Deck 6: Supply of Labor to the Economy: The Decision to Work
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/49
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Supply of Labor to the Economy: The Decision to Work
1
Empirical studies suggest that the responsiveness of married working women's hours to wage changes is ________ than for men and that they are ________ to enter or leave the labor force due to changes in their wages.
A) no different; more likely
B) no different; less likely
C) greater; more likely
D) greater; less likely
A) no different; more likely
B) no different; less likely
C) greater; more likely
D) greater; less likely
A
2
Fixed costs of working will cause ________ the number of people choosing to work zero hours.
A) an increase in
B) a decrease in
C) no change in
D) an ambiguous change in
A) an increase in
B) a decrease in
C) no change in
D) an ambiguous change in
A
3
An Earned Income Tax Credit will
A) increase the reservation wage of low-wage workers.
B) increase the wage rate of some low-wage workers to a rate which is above the reservation wage.
C) create only an income effect.
D) create only a substitution effect.
A) increase the reservation wage of low-wage workers.
B) increase the wage rate of some low-wage workers to a rate which is above the reservation wage.
C) create only an income effect.
D) create only a substitution effect.
B
4
The Earned Income Tax Credit will probably ________ the labor force participation of low-wage workers and ________ the labor market hours of those with earning in the range that the tax credit is being phased out.
A) increase; decrease
B) increase; increase
C) decrease; increase
D) decrease; decrease
A) increase; decrease
B) increase; increase
C) decrease; increase
D) decrease; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Through the substitution effect,a decrease in the wage rate will cause ________ in the quantity of leisure desired.
A) an increase
B) a decrease
C) no change
D) an ambiguous change
A) an increase
B) a decrease
C) no change
D) an ambiguous change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If Gene receives a raise in his hourly wage and decides he would like to increase his hours of work,we know that
A) his income effect is greater than his substitution effect.
B) his substitution effect is greater than his income effect.
C) his income and substitution effects are equal.
D) his income and substitution effects reinforce each other.
A) his income effect is greater than his substitution effect.
B) his substitution effect is greater than his income effect.
C) his income and substitution effects are equal.
D) his income and substitution effects reinforce each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A decrease in the implicit tax rate on welfare benefits serves as
A) an incentive to work fewer hours.
B) an incentive to work more hours.
C) a way to decrease the incomes of welfare recipients.
D) a way to decrease spending on benefits.
A) an incentive to work fewer hours.
B) an incentive to work more hours.
C) a way to decrease the incomes of welfare recipients.
D) a way to decrease spending on benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A person with ________ indifference curves is most likely to decide not to participate in the labor force.
A) flat
B) steep
C) straight
D) upward-sloping
A) flat
B) steep
C) straight
D) upward-sloping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If income is held constant and the wage rate increases,the desired hours of work will
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) stay the same.
D) change ambiguously.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) stay the same.
D) change ambiguously.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An increase in nonlabor income due to a rise in the value of stocks and bonds will cause
A) a pure income effect.
B) a pure substitution effect.
C) both an income and a substitution effect.
D) neither an income nor a substitution effect.
A) a pure income effect.
B) a pure substitution effect.
C) both an income and a substitution effect.
D) neither an income nor a substitution effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A wage increase creates a substitution effect which leads the worker to desire ________ leisure,and an income effect which leads the worker to desire ________ leisure.
A) more; less
B) less; more
C) less; less
D) more; more
A) more; less
B) less; more
C) less; less
D) more; more

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Studies of the hours of work of older men have found that the substitution effect dominates the income effect.This suggests that,other things the same,
A) an increase in non-work expenses will cause older men to work shorter hours.
B) an increase in the tax rate on income will cause older men to work longer hours.
C) tax changes have no effect on their labor supply.
D) older men will retire earlier in those careers where wages fall more as they get older.
A) an increase in non-work expenses will cause older men to work shorter hours.
B) an increase in the tax rate on income will cause older men to work longer hours.
C) tax changes have no effect on their labor supply.
D) older men will retire earlier in those careers where wages fall more as they get older.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If a worker's desired hours of labor do not change after a decrease in his wage rate,then
A) his income effect dominates his substitution effect.
B) his substitution effect dominates his income effect.
C) his income and substitution effects are of equal magnitude.
D) his income and substitution effects are small in absolute value.
A) his income effect dominates his substitution effect.
B) his substitution effect dominates his income effect.
C) his income and substitution effects are of equal magnitude.
D) his income and substitution effects are small in absolute value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Empirical estimates show that for men
A) the income effect is greater than the substitution effect.
B) the substitution effect is greater than the income effect.
C) the income and substitution effects are both large so that wage changes have no effect on hours.
D) the income and substitution effects are both small so that wage changes have no effect on hours.
A) the income effect is greater than the substitution effect.
B) the substitution effect is greater than the income effect.
C) the income and substitution effects are both large so that wage changes have no effect on hours.
D) the income and substitution effects are both small so that wage changes have no effect on hours.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If leisure is a normal good,then an increase in non-labor income will cause desired hours of work to
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) stay the same.
D) either decrease or increase.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) stay the same.
D) either decrease or increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
On the portion of a worker's labor supply curve that is backward-bending,
A) the substitution effect outweighs the income effect.
B) the income effect outweighs the substitution effect.
C) the income effect is negative.
D) the substitution effect is negative.
A) the substitution effect outweighs the income effect.
B) the income effect outweighs the substitution effect.
C) the income effect is negative.
D) the substitution effect is negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A person who receives time-and-a-half overtime for working more than 8 hours per day will have a ________ which is ________ beyond 8 hours of labor.
A) budget constraint; flatter
B) indifference curve; flatter
C) budget constraint; steeper
D) indifference curve; steeper
A) budget constraint; flatter
B) indifference curve; flatter
C) budget constraint; steeper
D) indifference curve; steeper

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If Alice's wage increases from $6.00 per hour to $6.50 per hour,then
A) she will want to work more hours than before her raise.
B) she will want to work fewer hours than before her raise.
C) she will want to work the same number of hours as before her raise.
D) she may want to work more, fewer, or the same number of hours as before her raise.
A) she will want to work more hours than before her raise.
B) she will want to work fewer hours than before her raise.
C) she will want to work the same number of hours as before her raise.
D) she may want to work more, fewer, or the same number of hours as before her raise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An increase in the marginal tax rate will cause
A) a pure income effect.
B) a pure substitution effect.
C) both an income and a substitution effect.
D) neither an income nor a substitution effect.
A) a pure income effect.
B) a pure substitution effect.
C) both an income and a substitution effect.
D) neither an income nor a substitution effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Indifference curves drawn with leisure and income on the axes have negative slopes
A) because people are willing to give up income to obtain more leisure and vice versa.
B) if a person likes leisure more than income.
C) because they cannot cross one another.
D) unless one of the goods is inferior.
A) because people are willing to give up income to obtain more leisure and vice versa.
B) if a person likes leisure more than income.
C) because they cannot cross one another.
D) unless one of the goods is inferior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Frankie and Johnny can both earn a wage rate of $10 per hour and,coincidentally,both have $100 per week in non-labor income.Assume that both have T = 100 hours per week to allocate to leisure and work.Frankie chooses to work 40 hours per week.Johnny,on the other hand,chooses not to work at all! Use indifference curve analysis to account for why two individuals confronting the same wage rate and with the same amount of non-labor income make such different labor supply choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A worker is indifferent between job one lasting 4 hours a day,job two lasting 8 hours a day,and job three lasting 12 hours a day.Job two pays $10 an hour and tangency between the indifference curve and the budget constraint occurs at 8 hours.One can conclude that
A) job one pays less per day but more per hour.
B) job three pays more per day and more per hour.
C) both A and B are true.
D) neither A nor B is true.
A) job one pays less per day but more per hour.
B) job three pays more per day and more per hour.
C) both A and B are true.
D) neither A nor B is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
An individual's reservation wage
A) is determined by supply and demand in the labor market.
B) is the value of the marginal hour of leisure time if the individual does no work.
C) is the amount of money the individual earns by working an additional hour.
D) decreases as non-labor income increases.
A) is determined by supply and demand in the labor market.
B) is the value of the marginal hour of leisure time if the individual does no work.
C) is the amount of money the individual earns by working an additional hour.
D) decreases as non-labor income increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Why are indifference curves between money income and leisure convex to the origin of the graph? In your discussion,introduce the concept of marginal rate of substitution between leisure and money income and explain its relevance to the convexity property of the indifference curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
"The wage rate (w)is the 'price' that the labor market attaches to an hour of the individual's time." How is this any different from the individual's marginal rate of substitution between leisure and income? Explain carefully.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
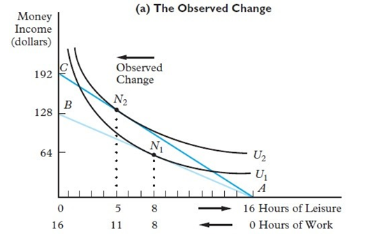
Consider the above figure.If the wage rate is initially $8 per hour and subsequently increases to $12 per hour,then
A) the income effect dominates and optimal hours of work increase by 3 hours.
B) the income effect dominates and optimal hours of work decrease by 3 hours.
C) the substitution effect dominates and optimal hours of work increase by 3 hours.
D) the substitution effect dominates and optimal hours of work decrease by 3 hours.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The figure above illustrates a "spiked" budget constraint attendant to income replacement programs such as workers' compensation and unemployment insurance.Assume that,prior to injury or unemployment,the worker earns $E? per time period,works H? = A - L? hours,and enjoys utility level U?.In order to minimize the work disincentives associated with income replacement while maintaining the worker near the original level of utility,the program ought to pay a benefit
A) a little bit less than Ag.
B) equal to the original earnings level, E?.
C) greater than AC.
D) a little bit less than AC.
A) a little bit less than Ag.
B) equal to the original earnings level, E?.
C) greater than AC.
D) a little bit less than AC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Jack currently works 38 hours per week at a wage rate of $15 per hour.His marginal rate of substitution is $20 per hour.Is Jack's utility maximized? If yes,explain why.If no,explain why not and discuss what Jack should do in order to further increase utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
An increase in the wage rate when the substitution effect dominates will ________ labor force participation and ________ hours of work.
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; decrease
D) decrease; increase
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; decrease
D) decrease; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A welfare program offers $4000 of benefits to those not working.For those working,it reduces benefits dollar for dollar until there are no benefits to be paid.The program is then modified so that for every dollar earned,benefits are only reduced by 50 cents.Mr.X earned $6000 under the old program.What will be the effect of the new program (noting that he is in the range to receive benefits)?
A) Both his income and substitution effect will decrease his desired hours of work.
B) Both his income and substitution effect will increase his desired hours of work.
C) His income effect will increase his desired hours of work, but his substitution effect will decrease his desired hours of work.
D) His income effect will decrease his desired hours of work, but his substitution effect will increase his desired hours of work.
A) Both his income and substitution effect will decrease his desired hours of work.
B) Both his income and substitution effect will increase his desired hours of work.
C) His income effect will increase his desired hours of work, but his substitution effect will decrease his desired hours of work.
D) His income effect will decrease his desired hours of work, but his substitution effect will increase his desired hours of work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A country has no welfare program.Then it introduces the following program: everyone gets $4000 if they work more than 1000 hours a year (on top of what they earn).The effect of this event will be to ________ the labor force participation and the effect of this event on those who were working more than 1000 hours will be to ________ hours of work.
A) increase, increase
B) decrease, increase
C) increase, decrease
D) decrease, decrease
A) increase, increase
B) decrease, increase
C) increase, decrease
D) decrease, decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Mary earns $20 an hour and works 10 hours a week.She gets a raise to $30 an hour but at the same time her fixed weekly work expenses go up $100.If she continues to work,she will most likely
A) continue to work 10 hours.
B) increase her hours of work.
C) decrease her hours of work.
D) decrease her hours of work if the income effect dominates the substitution effect.
A) continue to work 10 hours.
B) increase her hours of work.
C) decrease her hours of work.
D) decrease her hours of work if the income effect dominates the substitution effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
How does an increase in non-labor income affect desired hours of work for a labor force participant? Use indifference curve analysis to illustrate and support your answer.State any assumptions that you make.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In 1986 Congress drastically cut the marginal tax rate on upper income levels from 50% to 28%.Empirical evidence analyzing the labor supply effects of the tax cut found that women in the high income tax bracket
A) did not respond in any significant way to the tax cut, as their high level of income ensured that they were already content with their labor supply choices.
B) experienced offsetting substitution and income effects.
C) increased both labor force participation and hours of work significantly.
D) reduced their labor force participation and hours worked significantly because of a dominant income effect.
A) did not respond in any significant way to the tax cut, as their high level of income ensured that they were already content with their labor supply choices.
B) experienced offsetting substitution and income effects.
C) increased both labor force participation and hours of work significantly.
D) reduced their labor force participation and hours worked significantly because of a dominant income effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Many working mothers have to pay for childcare costs.If they don't work,they do not have to pay for these costs.If childcare costs go up dramatically,the effect will be to ________ the labor force participation of working mothers and to ________ the hours of work for those mothers who continue to work.
A) decrease, decrease
B) increase, increase
C) increase, decrease
D) decrease, increase
A) decrease, decrease
B) increase, increase
C) increase, decrease
D) decrease, increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A professor declared "with the recent drop in the value of my stock portfolio,I will have to put off retirement by another two years." This decision reflects
A) the substitution effect.
B) the income effect.
C) the portfolio effect.
D) the effect of a budget constraint with a spike.
A) the substitution effect.
B) the income effect.
C) the portfolio effect.
D) the effect of a budget constraint with a spike.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The property tax goes up $4000 a year.This will cause those who are working to work ________ hours and their annual income to go ________ $4000.
A) more, up by more than
B) more, up by less than
C) fewer, down by less than
D) fewer, down by more than
A) more, up by more than
B) more, up by less than
C) fewer, down by less than
D) fewer, down by more than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Indifference curves drawn with income and leisure on the axes are convex to the origin of the graph because
A) people are willing to give up income to obtain more leisure and vice versa.
B) the marginal hour of leisure time becomes less valuable as one works fewer hours and more valuable as one works more hours.
C) the marginal hour of leisure time becomes more valuable as one works fewer hours and less valuable as one works more hours.
D) utility increases as income and leisure increase.
A) people are willing to give up income to obtain more leisure and vice versa.
B) the marginal hour of leisure time becomes less valuable as one works fewer hours and more valuable as one works more hours.
C) the marginal hour of leisure time becomes more valuable as one works fewer hours and less valuable as one works more hours.
D) utility increases as income and leisure increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Empirical evidence on the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC)shows that expansions in that program from the latter 1980s through the mid-1990s caused
A) significant withdrawal from the labor force by teenagers.
B) significant increase in the labor force participation of single mothers.
C) adult men to significantly increase their total hours of work.
D) married women to significantly increase their hours of work.
A) significant withdrawal from the labor force by teenagers.
B) significant increase in the labor force participation of single mothers.
C) adult men to significantly increase their total hours of work.
D) married women to significantly increase their hours of work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
An increase in travel time to work will likely ________ labor force participation and ________ hours spent working and traveling (of those working and traveling before and after the wage increase).
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; decrease
D) decrease; increase
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; decrease
D) decrease; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
"People who value leisure more highly have indifference curves that are generally steeper.People who do not value leisure highly have relatively flat indifference curves." Explain the quote.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The opportunity cost of leisure
A) is the wage that one could earn by working an additional hour.
B) is the amount of income that would be necessary to hold an individual's utility level constant were they to work an additional hour (that is, give up an hour of leisure time).
C) is equivalent to the individual's non-labor income.
D) is directly related to the individual's level of leisure consumption per time period.
A) is the wage that one could earn by working an additional hour.
B) is the amount of income that would be necessary to hold an individual's utility level constant were they to work an additional hour (that is, give up an hour of leisure time).
C) is equivalent to the individual's non-labor income.
D) is directly related to the individual's level of leisure consumption per time period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
"When a worker's wage rate changes,there are two opposing effects-an income effect and a substitution effect." Explain the meaning of the quote.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Other things equal,the less convex is an individual's indifference curve,the greater will be the substitution effect of a wage change.Explain why.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is the earned income tax credit (EITC)? The EITC probably increases labor force participation but probably also reduces hours worked by those already working.Explain why in both instances using indifference curve analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If an individual's income effect is stronger than the individual's substitution effect,a wage increase will cause that individual to
A) increase hours worked, and this increase will be larger than if the same change in wealth were caused by a change in non-labor income.
B) decrease hours worked, but this decrease will be smaller than if the same change in wealth were caused by a change in non-labor income.
C) decrease hours worked, and this decrease will be larger than if the same change in wealth were caused by a change in non-labor income.
D) increase hours worked, but this increase will be smaller than if the same change in wealth were caused by a change in non-labor income.
A) increase hours worked, and this increase will be larger than if the same change in wealth were caused by a change in non-labor income.
B) decrease hours worked, but this decrease will be smaller than if the same change in wealth were caused by a change in non-labor income.
C) decrease hours worked, and this decrease will be larger than if the same change in wealth were caused by a change in non-labor income.
D) increase hours worked, but this increase will be smaller than if the same change in wealth were caused by a change in non-labor income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The average workweek in U.S.manufacturing plants
A) has dropped steadily since 1960 from about 60 hours per week to 35 hours per week currently.
B) has increased from about 35 hours per week in 1970 to about 45 hours per week by 2010.
C) fluctuates significantly over the business cycle, averaging about 50 hours per week at business cycle peaks and 32 hours per week at business cycle troughs.
D) dropped from about 55 hours per week in the early part of the 20th century to approximately 40 hours per week by 1950 and since 1950, aside from small variation over the business cycle, has remained at about 40 hours per week with no trend in either direction.
A) has dropped steadily since 1960 from about 60 hours per week to 35 hours per week currently.
B) has increased from about 35 hours per week in 1970 to about 45 hours per week by 2010.
C) fluctuates significantly over the business cycle, averaging about 50 hours per week at business cycle peaks and 32 hours per week at business cycle troughs.
D) dropped from about 55 hours per week in the early part of the 20th century to approximately 40 hours per week by 1950 and since 1950, aside from small variation over the business cycle, has remained at about 40 hours per week with no trend in either direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Consider two workers-Averil and Taylor.They both earn the same wage rate and neither has any non-labor income.Averil chooses to work 40 hours per week and Taylor chooses to work 10 hours per week.Due to improving macroeconomic conditions both workers experience an exogenous 10% increase in their common wage rate.Explain which worker is likely to have a larger income effect as a result of the wage increase.Illustrate with the appropriate graph.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The female labor force participation rate
A) doubled because of World War II and has remained roughly constant at near 50% since that time.
B) dropped sharply from approximately 60% in 2000 to under 45% in 2011 because of the Great Recession.
C) increased steadily from about 30% in 1950 to approximately 60% in 2000.
D) is now about the same as the overall male labor force participation rate thanks to the eradication of gender inequality.
A) doubled because of World War II and has remained roughly constant at near 50% since that time.
B) dropped sharply from approximately 60% in 2000 to under 45% in 2011 because of the Great Recession.
C) increased steadily from about 30% in 1950 to approximately 60% in 2000.
D) is now about the same as the overall male labor force participation rate thanks to the eradication of gender inequality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 49 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



