Deck 4: Economic Efficiency and Markets
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/26
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Economic Efficiency and Markets
1
In the case of open access resources and public goods, the competitive market output level will be ___________.
A)equal to the socially efficient level of output
B)lower than the socially efficient level of output
C)unequal to the socially efficient level of output
D)higher than the socially efficient level of output
A)equal to the socially efficient level of output
B)lower than the socially efficient level of output
C)unequal to the socially efficient level of output
D)higher than the socially efficient level of output
C
2
Figure 4.5
Individual Demand for Lowering Indoor Air Pollution (CO2) in $/yr
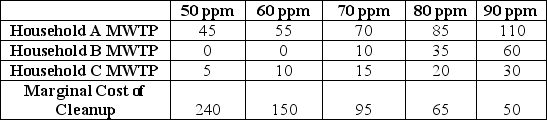
Refer to Figure 4.5.If the market consists of Homeowners A,B, and C, the aggregate willingness to pay to reduce CO2 concentration to 80 ppm is ______.
A)$65/yr
B)$140/yr
C)$85/yr
D)indeterminate
Individual Demand for Lowering Indoor Air Pollution (CO2) in $/yr

Refer to Figure 4.5.If the market consists of Homeowners A,B, and C, the aggregate willingness to pay to reduce CO2 concentration to 80 ppm is ______.
A)$65/yr
B)$140/yr
C)$85/yr
D)indeterminate
B
3
A small coastal community with the power to control access to its scallop fishery is an example of ________.
A)common property rights
B)private property rights
C)an open access resource
D)a positive externality
A)common property rights
B)private property rights
C)an open access resource
D)a positive externality
A
4
In the case of an open access resource, a(n) ________ takes place due to a lack of ________.
A)externality; regulation
B)free rider problem; property rights
C)market failure; property rights
D)external benefit; rivalry in consumption
A)externality; regulation
B)free rider problem; property rights
C)market failure; property rights
D)external benefit; rivalry in consumption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When production results in environmental degradation, private firms do not take the ________ into consideration when making their output decisions resulting in ________.
A)external costs; a market failure
B)market failure; an externality
C)social costs; pollution
D)market failure; pollution
A)external costs; a market failure
B)market failure; an externality
C)social costs; pollution
D)market failure; pollution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When we drive our cars, we get the ________ of transportation services, while others experience the detrimental effects such as pollution and congestion which environmental economists refer to as a(n) ________.
A)positive externality; negative externality
B)direct benefit; opportunity cost
C)direct benefit; negative externality
D)positive externality; opportunity cost
A)positive externality; negative externality
B)direct benefit; opportunity cost
C)direct benefit; negative externality
D)positive externality; opportunity cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A common pasture on which anyone is allowed to freely graze sheep or cattle is an example of ________.
A)private property rights
B)an open access resource
C)common property rights
D)community property rights
A)private property rights
B)an open access resource
C)common property rights
D)community property rights

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If social values are not reflected in the market values determined by the market demand and market supply curves, the competitive market equilibrium output will ______________.
A)always be the socially efficient level of output
B)not be the socially efficient level of output
C)always be higher than the socially efficient level of output
D)always be lower than the socially efficient level of output
A)always be the socially efficient level of output
B)not be the socially efficient level of output
C)always be higher than the socially efficient level of output
D)always be lower than the socially efficient level of output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
External costs can drive a wedge between the ???_______ and the _________ resulting in a market failure.
A)private marginal WTP curve; social marginal WTP curve
B)market demand curve; social marginal WTP curve
C)market supply curve; social marginal costs
D)none of the choices are correct
A)private marginal WTP curve; social marginal WTP curve
B)market demand curve; social marginal WTP curve
C)market supply curve; social marginal costs
D)none of the choices are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Suppose for a given market that the MWTP and MC curves are represented in Figure 4.1.Assuming all market and non-market values are incorporated into the data, the MWTP at the socially efficient level of output is equal to ________.
A)100 units
B)140 units
C)$230
D)$250
A)100 units
B)140 units
C)$230
D)$250

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When the rate of output is at the socially efficient level, _______________.
A)net social value which is equal to total WTP minus total costs is as large as possible
B)the total willingness to pay is as large as possible
C)profit is a large as possible
D)output is as large as possible
A)net social value which is equal to total WTP minus total costs is as large as possible
B)the total willingness to pay is as large as possible
C)profit is a large as possible
D)output is as large as possible

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Figure 4.5
Individual Demand for Lowering Indoor Air Pollution (CO2) in $/yr

Refer to Figure 4.5.If the market consists of Homeowners A, B, and C, the socially optimal level of CO2 concentrations is _________.
A)$70/yr
B)70 ppm
C)$95/yr
D)50 ppm
Individual Demand for Lowering Indoor Air Pollution (CO2) in $/yr

Refer to Figure 4.5.If the market consists of Homeowners A, B, and C, the socially optimal level of CO2 concentrations is _________.
A)$70/yr
B)70 ppm
C)$95/yr
D)50 ppm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Figure 4.3 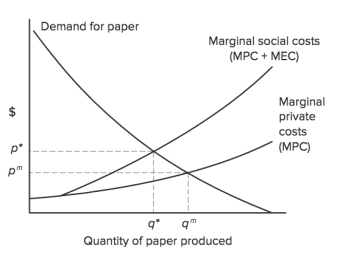
In the Figure 4.3, the socially efficient level of output is equal to ________.
A)q*
B)qm
C)p*
D)none of the choices are correct

In the Figure 4.3, the socially efficient level of output is equal to ________.
A)q*
B)qm
C)p*
D)none of the choices are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Figure 4.2 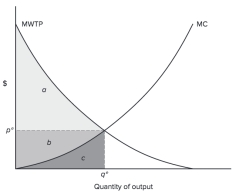
In the Figure 4.2 the net social value is equal to ________.
A)area c
B)areas a + b - c
C)areas a + b + c
D)areas a + b

In the Figure 4.2 the net social value is equal to ________.
A)area c
B)areas a + b - c
C)areas a + b + c
D)areas a + b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
External benefits can drive a wedge between the _______ and the _______ resulting in a market failure.
A)private marginal WTP curve; social marginal WTP curve
B)market demand curve; social marginal WTP curve
C)market supply curve; social marginal costs
D)none of the choices are correct
A)private marginal WTP curve; social marginal WTP curve
B)market demand curve; social marginal WTP curve
C)market supply curve; social marginal costs
D)none of the choices are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The number of miles a household drives its vehicles each year is determined by its ________ of driving.
A)opportunity cost
B)private cost
C)social cost
D)external cost
A)opportunity cost
B)private cost
C)social cost
D)external cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Figure 4.5
Individual Demand for Lowering Indoor Air Pollution (CO2) in $/yr

Refer to Figure 4.5.If the market is reduced to Homeowners A and C, aggregate willingness to pay for all CO2 levels _________.
A)increases
B)declines
C)remains unchanged
D)is unpredictable
Individual Demand for Lowering Indoor Air Pollution (CO2) in $/yr

Refer to Figure 4.5.If the market is reduced to Homeowners A and C, aggregate willingness to pay for all CO2 levels _________.
A)increases
B)declines
C)remains unchanged
D)is unpredictable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
________ cause private and social marginal cost curves to diverge while ________ cause private demand and social marginal WTP to diverge.
A)External benefits; external costs
B)External costs; external benefits
C)Market failures; public goods
D)Taxes; subsidies
A)External benefits; external costs
B)External costs; external benefits
C)Market failures; public goods
D)Taxes; subsidies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When you enjoy the view of your neighbor's prize-winning garden, this is an example of ________.
A)common property rights
B)a positive externality
C)a negative externality
D)a public good
A)common property rights
B)a positive externality
C)a negative externality
D)a public good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
By definition, a free rider is a person _______________.
A)who underpays for a public good relative to the benefits that they receive
B)who refuses to pay for a public good because they receive no value from it
C)who contributes less than others toward payment of a public good
D)who pays less than the marginal cost of producing a public good
A)who underpays for a public good relative to the benefits that they receive
B)who refuses to pay for a public good because they receive no value from it
C)who contributes less than others toward payment of a public good
D)who pays less than the marginal cost of producing a public good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Due to free riding, public goods are typically ____________.
A)under supplied
B)supplied by private firms who can restrict access
C)taxed
D)over supplied
A)under supplied
B)supplied by private firms who can restrict access
C)taxed
D)over supplied

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Figure 4.7
Willingness to pay for a Public Park
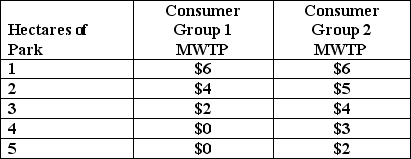
Refer to Figure 4.7.As MWTP _______, total willingness to pay _______.
A)increases; increases
B)declines; declines
C)declines; increases
D)the table does yield enough information
Willingness to pay for a Public Park

Refer to Figure 4.7.As MWTP _______, total willingness to pay _______.
A)increases; increases
B)declines; declines
C)declines; increases
D)the table does yield enough information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Figure 4.7
Willingness to pay for a Public Park

Refer to Figure 4.7.If the marginal cost to provide the park is $3/hectare, __________.
A)the socially efficient size of the park is 4 hectares
B)the socially efficient size of the park is 3 hectares
C)there is no socially efficient solution
D)none of the above are true
Willingness to pay for a Public Park

Refer to Figure 4.7.If the marginal cost to provide the park is $3/hectare, __________.
A)the socially efficient size of the park is 4 hectares
B)the socially efficient size of the park is 3 hectares
C)there is no socially efficient solution
D)none of the above are true

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The central idea of economic efficiency is that ___________________.
A)all people must value the production of the goods that society produces
B)there should be a balance between aggregate marginal willingness to pay and the marginal costs of production
C)the marginal willingness to pay of all consumers should be equal to the total cost of production
D)production should be maximaized
A)all people must value the production of the goods that society produces
B)there should be a balance between aggregate marginal willingness to pay and the marginal costs of production
C)the marginal willingness to pay of all consumers should be equal to the total cost of production
D)production should be maximaized

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Figure 4.6 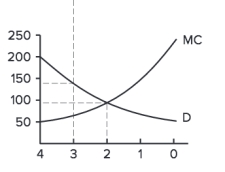
Refer to Figure 4.6.At quantities lower than the socially efficient level, __________.
A)MWTP is higher than the marginal cost of production, the good is under supplied
B)quantity demanded is greater than the willingness to supply, the good is over supplied
C)MWTP is less than willingness to supply, the good will not be produced
D)the graph does not depict quantities that are lower than the socially efficient level

Refer to Figure 4.6.At quantities lower than the socially efficient level, __________.
A)MWTP is higher than the marginal cost of production, the good is under supplied
B)quantity demanded is greater than the willingness to supply, the good is over supplied
C)MWTP is less than willingness to supply, the good will not be produced
D)the graph does not depict quantities that are lower than the socially efficient level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In judging whether people from Chicago can justifiably claim that they have been damaged by species endangerment in Africa, the presence or absence of ___________ is the economic index used to validate that claim.
A)public goods
B)social costs
C)willingness to pay
D)market efficiency
A)public goods
B)social costs
C)willingness to pay
D)market efficiency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



