Deck 3: The Demand for Labor
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/53
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: The Demand for Labor
1
Table 3.1
-Referring to Table 3.1,if wages are $50.00 per day and pots sell for $20.00 each,how many potters will the firm hire?
A) two
B) three
C) four
D) five
-Referring to Table 3.1,if wages are $50.00 per day and pots sell for $20.00 each,how many potters will the firm hire?
A) two
B) three
C) four
D) five
four
2
If a tax is placed on an employer,
A) workers will not have to pay the tax.
B) both wages and employment levels will usually decrease.
C) customers will not have to pay the tax.
D) wages will decrease, but employment levels will increase.
A) workers will not have to pay the tax.
B) both wages and employment levels will usually decrease.
C) customers will not have to pay the tax.
D) wages will decrease, but employment levels will increase.
B
3
Table 3.1
-Referring to Table 3.1,which of the following answers is INCORRECT? If pots sell for $20 each,then
A) the marginal revenue product of labor of the second worker is $260.
B) the marginal product of the third worker is five pots.
C) the marginal revenue from selling the eighteenth pot is $20.
D) the marginal revenue product of labor equals the marginal product of labor multiplied by the additional revenue that is received per unit of output.
-Referring to Table 3.1,which of the following answers is INCORRECT? If pots sell for $20 each,then
A) the marginal revenue product of labor of the second worker is $260.
B) the marginal product of the third worker is five pots.
C) the marginal revenue from selling the eighteenth pot is $20.
D) the marginal revenue product of labor equals the marginal product of labor multiplied by the additional revenue that is received per unit of output.
the marginal revenue product of labor of the second worker is $260.
4
Employee subsidies will be most effective at raising the effective wage of the poor when
A) demand for labor is elastic.
B) supply for labor is inelastic.
C) both A and B
D) neither A nor B
A) demand for labor is elastic.
B) supply for labor is inelastic.
C) both A and B
D) neither A nor B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Most of a payroll tax is eventually paid by
A) employers if the supply of labor curve is very inelastic.
B) employers if the labor demand curve is very elastic.
C) workers if the supply of labor curve is very inelastic.
D) workers if the supply of labor curve is very elastic.
A) employers if the supply of labor curve is very inelastic.
B) employers if the labor demand curve is very elastic.
C) workers if the supply of labor curve is very inelastic.
D) workers if the supply of labor curve is very elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The firm's labor demand curve in the short run
A) is upward sloping.
B) is horizontal.
C) is the downward sloping segment of the marginal revenue schedule.
D) is the downward sloping segment of the marginal product of labor schedule.
A) is upward sloping.
B) is horizontal.
C) is the downward sloping segment of the marginal revenue schedule.
D) is the downward sloping segment of the marginal product of labor schedule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If the firm hires to a point where the marginal expense of labor is greater than the marginal revenue product of labor,then
A) profits could be increased by increasing employment.
B) profits could be increased by reducing employment.
C) profits are maximized.
D) total cost must be greater than total revenue.
A) profits could be increased by increasing employment.
B) profits could be increased by reducing employment.
C) profits are maximized.
D) total cost must be greater than total revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When a firm moves to a higher isoquant,
A) the utility level of the firm's managers increases.
B) the firm now produces more output.
C) the firm now produces less output.
D) the firm produces the same output, but at a higher price.
A) the utility level of the firm's managers increases.
B) the firm now produces more output.
C) the firm now produces less output.
D) the firm produces the same output, but at a higher price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When deciding the salary of a sports star,
A) the team must consider how much money the sports star should earn.
B) the team must consider how much the sports star will cause revenues to increase.
C) the team estimates the sports star's marginal product; because this is a guess, sports stars are generally underpaid.
D) the team will hire the sports star if doing so will increase the team's revenues.
A) the team must consider how much money the sports star should earn.
B) the team must consider how much the sports star will cause revenues to increase.
C) the team estimates the sports star's marginal product; because this is a guess, sports stars are generally underpaid.
D) the team will hire the sports star if doing so will increase the team's revenues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Declining marginal product of labor
A) is needed if competitive firms are to stop hiring workers at some point.
B) allows firms to make the most profit.
C) mainly exists because workers get tired after many hours of work.
D) implies workers get more productive as more of them are hired.
A) is needed if competitive firms are to stop hiring workers at some point.
B) allows firms to make the most profit.
C) mainly exists because workers get tired after many hours of work.
D) implies workers get more productive as more of them are hired.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A competitive industry hires 1000 workers.The 1000th worker adds $500 a week to their employer's revenue.If a monopoly took over the industry,then the 1000th worker would likely
A) add less than $500 a week to their employer's revenue.
B) still add $500 a week to their employer's revenue.
C) add more than $500 a week to their employer's revenue.
D) uncertain; it depends on the shape of the demand curve for output.
A) add less than $500 a week to their employer's revenue.
B) still add $500 a week to their employer's revenue.
C) add more than $500 a week to their employer's revenue.
D) uncertain; it depends on the shape of the demand curve for output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
An employer who is a monopolist in the product market,other things being equal,will probably
A) hire more employees than a perfect competitor would.
B) hire fewer employees than a perfect competitor would.
C) hire the same number of employees as a perfect competitor, due to competitiveness in the labor market.
D) hire fewer workers at a higher wage than a perfect competitor would.
A) hire more employees than a perfect competitor would.
B) hire fewer employees than a perfect competitor would.
C) hire the same number of employees as a perfect competitor, due to competitiveness in the labor market.
D) hire fewer workers at a higher wage than a perfect competitor would.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
For two substitutes in production,if the scale effect dominates,
A) then the inputs are gross complements.
B) then the inputs are gross substitutes.
C) then the inputs could be either gross complements or gross substitutes.
D) then the inputs cannot be used at the same time.
A) then the inputs are gross complements.
B) then the inputs are gross substitutes.
C) then the inputs could be either gross complements or gross substitutes.
D) then the inputs cannot be used at the same time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In the long run,a profit-maximizing firm will select capital and labor so that
A) the marginal product of labor equals the marginal product of capital.
B) the wage divided by the marginal product of labor equals the rental cost of a unit of capital divided by the marginal product of capital.
C) labor equals capital.
D) the wage equals the rental cost of a unit of capital.
A) the marginal product of labor equals the marginal product of capital.
B) the wage divided by the marginal product of labor equals the rental cost of a unit of capital divided by the marginal product of capital.
C) labor equals capital.
D) the wage equals the rental cost of a unit of capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
For two substitutes in production,if the substitution effect dominates,
A) then the inputs are gross complements.
B) then the inputs are gross substitutes.
C) then the inputs could be either gross complements or gross substitutes.
D) then the inputs cannot be used at the same time.
A) then the inputs are gross complements.
B) then the inputs are gross substitutes.
C) then the inputs could be either gross complements or gross substitutes.
D) then the inputs cannot be used at the same time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If two inputs are substitutes in production,and an increase in the price of one input shifts the demand curve for the other input to the left,then
A) the scale effect is greater than the substitution effect, and the two are gross complements.
B) the scale effect is less than the substitution effect, and the two are gross complements.
C) the scale effect is greater than the substitution effect, and the two are gross substitutes.
D) the scale effect is less than the substitution effect, and the two are gross substitutes.
A) the scale effect is greater than the substitution effect, and the two are gross complements.
B) the scale effect is less than the substitution effect, and the two are gross complements.
C) the scale effect is greater than the substitution effect, and the two are gross substitutes.
D) the scale effect is less than the substitution effect, and the two are gross substitutes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The marginal product of labor tells us
A) which employee is the most productive.
B) the average output produced by each employee.
C) the additional output produced by the last employee hired.
D) how much money the firm can make from hiring each employee.
A) which employee is the most productive.
B) the average output produced by each employee.
C) the additional output produced by the last employee hired.
D) how much money the firm can make from hiring each employee.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Diminishing marginal returns occur because
A) hiring more employees means that each has less capital with which to work.
B) it is more difficult to manage a firm as the size of the workforce and capital stock both grow.
C) the best employees will always be hired first.
D) hiring more employees means that they will subdivide tasks and therefore become more efficient.
A) hiring more employees means that each has less capital with which to work.
B) it is more difficult to manage a firm as the size of the workforce and capital stock both grow.
C) the best employees will always be hired first.
D) hiring more employees means that they will subdivide tasks and therefore become more efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If two inputs are complements in production,
A) then the inputs cannot be used at the same time.
B) then the inputs can be either gross complements or gross substitutes.
C) then the inputs are gross complements.
D) then the inputs are gross substitutes.
A) then the inputs cannot be used at the same time.
B) then the inputs can be either gross complements or gross substitutes.
C) then the inputs are gross complements.
D) then the inputs are gross substitutes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Table 3.1
-Referring to Table 3.1,diminishing marginal returns begins with the ________ employee.
A) first
B) second
C) third
D) sixth
-Referring to Table 3.1,diminishing marginal returns begins with the ________ employee.
A) first
B) second
C) third
D) sixth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Workers will bear less of a payroll tax if
A) the supply of labor curve is steeper.
B) employers are made to pay more of the tax.
C) the supply of labor curve is flatter.
D) employers are made to pay less of the tax.
A) the supply of labor curve is steeper.
B) employers are made to pay more of the tax.
C) the supply of labor curve is flatter.
D) employers are made to pay less of the tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A profit-maximizing firm decides to produce 100 units of output.This implies that the firm will
A) produce on its lowest isoexpenditure line.
B) produce at a point where its isoexpenditure line is everywhere below the isoquant curve for 100 units of output.
C) produce at a point where its isoexpenditure line is tangent to the isoquant curve for 100 units of output.
D) produce where the marginal rate of technical substitution equals the wage rate.
A) produce on its lowest isoexpenditure line.
B) produce at a point where its isoexpenditure line is everywhere below the isoquant curve for 100 units of output.
C) produce at a point where its isoexpenditure line is tangent to the isoquant curve for 100 units of output.
D) produce where the marginal rate of technical substitution equals the wage rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A worker's hourly wage is $25 and output sells for $5 a unit.What is the minimum marginal product a worker must produce in order for a competitive employer to break even when hiring the worker?
A) 1/5
B) 5
C) 25
D) 125
A) 1/5
B) 5
C) 25
D) 125

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If the hourly wage is $50 and the price of output is $25,then,in the short run,
A) the firm should add workers if they add 1/2 or more units to output.
B) the firm should add workers if they add 2 or more units to output.
C) the firm should hire two workers.
D) the firm should reduce employment until the wage falls to $25.
A) the firm should add workers if they add 1/2 or more units to output.
B) the firm should add workers if they add 2 or more units to output.
C) the firm should hire two workers.
D) the firm should reduce employment until the wage falls to $25.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Consider a firm using three inputs: unskilled labor,skilled labor,and capital.Unskilled labor and capital are substitutes in production,while skilled labor and capital are complements in production.If the price of capital decreases,then
A) employment of skilled labor increases and employment of unskilled labor decreases.
B) employment of both skilled and unskilled labor decreases.
C) employment of skilled labor increases but the effect on employment of unskilled labor is ambiguous.
D) employment of skilled labor could increase or decrease and the employment of unskilled labor definitely decreases.
A) employment of skilled labor increases and employment of unskilled labor decreases.
B) employment of both skilled and unskilled labor decreases.
C) employment of skilled labor increases but the effect on employment of unskilled labor is ambiguous.
D) employment of skilled labor could increase or decrease and the employment of unskilled labor definitely decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If an increase in the cost of labor causes the firm to use less capital,then
A) the scale effect has dominated over the substitution effect.
B) the substitution effect has dominated over the scale effect.
C) the firm has moved along an isoquant curve.
D) the firm has moved onto a higher isoquant.
A) the scale effect has dominated over the substitution effect.
B) the substitution effect has dominated over the scale effect.
C) the firm has moved along an isoquant curve.
D) the firm has moved onto a higher isoquant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A competitive firm uses two inputs: capital and labor.At its current level of hiring of both inputs,capital's marginal product is 12 while labor's marginal product is 18.Capital's cost (C)is $8 per unit while labor's cost (W)is $9.In the long run,to produce the same output at a lower cost,the firm should
A) hire more labor and less capital.
B) hire less labor and less capital.
C) hire more labor and more capital.
D) hire less labor and more capital.
A) hire more labor and less capital.
B) hire less labor and less capital.
C) hire more labor and more capital.
D) hire less labor and more capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If a firm hires another unit of labor,output goes up by 12 units.The wage rate for the unit of labor is $6.What is the firm's cost of producing another unit of output using labor?
A) $18
B) $9
C) $1.50
D) $0.50
A) $18
B) $9
C) $1.50
D) $0.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The marginal income associated with a unit of input is found by
A) multiplying the additional output produced by the unit of input and the additional revenue generated per unit of physical output.
B) dividing total income generated by the number of units of output produced.
C) multiplying the price that the good sells for by the additional revenue generated per unit of physical output.
D) dividing the change in output produced by the change in units of the input employed.
A) multiplying the additional output produced by the unit of input and the additional revenue generated per unit of physical output.
B) dividing total income generated by the number of units of output produced.
C) multiplying the price that the good sells for by the additional revenue generated per unit of physical output.
D) dividing the change in output produced by the change in units of the input employed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
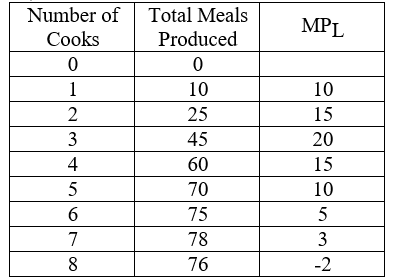
Consider the short run production function for a hypothetical restaurant shown in the table.Cooks are equally talented and hardworking.The MPL column in the table illustrates
A) that firms tend to hire the best workers first.
B) the law of supply.
C) diminishing marginal returns in labor that derives from the fact that as employment expands cooks have less capital per person to work with.
D) increasing returns to scale followed by decreasing returns to scale, which is a fundamental empirical proposition in economics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Studies show that most of a payroll tax is paid by workers in the form of lowered wages.If true,these studies imply
A) the supply of labor curve is very steep.
B) the supply of labor curve is very flat.
C) it would be better if employers were made to pay all of the tax.
D) the demand for labor curve is very steep.
A) the supply of labor curve is very steep.
B) the supply of labor curve is very flat.
C) it would be better if employers were made to pay all of the tax.
D) the demand for labor curve is very steep.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In the short run,
A) a firm cannot hire new workers.
B) wage rates and product prices cannot change.
C) a firm cannot add on to an assembly line or introduce new machines to the production process.
D) employment levels cannot change.
A) a firm cannot hire new workers.
B) wage rates and product prices cannot change.
C) a firm cannot add on to an assembly line or introduce new machines to the production process.
D) employment levels cannot change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If employers are paid a subsidy of $0.75 per hour for hiring teenaged workers,then
A) the teenagers' wage rate will usually increase by less than $0.75 per hour.
B) the teenagers' wage rate will usually increase by more than $0.75 per hour.
C) the teenagers' wage rate will usually increase by exactly $0.75 per hour.
D) the teenagers' wage rate will usually decrease.
A) the teenagers' wage rate will usually increase by less than $0.75 per hour.
B) the teenagers' wage rate will usually increase by more than $0.75 per hour.
C) the teenagers' wage rate will usually increase by exactly $0.75 per hour.
D) the teenagers' wage rate will usually decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
All of the following firms are producing on the same output isoquant.Which firm will use the most labor?
A) Wage $120; Hourly Price of Capital $240
B) Wage $60; Hourly Price of Capital $40
C) Wage $6; Hourly Price of Capital $2
D) Wage $15; Hourly Price of Capital $15
A) Wage $120; Hourly Price of Capital $240
B) Wage $60; Hourly Price of Capital $40
C) Wage $6; Hourly Price of Capital $2
D) Wage $15; Hourly Price of Capital $15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
When a competitive firm hired nine workers,its profits were $100.When it hired 10 workers,its output went from 9 to 11 units.Each unit of output sold for $10 while the wage of each worker was $12.What is the firm's new profit level?
A) $20
B) $8
C) $108
D) $12
A) $20
B) $8
C) $108
D) $12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
When the price of capital increases,a firm will
A) employ more labor because labor has become relatively cheaper.
B) employ less labor due to the increase in costs.
C) employ the same amount of labor.
D) employ more, less, or the same amount of labor.
A) employ more labor because labor has become relatively cheaper.
B) employ less labor due to the increase in costs.
C) employ the same amount of labor.
D) employ more, less, or the same amount of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If skilled workers are gross complements with low-skilled immigrant labor,then,when there is an increase in low-skilled immigrant labor,
A) skilled workers wages will go down but their employment will go up.
B) skilled workers wages will go down and their employment will go down.
C) skilled workers wages will go up and their employment will go up.
D) skilled workers wages will go up and their employment will go down.
A) skilled workers wages will go down but their employment will go up.
B) skilled workers wages will go down and their employment will go down.
C) skilled workers wages will go up and their employment will go up.
D) skilled workers wages will go up and their employment will go down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If labor costs twice as much as capital (per unit),then,in the long run,
A) labor will be half as productive as capital.
B) labor's marginal product will be twice that of capital.
C) the firm will hire twice as much labor as capital.
D) the firm will hire less labor and more capital.
A) labor will be half as productive as capital.
B) labor's marginal product will be twice that of capital.
C) the firm will hire twice as much labor as capital.
D) the firm will hire less labor and more capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If the firm operates in a competitive labor market,
A) it faces a positively sloped labor supply curve, and the marginal expense of labor is less than the market wage.
B) it faces a horizontal labor supply curve, and the marginal expense of labor equals the market wage.
C) it must compete against other employers by offering a generous compensation package.
D) it faces a vertical labor supply curve, and it competes against other employers by moving to the lowest attainable point on the labor supply curve.
A) it faces a positively sloped labor supply curve, and the marginal expense of labor is less than the market wage.
B) it faces a horizontal labor supply curve, and the marginal expense of labor equals the market wage.
C) it must compete against other employers by offering a generous compensation package.
D) it faces a vertical labor supply curve, and it competes against other employers by moving to the lowest attainable point on the labor supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The marginal product of an individual
A) depends on the number of similar workers that the firm employs as well as on the size of the firm's capital stock.
B) is solely a function of the worker's personal characteristics.
C) is a poorly defined concept because individual effort is difficult to identify and measure.
D) initially decreases but ultimately increases beyond the minimum effort level.
A) depends on the number of similar workers that the firm employs as well as on the size of the firm's capital stock.
B) is solely a function of the worker's personal characteristics.
C) is a poorly defined concept because individual effort is difficult to identify and measure.
D) initially decreases but ultimately increases beyond the minimum effort level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If a payroll tax of $X per hour is collected from employers,then the
A) labor demand curve shifts down by $X at any given employment level.
B) labor demand curve shifts down by amount $X at any given employment level.
C) labor supply curve shifts left by $X at any given employment level.
D) labor supply curve shifts down by $X at any given employment level.
A) labor demand curve shifts down by $X at any given employment level.
B) labor demand curve shifts down by amount $X at any given employment level.
C) labor supply curve shifts left by $X at any given employment level.
D) labor supply curve shifts down by $X at any given employment level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Other things being equal,how does the labor demand curve of a firm that is not perfectly competitive in the product market (that is,the firm has some ability to set product price)differ from the labor demand curve of a firm that sells in a perfectly competitive product market? Suppose that the equilibrium wage rate increases from $15 per hour to $18 per hour.Discuss the response likely to be observed at each type of firm.Comment specifically on and explain the responses in employment likely to be observed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Is the firm's labor demand curve more wage sensitive in the short run or in the long run? Explain and use the concepts of substitution effect and scale effect in answering the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
State and discuss the two kinds of objections raised to the marginal productivity theory of labor demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Suppose that the XYZ Company hires labor and capital in competitive input markets.Assume that labor costs W = $200 per day and that a unit of capital costs C = $150 per day.At the current level of production,labor's marginal product is MPL = 40 units of output produced per day and capital's marginal product is MPK = 30 units of output per day.Given the information provided,is the firm minimizing the cost of current production? Explain why or why not.If the wage were to increase to  = $240 per day,discuss and explain the long run adjustments that the firm would make in response to the wage increase.
= $240 per day,discuss and explain the long run adjustments that the firm would make in response to the wage increase.
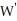 = $240 per day,discuss and explain the long run adjustments that the firm would make in response to the wage increase.
= $240 per day,discuss and explain the long run adjustments that the firm would make in response to the wage increase.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Suppose that a firm rents labor services in a competitive labor market where the equilibrium wage rate is $15 per hour.Sketch the labor supply curve that the firm faces (label the axes of your graph and relevant numeric reference points appropriately).Explain why the graph looks as you have drawn it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In constructing a model of firm-level labor demand,we assume that labor is subject to diminishing marginal productivity.Explain the rationale for this assumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Consider an employer that is a monopolist in its product market versus an otherwise comparable employer that is a competitor in its product market.A wage increase will have
A) a comparatively larger effect on employment of the monopolist because the monopolist is the only seller of the good.
B) no effect on employment of the monopolist because the monopolist will simply pass the increase in wage cost on to consumers by charging a higher price.
C) the same effect on employment because the profit maximization condition is MRP = MEL whether the firm is a monopolist or whether it is competitive in the product market.
D) a comparatively smaller effect on employment of the monopolist because the monopolist will be able to pass some of the increase in wage cost on to consumers by charging a higher price.
A) a comparatively larger effect on employment of the monopolist because the monopolist is the only seller of the good.
B) no effect on employment of the monopolist because the monopolist will simply pass the increase in wage cost on to consumers by charging a higher price.
C) the same effect on employment because the profit maximization condition is MRP = MEL whether the firm is a monopolist or whether it is competitive in the product market.
D) a comparatively smaller effect on employment of the monopolist because the monopolist will be able to pass some of the increase in wage cost on to consumers by charging a higher price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The output of workers at a factory depends on the number of supervisors employed.The factory sells its good in a competitive product market at a price of P = $5.The daily wage of supervisors is W = $600.Fill in the MPL and MRPL columns in the table below.
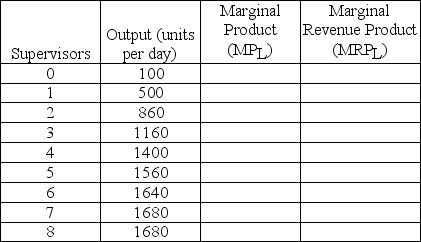
How many supervisors should the firm employ? Explain why.

How many supervisors should the firm employ? Explain why.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Suppose that a firm is competitive in both the product market and the labor market.Graph the firm's marginal revenue product curve (be sure to label the axes of your graph appropriately).Explain why the marginal revenue product curve is also the firm's short run labor demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Suppose that a firm is competitive in both the product market and the labor market.If the market determined wage rate decreases,the firm's demand for labor increases.Explain why using the marginal productivity theory of input demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Suppose that the marginal revenue product function for the firm is MRPL = 40 - .75L.Assume that the firm hires labor in a competitive labor market at a wage of W = $10 per hour.Explain why employment of L = 20 is not profit maximizing (show exactly how profit could be increased).What is the profit maximizing level of employment for this firm?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
When unemployment is widespread and the wage is above its market clearing level,a cut in employer payroll tax will
A) be largely ineffective.
B) benefit employers and have no effect on workers.
C) increase employment, reduce unemployment, and have little to no effect on wages.
D) drive up wages but have little to no effect on employment and unemployment.
A) be largely ineffective.
B) benefit employers and have no effect on workers.
C) increase employment, reduce unemployment, and have little to no effect on wages.
D) drive up wages but have little to no effect on employment and unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



