Deck 5: Classical Linear Regression Model Assumptions and Diagnostic Tests
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/20
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Classical Linear Regression Model Assumptions and Diagnostic Tests
1
Assuming that the restricted sum of squares of the restricted regression in question 3 is 436.1 and the unrestricted sum of squares is 397.2, what would the conclusion of the hypothesis test be? (The significance level is 5%)
A) Reject the null hypothesis
B) Do not reject the null hypothesis
C) Reject the alternative hypothesis
D) Cannot say
A) Reject the null hypothesis
B) Do not reject the null hypothesis
C) Reject the alternative hypothesis
D) Cannot say
Reject the null hypothesis
2
Question refers to the following regression estimated on 64 observations:
Yt = 1 + 2X2t + 3X3t + 4X4t + ut
-Which of the following null hypotheses could we test using an F-test?
(I) 2 = 0
(ii) 2 = 1 and 3 + 4 = 1
(iii) 3 4 = 1
(iv) 2 - 3 - 4 = 1
A) (i) and (ii) only
B) (ii) and (iv) only
C) (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
D) (i), (ii), and (iv) only
Yt = 1 + 2X2t + 3X3t + 4X4t + ut
-Which of the following null hypotheses could we test using an F-test?
(I) 2 = 0
(ii) 2 = 1 and 3 + 4 = 1
(iii) 3 4 = 1
(iv) 2 - 3 - 4 = 1
A) (i) and (ii) only
B) (ii) and (iv) only
C) (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
D) (i), (ii), and (iv) only
(i), (ii), and (iv) only
3
Which one of the following is the most appropriate as a definition of R2 in the context that the term is usually used?
A) It is the proportion of the total variability of y that is explained by the model
B) It is the proportion of the total variability of y about its mean value that is explained by the model
C) It is the correlation between the fitted values and the residuals
D) It is the correlation between the fitted values and the mean.
A) It is the proportion of the total variability of y that is explained by the model
B) It is the proportion of the total variability of y about its mean value that is explained by the model
C) It is the correlation between the fitted values and the residuals
D) It is the correlation between the fitted values and the mean.
It is the proportion of the total variability of y about its mean value that is explained by the model
4
Consider the following two regressions 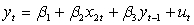
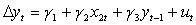 Which of the following statements are true?
Which of the following statements are true?
(I) The RSS will be the same for the two models
(ii) The R2 will be the same for the two models
(iii) The adjusted R2 will be different for the two models
(iv) The regression F-test will be the same for the two models
A) (ii) and (iv) only
B) (i) and (iii) only
C) (i), (ii), and (iii) only
D) (i), (ii), (iii), and (iv).
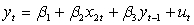
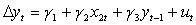 Which of the following statements are true?
Which of the following statements are true?(I) The RSS will be the same for the two models
(ii) The R2 will be the same for the two models
(iii) The adjusted R2 will be different for the two models
(iv) The regression F-test will be the same for the two models
A) (ii) and (iv) only
B) (i) and (iii) only
C) (i), (ii), and (iii) only
D) (i), (ii), (iii), and (iv).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Why is R2 a commonly used and perhaps better measure of how well a regression model fit the data than the residual sum of squares (RSS)?
A) The RSS is often too large
B) The RSS does not depend on the scale of the dependent variable whereas the R2 does
C) The RSS depends on the scale of the dependent variable whereas the R2 does not
D) The RSS depends on the scale of the independent variable whereas the R2 does not
A) The RSS is often too large
B) The RSS does not depend on the scale of the dependent variable whereas the R2 does
C) The RSS depends on the scale of the dependent variable whereas the R2 does not
D) The RSS depends on the scale of the independent variable whereas the R2 does not

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Suppose that the value of R2 for an estimated regression model is exactly one. Which of the following are true?
(I) All of the data points must lie exactly on the line
(ii) All of the residuals must be zero
(iii) All of the variability of y about is mean have has been explained by the model
(I) The fitted line will be horizontal with respect to all of the explanatory variables
A) (ii) and (iv) only
B) (i) and (iii) only
C) (i), (ii), and (iii) only
(I), (ii), (iii), and (iv)
(I) All of the data points must lie exactly on the line
(ii) All of the residuals must be zero
(iii) All of the variability of y about is mean have has been explained by the model
(I) The fitted line will be horizontal with respect to all of the explanatory variables
A) (ii) and (iv) only
B) (i) and (iii) only
C) (i), (ii), and (iii) only
(I), (ii), (iii), and (iv)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What would the restricted regression be if you are interested in testing the null hypothesis and against the alternative hypothesis or for a regression ,? 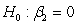
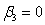
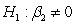
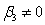
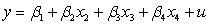
A)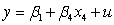
B)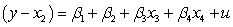
C)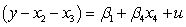
D)
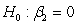
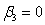
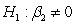
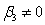
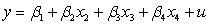
A)
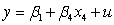
B)
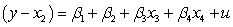
C)
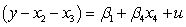
D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Use the following to answer questions
Assuming you have two regression models and .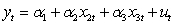
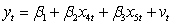
How can the two models be validly compared to determine the model that better represents the data yt?
A) By observing their respective R2
B) By observing their respective Adjusted R2
C) By estimating an encompassing or hybrid model
D) All of the above
Assuming you have two regression models and .
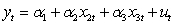
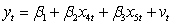
How can the two models be validly compared to determine the model that better represents the data yt?
A) By observing their respective R2
B) By observing their respective Adjusted R2
C) By estimating an encompassing or hybrid model
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Consider the following regression estimated using 84 observations: yt = 1 + 2X2t + 3X3t + 4X4t + ut
Suppose that a researcher wishes to test the null hypothesis: 2 = 1 and 3 + 4 = 1. The TABULATED value of the F-distribution that we would compare the result of testing this hypothesis with at the 10% level would be approximately
A) 19.48
B) 2.76
C) 2.37
D) 3.11
Suppose that a researcher wishes to test the null hypothesis: 2 = 1 and 3 + 4 = 1. The TABULATED value of the F-distribution that we would compare the result of testing this hypothesis with at the 10% level would be approximately
A) 19.48
B) 2.76
C) 2.37
D) 3.11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following are often considered disadvantages of the use of adjusted R2 as a variable addition / variable deletion rule?
(I) Adjusted R2 always rises as more variables are added
(ii) Adjusted R2 often leads to large models with many marginally significant or marginally insignificant variables
(iii) Adjusted R2 cannot be compared for models with different explanatory variables
(iv) Adjusted R2 cannot be compared for models with different explained variables.
A) (ii) and (iv) only
B) (i) and (iii) only
C) (i), (ii), and (iii) only
D) (i), (ii), (iii), and (iv).
(I) Adjusted R2 always rises as more variables are added
(ii) Adjusted R2 often leads to large models with many marginally significant or marginally insignificant variables
(iii) Adjusted R2 cannot be compared for models with different explanatory variables
(iv) Adjusted R2 cannot be compared for models with different explained variables.
A) (ii) and (iv) only
B) (i) and (iii) only
C) (i), (ii), and (iii) only
D) (i), (ii), (iii), and (iv).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which one of the following statements must hold for EVERY CASE concerning the residual sums of squares for the restricted and unrestricted regressions?
A) URSS > RRSS
B) URSS RRSS
C) RRSS > URSS
D) RRSS URSS
A) URSS > RRSS
B) URSS RRSS
C) RRSS > URSS
D) RRSS URSS

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If our regression equation is y = X + u, where we have T observations and k regressors, what will be the dimension of using the standard matrix notation 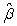
A) T * k
B) T * 1
C) k *1
D) k * k
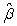
A) T * k
B) T * 1
C) k *1
D) k * k

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Use the following to answer questions
Assuming you have two regression models and .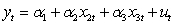
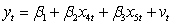
What is the relevant encompassing model required to compare the two regression models?
A)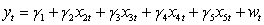
B)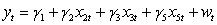
C)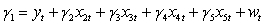
D) Encompassing models cannot be used to compare these specifications
Assuming you have two regression models and .
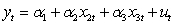
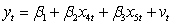
What is the relevant encompassing model required to compare the two regression models?
A)
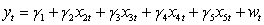
B)
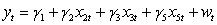
C)
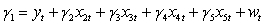
D) Encompassing models cannot be used to compare these specifications

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of these statements is a characteristic of the stepwise regression procedure?
(I) It chooses the jointly most 'important' explanatory variable from a set of candidate variables
(II) It can start with no variables in the regression and then it selects first the variable with the lowest p-value
(III) It can start with no variables in the regression and then it selects first the variable with the highest p-value
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) Both I and II
(I) It chooses the jointly most 'important' explanatory variable from a set of candidate variables
(II) It can start with no variables in the regression and then it selects first the variable with the lowest p-value
(III) It can start with no variables in the regression and then it selects first the variable with the highest p-value
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) Both I and II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of these statements is not true about quantile regressions?
A) No distributional assumptions are required to optimally estimate the parameters
B) It is a non-parametric technique
C) It is a parametric technique
D) The response variable is usually assumed to be independently distributed and homoscedastic
A) No distributional assumptions are required to optimally estimate the parameters
B) It is a non-parametric technique
C) It is a parametric technique
D) The response variable is usually assumed to be independently distributed and homoscedastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If you are interested in conducting a multiple hypotheses test to determine whether and are both unity for a regression , what would the restricted regression be? 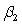
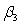
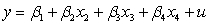
A)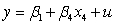
B)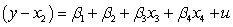
C)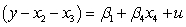
D)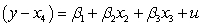
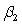
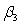
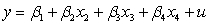
A)
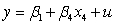
B)
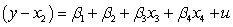
C)
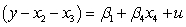
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
For question , you are given the following data 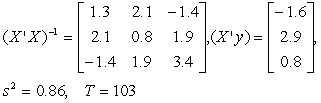
The regression equation is
Yt = 1 + 2X2t + 3X3t + ut
-Which of the following is the correct value for ?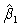
A) 2.89
B) 1.30
C) 0.84
D) We cannot determine the value of from the information given in the question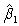
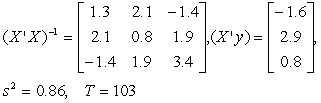
The regression equation is
Yt = 1 + 2X2t + 3X3t + ut
-Which of the following is the correct value for ?
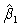
A) 2.89
B) 1.30
C) 0.84
D) We cannot determine the value of from the information given in the question

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the relationship, if any, between t-distributed and F-distributed random variables?
A) A t-variate with z degrees of freedom is also an F(1, z)
B) The square of a t-variate with z degrees of freedom is also an F(1, z)
C) A t-variate with z degrees of freedom is also an F(z, 1)
D) There is no relationship between the two distributions.
A) A t-variate with z degrees of freedom is also an F(1, z)
B) The square of a t-variate with z degrees of freedom is also an F(1, z)
C) A t-variate with z degrees of freedom is also an F(z, 1)
D) There is no relationship between the two distributions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Trying many variables in a regression without basing the selection of candidate variables on a financial or economic theory is popularly referred to as
A) Data fitting
B) Data clipping
C) Data mining
D) None of the above
A) Data fitting
B) Data clipping
C) Data mining
D) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of these is a mathematical expression of the residual sum of squares?
(I)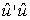 (II)
(II) 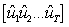 (III)
(III) 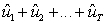
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) I and III only
D) I, II and III
(I)
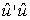 (II)
(II) 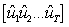 (III)
(III) 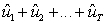
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) I and III only
D) I, II and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



