Deck 30: Acute Gingival and Periodontal Conditions, lesions of Endodontic Origin, and Avulsed Teeth
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/20
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 30: Acute Gingival and Periodontal Conditions, lesions of Endodontic Origin, and Avulsed Teeth
1
A 16-year-old adolescent has just had an anterior permanent tooth knocked out during a physical education class at school.The school nurse has called the dental office to inquire about transporting the child to the dental office.What advice should the dental hygienist give to the school nurse about transporting the tooth in order to maximize the vitality of the periodontal ligament?
A) Place the tooth in physiologic saline.
B) Have the child hold the tooth in his mouth so that it is bathed in saliva.
C) Place the tooth in milk.
D) Place the tooth back in the socket.
A) Place the tooth in physiologic saline.
B) Have the child hold the tooth in his mouth so that it is bathed in saliva.
C) Place the tooth in milk.
D) Place the tooth back in the socket.
Place the tooth back in the socket.
2
Of the characteristics given,what is one main difference between acute periodontal abscess and chronic periodontal abscess?
A) Size
B) Shape
C) Radiopacity at the apex of a tooth on a periapical radiograph
D) Pain and swelling
A) Size
B) Shape
C) Radiopacity at the apex of a tooth on a periapical radiograph
D) Pain and swelling
Pain and swelling
3
Following the completion of nonsurgical periodontal therapy,the client should be placed on a continued-care schedule for supportive periodontal therapy.What time interval should be used,assuming the client responded well to therapy and therapeutic endpoints were achieved?
A) 6 months
B) 5 months
C) 3 months
D) 2 months
A) 6 months
B) 5 months
C) 3 months
D) 2 months
3 months
4
What is the initial treatment for acute periodontal abscess?
A) Drainage
B) Extraction of tooth
C) Oral hygiene instruction
D) Desensitization therapy
A) Drainage
B) Extraction of tooth
C) Oral hygiene instruction
D) Desensitization therapy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is the most common dental emergency?
A) Lesion of endodontic origin (LEO)
B) Lesion of abscess origin
C) Lesion of pathogenic origin
D) Lesion of unknown origin
A) Lesion of endodontic origin (LEO)
B) Lesion of abscess origin
C) Lesion of pathogenic origin
D) Lesion of unknown origin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Where are gingival abscesses most frequently found?
A) On the anterior teeth
B) At the root of the tooth
C) On the marginal gingiva
D) Not found in any certain place
A) On the anterior teeth
B) At the root of the tooth
C) On the marginal gingiva
D) Not found in any certain place

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is not a sign or symptom of an acute periodontal abscess?
A) Tooth mobility
B) Localized swelling of the gingiva
C) Absence of pain
D) Cervical lymphadenopathy
A) Tooth mobility
B) Localized swelling of the gingiva
C) Absence of pain
D) Cervical lymphadenopathy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is the first clinical feature of inflammatory periodontal disease?
A) Tooth mobility
B) Drifting of the anterior teeth
C) Bleeding on probing
D) Fremitus
A) Tooth mobility
B) Drifting of the anterior teeth
C) Bleeding on probing
D) Fremitus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is not a sign or symptom of gingival abscess?
A) Pain
B) Tooth mobility
C) Swelling
D) Redness
A) Pain
B) Tooth mobility
C) Swelling
D) Redness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
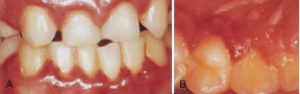
The ulcer is most likely:
A) Angular cheilitis
B) Herpes simplex labialis
C) Herpetic whitlow
D) Herpetic gingivostomatitis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following initiates gingivitis most often?
A) Malocclusion
B) Plaque biofilm
C) Vitamin deficiency
D) Hormonal imbalance
A) Malocclusion
B) Plaque biofilm
C) Vitamin deficiency
D) Hormonal imbalance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is the relationship between gingivitis and periodontitis?
A) Gingivitis will always progress to periodontitis.
B) Both gingivitis and periodontitis result in clinical attachment loss.
C) Periodontitis succeeds gingivitis.
D) Both periodontitis and gingivitis are characterized by clinical attachment levels greater than 3 mm.
A) Gingivitis will always progress to periodontitis.
B) Both gingivitis and periodontitis result in clinical attachment loss.
C) Periodontitis succeeds gingivitis.
D) Both periodontitis and gingivitis are characterized by clinical attachment levels greater than 3 mm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is the term used to indicate an odontogenic infection from various possible sources including periodontal infections,pulpal infections,and trauma?
A) Periodontal abscess
B) Gingival abscess
C) Fistula
D) Periapical abscess
A) Periodontal abscess
B) Gingival abscess
C) Fistula
D) Periapical abscess

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What specific intervention is used to treat a gingival abscess caused by the intrusion of a foreign object to the area?
A) Drainage and foreign object removal
B) Tooth extraction
C) Oral hygiene instruction
D) Oral irrigation to remove the foreign object
A) Drainage and foreign object removal
B) Tooth extraction
C) Oral hygiene instruction
D) Oral irrigation to remove the foreign object

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The generalized presence of blunted interdental papilla,fetid mouth odor,mouth pain,and pseudomembranous films over the gingiva is characteristic of which of the following?
A) Necrotizing ulcerative periodontitis
B) Gingival abscess
C) Pericoronitis
D) Herpetic gingivostomatitis
A) Necrotizing ulcerative periodontitis
B) Gingival abscess
C) Pericoronitis
D) Herpetic gingivostomatitis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
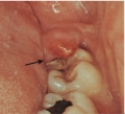
What is the client's most likely problem?
A) Gingival abscess
B) Pericoronitis
C) Necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
D) Necrotizing ulcerative periodontitis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Acute periodontal abscesses may be associated with which of the following?
A) Any tooth in the mouth
B) Only anterior teeth
C) Only maxillary teeth
D) Only mandibular teeth
A) Any tooth in the mouth
B) Only anterior teeth
C) Only maxillary teeth
D) Only mandibular teeth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18

What initial treatment is indicated for the client?
A) A microbiological cultural analysis is indicated to determine the presence of specific marker bacteria associated with the condition.Once the bacteria are identified,the dentist can prescribe an appropriate antibiotic.
B) Scaling is performed,usually requiring local anesthesia of the area,and the client should return within 24 to 48 hours for further diagnosis.
C) Treatment requires endodontic therapy to remove the pulp of the tooth and to replace it with an inert material.
D) Topical anesthetic is applied first.The infected area is debrided,usually by gentle flushing with warm water or dilute hydrogen peroxide delivered in a disposable irrigating syringe with a blunt needle.The dentist may prescribe an antibiotic,given that the client is febrile and has cervical lymphadenopathy.Treatment is repeated the following day.Dental instrumentation to further debride the area can then be used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is not a sign or symptom of a lesion of endodontic origin (LEO)?
A) Redness of tissues in a localized area
B) Sharp pain,likely to be intermittent
C) Swelling of tissues in a localized area
D) Metallic taste in the mouth
A) Redness of tissues in a localized area
B) Sharp pain,likely to be intermittent
C) Swelling of tissues in a localized area
D) Metallic taste in the mouth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Given the clinical description of the lesion,the dental hygienist should do which of the following?
A) Terminate the appointment and reschedule the client in order to prevent risk of virus transmission to other head and neck areas of the client,to the hygienist,and to others.
B) Cover the lesion with a protective lubricant and continue with the plan of care.
C) Complete the client assessment and treatment plan but do not initiate the care planned.Dismiss the client and reschedule.
D) Have the dentist prescribe an antiviral agent,and continue with the plan of care.
A) Terminate the appointment and reschedule the client in order to prevent risk of virus transmission to other head and neck areas of the client,to the hygienist,and to others.
B) Cover the lesion with a protective lubricant and continue with the plan of care.
C) Complete the client assessment and treatment plan but do not initiate the care planned.Dismiss the client and reschedule.
D) Have the dentist prescribe an antiviral agent,and continue with the plan of care.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



