Deck 6: Univariate Time Series Modelling and Forecasting
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/29
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Univariate Time Series Modelling and Forecasting
1
Which of the following would NOT be a potential remedy for the problem of multicollinearity between regressors?
A) Removing one of the explanatory variables
B) Transforming the data into logarithms
C) Transforming two of the explanatory variables into ratios
D) Collecting higher frequency data on all of the variables
A) Removing one of the explanatory variables
B) Transforming the data into logarithms
C) Transforming two of the explanatory variables into ratios
D) Collecting higher frequency data on all of the variables
Transforming the data into logarithms
2
Assuming you are interested in conducting a Goldfeld-Quandt test at a 5% significance level and the regression model is estimated on each sub-sample with residual variances and , , and . What would your conclusion be? 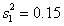
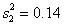
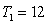
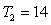
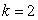
A) Do not reject the null hypothesis of heteroscedasticity
B) Reject the null hypothesis of homoscedasticity
C) Reject the null hypothesis of heteroscedasticity
D) Do not reject the null hypothesis of homoscedasticity
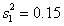
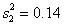
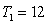
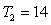
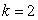
A) Do not reject the null hypothesis of heteroscedasticity
B) Reject the null hypothesis of homoscedasticity
C) Reject the null hypothesis of heteroscedasticity
D) Do not reject the null hypothesis of homoscedasticity
Do not reject the null hypothesis of homoscedasticity
3
Test statistics for the LM test and the Wald test are usually constructed to follow a
A) χ2 distribution and F-distribution, respectively
B) χ2 distribution and t-distribution, respectively
C) F-distribution and χ2 distribution, respectively
D) t-distribution and χ2 distribution, respectively
A) χ2 distribution and F-distribution, respectively
B) χ2 distribution and t-distribution, respectively
C) F-distribution and χ2 distribution, respectively
D) t-distribution and χ2 distribution, respectively
χ2 distribution and F-distribution, respectively
4
The assumption of homoscedasticity can be written mathematically as
A)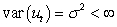
B)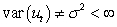
C)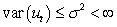
D)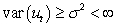
A)
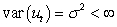
B)
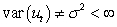
C)
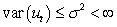
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If the residuals of a regression on a large sample are found to be heteroscedastic which of the following might be a likely consequence?
(I) The coefficient estimates are biased
(ii) The standard error estimates for the slope coefficients may be too small
(iii) Statistical inferences may be wrong
A) (i) only
B) (ii) and (iii) only
C) (i), (ii) and (iii)
D) (i) and (ii) only
(I) The coefficient estimates are biased
(ii) The standard error estimates for the slope coefficients may be too small
(iii) Statistical inferences may be wrong
A) (i) only
B) (ii) and (iii) only
C) (i), (ii) and (iii)
D) (i) and (ii) only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If OLS is used in the presence of heteroscedasticity, which of the following will be likely consequences?
(I) Coefficient estimates may be misleading
(ii) Hypothesis tests could reach the wrong conclusions
(iii) Forecasts made from the model could be biased
(iv) Standard errors may inappropriate
A) (ii) and (iv) only
B) (i) and (iii) only
C) (i), (ii), and (iii) only
D) (i), (ii), (iii), and (iv).
(I) Coefficient estimates may be misleading
(ii) Hypothesis tests could reach the wrong conclusions
(iii) Forecasts made from the model could be biased
(iv) Standard errors may inappropriate
A) (ii) and (iv) only
B) (i) and (iii) only
C) (i), (ii), and (iii) only
D) (i), (ii), (iii), and (iv).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following would you expect to be a problem associated with adding lagged values of the dependent variable into a regression equation?
A) The assumption that the regressors are non-stochastic is violated
B) A model with many lags may lead to residual non-normality
C) Adding lags may induce multicollinearity with current values of variables
D) The standard errors of the coefficients will fall as a result of adding more explanatory variables
A) The assumption that the regressors are non-stochastic is violated
B) A model with many lags may lead to residual non-normality
C) Adding lags may induce multicollinearity with current values of variables
D) The standard errors of the coefficients will fall as a result of adding more explanatory variables

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which one of the following would be the most appropriate auxiliary regression for a Ramsey RESET test of functional form?
A)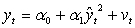
B)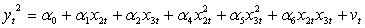
C)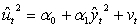
D)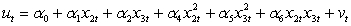
A)
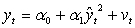
B)
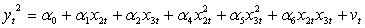
C)
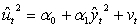
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following would probably NOT be a potential "cure" for non-normal residuals?
A) Transforming two explanatory variables into a ratio
B) Removing large positive residuals
C) Using a procedure for estimation and inference which did not assume normality
D) Removing large negative residuals
A) Transforming two explanatory variables into a ratio
B) Removing large positive residuals
C) Using a procedure for estimation and inference which did not assume normality
D) Removing large negative residuals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If the residuals of a model containing lags of the dependent variable are autocorrelated, which one of the following could this lead to?
A) Biased but consistent coefficient estimates
B) Biased and inconsistent coefficient estimates
C) Unbiased but inconsistent coefficient estimates
D) Unbiased and consistent but inefficient coefficient estimates.
A) Biased but consistent coefficient estimates
B) Biased and inconsistent coefficient estimates
C) Unbiased but inconsistent coefficient estimates
D) Unbiased and consistent but inefficient coefficient estimates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is NOT a good reason for including lagged variables in a regression?
A) Slow response of the dependent variable to changes in the independent variables
B) Over-reactions of the dependent variables
C) The dependent variable is a centred moving average of the past 4 values of the series
D) The residuals of the model appear to be non-normal
A) Slow response of the dependent variable to changes in the independent variables
B) Over-reactions of the dependent variables
C) The dependent variable is a centred moving average of the past 4 values of the series
D) The residuals of the model appear to be non-normal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following conditions must be fulfilled for the Durbin Watson test to be valid?
(I) The regression includes a constant term
(ii) The regressors are non-stochastic
(iii) There are no lags of the dependent variable in the regression
(iv) There are no lags of the independent variables in the regression
A) (i), (ii) and (iii) only
B) (i) and (ii) only
C) (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
D) (i), (ii), and (iv) only
(I) The regression includes a constant term
(ii) The regressors are non-stochastic
(iii) There are no lags of the dependent variable in the regression
(iv) There are no lags of the independent variables in the regression
A) (i), (ii) and (iii) only
B) (i) and (ii) only
C) (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
D) (i), (ii), and (iv) only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is the long run solution to the following dynamic econometric model? yt = 1 + 2 X2t + 3 X3t + ut
A) y = 1 + 2X2 + 3X3
B) yt = 1 + 2X2t + 3X3t
C) y = - ( 2/ 1) X2 - ( 3 / 1)X3
D) There is no long run solution to this equation
A) y = 1 + 2X2 + 3X3
B) yt = 1 + 2X2t + 3X3t
C) y = - ( 2/ 1) X2 - ( 3 / 1)X3
D) There is no long run solution to this equation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which one of the following is NOT a symptom of near multicollinearity?
A) The R2 value is high
B) The regression results change substantively when one particular variable is deleted
C) Confidence intervals on parameter estimates are narrow
D) Individual parameter estimates are insignificant
A) The R2 value is high
B) The regression results change substantively when one particular variable is deleted
C) Confidence intervals on parameter estimates are narrow
D) Individual parameter estimates are insignificant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The value of the Durbin Watson test statistic in a regression with 4 regressors (including the constant term) estimated on 100 observations is 3.6. What might we suggest from this?
A) The residuals are positively autocorrelated
B) The residuals are negatively autocorrelated
C) There is no autocorrelation in the residuals
D) The test statistic has fallen in the intermediate region
A) The residuals are positively autocorrelated
B) The residuals are negatively autocorrelated
C) There is no autocorrelation in the residuals
D) The test statistic has fallen in the intermediate region

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If a regression equation contains an irrelevant variable, the parameter estimates will be
A) Consistent and unbiased but inefficient
B) Consistent and asymptotically efficient but biased
C) Inconsistent
D) Consistent, unbiased and efficient.
A) Consistent and unbiased but inefficient
B) Consistent and asymptotically efficient but biased
C) Inconsistent
D) Consistent, unbiased and efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Put the following steps of the model-building process in the order in which it would be statistically most appropriate to do them:
(I) Estimate model
(ii) Conduct hypothesis tests on coefficients
(iii) Remove irrelevant variables
(iv) Conduct diagnostic tests on the model residuals
A) (i) then (ii) then (iii) then (iv)
B) (i) then (iv) then (ii) then (iii)
C) (i) then (iv) then (iii) then (ii)
D) (i) then (iii) then (ii) then (iv).
(I) Estimate model
(ii) Conduct hypothesis tests on coefficients
(iii) Remove irrelevant variables
(iv) Conduct diagnostic tests on the model residuals
A) (i) then (ii) then (iii) then (iv)
B) (i) then (iv) then (ii) then (iii)
C) (i) then (iv) then (iii) then (ii)
D) (i) then (iii) then (ii) then (iv).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If a residual series is negatively autocorrelated, which one of the following is the most likely value of the Durbin Watson statistic?
A) Close to zero
B) Close to two
C) Close to four
D) Close to one.
A) Close to zero
B) Close to two
C) Close to four
D) Close to one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of these statements is true?
(I) The F-distribution has 2 degrees of freedom parameters
(II) Asymptotically, the LM test and the Wald test are equivalent
(III) The results from the LM and Wald tests may differ somewhat in small samples
(IV) The F-distribution is a special case of the t-distribution
A) I only
B) I and II
C) I, II and III
D) I, II, III and IV
(I) The F-distribution has 2 degrees of freedom parameters
(II) Asymptotically, the LM test and the Wald test are equivalent
(III) The results from the LM and Wald tests may differ somewhat in small samples
(IV) The F-distribution is a special case of the t-distribution
A) I only
B) I and II
C) I, II and III
D) I, II, III and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A normal distribution has coefficients of skewness and excess kurtosis which are respectively
A) 0 and 0
B) 0 and 3
C) 3 and 0
D) Will vary from one normal distribution to another
A) 0 and 0
B) 0 and 3
C) 3 and 0
D) Will vary from one normal distribution to another

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of these is not a consequence of ignoring autocorrelation if it is present?
A) The coefficient estimates derived using OLS are inefficient
B) Standard error estimates are inappropriate
C) The coefficient estimates derived using OLS are biased
D) The coefficient estimates derived using OLS are not the best linear unbiased estimators
A) The coefficient estimates derived using OLS are inefficient
B) Standard error estimates are inappropriate
C) The coefficient estimates derived using OLS are biased
D) The coefficient estimates derived using OLS are not the best linear unbiased estimators

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following statements are true about parameter stability tests?
(I) Parameter stability tests test the assumption that the estimated parameters of a model are constant for the entire sample
(II) Chow test and predictive failure tests are two types of parameter stability tests
(III) Backward and forward predictive failure tests are two types of parameter stability tests
(IV) Parameter stability tests examine violations of the classical linear regression model assumptions
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) I, II and III only
D) I, II, III and IV
(I) Parameter stability tests test the assumption that the estimated parameters of a model are constant for the entire sample
(II) Chow test and predictive failure tests are two types of parameter stability tests
(III) Backward and forward predictive failure tests are two types of parameter stability tests
(IV) Parameter stability tests examine violations of the classical linear regression model assumptions
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) I, II and III only
D) I, II, III and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of these is a viable solution to the problem of multicollinearity?
(I) Ignore it
(II) Drop one of the collinear variables
(III) Transform the highly correlated variables into a ratio
(IV) Take the logs of the variables
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) I, II and III only
D) I, II, III and IV
(I) Ignore it
(II) Drop one of the collinear variables
(III) Transform the highly correlated variables into a ratio
(IV) Take the logs of the variables
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) I, II and III only
D) I, II, III and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Assuming a researcher runs the following regression where is residual from a regression. If the researcher conducts a hypothesis test with null hypothesis of against an alternative hypothesis of , what type of test is he/she conducting? 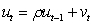
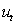
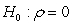
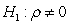
A) Test for heteroscedasticity
B) Test for autocorrelation
C) Test for non-normality
D) Test for homoscedasticity
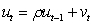
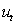
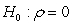
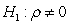
A) Test for heteroscedasticity
B) Test for autocorrelation
C) Test for non-normality
D) Test for homoscedasticity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Simultaneous equations bias is a situation where
A) There is a two-way causal relationship between the explanatory and explained variable
B) There is a two-way causal relationship between two selected explanatory variables
C) There is a two-way causal relationship between two selected independent variables
D) There is a two-way causal relationship between the residuals of two regression models
A) There is a two-way causal relationship between the explanatory and explained variable
B) There is a two-way causal relationship between two selected explanatory variables
C) There is a two-way causal relationship between two selected independent variables
D) There is a two-way causal relationship between the residuals of two regression models

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A)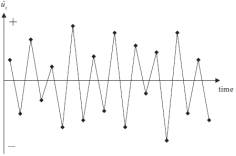 B)
B)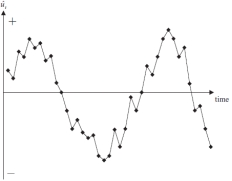
The graphs above are time series plots of residuals from two separate regressions. Which of these combinations is true?
A) A shows negative autocorrelation and B shows positive autocorrelation
B) A shows positive autocorrelation and B shows negative autocorrelation
C) A shows heteroscasticity and B shows homoscedasticity
D) A shows homoscedasticity and B shows heteroscasticity
 B)
B)
The graphs above are time series plots of residuals from two separate regressions. Which of these combinations is true?
A) A shows negative autocorrelation and B shows positive autocorrelation
B) A shows positive autocorrelation and B shows negative autocorrelation
C) A shows heteroscasticity and B shows homoscedasticity
D) A shows homoscedasticity and B shows heteroscasticity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of these is a test for heteroscedasticity?
A) Breusch-Godfrey test
B) White test
C) Bera-Jarque test
D) Breusch-Jagan test
A) Breusch-Godfrey test
B) White test
C) Bera-Jarque test
D) Breusch-Jagan test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Assuming the researcher now runs the following regression where is residual from a regression. If the researcher conducts a test with a null hypothesis of and and ... and against an alternative hypothesis of or or ... or , what type of test is he/she conducting? 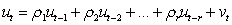

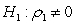
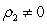
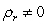
A) Test for rth order of heteroscedasticity
B) Test for rth order of autocorrelation
C) Test for rth order of non-normality
D) Test for rth order of homoscedasticity
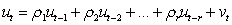

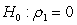
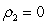
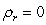
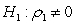
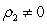
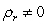
A) Test for rth order of heteroscedasticity
B) Test for rth order of autocorrelation
C) Test for rth order of non-normality
D) Test for rth order of homoscedasticity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of these is not a viable 'solution' for heteroscedasticity?
A) Using generalised least squares ifr the form of heteroscedasticity is known
B) Transforming the variables into logs
C) Using heteroscedasticity-consistent standard error estimates
D) Taking the first differences of the series
A) Using generalised least squares ifr the form of heteroscedasticity is known
B) Transforming the variables into logs
C) Using heteroscedasticity-consistent standard error estimates
D) Taking the first differences of the series

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



