Deck 10: Fiscal Policy and Debt
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/365
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Fiscal Policy and Debt
1
A shift of the long-run aggregate supply curve to the right suggests which of the following?
A) an increase in productivity
B) an increase in tax revenue
C) a decrease in the average standard of living
D) a decrease in economic growth
A) an increase in productivity
B) an increase in tax revenue
C) a decrease in the average standard of living
D) a decrease in economic growth
A
2
What did Arthur Laffer suggest President Reagan do in the 1980s?
A) increase corporate taxes
B) increase income taxes
C) increase welfare benefits
D) decrease income taxes
A) increase corporate taxes
B) increase income taxes
C) increase welfare benefits
D) decrease income taxes
D
3
Which of the following fiscal policies would least likely result in an increase in aggregate supply?
A) an increase in infrastructure spending
B) an increase in business regulations
C) an increase in grants to fund higher education
D) a reduction in marginal tax rates
A) an increase in infrastructure spending
B) an increase in business regulations
C) an increase in grants to fund higher education
D) a reduction in marginal tax rates
B
4
If an economy is in a recession, what would expansionary fiscal policy do?
A) shift AD to the right
B) shift AD to the left
C) shift SRAS to the right
D) shift SRAS to the left
A) shift AD to the right
B) shift AD to the left
C) shift SRAS to the right
D) shift SRAS to the left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is the one major category that separates national debt from public debt?
A) debt held by U.S. citizens
B) debt held by foreigners
C) debt held by U.S. banks
D) debt held by other government agencies
A) debt held by U.S. citizens
B) debt held by foreigners
C) debt held by U.S. banks
D) debt held by other government agencies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If the national debt is $55 million and this year's deficit is $5 million, what would the new national debt be?
A) $11 million
B) $50 million
C) 60 million
D) $275 million
A) $11 million
B) $50 million
C) 60 million
D) $275 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Automatic stabilizers have _____ effects during times of economic prosperity and _____ effects during times of economic downturn.
A) contractionary; contractionary
B) contractionary; expansionary
C) expansionary; contractionary
D) expansionary; expansionary
A) contractionary; contractionary
B) contractionary; expansionary
C) expansionary; contractionary
D) expansionary; expansionary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following statements do economists generally disagree on?
A) No tax revenues would be collected when average tax rates are 0%.
B) No tax revenues would be collected when average tax rates are 100%.
C) At very high average tax rates, increasing tax rates further would decrease tax revenues.
D) At an average tax rate of 50%, tax revenues are maximized for a government.
A) No tax revenues would be collected when average tax rates are 0%.
B) No tax revenues would be collected when average tax rates are 100%.
C) At very high average tax rates, increasing tax rates further would decrease tax revenues.
D) At an average tax rate of 50%, tax revenues are maximized for a government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is an example of an automatic stabilizer?
A) consumers spending more when the economy is strong
B) business laying off workers during a recession
C) unemployed workers claiming unemployment benefits during a recession
D) the government raising interest rates to reduce inflation
A) consumers spending more when the economy is strong
B) business laying off workers during a recession
C) unemployed workers claiming unemployment benefits during a recession
D) the government raising interest rates to reduce inflation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
All of the following programs are considered mandatory spending EXCEPT:
A) Social Security.
B) Medicare.
C) national defense.
D) interest on national debt.
A) Social Security.
B) Medicare.
C) national defense.
D) interest on national debt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is a form of U.S. public debt?
A) savings bonds
B) stocks
C) loans from relatives
D) private bank mortgages
A) savings bonds
B) stocks
C) loans from relatives
D) private bank mortgages

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If the ultimate goal of fiscal policy aimed at aggregate supply is achieved, what happens to the aggregate price level and aggregate output?
A) aggregate price level decreases; aggregate output decreases
B) aggregate price level increases; aggregate output increases
C) aggregate price level decreases; aggregate output increases
D) aggregate price level increases; aggregate output decreases
A) aggregate price level decreases; aggregate output decreases
B) aggregate price level increases; aggregate output increases
C) aggregate price level decreases; aggregate output increases
D) aggregate price level increases; aggregate output decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following requires the government to balance its budget over the business cycle?
A) annually balanced budget
B) cyclically balanced budget
C) biannually balanced budget
D) functional finance
A) annually balanced budget
B) cyclically balanced budget
C) biannually balanced budget
D) functional finance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The fact that it takes a very long time for Congress to debate and enact fiscal policies such as a tax cut for low-income households is an example of a(n):
A) information lag.
B) recognition lag.
C) decision lag.
D) implementation lag.
A) information lag.
B) recognition lag.
C) decision lag.
D) implementation lag.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Evidence has suggested that borrowing is _____ than taxation by politicians to finance fiscal policy spending, which has led to a(n) _____ of the federal government over the last few decades.
A) more favored; expansion
B) more favored; contraction
C) less favored; expansion
D) less favored; contraction
A) more favored; expansion
B) more favored; contraction
C) less favored; expansion
D) less favored; contraction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is a critical dilemma when implementing fiscal policy in reference to timing lags?
A) Fiscal policy requires a short and contentious legislative process.
B) Short-term variations in key indicators are common and present randomness in the data.
C) The information lag takes up too much time and is too costly.
D) The economy may already be in a recovery before fiscal policy is enacted.
A) Fiscal policy requires a short and contentious legislative process.
B) Short-term variations in key indicators are common and present randomness in the data.
C) The information lag takes up too much time and is too costly.
D) The economy may already be in a recovery before fiscal policy is enacted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If a government collects $550 billion in taxes and spends $700 billion, it would have a:
A) surplus of $150 billion.
B) surplus of $1,250 billion.
C) deficit of $150 billion.
D) deficit of $1,250 billion.
A) surplus of $150 billion.
B) surplus of $1,250 billion.
C) deficit of $150 billion.
D) deficit of $1,250 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Suppose the government collected $3.2 trillion in tax revenues and spent $3.8 trillion, and discretionary spending was $1.5 trillion. For the government to fully balance the budget this year, how much discretionary spending needs to be cut?
A) 10%
B) 20%
C) 30%
D) 40%
A) 10%
B) 20%
C) 30%
D) 40%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Reducing government spending, reducing transfer payments, or raising taxes describes which policy?
A) contractionary fiscal policy
B) expansionary fiscal policy
C) monetary policy
D) supply-side fiscal policy
A) contractionary fiscal policy
B) expansionary fiscal policy
C) monetary policy
D) supply-side fiscal policy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If the government raises taxes, what will this do to the AD curve?
A) AD shifts right.
B) AD shifts left.
C) AD would not shift.
D) AD would shift but in a random direction.
A) AD shifts right.
B) AD shifts left.
C) AD would not shift.
D) AD would shift but in a random direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
_____ are all examples of discretionary spending.
A) Social Security, interest on the national debt, and Medicare
B) National defense, income security, and veterans' benefits
C) National defense, Social Security, and veterans' benefits
D) Social Security, veterans' benefits, and Medicare
A) Social Security, interest on the national debt, and Medicare
B) National defense, income security, and veterans' benefits
C) National defense, Social Security, and veterans' benefits
D) Social Security, veterans' benefits, and Medicare

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
_____ government spending, _____ transfer payments, and _____ taxes are all examples of expansionary fiscal policy.
A) Increasing; increasing; lowering
B) Increasing; reducing; raising
C) Reducing; increasing; lowering
D) Reducing; increasing; raising
A) Increasing; increasing; lowering
B) Increasing; reducing; raising
C) Reducing; increasing; lowering
D) Reducing; increasing; raising

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which one of the following is a reason the crowding-out effect could be mitigated?
A) an increase in the saving rate
B) deficit spending used for public investment
C) an increase in consumer consumption
D) a decrease in tax revenues
A) an increase in the saving rate
B) deficit spending used for public investment
C) an increase in consumer consumption
D) a decrease in tax revenues

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
_____ are all examples of mandatory spending.
A) Social Security, interest on the national debt, and Medicare
B) National defense, income security, and veterans' benefits
C) National defense, Social Security, and veterans' benefits
D) Social Security, veterans' benefits, and Medicare
A) Social Security, interest on the national debt, and Medicare
B) National defense, income security, and veterans' benefits
C) National defense, Social Security, and veterans' benefits
D) Social Security, veterans' benefits, and Medicare

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
_____ policy involves adjusting government spending and tax policies to move the economy toward full employment, economic growth, and low inflation.
A) Goal-oriented fiscal
B) Classical economic
C) Monetary
D) Discretionary fiscal
A) Goal-oriented fiscal
B) Classical economic
C) Monetary
D) Discretionary fiscal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The portion of the national debt that is not held by the Federal Reserve and government agencies include:
A) only the internally held debt.
B) only the externally held debt.
C) neither the internally nor externally held debt.
D) both the internally and externally held debt.
A) only the internally held debt.
B) only the externally held debt.
C) neither the internally nor externally held debt.
D) both the internally and externally held debt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
_____ is the part of the budget that works its way through Congress each year; it includes programs such as national defense, transportation, Medicaid, and education.
A) Discretionary spending
B) Mandatory spending
C) Consumer spending
D) Contractionary spending
A) Discretionary spending
B) Mandatory spending
C) Consumer spending
D) Contractionary spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following statements regarding discretionary and mandatory spending is correct?
A) Discretionary spending is authorized by permanent laws.
B) Mandatory spending may act as an automatic stabilizing force in the macro economy.
C) Discretionary spending has steadily grown as a percentage of the federal budget since the 1960s.
D) Mandatory spending programs include national defense, income security, and education.
A) Discretionary spending is authorized by permanent laws.
B) Mandatory spending may act as an automatic stabilizing force in the macro economy.
C) Discretionary spending has steadily grown as a percentage of the federal budget since the 1960s.
D) Mandatory spending programs include national defense, income security, and education.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Federal spending that is authorized by permanent laws and does not go through the annual appropriation process is called _____ spending.
A) discretionary
B) mandatory
C) long-term
D) infrastructure
A) discretionary
B) mandatory
C) long-term
D) infrastructure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Social Security and Medicare are considered _____ liabilities and are expected to _____ over the next generation.
A) unfunded; rise
B) unfunded; fall
C) funded; rise
D) funded; fall
A) unfunded; rise
B) unfunded; fall
C) funded; rise
D) funded; fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When economists warn about the crowding-out effect, they are referring to:
A) when prices set too low lead to large crowds.
B) when a firm earns a high profit over the past month.
C) when banks run out of money to lend.
D) when government borrowing reduces private investment.
A) when prices set too low lead to large crowds.
B) when a firm earns a high profit over the past month.
C) when banks run out of money to lend.
D) when government borrowing reduces private investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
_____ government spending, _____ transfer payments, and _____ taxes are all examples of contractionary fiscal policy.
A) Reducing; increasing; raising
B) Reducing; reducing; raising
C) Reducing; reducing; reducing
D) Raising; increasing; raising
A) Reducing; increasing; raising
B) Reducing; reducing; raising
C) Reducing; reducing; reducing
D) Raising; increasing; raising

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The largest source of federal government revenues is:
A) corporate income taxes.
B) Social Security taxes.
C) individual income taxes.
D) excise and estate taxes.
A) corporate income taxes.
B) Social Security taxes.
C) individual income taxes.
D) excise and estate taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If the marginal propensity to consume is 0.9, by how much will $100 of government spending increase GDP?
A) $90
B) $100
C) $1,000
D) $900
A) $90
B) $100
C) $1,000
D) $900

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Mandatory spending comprises nearly _____ of the federal budget.
A) one-fourth
B) one-third
C) one-half
D) two-thirds
A) one-fourth
B) one-third
C) one-half
D) two-thirds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following categories is an example of discretionary spending?
A) Social Security
B) Medicare
C) food stamps
D) hurricane relief funds
A) Social Security
B) Medicare
C) food stamps
D) hurricane relief funds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which three U.S. presidents implemented well-known tax cuts designed to stimulate aggregate demand?
A) Bill Clinton, Ronald Reagan, and George H. W. Bush
B) John F. Kennedy, Ronald Reagan, and George W. Bush
C) John F. Kennedy, Ronald Reagan, and Bill Clinton
D) Bill Clinton, Ronald Reagan, and George W. Bush
A) Bill Clinton, Ronald Reagan, and George H. W. Bush
B) John F. Kennedy, Ronald Reagan, and George W. Bush
C) John F. Kennedy, Ronald Reagan, and Bill Clinton
D) Bill Clinton, Ronald Reagan, and George W. Bush

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which measure is NOT a channel through which the government can influence aggregate demand?
A) direct spending on goods and services
B) transfer payments to households and firms
C) taxes on households and firms
D) regulation on businesses
A) direct spending on goods and services
B) transfer payments to households and firms
C) taxes on households and firms
D) regulation on businesses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The most important measure in determining whether a country's national debt is a significant problem is:
A) the size of the debt in nominal terms.
B) the interest rate paid on the debt.
C) interest paid on the national debt as a portion of GDP.
D) the proportion of the national debt that is held by government agencies.
A) the size of the debt in nominal terms.
B) the interest rate paid on the debt.
C) interest paid on the national debt as a portion of GDP.
D) the proportion of the national debt that is held by government agencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The largest category of federal government spending in 2015 was:
A) defense.
B) Social Security.
C) education.
D) net interest.
A) defense.
B) Social Security.
C) education.
D) net interest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When the economy is in equilibrium:
A) GDP = C + I.
B) GDP = C + I + G + (X - M).
C) Y + C = I.
D) Y = C / I.
A) GDP = C + I.
B) GDP = C + I + G + (X - M).
C) Y + C = I.
D) Y = C / I.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Changes in taxes first cause changes in _____, and thus the government tax multiplier is _____ than the government spending multiplier.
A) aggregate spending; larger
B) aggregate spending; smaller
C) disposable income; larger
D) disposable income; smaller
A) aggregate spending; larger
B) aggregate spending; smaller
C) disposable income; larger
D) disposable income; smaller

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
When government spending increases, the aggregate demand curve shifts to the _____ and the multiplier effect is dampened by a _____ in the aggregate price level.
A) right; fall
B) right; rise
C) left; fall
D) left; rise
A) right; fall
B) right; rise
C) left; fall
D) left; rise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An increase in taxes:
A) removes money from the economy's spending stream.
B) stimulates aggregate demand.
C) is the right policy proposition for fighting a recession.
D) always helps balance the budget.
A) removes money from the economy's spending stream.
B) stimulates aggregate demand.
C) is the right policy proposition for fighting a recession.
D) always helps balance the budget.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following measures is NOT an example of discretionary fiscal policy?
A) The unemployment compensation program pays out more money as the unemployment rate rises.
B) Tax rates are increased in the hope of slowing down the rate of inflation.
C) Tax increases are enacted to reduce the government deficit.
D) Government spending is increased to reduce the problems caused by a recession.
A) The unemployment compensation program pays out more money as the unemployment rate rises.
B) Tax rates are increased in the hope of slowing down the rate of inflation.
C) Tax increases are enacted to reduce the government deficit.
D) Government spending is increased to reduce the problems caused by a recession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is NOT an element of expansionary fiscal policy?
A) expanding immigration policies
B) increasing government spending
C) cutting taxes
D) increasing transfer payments
A) expanding immigration policies
B) increasing government spending
C) cutting taxes
D) increasing transfer payments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
An expansionary fiscal policy can result in:
A) higher unemployment rates.
B) inflation and higher GDP.
C) lower prices.
D) a recession.
A) higher unemployment rates.
B) inflation and higher GDP.
C) lower prices.
D) a recession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Assume taxes increase by $200 and the marginal propensity to consumer is 0.75. We would expect:
A) equilibrium income to remain the same.
B) equilibrium income to rise by $800.
C) equilibrium income to fall by $800.
D) equilibrium income to fall by $600.
A) equilibrium income to remain the same.
B) equilibrium income to rise by $800.
C) equilibrium income to fall by $800.
D) equilibrium income to fall by $600.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Using demand-side fiscal policy to stimulate aggregate demand when the economy is at full employment will primarily result in:
A) unemployment.
B) underemployment.
C) inflation.
D) a large economic expansion.
A) unemployment.
B) underemployment.
C) inflation.
D) a large economic expansion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Suppose the economy is in a recession. To increase demand using discretionary fiscal policy, the government can:
A) raise interest rates.
B) raise taxes or reduce government spending.
C) increase government spending or reduce taxes.
D) reduce interest rates.
A) raise interest rates.
B) raise taxes or reduce government spending.
C) increase government spending or reduce taxes.
D) reduce interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is NOT a leakage that reduces the size of the spending multiplier?
A) purchases of imports
B) personal income tax
C) savings
D) personal investment in human capital
A) purchases of imports
B) personal income tax
C) savings
D) personal investment in human capital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The $787 billion stimulus package passed in the United States in 2009 focused more on spending than on taxes partly because:
A) increased spending leads to a larger increase in GDP than does the same reduction in taxes.
B) increased spending leads to a smaller increase in GDP than does the same reduction in taxes.
C) the government tax multiplier is more than the government spending multiplier.
D) the government revenue multiplier is about the same as the government tax multiplier.
A) increased spending leads to a larger increase in GDP than does the same reduction in taxes.
B) increased spending leads to a smaller increase in GDP than does the same reduction in taxes.
C) the government tax multiplier is more than the government spending multiplier.
D) the government revenue multiplier is about the same as the government tax multiplier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following is NOT an explicit short-run goal of discretionary fiscal policy?
A) full employment
B) economic growth
C) inflation control
D) zero unemployment
A) full employment
B) economic growth
C) inflation control
D) zero unemployment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
If the economy is producing at an output level below full employment, the government should _____ spending and _____ taxes.
A) decrease; increase
B) decrease; decrease
C) increase; decrease
D) increase; increase
A) decrease; increase
B) decrease; decrease
C) increase; decrease
D) increase; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Anne and Charlie are discussing the best possible fiscal policy to bring the country out of a recession. Charlie wants to see government reduce taxes by $100 billion. Anne prefers to see government spending increase by $100 billion. Whose proposition would have the larger total impact on aggregate demand?
A) Anne's, because the government has more information available to it than do households and firms
B) Anne's, because all of the additional government spending will enter the spending stream, while part of a tax cut would be saved and not spent
C) Charlie's, because households and firms have a higher marginal propensity to consume than the government
D) Charlie's, because firms and households are better spenders than the government, whose spending decisions are bogged down in political debating
A) Anne's, because the government has more information available to it than do households and firms
B) Anne's, because all of the additional government spending will enter the spending stream, while part of a tax cut would be saved and not spent
C) Charlie's, because households and firms have a higher marginal propensity to consume than the government
D) Charlie's, because firms and households are better spenders than the government, whose spending decisions are bogged down in political debating

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Disposable income is equal to:
A) Y - T.
B) Y + T.
C) T - Y.
D) X - M.
A) Y - T.
B) Y + T.
C) T - Y.
D) X - M.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Transfer payments are:
A) monies paid directly to individuals by the government.
B) not part of the government budget.
C) a vital part of discretionary fiscal policy.
D) payments made to government officials who transfer them back to private companies.
A) monies paid directly to individuals by the government.
B) not part of the government budget.
C) a vital part of discretionary fiscal policy.
D) payments made to government officials who transfer them back to private companies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Without government spending, which of the following equations is true?
A) Y = C + S
B) S - I = 1
C) I - S = 1
D) I + S = 1
A) Y = C + S
B) S - I = 1
C) I - S = 1
D) I + S = 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Increased government _____ leads to a larger increase in GDP when compared to the same reduction in _____.
A) spending; taxes
B) taxes; spending
C) revenue; government expenditures
D) expenditures; prices
A) spending; taxes
B) taxes; spending
C) revenue; government expenditures
D) expenditures; prices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If the economy is at full employment, increases in government spending:
A) have a multiplier effect on equilibrium output.
B) have no effect on the aggregate price level.
C) are primarily absorbed by price increases.
D) reduce aggregate output.
A) have a multiplier effect on equilibrium output.
B) have no effect on the aggregate price level.
C) are primarily absorbed by price increases.
D) reduce aggregate output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following is an example of contractionary fiscal policy?
A) increasing federal spending to renovate college campuses
B) reducing military spending
C) building a new interstate highway
D) sending taxpayers a $600 rebate
A) increasing federal spending to renovate college campuses
B) reducing military spending
C) building a new interstate highway
D) sending taxpayers a $600 rebate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
When the economy is below full employment, expansionary fiscal policy:
A) shifts the aggregate demand curve to the left.
B) shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve to the right.
C) causes a movement down along the aggregate demand curve.
D) shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right.
A) shifts the aggregate demand curve to the left.
B) shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve to the right.
C) causes a movement down along the aggregate demand curve.
D) shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Suppose policymakers wish to use fiscal policy to fight inflation. Which statement, then, is MOST accurate?
A) Using fiscal policy, the government can have the best of both worlds in the form of low inflation and economic growth.
B) Essentially, the way to lower the inflation rate is to decrease aggregate demand, causing a rise in unemployment.
C) They should not use fiscal policy because in the long run the economy will always go back to equilibrium.
D) Policymakers should use an expansionary policy because job creation is more important than inflation.
A) Using fiscal policy, the government can have the best of both worlds in the form of low inflation and economic growth.
B) Essentially, the way to lower the inflation rate is to decrease aggregate demand, causing a rise in unemployment.
C) They should not use fiscal policy because in the long run the economy will always go back to equilibrium.
D) Policymakers should use an expansionary policy because job creation is more important than inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following measures is an example of expansionary fiscal policy?
A) decreasing government spending
B) reducing welfare payments
C) increasing unemployment compensation
D) raising taxes
A) decreasing government spending
B) reducing welfare payments
C) increasing unemployment compensation
D) raising taxes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which type of fiscal policy involves reducing government spending, reducing transfer payments, or raising taxes to decrease aggregate demand?
A) expansionary fiscal policy
B) contractionary fiscal policy
C) diminishment fiscal policy
D) reductionist fiscal policy
A) expansionary fiscal policy
B) contractionary fiscal policy
C) diminishment fiscal policy
D) reductionist fiscal policy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
(Figure: Determining Fiscal Policy) Expansionary fiscal policies could: 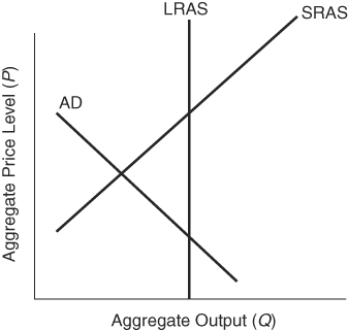
A) move the economy to full employment.
B) move the economy away from full employment.
C) lead to a lower price level.
D) lead to a lower price level and lower unemployment.

A) move the economy to full employment.
B) move the economy away from full employment.
C) lead to a lower price level.
D) lead to a lower price level and lower unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Contractionary fiscal policy:
A) increases aggregate demand.
B) decreases aggregate demand.
C) increases aggregate supply.
D) leaves aggregate demand unchanged.
A) increases aggregate demand.
B) decreases aggregate demand.
C) increases aggregate supply.
D) leaves aggregate demand unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
(Figure: Effects of Policy Shifts) If government spending increases, shifting aggregate demand from _____ to _____, aggregate output will increase from _____ to _____. 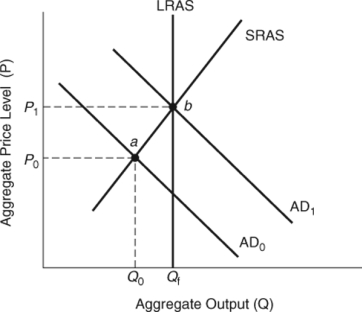
A) AD1; AD0; Qf; Q0
B) AD1; AD0; Q0; Qf
C) AD0; AD1; Q0; Qf
D) AD0; AD1; Qf; Q0

A) AD1; AD0; Qf; Q0
B) AD1; AD0; Q0; Qf
C) AD0; AD1; Q0; Qf
D) AD0; AD1; Qf; Q0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
When the economy is underperforming and policymakers pursue expansionary fiscal policy, they express a willingness to trade off _____ output for a _____ price level.
A) higher; higher
B) higher; lower
C) lower; higher
D) lower; lower
A) higher; higher
B) higher; lower
C) lower; higher
D) lower; lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Expansionary fiscal policy is typically used to _____ aggregate demand in order to _____.
A) increase; avoid a recession
B) decrease; avoid a recession
C) increase; slow down an overheated economy
D) decrease; slow down an overheated economy
A) increase; avoid a recession
B) decrease; avoid a recession
C) increase; slow down an overheated economy
D) decrease; slow down an overheated economy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
_____ government spending, _____ transfer payments, and _____ taxes all increase aggregate demand.
A) Increasing; increasing; increasing
B) Increasing; decreasing; decreasing
C) Increasing; increasing; decreasing
D) Decreasing; decreasing; increasing
A) Increasing; increasing; increasing
B) Increasing; decreasing; decreasing
C) Increasing; increasing; decreasing
D) Decreasing; decreasing; increasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When the economy is overheating and policymakers pursue contractionary fiscal policy, they express a willingness to trade off _____ output for a _____ price level.
A) higher; higher
B) higher; lower
C) lower; higher
D) lower; lower
A) higher; higher
B) higher; lower
C) lower; higher
D) lower; lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
(Figure: Determining Fiscal Policy) The best discretionary fiscal policy option is: 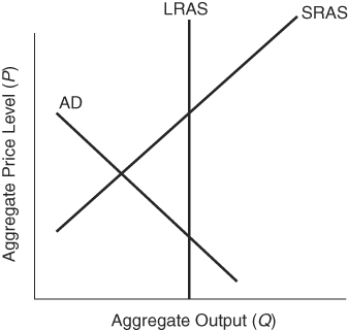
A) expansionary fiscal policy that leads to full employment.
B) contractionary fiscal policy that leads to full employment.
C) a combination of expansionary and contractionary fiscal policies to achieve full employment and stable prices.
D) only fiscal policies that lead to a lower price level.

A) expansionary fiscal policy that leads to full employment.
B) contractionary fiscal policy that leads to full employment.
C) a combination of expansionary and contractionary fiscal policies to achieve full employment and stable prices.
D) only fiscal policies that lead to a lower price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
(Figure: Effects of Policy Shifts) If the economy starts below full employment, an expansionary fiscal policy will shift the aggregate demand curve from _____ to _____, and equilibrium will move from point _____ to _____. 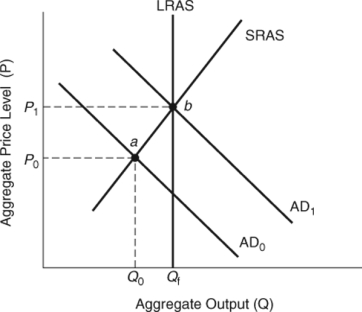
A) AD1; AD0; a; b
B) AD1; AD0; b; a
C) AD0; AD1; b; a
D) AD0; AD1; a; b

A) AD1; AD0; a; b
B) AD1; AD0; b; a
C) AD0; AD1; b; a
D) AD0; AD1; a; b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Suppose the government increases aggregate demand to a level that increases GDP above its long-run equilibrium level. What sequence of events would follow?
A) prices rise; GDP increases; workers demand higher wages; short-run aggregate supply shifts to the left; GDP drops
B) prices fall; workers receive lower wages; short-run aggregate supply shifts to the right; GDP rises
C) prices rise; GDP increases; workers demand higher wages; long-run aggregate supply shifts to the left; GDP falls
D) prices fall; workers receive lower wages; aggregate supply shifts to the right; GDP rises
A) prices rise; GDP increases; workers demand higher wages; short-run aggregate supply shifts to the left; GDP drops
B) prices fall; workers receive lower wages; short-run aggregate supply shifts to the right; GDP rises
C) prices rise; GDP increases; workers demand higher wages; long-run aggregate supply shifts to the left; GDP falls
D) prices fall; workers receive lower wages; aggregate supply shifts to the right; GDP rises

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
An economy is operating at long-run equilibrium. What is the most likely result of an aggressive expansionary fiscal policy?
A) no change in long-run GDP and employment
B) a decrease in the unemployment rate
C) a decrease in prices
D) a rise in long-run employment
A) no change in long-run GDP and employment
B) a decrease in the unemployment rate
C) a decrease in prices
D) a rise in long-run employment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
When the economy is at full employment, expansionary fiscal policy results in a new long-run equilibrium at an output level _____ full employment and a _____ price level.
A) equal to; higher
B) above; higher
C) below; higher
D) equal to; lower
A) equal to; higher
B) above; higher
C) below; higher
D) equal to; lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
If an economy is producing at a level beyond full employment, using contractionary fiscal policy to reduce aggregate demand means a tradeoff between _____ price levels and _____ output.
A) higher; higher
B) higher; lower
C) lower; lower
D) lower; higher
A) higher; higher
B) higher; lower
C) lower; lower
D) lower; higher

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
(Figure: Effects of Contractionary Fiscal Policies) Contractionary fiscal policies could: 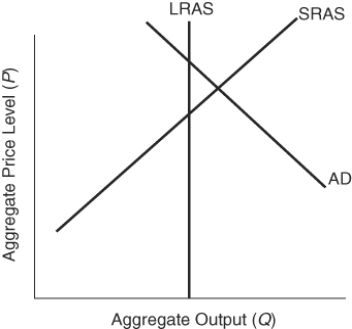
A) move the economy to full employment.
B) move the economy away from full employment.
C) lead to a higher price level.
D) lead to a higher price level and lower employment.

A) move the economy to full employment.
B) move the economy away from full employment.
C) lead to a higher price level.
D) lead to a higher price level and lower employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
If the economy is below full employment and the government uses expansionary fiscal policy in an attempt to reduce unemployment:
A) output and the price level will rise.
B) it will have no effect, as fiscal policy does not work during times of unemployment.
C) output and the price level will fall.
D) output will rise, but the price level will fall.
A) output and the price level will rise.
B) it will have no effect, as fiscal policy does not work during times of unemployment.
C) output and the price level will fall.
D) output will rise, but the price level will fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 365 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



