Deck 12: Glm 1: Comparing Several Independent Means
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/41
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Glm 1: Comparing Several Independent Means
1
Analyse the cycling time-trial data below. Thirty-two elite cyclists were randomly allocated into one of four groups. Without using SPSS, calculate the mean and total for each group. The groups were as follows
i. Received caffeine and were told it was
ii. Received caffeine and were told it was not
iii. Received no caffeine and were told it was not
iv. Received no caffeine but were told it was
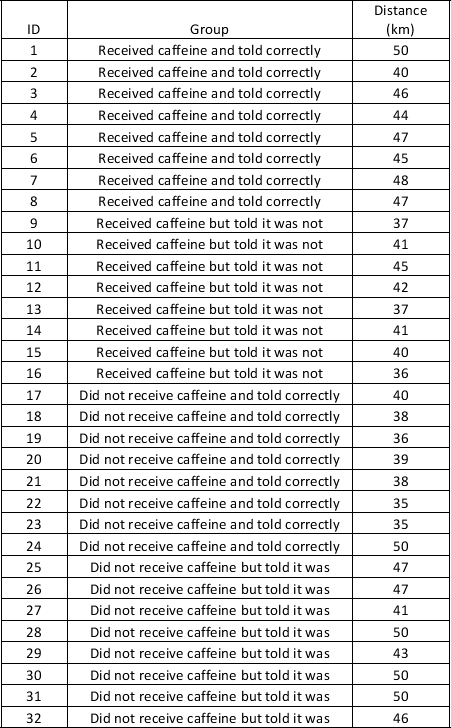 Group 1-
Group 1-
v. Mean: 45.9 km
vi. Total:367 km
Group 2
vii. Mean:39.9 km
Viii. Total:319 km
Group 3
ix. Mean:38.9 km
x. Total:311 km
Group 4
xi. Mean:46.8 km
xii. Total:374 km
How would you calculate the total sum of squares?
A) SST = SSW + SSB
B) SST = SSW - SSB
C) SST = SSB / SSW
D) SST = SSB × SSW
i. Received caffeine and were told it was
ii. Received caffeine and were told it was not
iii. Received no caffeine and were told it was not
iv. Received no caffeine but were told it was
 Group 1-
Group 1-v. Mean: 45.9 km
vi. Total:367 km
Group 2
vii. Mean:39.9 km
Viii. Total:319 km
Group 3
ix. Mean:38.9 km
x. Total:311 km
Group 4
xi. Mean:46.8 km
xii. Total:374 km
How would you calculate the total sum of squares?
A) SST = SSW + SSB
B) SST = SSW - SSB
C) SST = SSB / SSW
D) SST = SSB × SSW
SST = SSW + SSB
2
An ANOVA works on the basis of comparing systematic and systematic variance, but how is this achieved?
A) Systematic variance / unsystematic variance
B) Systematic variance × unsystematic variance
C) Unsystematic variance / systematic variance
D) Unsystematic variance - systematic variance
A) Systematic variance / unsystematic variance
B) Systematic variance × unsystematic variance
C) Unsystematic variance / systematic variance
D) Unsystematic variance - systematic variance
Systematic variance / unsystematic variance
3
If the value for F-statistic in Q15 were to decrease, what would happen to the p-value?
A) Decrease - become more significant.
B) Increase - become less significant.
C) The p-value is unaffected by the F-statistic
D) The p-value could increase or decrease depending on the between- and within-groups degrees of freedom.
A) Decrease - become more significant.
B) Increase - become less significant.
C) The p-value is unaffected by the F-statistic
D) The p-value could increase or decrease depending on the between- and within-groups degrees of freedom.
Increase - become less significant.
4
How would you calculate the between sum of squares?
A) SSB = SST - SSW
B) SSB = SST + SSW
C) SSB = SSW / SST
D) SSB = SSW × SST
A) SSB = SST - SSW
B) SSB = SST + SSW
C) SSB = SSW / SST
D) SSB = SSW × SST

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Based on the answers provided in Q7, calculate the between sum of squares for the time-trial data.
A) 392.1
B) 377.7
C) 364.2 d .369.9
A) 392.1
B) 377.7
C) 364.2 d .369.9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Based on the information presented in Q15, what can be assumed from the result?
A) There is a significant difference somewhere between the four groups but the location of the differences is not known.
B) There are no significant differences between the four groups.
C) Significant differences are only located between those that received caffeine and those that did not receive caffeine.
D) Significant differences were identified between all of the groups.
A) There is a significant difference somewhere between the four groups but the location of the differences is not known.
B) There are no significant differences between the four groups.
C) Significant differences are only located between those that received caffeine and those that did not receive caffeine.
D) Significant differences were identified between all of the groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Using an F-distribution table, locate the critical value required to produce a p-value equal to .05.
A) 2.95
B) 2.71
C) 2.56
D) 2.46
A) 2.95
B) 2.71
C) 2.56
D) 2.46

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is the correct expression for the one-way ANOVA based on the information presented in the table below? 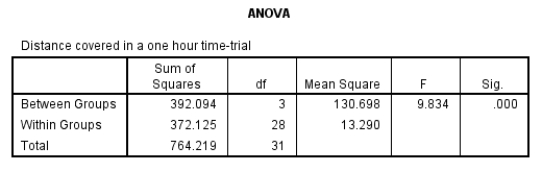
A) F(3, 28) = 9.83, p < .001
B) F(3, 28) = 9.83, p = .000
C) F(3, 28) = .001, p < 9.83
D) F(3, 28) = .001, p = 9.83

A) F(3, 28) = 9.83, p < .001
B) F(3, 28) = 9.83, p = .000
C) F(3, 28) = .001, p < 9.83
D) F(3, 28) = .001, p = 9.83

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) performs which type of test?
A) F-test
B) t-test
C) z-test
D) xy-test
A) F-test
B) t-test
C) z-test
D) xy-test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What type of research design does a one-way ANOVA adopt?
A) Independent-groups design
B) Repeated-measures design
C) Within-groups design
D) Mixed model design
A) Independent-groups design
B) Repeated-measures design
C) Within-groups design
D) Mixed model design

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Examine the Levene's test table. What can be deduced from the finding? 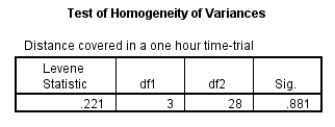
A) The Levene's test is not significant and therefore the null hypothesis is rejected.
B) The Levene's test is not significant and therefore the null hypothesis is accepted.
C) The Levene's test is significant and therefore the null hypothesis is rejected.
D) The Levene's test is significant and therefore the null hypothesis is accepted.

A) The Levene's test is not significant and therefore the null hypothesis is rejected.
B) The Levene's test is not significant and therefore the null hypothesis is accepted.
C) The Levene's test is significant and therefore the null hypothesis is rejected.
D) The Levene's test is significant and therefore the null hypothesis is accepted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Does an ANOVA test identify specifically where the differences exist between the groups?
A) No
B) Yes
C) Yes, provided the data are normally distributed
D) Yes, provided the data are not normally distributed
A) No
B) Yes
C) Yes, provided the data are normally distributed
D) Yes, provided the data are not normally distributed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If a one-way ANOVA is considered a parametric test, what is its non-parametric equivalent?
A) Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA
B) Friedman's ANOVA
C) Roy's largest root
D) There is no non-parametric equivalent, therefore multiple Mann-Whitney tests should be used.
A) Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA
B) Friedman's ANOVA
C) Roy's largest root
D) There is no non-parametric equivalent, therefore multiple Mann-Whitney tests should be used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Suppose you decided to run multiple independent t-tests as opposed to a one-way ANOVA and subsequent contrasts and/or post hoc tests. How should you correct for the p-value?
A) Apply a Bonferroni correction.
B) No adjustment to the p-value is necessary.
C) You should never use multiple t-tests.
D) Conduct a Levene's adjustment.
A) Apply a Bonferroni correction.
B) No adjustment to the p-value is necessary.
C) You should never use multiple t-tests.
D) Conduct a Levene's adjustment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Based on the answers provided in Q7, calculate the within sum of squares for the time-trial data.
A) 372.1
B) 389.7
C) 401.7
D) 456.8
A) 372.1
B) 389.7
C) 401.7
D) 456.8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is the purpose of a post hoc test?
A) It identifies where differences between the study groups exist.
B) It identifies the overall appropriateness of the ANOVA model.
C) It identifies differences between and within study groups.
D) It identifies where differences within the study group exist.
A) It identifies where differences between the study groups exist.
B) It identifies the overall appropriateness of the ANOVA model.
C) It identifies differences between and within study groups.
D) It identifies where differences within the study group exist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Based on the answers provided in Q7, calculate the total sum of squares for the time-trial data.
A) 764.2
B) 746.2
C) 801.3
D) 822.6
A) 764.2
B) 746.2
C) 801.3
D) 822.6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Calculate the η2 (eta squared) value based on the sum of squares between groups and the sum of squares within groups.
A) .7
B) .5
C) .3
D) .1
A) .7
B) .5
C) .3
D) .1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
For an ANOVA to be used, what is the minimum number of data sets required?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When would it be appropriate to use the planned comparisons instead of the post hoc tests to identify differences in the time-trial groups?
A) When specific hypotheses have been generated before the experiment.
B) Comparisons should always be run with post hoc tests.
C) Comparisons should be run in place of post hoc tests when no hypothesis has been planned prior to the experiment.
D) Neither post hoc tests or comparisons are really necessary, as they only provide supplementary information.
A) When specific hypotheses have been generated before the experiment.
B) Comparisons should always be run with post hoc tests.
C) Comparisons should be run in place of post hoc tests when no hypothesis has been planned prior to the experiment.
D) Neither post hoc tests or comparisons are really necessary, as they only provide supplementary information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Suppose you decided to run multiple independent t-tests as opposed to a one-way ANOVA and subsequent contrasts and/or post hoc tests. How should you correct for the p-value?
A) Apply a Bonferroni correction.
B) No adjustment to the p-value is necessary.
C) You should never use multiple t-tests.
D) Conduct a Levene's adjustment.
A) Apply a Bonferroni correction.
B) No adjustment to the p-value is necessary.
C) You should never use multiple t-tests.
D) Conduct a Levene's adjustment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Analyse the cycling time-trial data below. Thirty-two elite cyclists were randomly allocated into one of four groups. Without using SPSS, calculate the mean and total for each group. The groups were as follows
i. Received caffeine and were told it was
ii. Received caffeine and were told it was not
iii. Received no caffeine and were told it was not
iv. Received no caffeine but were told it was
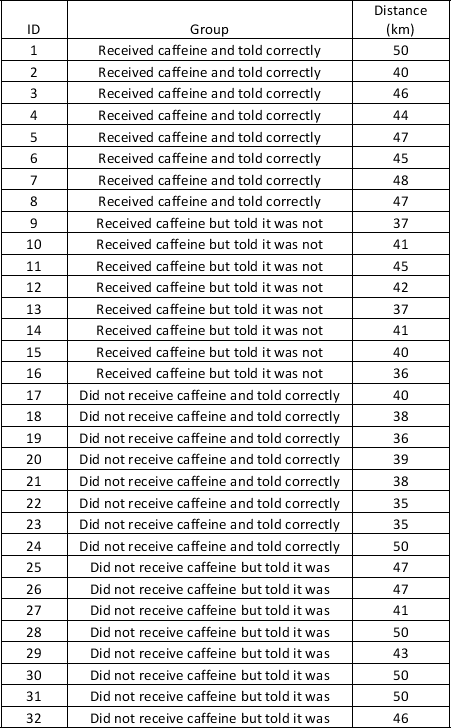 Group 1-
Group 1-
v. Mean: 45.9 km
vi. Total:367 km
Group 2
vii. Mean:39.9 km
Viii. Total:319 km
Group 3
ix. Mean:38.9 km
x. Total:311 km
Group 4
xi. Mean:46.8 km
xii. Total:374 km
How would you calculate the total sum of squares?
A) SST = SSW + SSB
B) SST = SSW - SSB
C) SST = SSB / SSW
D) SST = SSB × SSW
i. Received caffeine and were told it was
ii. Received caffeine and were told it was not
iii. Received no caffeine and were told it was not
iv. Received no caffeine but were told it was
 Group 1-
Group 1-v. Mean: 45.9 km
vi. Total:367 km
Group 2
vii. Mean:39.9 km
Viii. Total:319 km
Group 3
ix. Mean:38.9 km
x. Total:311 km
Group 4
xi. Mean:46.8 km
xii. Total:374 km
How would you calculate the total sum of squares?
A) SST = SSW + SSB
B) SST = SSW - SSB
C) SST = SSB / SSW
D) SST = SSB × SSW

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If the value for F-statistic in Q15 were to decrease, what would happen to the p-value?
A) Decrease - become more significant.
B) Increase - become less significant.
C) The p-value is unaffected by the F-statistic
D) The p-value could increase or decrease depending on the between- and within-groups degrees of freedom.
A) Decrease - become more significant.
B) Increase - become less significant.
C) The p-value is unaffected by the F-statistic
D) The p-value could increase or decrease depending on the between- and within-groups degrees of freedom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
For an ANOVA to be used, what is the minimum number of data sets required?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
An ANOVA works on the basis of comparing systematic and systematic variance, but how is this achieved?
A) Systematic variance / unsystematic variance
B) Systematic variance × unsystematic variance
C) Unsystematic variance / systematic variance
D) Unsystematic variance - systematic variance
A) Systematic variance / unsystematic variance
B) Systematic variance × unsystematic variance
C) Unsystematic variance / systematic variance
D) Unsystematic variance - systematic variance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What type of research design does a one-way ANOVA adopt?
A) Independent-groups design
B) Repeated-measures design
C) Within-groups design
D) Mixed model design
A) Independent-groups design
B) Repeated-measures design
C) Within-groups design
D) Mixed model design

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) performs which type of test?
A) F-test
B) t-test
C) z-test
D) xy-test
A) F-test
B) t-test
C) z-test
D) xy-test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the purpose of a post hoc test?
A) It identifies where differences between the study groups exist.
B) It identifies the overall appropriateness of the ANOVA model.
C) It identifies differences between and within study groups.
D) It identifies where differences within the study group exist.
A) It identifies where differences between the study groups exist.
B) It identifies the overall appropriateness of the ANOVA model.
C) It identifies differences between and within study groups.
D) It identifies where differences within the study group exist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Based on the answers provided in Q7, calculate the between sum of squares for the time-trial data.
A) 392.1
B) 377.7
C) 364.2 d .369.9
A) 392.1
B) 377.7
C) 364.2 d .369.9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Calculate the η2 (eta squared) value based on the sum of squares between groups and the sum of squares within groups.
A) .7
B) .5
C) .3
D) .1
A) .7
B) .5
C) .3
D) .1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Examine the Levene's test table. What can be deduced from the finding? 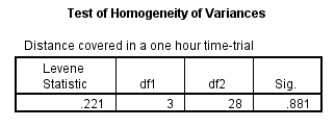
A) The Levene's test is not significant and therefore the null hypothesis is rejected.
B) The Levene's test is not significant and therefore the null hypothesis is accepted.
C) The Levene's test is significant and therefore the null hypothesis is rejected.
D) The Levene's test is significant and therefore the null hypothesis is accepted.

A) The Levene's test is not significant and therefore the null hypothesis is rejected.
B) The Levene's test is not significant and therefore the null hypothesis is accepted.
C) The Levene's test is significant and therefore the null hypothesis is rejected.
D) The Levene's test is significant and therefore the null hypothesis is accepted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Based on the information presented in Q15, what can be assumed from the result?
A) There is a significant difference somewhere between the four groups but the location of the differences is not known.
B) There are no significant differences between the four groups.
C) Significant differences are only located between those that received caffeine and those that did not receive caffeine.
D) Significant differences were identified between all of the groups.
A) There is a significant difference somewhere between the four groups but the location of the differences is not known.
B) There are no significant differences between the four groups.
C) Significant differences are only located between those that received caffeine and those that did not receive caffeine.
D) Significant differences were identified between all of the groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
How would you calculate the between sum of squares?
A) SSB = SST - SSW
B) SSB = SST + SSW
C) SSB = SSW / SST
D) SSB = SSW × SST
A) SSB = SST - SSW
B) SSB = SST + SSW
C) SSB = SSW / SST
D) SSB = SSW × SST

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
When would it be appropriate to use the planned comparisons instead of the post hoc tests to identify differences in the time-trial groups?
A) When specific hypotheses have been generated before the experiment.
B) Comparisons should always be run with post hoc tests.
C) Comparisons should be run in place of post hoc tests when no hypothesis has been planned prior to the experiment.
D) Neither post hoc tests or comparisons are really necessary, as they only provide supplementary information.
A) When specific hypotheses have been generated before the experiment.
B) Comparisons should always be run with post hoc tests.
C) Comparisons should be run in place of post hoc tests when no hypothesis has been planned prior to the experiment.
D) Neither post hoc tests or comparisons are really necessary, as they only provide supplementary information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If a one-way ANOVA is considered a parametric test, what is its non-parametric equivalent?
A) Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA
B) Friedman's ANOVA
C) Roy's largest root
D) There is no non-parametric equivalent, therefore multiple Mann-Whitney tests should be used.
A) Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA
B) Friedman's ANOVA
C) Roy's largest root
D) There is no non-parametric equivalent, therefore multiple Mann-Whitney tests should be used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Based on the answers provided in Q7, calculate the within sum of squares for the time-trial data.
A) 372.1
B) 389.7
C) 401.7
D) 456.8
A) 372.1
B) 389.7
C) 401.7
D) 456.8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Using an F-distribution table, locate the critical value required to produce a p-value equal to .05.
A) 2.95
B) 2.71
C) 2.56
D) 2.46
A) 2.95
B) 2.71
C) 2.56
D) 2.46

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Based on the answers provided in Q7, calculate the total sum of squares for the time-trial data.
A) 764.2
B) 746.2
C) 801.3
D) 822.6
A) 764.2
B) 746.2
C) 801.3
D) 822.6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Does an ANOVA test identify specifically where the differences exist between the groups?
A) No
B) Yes
C) Yes, provided the data are normally distributed
D) Yes, provided the data are not normally distributed
A) No
B) Yes
C) Yes, provided the data are normally distributed
D) Yes, provided the data are not normally distributed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is the correct expression for the one-way ANOVA based on the information presented in the table below? 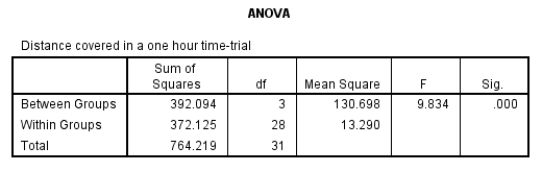
A) F(3, 28) = 9.83, p < .001
B) F(3, 28) = 9.83, p = .000
C) F(3, 28) = .001, p < 9.83
D) F(3, 28) = .001, p = 9.83

A) F(3, 28) = 9.83, p < .001
B) F(3, 28) = 9.83, p = .000
C) F(3, 28) = .001, p < 9.83
D) F(3, 28) = .001, p = 9.83

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
How would you describe this effect?
A) Large effect
B) Medium effect
C) Small effect
D) Very small effect
A) Large effect
B) Medium effect
C) Small effect
D) Very small effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



