Deck 14: Macroeconomic Policy: Challenges in a Global Economy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/265
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Macroeconomic Policy: Challenges in a Global Economy
1
One of the trigger points for the financial crisis of 2007-2009 was when:
A) interest rates on adjustable-rate mortgages were reset at a higher level.
B) foreigners started to sell off their holdings of U.S. financial instruments.
C) the Federal Reserve started to raise short-term interest rates.
D) the federal government started to engage in deficit spending.
A) interest rates on adjustable-rate mortgages were reset at a higher level.
B) foreigners started to sell off their holdings of U.S. financial instruments.
C) the Federal Reserve started to raise short-term interest rates.
D) the federal government started to engage in deficit spending.
A
2
Some analysts blame the financial crisis of 2007-2009 on Federal Reserve policy. They argue that:
A) a restrictive policy lowered aggregate demand and GDP.
B) low interest rates encouraged excessive mortgage borrowing, leading to the housing bubble.
C) the Fed securitized the mortgages into collateralized debt obligations and encouraged excessive risk taking.
D) did not adequately regulate the mortgage market's credit standards for issuing loans as required by the Federal Reserve Act.
A) a restrictive policy lowered aggregate demand and GDP.
B) low interest rates encouraged excessive mortgage borrowing, leading to the housing bubble.
C) the Fed securitized the mortgages into collateralized debt obligations and encouraged excessive risk taking.
D) did not adequately regulate the mortgage market's credit standards for issuing loans as required by the Federal Reserve Act.
B
3
Adaptive expectations is a _____-looking model, and rational expectations is a _____-looking model.
A) forward; forward
B) forward; backward
C) backward; forward
D) backward; backward
A) forward; forward
B) forward; backward
C) backward; forward
D) backward; backward
C
4
Which of these is a major contributor to "jobless recoveries"?
A) a sharp decline in productivity
B) firms using fewer part-time and temporary employees
C) an increase in offshoring by major corporations
D) All of these are major contributors to jobless recoveries.
A) a sharp decline in productivity
B) firms using fewer part-time and temporary employees
C) an increase in offshoring by major corporations
D) All of these are major contributors to jobless recoveries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
According to the rational expectations model, how would an announcement of expansionary monetary policy affect aggregate output?
A) It would have no effect on aggregate output.
B) It would decrease aggregate output.
C) It would increase aggregate output in the short run.
D) It would increase aggregate output in both the short run and the long run.
A) It would have no effect on aggregate output.
B) It would decrease aggregate output.
C) It would increase aggregate output in the short run.
D) It would increase aggregate output in both the short run and the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of these is a financial institution that sold credit default swaps insuring investors against securities defaults prior to the financial crisis in 2008?
A) Bear Stearns
B) Lehman Brothers
C) American International Group (AIG)
D) TARP
A) Bear Stearns
B) Lehman Brothers
C) American International Group (AIG)
D) TARP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Adjustable-rate mortgages are attractive to many homebuyers because these mortgages start out with a _____ interest rate and then _____ in later years.
A) low; adjust upward
B) low; stay the same
C) high; stay the same
D) high; adjust upward
A) low; adjust upward
B) low; stay the same
C) high; stay the same
D) high; adjust upward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If inflation is 3% but wages rise by 5% and there are no additional inflationary expectations, what is the rate of increase in labor productivity?
A) 2%
B) 3%
C) 5%
D) 8%
A) 2%
B) 3%
C) 5%
D) 8%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
According to the Phillips curve, a rise in inflation would correspond to _____ while a rise in unemployment would correspond to _____.
A) an increase in unemployment; an increase in inflation
B) a decrease in unemployment; an increase in inflation
C) an increase in unemployment; a decrease in inflation
D) a decrease in unemployment; a decrease in inflation
A) an increase in unemployment; an increase in inflation
B) a decrease in unemployment; an increase in inflation
C) an increase in unemployment; a decrease in inflation
D) a decrease in unemployment; a decrease in inflation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If an account valued at $1,000 is leveraged 5:1, a 10% drop in the value of invested assets would cause the value of the account to decrease by:
A) $20.
B) $100.
C) $500.
D) $1,000.
A) $20.
B) $100.
C) $500.
D) $1,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In the slow economic recovery following the last financial crisis, which of these was NOT a major concern affecting the U.S. economy?
A) very high short-term inflation
B) the existence of a jobless recovery
C) very slow economic growth
D) a rapidly rising national debt
A) very high short-term inflation
B) the existence of a jobless recovery
C) very slow economic growth
D) a rapidly rising national debt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Combating stagflation generally requires policymakers to _____ in order to reduce inflationary expectations.
A) increase aggregate demand
B) decrease aggregate demand
C) increase short-run aggregate supply
D) decrease short-run aggregate supply
A) increase aggregate demand
B) decrease aggregate demand
C) increase short-run aggregate supply
D) decrease short-run aggregate supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of these expenses are NOT fully reflected in statistics on the current national debt?
A) the cost of health care
B) the cost of Social Security
C) the cost of both health care and Social Security
D) neither the cost of health care nor the cost of Social Security
A) the cost of health care
B) the cost of Social Security
C) the cost of both health care and Social Security
D) neither the cost of health care nor the cost of Social Security

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The cost of financing the national debt (in terms of average interest rate paid on the debt) has generally _____ over the last 30 years.
A) risen
B) fallen
C) stayed the same
D) fluctuated wildly
A) risen
B) fallen
C) stayed the same
D) fluctuated wildly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
New oversight on financial firms will probably include:
A) lower capital requirements.
B) fewer restrictions on leverage.
C) higher returns on equity.
D) much tighter regulations.
A) lower capital requirements.
B) fewer restrictions on leverage.
C) higher returns on equity.
D) much tighter regulations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Both _____ on credit by households and _____ interest rates set in motion the events that led to the 2007-2009 financial crisis.
A) overspending; high
B) underspending; high
C) underspending; low
D) overspending; low
A) overspending; high
B) underspending; high
C) underspending; low
D) overspending; low

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of these is NOT a major effect of globalization?
A) increased international trade
B) increased global movement of capital and labor
C) an increase in offshoring to countries with lower input costs
D) an increase in the growth rates of developed countries compared to developing countries
A) increased international trade
B) increased global movement of capital and labor
C) an increase in offshoring to countries with lower input costs
D) an increase in the growth rates of developed countries compared to developing countries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of these was NOT a response by the government to mitigate the effects of the financial crisis?
A) It made large loans to the U.S. automobile industry.
B) It lent over $100 billion to Lehman Brothers to keep it from bankruptcy.
C) It engaged in quantitative easing programs to remove risky assets from bank balance sheets.
D) It passed a very large stimulus package to boost aggregate demand.
A) It made large loans to the U.S. automobile industry.
B) It lent over $100 billion to Lehman Brothers to keep it from bankruptcy.
C) It engaged in quantitative easing programs to remove risky assets from bank balance sheets.
D) It passed a very large stimulus package to boost aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of these did NOT contribute significantly to the financial crisis of 2008?
A) bond rating agencies assigning very low ratings to mortgage-backed securities
B) weak enforcement of lending standards that resulted in many risky loans
C) a large rise in home foreclosures
D) excessive leveraging and issuance of credit default swaps
A) bond rating agencies assigning very low ratings to mortgage-backed securities
B) weak enforcement of lending standards that resulted in many risky loans
C) a large rise in home foreclosures
D) excessive leveraging and issuance of credit default swaps

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Subprime mortgages were loans made to borrowers with _____ credit and who, as a result, were charged _____ interest rates.
A) excellent; low
B) excellent; high
C) poor; low
D) poor; high
A) excellent; low
B) excellent; high
C) poor; low
D) poor; high

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The 2007-2009 recession can be shown as a combination of a(n) _____ in aggregate demand and _____ in the short-run aggregate supply.
A) decline; an increase
B) increase; an increase
C) decrease; a decrease
D) decline; no change
A) decline; an increase
B) increase; an increase
C) decrease; a decrease
D) decline; no change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The 2007-2009 recession was caused by a(n):
A) increase in demand following a rapid increase in the money supply.
B) drop in aggregate supply caused by a slowdown in productivity growth.
C) decrease in supply caused by an increase in oil prices.
D) decrease in aggregate demand triggered by a financial crisis.
A) increase in demand following a rapid increase in the money supply.
B) drop in aggregate supply caused by a slowdown in productivity growth.
C) decrease in supply caused by an increase in oil prices.
D) decrease in aggregate demand triggered by a financial crisis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
During the period 2008-2009, _____ million people lost their jobs.
A) 3
B) 4
C) 7
D) 12
A) 3
B) 4
C) 7
D) 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A financial instrument backed by a collection of mortgages is called a(n):
A) adjustable-rate mortgage.
B) collateralized debt obligation.
C) credit default swap.
D) collateralized mortgage obligation.
A) adjustable-rate mortgage.
B) collateralized debt obligation.
C) credit default swap.
D) collateralized mortgage obligation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Deflation can be a problem because it:
A) leads to higher wages.
B) makes it more difficult to pay off debt.
C) can easily become hyperinflation.
D) increases interest rates.
A) leads to higher wages.
B) makes it more difficult to pay off debt.
C) can easily become hyperinflation.
D) increases interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Some argue that the financial crisis of 2007-2009 was caused by a poor understanding of risks in the economy. One reason for that thinking is that:
A) credit card companies did not disclose who defaulted on their loans.
B) banks' secrecy laws prevented them from reporting which homeowners were behind in their mortgage payments.
C) mortgage brokers did not use the Internet to check on default rates.
D) some bond rating agencies' ratings did not disclose the true extent of the riskiness of mortgage-backed assets.
A) credit card companies did not disclose who defaulted on their loans.
B) banks' secrecy laws prevented them from reporting which homeowners were behind in their mortgage payments.
C) mortgage brokers did not use the Internet to check on default rates.
D) some bond rating agencies' ratings did not disclose the true extent of the riskiness of mortgage-backed assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What types of loans are NOT typically included in collateralized debt obligations?
A) subprime mortgages
B) home equity loans
C) adjustable-rate mortgages
D) student loans
A) subprime mortgages
B) home equity loans
C) adjustable-rate mortgages
D) student loans

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If the interest rate on a mortgage changes with the market interest rate, then the mortgage is:
A) a 30-year fixed mortgage.
B) a collateralized debt obligation.
C) an adjustable-rate mortgage.
D) a credit default swap.
A) a 30-year fixed mortgage.
B) a collateralized debt obligation.
C) an adjustable-rate mortgage.
D) a credit default swap.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The difference between Bear Stearns and Lehman Brothers was that:
A) the Fed bailed out Bear Stearns and did not bail out Lehman Brothers.
B) the Fed bailed out Lehman Brothers and did not bail out Bear Stearns.
C) Lehman Brothers was an investment bank and Bear Stearns was a commercial bank.
D) Bear Stearns was a commercial bank and Lehman Brothers was an investment bank.
A) the Fed bailed out Bear Stearns and did not bail out Lehman Brothers.
B) the Fed bailed out Lehman Brothers and did not bail out Bear Stearns.
C) Lehman Brothers was an investment bank and Bear Stearns was a commercial bank.
D) Bear Stearns was a commercial bank and Lehman Brothers was an investment bank.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Adjustable-rate mortgages:
A) are mortgages whose interest rates can change.
B) are mortgages whose interest rates cannot change.
C) usually have interest rates higher than market rates during the first year.
D) are more attractive when interest rates on fixed mortgages fall.
A) are mortgages whose interest rates can change.
B) are mortgages whose interest rates cannot change.
C) usually have interest rates higher than market rates during the first year.
D) are more attractive when interest rates on fixed mortgages fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The recession of 2007-2009 was:
A) deeper than the recessions of 1990 and 2001.
B) longer and more severe than the Great Depression.
C) one of the shortest on record.
D) dissimilar to the Great Depression in that the financial sector was not involved.
A) deeper than the recessions of 1990 and 2001.
B) longer and more severe than the Great Depression.
C) one of the shortest on record.
D) dissimilar to the Great Depression in that the financial sector was not involved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A leveraged account:
A) magnifies both gains and losses.
B) magnifies gains and reduces losses.
C) reduces gains and magnifies losses.
D) reduces both gains and losses.
A) magnifies both gains and losses.
B) magnifies gains and reduces losses.
C) reduces gains and magnifies losses.
D) reduces both gains and losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A credit default swap:
A) is essentially the same as an adjustable-rate mortgage.
B) is essentially the same as insurance against a default.
C) prevents investors from defaulting on a swap.
D) allows investors to trade one bad stock for another.
A) is essentially the same as an adjustable-rate mortgage.
B) is essentially the same as insurance against a default.
C) prevents investors from defaulting on a swap.
D) allows investors to trade one bad stock for another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Using real GDP and employment growth relative to the peak of the business cycle, the 2007-2009 recession, as compared to previous two recessions, in 1990 and 2001:
A) was deeper.
B) was less severe.
C) was shorter.
D) was shorter but more severe.
A) was deeper.
B) was less severe.
C) was shorter.
D) was shorter but more severe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which action was NOT taken in response to the financial crisis?
A) a bailout of Lehman Brothers
B) purchases of over $1 trillion in mortgage-backed securities by the Federal Reserve
C) an increase in the FDIC's guarantee on deposits from $100,000 to $250,000 per account
D) over $100 billion in loans by the Fed to AIG
A) a bailout of Lehman Brothers
B) purchases of over $1 trillion in mortgage-backed securities by the Federal Reserve
C) an increase in the FDIC's guarantee on deposits from $100,000 to $250,000 per account
D) over $100 billion in loans by the Fed to AIG

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act, signed into law in February 2009, was designed to shift aggregate:
A) demand rightward.
B) demand leftward.
C) supply rightward.
D) supply leftward.
A) demand rightward.
B) demand leftward.
C) supply rightward.
D) supply leftward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Deflation is a problem because:
A) the rate of inflation, though still positive, decreases.
B) the dollar loses purchasing power.
C) debt becomes easier to pay off.
D) it takes more purchasing power to make interest payments or pay off debt.
A) the rate of inflation, though still positive, decreases.
B) the dollar loses purchasing power.
C) debt becomes easier to pay off.
D) it takes more purchasing power to make interest payments or pay off debt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
One of the key factors leading to the Great Recession was:
A) a worldwide savings glut.
B) a shortage of housing in the United States.
C) a surplus in the federal budget.
D) the war in Iraq.
A) a worldwide savings glut.
B) a shortage of housing in the United States.
C) a surplus in the federal budget.
D) the war in Iraq.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of these was NOT a factor leading to the financial crisis of 2007-2009?
A) Low interest rates encouraged a housing boom.
B) Policymakers underestimated the level of risk inherent in the mortgage market.
C) The public lacked faith in the ability of the U.S. Treasury to pay government bonds.
D) Investors borrowed heavily to purchase securitized mortgages.
A) Low interest rates encouraged a housing boom.
B) Policymakers underestimated the level of risk inherent in the mortgage market.
C) The public lacked faith in the ability of the U.S. Treasury to pay government bonds.
D) Investors borrowed heavily to purchase securitized mortgages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The United States underwent _____ throughout most of 2009.
A) deflation
B) disinflation
C) moderate inflation
D) stable prices
A) deflation
B) disinflation
C) moderate inflation
D) stable prices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which company did the Federal Reserve and the Treasury allow to fail to send a message to the financial markets about the costs of risky behavior?
A) AIG
B) Chrysler
C) Ford
D) Lehman Brothers
A) AIG
B) Chrysler
C) Ford
D) Lehman Brothers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The original Phillips curve showed a _____ relationship between _____ and unemployment rates.
A) negative; price inflation
B) negative; money wage rates
C) positive; price inflation
D) positive; money wage rates
A) negative; price inflation
B) negative; money wage rates
C) positive; price inflation
D) positive; money wage rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
(Figure: Determining Curves) The curve in the graph represents a: 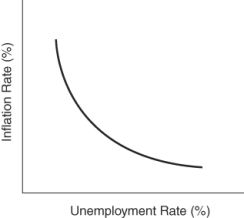
A) demand curve.
B) Phillips curve.
C) labor demand curve.
D) production possibilities curve.

A) demand curve.
B) Phillips curve.
C) labor demand curve.
D) production possibilities curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of these is(are) true? I. A leveraged account magnifies both gains and losses.
II) The risk of highly leveraged investments is that a small decrease in price can wipe out one's account.
III) Subprime mortgage packages were seen as low-risk investments, leading many investors to borrow money at the low prevailing interest rates to purchase greater quantities.
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and II
D) I, II, and III
II) The risk of highly leveraged investments is that a small decrease in price can wipe out one's account.
III) Subprime mortgage packages were seen as low-risk investments, leading many investors to borrow money at the low prevailing interest rates to purchase greater quantities.
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and II
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Assume that nominal wages increase 10% and productivity increases 20%. Using the equation for the Phillips curve, inflation is:
A) 10%.
B) 20%.
C) 30%.
D) -10%.
A) 10%.
B) 20%.
C) 30%.
D) -10%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The natural rate of unemployment is:
A) the rate that produces worker revolutions.
B) zero unemployment.
C) the rate at which there are no inflationary pressures on the economy.
D) the equilibrium to which the economy naturally tends.
A) the rate that produces worker revolutions.
B) zero unemployment.
C) the rate at which there are no inflationary pressures on the economy.
D) the equilibrium to which the economy naturally tends.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of these is(are) true? I. The 18-month economic downturn that lasted from December 2007 to July 2009 was dubbed the Great Depression.
II) The economic recovery that took place after the 2007-2009 economic downturn was slow, requiring many years for economic indicators to return to their prerecession levels.
III) The housing boom of 2003 to 2007 did not contribute to the 2007-2009 economic downturn.
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and II
D) II and III
II) The economic recovery that took place after the 2007-2009 economic downturn was slow, requiring many years for economic indicators to return to their prerecession levels.
III) The housing boom of 2003 to 2007 did not contribute to the 2007-2009 economic downturn.
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and II
D) II and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The graph that shows the tradeoff between inflation and money wages is called the:
A) misery index.
B) employment line.
C) Phillips curve.
D) minimization curve.
A) misery index.
B) employment line.
C) Phillips curve.
D) minimization curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
When labor demand rises, unemployment _____ and wages _____.
A) falls; rise
B) falls; decline
C) rises; decline
D) rises; rise
A) falls; rise
B) falls; decline
C) rises; decline
D) rises; rise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
According to the equation for the Phillips curve, if nominal wages increase by 3% and productivity increases 2%, then inflation will change by:
A) -5%.
B) -1%.
C) 1%.
D) 5%.
A) -5%.
B) -1%.
C) 1%.
D) 5%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The decrease in short-run aggregate supply during the Great Recession was caused by:
A) excessive consumer debt.
B) miscalculation of the risk of subprime mortgages.
C) the worldwide glut of savings.
D) businesses that reduced their production capacity by closing plants and laying off workers.
A) excessive consumer debt.
B) miscalculation of the risk of subprime mortgages.
C) the worldwide glut of savings.
D) businesses that reduced their production capacity by closing plants and laying off workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Collateralized debt obligations:
A) are mortgages whose interest rates can change.
B) are financial instruments backed by a collection of mortgages.
C) are financial instruments that provide insurance against a default.
D) are home loans made to borrowers with poor credit.
A) are mortgages whose interest rates can change.
B) are financial instruments backed by a collection of mortgages.
C) are financial instruments that provide insurance against a default.
D) are home loans made to borrowers with poor credit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
One implication of the Phillips curve when it is unable to shift in the short run, is that:
A) fiscal and monetary policies have no impact on the economy.
B) the economy is in a liquidity trap.
C) policymakers face a tradeoff between low unemployment and low inflation.
D) fiscal policy is more effective than monetary policy.
A) fiscal and monetary policies have no impact on the economy.
B) the economy is in a liquidity trap.
C) policymakers face a tradeoff between low unemployment and low inflation.
D) fiscal policy is more effective than monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The Federal Reserve undertook _____ rounds of quantitative easing (QE) after short-term interest rates were effectively lowered to 0%. The total value of all assets purchased over all rounds was _____.
A) 1; $1,425 billion
B) 2; $600 billion
C) 3; $3,725 billion
D) 4; $1,700 billion
A) 1; $1,425 billion
B) 2; $600 billion
C) 3; $3,725 billion
D) 4; $1,700 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
According to the equation for the Phillips curve, if nominal wages rise by 8% and labor productivity rises by 5%, then we can expect:
A) prices to drop by 3%.
B) no change in prices.
C) prices to rise by 3%.
D) prices to drop by 5%.
A) prices to drop by 3%.
B) no change in prices.
C) prices to rise by 3%.
D) prices to drop by 5%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of these was a change in banks' lending practices that contributed to a housing bubble?
A) Lenders began to require borrowers to provide proof of income.
B) Banks began to originate subprime loans they did not intend to keep.
C) Banks developed fixed-rate mortgage loans.
D) Banks began to rigorously check borrowers' credit quality.
A) Lenders began to require borrowers to provide proof of income.
B) Banks began to originate subprime loans they did not intend to keep.
C) Banks developed fixed-rate mortgage loans.
D) Banks began to rigorously check borrowers' credit quality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The Phillips curve:
A) was developed by economists at Phillips 66.
B) shows the effectiveness of government policy.
C) is used by economists to determine optimal oil prices.
D) shows the relationship between unemployment and inflation.
A) was developed by economists at Phillips 66.
B) shows the effectiveness of government policy.
C) is used by economists to determine optimal oil prices.
D) shows the relationship between unemployment and inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
One of the problems with deflation is that it:
A) increases the real value of existing debt.
B) decreases the real value of existing debt.
C) shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right.
D) shifts the aggregate supply curve to the right.
A) increases the real value of existing debt.
B) decreases the real value of existing debt.
C) shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right.
D) shifts the aggregate supply curve to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Credit default swaps:
A) are a type of collateralized debt obligation.
B) are a type of insurance against defaults.
C) were accurately priced before the housing market collapsed.
D) made AIG the most profitable company in the United States.
A) are a type of collateralized debt obligation.
B) are a type of insurance against defaults.
C) were accurately priced before the housing market collapsed.
D) made AIG the most profitable company in the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which statement about adjustable-rate mortgages is true?
A) Interest rates cannot change over the life of the mortgage.
B) Adjustable-rate mortgages are especially attractive to high-income buyers.
C) Adjustable-rate mortgages usually have interest rates lower than market rates during their first year.
D) Adjustable-rate mortgages are more attractive when interest rates on fixed mortgages fall.
A) Interest rates cannot change over the life of the mortgage.
B) Adjustable-rate mortgages are especially attractive to high-income buyers.
C) Adjustable-rate mortgages usually have interest rates lower than market rates during their first year.
D) Adjustable-rate mortgages are more attractive when interest rates on fixed mortgages fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Using the equation for the Phillips curve, suppose that nominal wages increased by 5% and the inflation rate was 3%. What was the rate of increase in labor productivity?
A) 2%
B) 5%
C) 8%
D) 15%
A) 2%
B) 5%
C) 8%
D) 15%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
(Figure: Natural Rate of Unemployment) The natural rate of unemployment: 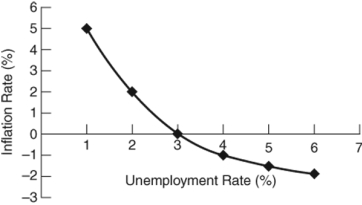
A) is zero.
B) is 3%.
C) is 6%.
D) cannot be determined.

A) is zero.
B) is 3%.
C) is 6%.
D) cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
According to the equation for the Phillips curve, if wages rise by 2%, inflation:
A) must also rise by 2%.
B) will be zero if productivity increases by 2%.
C) will be zero if productivity increases by more than 2%.
D) will be zero if productivity falls by 2%.
A) must also rise by 2%.
B) will be zero if productivity increases by 2%.
C) will be zero if productivity increases by more than 2%.
D) will be zero if productivity falls by 2%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
According to the Phillips curve analysis, the way to solve inflation is to _____ unemployment or _____.
A) increase; increase productivity
B) increase; decrease productivity
C) decrease; increase the money supply
D) increase; increase the money supply
A) increase; increase productivity
B) increase; decrease productivity
C) decrease; increase the money supply
D) increase; increase the money supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If policymakers attempt to reduce the rate of unemployment below its natural rate:
A) the federal deficit will rise.
B) interest rates will rise.
C) they run the risk of inflation.
D) worker productivity will drop.
A) the federal deficit will rise.
B) interest rates will rise.
C) they run the risk of inflation.
D) worker productivity will drop.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In effect, the Phillips curve framework implies that to fight inflationary expectations, policymakers must:
A) rapidly increase aggregate demand.
B) cause unemployment.
C) decrease aggregate supply.
D) increase exports.
A) rapidly increase aggregate demand.
B) cause unemployment.
C) decrease aggregate supply.
D) increase exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
_____ measure the rate of inflation expected by workers for any given period.
A) Rational expectations
B) Natural expectations
C) Wage expectations
D) Inflationary expectations
A) Rational expectations
B) Natural expectations
C) Wage expectations
D) Inflationary expectations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
An increase in worker productivity would cause the Phillips curve to:
A) shift to the left.
B) collapse about its origin.
C) shift to the right.
D) become linear.
A) shift to the left.
B) collapse about its origin.
C) shift to the right.
D) become linear.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The Phillips curve of the 1960s for the United States:
A) showed stagflation in the U.S. economy.
B) suggested to policymakers that they could keep unemployment low by accepting moderate inflation.
C) indicated that to keep unemployment low, policymakers had to accept double-digit rates of inflation.
D) was nearly a vertical line.
A) showed stagflation in the U.S. economy.
B) suggested to policymakers that they could keep unemployment low by accepting moderate inflation.
C) indicated that to keep unemployment low, policymakers had to accept double-digit rates of inflation.
D) was nearly a vertical line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If policymakers use contractionary policy to reduce inflation, the unemployment rate will be:
A) higher.
B) below its natural rate.
C) above its natural rate.
D) at its natural rate.
A) higher.
B) below its natural rate.
C) above its natural rate.
D) at its natural rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
When the growth in productivity is _____ the rate of change in wages, inflation is _____, and the level of unemployment at that point is _____ the natural rate of unemployment.
A) greater than; positive; less than
B) less than; zero; greater than
C) equal to; zero; equal to
D) equal to; negative; less than
A) greater than; positive; less than
B) less than; zero; greater than
C) equal to; zero; equal to
D) equal to; negative; less than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
According to the equation for the Phillips curve, if nominal wages and labor productivity both rise by 3%:
A) unemployment rises by 3%.
B) unemployment falls by 3%.
C) unemployment is at its natural rate.
D) inflation is increasing.
A) unemployment rises by 3%.
B) unemployment falls by 3%.
C) unemployment is at its natural rate.
D) inflation is increasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
According to the equation for the Phillips curve, if wages increase by 5% and productivity decreases by 2%, then inflation will be:
A) -3%.
B) 3%.
C) 7%.
D) 2.5%.
A) -3%.
B) 3%.
C) 7%.
D) 2.5%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
According to the equation for the Phillips curve, inflation is zero when the increase in nominal wages is _____ the rate of increase in labor productivity.
A) greater than
B) less than
C) equal to
D) Inflation is always zero in the Phillips curve model.
A) greater than
B) less than
C) equal to
D) Inflation is always zero in the Phillips curve model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
_____ occurs when both inflation and unemployment increase over time.
A) Disinflation
B) Stagflation
C) Inflation
D) Deflation
A) Disinflation
B) Stagflation
C) Inflation
D) Deflation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
During the early 1970s, the Phillips curve:
A) shifted inward as inflation rates fell.
B) shifted outward as inflation rates rose.
C) showed a long-run tradeoff between inflation and unemployment.
D) showed that moderate inflation rates were needed to keep the unemployment rate low.
A) shifted inward as inflation rates fell.
B) shifted outward as inflation rates rose.
C) showed a long-run tradeoff between inflation and unemployment.
D) showed that moderate inflation rates were needed to keep the unemployment rate low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
(Figure: Policy Changes in the Short Run) To move the economy from point b to point a in the short run, Federal Reserve policymakers implement _____ monetary policy, thereby accepting _____ to reduce _____. 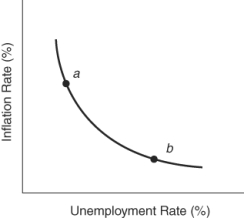
A) expansionary; more unemployment; the rate of inflation
B) contractionary ; a higher rate of inflation; unemployment
C) expansionary; a higher rate of inflation; unemployment
D) contractionary; more unemployment; the rate of inflation

A) expansionary; more unemployment; the rate of inflation
B) contractionary ; a higher rate of inflation; unemployment
C) expansionary; a higher rate of inflation; unemployment
D) contractionary; more unemployment; the rate of inflation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
According to the equation for the Phillips curve, if nominal wages and labor productivity both increase by 3%, then the inflation rate _____ and unemployment _____.
A) increases by 3%; falls
B) increases by 3%; rises
C) is zero; is at its natural rate
D) increases by 3%; is at its natural rate
A) increases by 3%; falls
B) increases by 3%; rises
C) is zero; is at its natural rate
D) increases by 3%; is at its natural rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
(Figure: Policy Changes in the Short Run) To move the economy from point a to point b in the short run, policymakers implement _____ monetary policy, thereby accepting _____ to reduce _____. 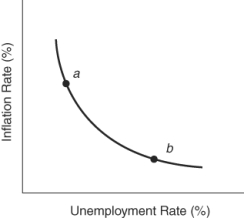
A) expansionary; more unemployment; the rate of inflation
B) contractionary; a higher rate of inflation; unemployment
C) expansionary; a higher rate of inflation; unemployment
D) contractionary; more unemployment; the rate of inflation

A) expansionary; more unemployment; the rate of inflation
B) contractionary; a higher rate of inflation; unemployment
C) expansionary; a higher rate of inflation; unemployment
D) contractionary; more unemployment; the rate of inflation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
According to the equation for the Phillips curve, if wages increase by 3% and productivity increases by 5%, then inflation will be:
A) -8%.
B) -2%.
C) 2%.
D) 8%.
A) -8%.
B) -2%.
C) 2%.
D) 8%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 265 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



