) a catastrophic hurricane hitting the northeastern United States
B) an increase in household debt
C) a decrease in taxes
D) a decrease in military spending
A) a catastrophic hurricane hitting the northeastern United States
B) an increase in household debt
C) a decrease in taxes
D) a decrease in military spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
(Figure: Predicting Aggregate Demand Shifts) Which of the following would shift the aggregate demand curve from AD2 to AD1? 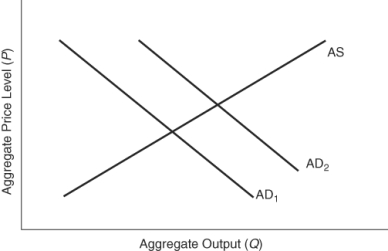
A) a tax cut
B) an increase in interest rates
C) an increase in government purchases
D) an improvement in consumer expectations about the future

A) a tax cut
B) an increase in interest rates
C) an increase in government purchases
D) an improvement in consumer expectations about the future

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following factors will cause the aggregate demand curve to shift to the right?
A) reduction in the aggregate price level
B) reduction in personal income taxes
C) increase in interest rates
D) decrease in foreign income
A) reduction in the aggregate price level
B) reduction in personal income taxes
C) increase in interest rates
D) decrease in foreign income

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following events will shift the aggregate demand curve to the right?
A) a decrease in exports
B) an increase in imports
C) a rise in the interest rate
D) a new government program to eliminate poverty
A) a decrease in exports
B) an increase in imports
C) a rise in the interest rate
D) a new government program to eliminate poverty

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 284 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



