Deck 11: Panel Data and Limited Dependent Variable Models
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/12
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Panel Data and Limited Dependent Variable Models
1
Logit and probit models are more appropriate than linear probability models because:
A) Logit and probit can estimate probabilities that are negative
B) Logit and probit cannot estimate probabilities that are greater than one
C) Logit and probit cannot estimate probabilities that are negative but not greater than one
D) Logit and probit cannot estimate probabilities that are negative or greater than one
A) Logit and probit can estimate probabilities that are negative
B) Logit and probit cannot estimate probabilities that are greater than one
C) Logit and probit cannot estimate probabilities that are negative but not greater than one
D) Logit and probit cannot estimate probabilities that are negative or greater than one
Logit and probit cannot estimate probabilities that are negative or greater than one
2
Appropriate modelling of limited dependent variables that are assigned numerical values having a natural ordering can be done using:
(I) Probit models
(II) Logit models
(III) Ordered probit models
(IV) Ordered logit models
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) II and III only
D) III and IV only
(I) Probit models
(II) Logit models
(III) Ordered probit models
(IV) Ordered logit models
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) II and III only
D) III and IV only
III and IV only
3
Running a cross-sectional regression on the time-averaged values of the variables is known as a:
A) Within estimator
B) Between estimator
C) Cross-sectional estimator
D) Demeaned estimator
A) Within estimator
B) Between estimator
C) Cross-sectional estimator
D) Demeaned estimator
Between estimator
4
Which of the following is a mathematical expression of a time-fixed effects model?
A)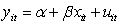
B)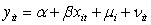
C) ,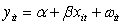
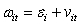
D)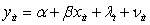
A)
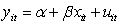
B)
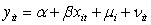
C) ,
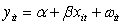
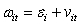
D)
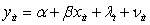

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Entity fixed effects models
A) Allow the intercept in the regression model to differ cross-sectionally but not over time, while all of the slope estimates are fixed both cross-sectionally and over time
B) Allow the slope in the regression model to differ cross-sectionally but not over time, while the intercept estimates are fixed both cross-sectionally and over time
C) Allow the intercept in the regression model to differ over time, while all of the slope estimates are different both cross-sectionally and over time
D) Any of the above could be true depending on the model specification
A) Allow the intercept in the regression model to differ cross-sectionally but not over time, while all of the slope estimates are fixed both cross-sectionally and over time
B) Allow the slope in the regression model to differ cross-sectionally but not over time, while the intercept estimates are fixed both cross-sectionally and over time
C) Allow the intercept in the regression model to differ over time, while all of the slope estimates are different both cross-sectionally and over time
D) Any of the above could be true depending on the model specification

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The acronym LSDV in panel model estimation stands for
A) Least squares dependent variable
B) Limited squares dependent variable
C) Least squares dummy variable
D) Limiting squares dummy variable
A) Least squares dependent variable
B) Limited squares dependent variable
C) Least squares dummy variable
D) Limiting squares dummy variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of these is a type of panel estimator approach?
(I) Fixed effects
(II) Random effects
(III) Seemingly unrelated regression effects
(IV) Time-varying effects
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) I, II and III only
D) I, II, III and IV only
(I) Fixed effects
(II) Random effects
(III) Seemingly unrelated regression effects
(IV) Time-varying effects
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) I, II and III only
D) I, II, III and IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of these are advantages of using panel data?
(I) We can address a broader range of issues and tackle more complex problems than would be possible with pure time-series or pure cross-sectional data alone
(II) It allows us to increase the number of degrees of freedom
(III) It allows us to increase the power of the tests
(IV) We can remove the impact of certain forms of omitted variables bias in regression results
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) I, II and III only
D) I, II, III and IV
(I) We can address a broader range of issues and tackle more complex problems than would be possible with pure time-series or pure cross-sectional data alone
(II) It allows us to increase the number of degrees of freedom
(III) It allows us to increase the power of the tests
(IV) We can remove the impact of certain forms of omitted variables bias in regression results
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) I, II and III only
D) I, II, III and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following statements about logit and probit models is true?
(I) They cannot be estimated by ordinary least squares
(II) They can be estimated using maximum likelihood
(III) They can be estimated using non-linear least squares
(IV) They can be estimated using instrumental variables
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) I, II and III only
D) I, II, III and IV
(I) They cannot be estimated by ordinary least squares
(II) They can be estimated using maximum likelihood
(III) They can be estimated using non-linear least squares
(IV) They can be estimated using instrumental variables
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) I, II and III only
D) I, II, III and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What of the following is a mathematical expression of a random effects model?
A)
B)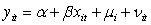
C) ,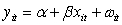
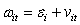
D)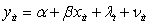
A)

B)
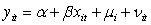
C) ,
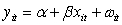
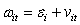
D)
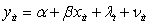

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If the maximised value of the log-likelihood function for a logit model is 34.55 and for a restricted model where all of the slope parameters are set to zero is 30.67, what is the pseudo-R2?
A) 0.13
B) -0.13
C) 0.11
D) -0.11
A) 0.13
B) -0.13
C) 0.11
D) -0.11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
To test for unit roots in panel data, Levin, Lin and Chu (2002) develop a test based on the equation . What is the appropriate null hypothesis for this test? 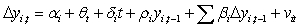
A)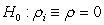
B)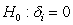
C)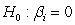
D)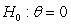
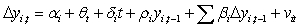
A)
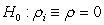
B)
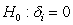
C)
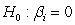
D)
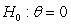

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 12 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



