Deck 24: Multistate Corporate Taxation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/204
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 24: Multistate Corporate Taxation
1
Roughly five percent of all taxes paid by businesses in the U.S. are to state, local, and municipal jurisdictions.
False
2
A typical state taxable income subtraction modification is the interest income earned from another state's bonds.
False
3
All of the U.S. states use an apportionment formula based on the sales, property, and payroll factors.
False
4
Typically, sales/use taxes constitute about 20 percent of a state's annual tax collections.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In most states, a taxpayer's income is apportioned on the basis of a formula measuring the extent of business contact, and allocated according to the location of property owned or used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
All of the U.S. states have adopted a tax based on the net taxable income of corporations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A service engineer spends 80% of her time maintaining the employer's productive business property, and 20% maintaining the employer's nonbusiness rental properties. This year, her compensation totaled $90,000. The payroll factor assigns $90,000 to the state in which the employer is based.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A typical U.S. state piggybacks its collections of the corporate income tax, by letting the Federal government collect and remit the corresponding tax to the state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
State and local politicians tend to apply new and increased taxes to taxpayers who are nonresident visitors to the jurisdiction, such as a tax on auto rentals and hotel stays, because the taxpayer cannot vote to reelect (or oust) the lawmaker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Property taxes generally are collected by local taxing jurisdictions, not the state or Federal governments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Under P.L. 86-272, the taxpayer is exempt from state taxes on income resulting from the mere solicitation of orders for the sale of stocks and bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Typical indicators of income-tax nexus include the presence of customers in the state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Most states begin the computation of corporate taxable income with an amount from the Federal income tax return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
An assembly worker earns a $50,000 salary and receives a fringe benefit package worth $15,000. The payroll factor assigns $65,000 for this employee.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If a state follows Federal income tax rules, the state's tax compliance and enforcement become easier to accomplish.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Double weighting the sales factor effectively decreases the corporate income tax burden on taxpayers based in the state, such as entities with in-state headquarters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Politicians frequently use tax credits and exemptions to create economic development incentives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A state can levy an income tax on a business only if the business was incorporated in the state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Usually a business chooses a location where it will build a new plant based chiefly on tax considerations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A typical state taxable income addition modification is for the state's NOL allowed the taxpayer for the tax year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Most states exempt consumer purchases of groceries from the collection of the local sales tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An LLC apportions and allocates its annual taxable income in the same manner used by any other business operating in the state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Typically included in the sales/use tax base is the purchase of tablet computers and cell phone equipment by a large manufacturing firm, whose sales force uses the items.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Typically exempt from the sales/use tax base is the purchase of prescription medicines by an individual.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A unitary group of entities files a combined return that includes all of the affiliates' income and apportionment data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Typically exempt from the sales/use tax base is the purchase of tools by a manufacturer to make the widgets that it sells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
S corporations flow-through income amounts to its shareholders, and most states require a withholding of shareholder taxes on the allocated amounts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The use tax is designed to complement the sales tax. A use tax typically covers purchases made out of state and brought into the jurisdiction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The property factor includes business assets that the taxpayer owns, but also those merely used under a lease agreement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
By making a water's edge election, the multinational taxpayer can limit the reach of unitary principles to the apportionment factors and income of its U.S. and E.U. affiliates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In most states, Federal S corporations must make a separate state-level election of the flow-through status.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Typically exempt from the sales/use tax base is the purchase of clothing from a neighbor's "garage sale."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Typically exempt from the sales/use tax base is the purchase by a symphony orchestra of printed music for its players.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Typically exempt from the sales/use tax base is the purchase of lumber by a do-it-yourself homeowner, when she builds a deck onto her patio. This exemption is known as the "homestead rule."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The individual seller of shares of stock in Facebook is liable for sales tax on the transaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Most states' consumer sales taxes are to be paid by the final purchaser of the taxable asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A taxpayer has nexus with a state for sales and use tax purposes if it has a physical presence in the state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A unitary business applies a combined apportionment formula, including data from operations of all of the affiliates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The property factor includes land and buildings used for business purposes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Almost all of the states assess some form of consumer-level sales/use tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Sales/use tax in most states applies to a restaurant meal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The typical local property tax falls on both an investor's principal residence and her stock portfolio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Zhao Company sold an asset on the first day of the tax year for $500,000. Zhao's Federal tax basis for the asset was $300,000. Because of differences in cost recovery schedules, the state regular-tax basis in the asset was $350,000. What adjustment, if any, should be made to Zhao's Federal taxable income in determining the correct taxable income for the typical state?
A) $0
B) ($50,000)
C) $50,000
D) $150,000
A) $0
B) ($50,000)
C) $50,000
D) $150,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Under P.L. 86-272, which of the following transactions by itself would create nexus with a state?
A) Order solicitation for a plot of real estate, approved and filled from another state.
B) Order solicitation for a computer, approved and filled from another state.
C) Order solicitation for a machine, with credit approval from another state.
D) The conduct of a training seminar for sales personnel as to how to install and operate a new software product.
A) Order solicitation for a plot of real estate, approved and filled from another state.
B) Order solicitation for a computer, approved and filled from another state.
C) Order solicitation for a machine, with credit approval from another state.
D) The conduct of a training seminar for sales personnel as to how to install and operate a new software product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Multistate income tax planning can be effective for the taxpayer because:
A) Different states use different definitions of taxable income.
B) State income tax rates generally are steeply progressive.
C) Both a. and b.
D) Neither a. nor b.
A) Different states use different definitions of taxable income.
B) State income tax rates generally are steeply progressive.
C) Both a. and b.
D) Neither a. nor b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Some of the states use, in determining whether an out-of-state entity has income tax nexus:
A) A factor-presence test.
B) An economic presence test.
C) Both a. and b are used by certain states.
D) Neither a. nor b is used by the states.
A) A factor-presence test.
B) An economic presence test.
C) Both a. and b are used by certain states.
D) Neither a. nor b is used by the states.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In the context of Federal and state corporate income taxation:
A) Many states collect their taxes using a "piggyback" on the Federal return.
B) Most state require that the taxpayer report to the state taxing agency the changes made to a return in a Federal audit.
C) Both a. and b.
D) Neither a. nor b.
A) Many states collect their taxes using a "piggyback" on the Federal return.
B) Most state require that the taxpayer report to the state taxing agency the changes made to a return in a Federal audit.
C) Both a. and b.
D) Neither a. nor b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In determining a corporation's taxable income for state income tax purposes, which of the following does not constitute a subtraction from Federal income?
A) Interest on U.S. obligations.
B) Expenses that are directly or indirectly related to state and municipal interest that is taxable for state purposes.
C) The amount by which the state depreciation deduction exceeds the corresponding Federal amount.
D) The amount by which the Federal depreciation deduction exceeds the corresponding state amount.
A) Interest on U.S. obligations.
B) Expenses that are directly or indirectly related to state and municipal interest that is taxable for state purposes.
C) The amount by which the state depreciation deduction exceeds the corresponding Federal amount.
D) The amount by which the Federal depreciation deduction exceeds the corresponding state amount.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Adams Corporation owns and operates two manufacturing facilities, one in State X and the other in State Y. Due to a temporary decline in the corporation's sales, Adams has rented 20% of its Y facility to an unaffiliated corporation. Adams generated $1,000,000 net rental income and $5,000,000 income from manufacturing. Adams is incorporated in Y. For X and Y purposes, rental income is classified as allocable nonbusiness income. By applying the statutes of each state, Adams determined that its apportionment factors are .65 for X and .35 for Y.
Adams's income attributed to X is:
A) $0.
B) $3,250,000.
C) $3,900,000.
D) $5,000,000.
E) $6,000,000.
Adams's income attributed to X is:
A) $0.
B) $3,250,000.
C) $3,900,000.
D) $5,000,000.
E) $6,000,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Flint Corporation is subject to a corporate income tax only in State X. The starting point in computing X taxable income is Federal taxable income. Flint's Federal taxable income is $750,000, which includes a $50,000 deduction for state income taxes. During the year, Flint received $10,000 interest on Federal obligations. X tax law does not allow a deduction for state income tax payments. Flint's taxable income for X purposes is:
A) $810,000.
B) $800,000.
C) $790,000.
D) $750,000.
A) $810,000.
B) $800,000.
C) $790,000.
D) $750,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A capital stock tax usually is structured as an excise tax imposed on a corporation's "net worth," using financial statement data to compute the tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Federal taxable income is used as the starting point in computing the state's income tax base, but numerous state adjustments or modifications generally are required to:
A) Reflect differences between state and Federal tax statutes.
B) Remove income that a state is constitutionally prohibited from taxing.
C) Allow for all of the states to use the same definition of taxable income.
D) a. and b.
A) Reflect differences between state and Federal tax statutes.
B) Remove income that a state is constitutionally prohibited from taxing.
C) Allow for all of the states to use the same definition of taxable income.
D) a. and b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following is not immune from state income taxation, even if P.L. 86-272 is in effect?
A) Sale of office equipment that is used in the taxpayer's business.
B) Sale of office equipment that constitutes inventory to the purchaser.
C) Sale of a warehouse used in the taxpayer's business.
D) All of the above are protected by P.L. 86-272 immunity provisions.
A) Sale of office equipment that is used in the taxpayer's business.
B) Sale of office equipment that constitutes inventory to the purchaser.
C) Sale of a warehouse used in the taxpayer's business.
D) All of the above are protected by P.L. 86-272 immunity provisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Under P.L. 86-272, which of the following transactions by itself would create nexus with a state?
A) Inspection by a sales employee of the customer's inventory for specific product lines.
B) Using a manufacturer's representative for the taxpayer through a sales office in the state.
C) Executing a sales campaign, using an advertising agency acting as an independent contractor for the taxpayer.
D) Maintenance of inventory in the state by an independent contractor under a consignment plan.
A) Inspection by a sales employee of the customer's inventory for specific product lines.
B) Using a manufacturer's representative for the taxpayer through a sales office in the state.
C) Executing a sales campaign, using an advertising agency acting as an independent contractor for the taxpayer.
D) Maintenance of inventory in the state by an independent contractor under a consignment plan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The typical state sales/use tax falls on sales of both real and personal property.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The model law relating to the assignment of income among the states for corporations is:
A) Public Law 86-272.
B) The Multistate Tax Treaty.
C) The Multistate Tax Commission (MTC).
D) The Uniform Division of Income for Tax Purposes Act (UDITPA).
A) Public Law 86-272.
B) The Multistate Tax Treaty.
C) The Multistate Tax Commission (MTC).
D) The Uniform Division of Income for Tax Purposes Act (UDITPA).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Ramirez Corporation is subject to income tax only in State a. Ramirez generated the following income and deductions. 
Federal taxable income is the starting point in computing A taxable income. State income taxes are not deductible for A tax purposes. Ramirez's A taxable income is:
A) $495,000.
B) $500,000.
C) $545,000.
D) $595,000.

Federal taxable income is the starting point in computing A taxable income. State income taxes are not deductible for A tax purposes. Ramirez's A taxable income is:
A) $495,000.
B) $500,000.
C) $545,000.
D) $595,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In most states, legal and accounting services are exempt from the sales/use tax base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In determining state taxable income, all of the following are adjustments to Federal income except:
A) Federal net operating loss.
B) State income tax expense.
C) Fringe benefits paid to officers and executives.
D) Dividends received from other U.S. corporations.
A) Federal net operating loss.
B) State income tax expense.
C) Fringe benefits paid to officers and executives.
D) Dividends received from other U.S. corporations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A city might assess a recording tax when a business takes out a mortgage on its real estate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Boot Corporation is subject to income tax in States A and B. Boot's operations generated $200,000 of apportionable income, and its sales and payroll activity and average property owned in each of the states is as follows. 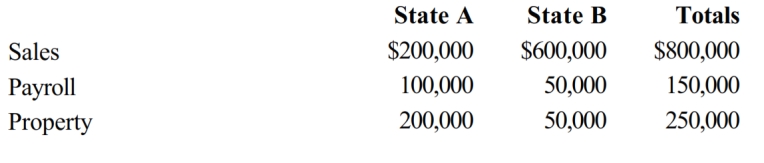
How much more (less) of Boot's income is subject to A income tax if, instead of using an equally-weighted three- factor apportionment formula, A uses a formula with a double-weighted sales factor?
A) ($50,000)
B) $50,000
C) $16,100
D) ($16,100)

How much more (less) of Boot's income is subject to A income tax if, instead of using an equally-weighted three- factor apportionment formula, A uses a formula with a double-weighted sales factor?
A) ($50,000)
B) $50,000
C) $16,100
D) ($16,100)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In the income tax apportionment formula, market-sourcing the sales factor means that:
A) Sales are sourced to the state of the seller.
B) Sales are sourced to the state of the customer.
C) Sales are sourced to the state of the seller's corporate headquarters, i.e., where the marketing department works.
D) Sales are sourced to the state(s) where the customer will use the product, i.e., to the customers markets.
A) Sales are sourced to the state of the seller.
B) Sales are sourced to the state of the customer.
C) Sales are sourced to the state of the seller's corporate headquarters, i.e., where the marketing department works.
D) Sales are sourced to the state(s) where the customer will use the product, i.e., to the customers markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
General Corporation is taxable in a number of states. This year, General made a $100,000 sale from its A headquarters to a customer in B. This activity is not sufficient for General to create nexus with B. State B applies a throwback rule, but State A does not. In which state(s) will the sale be included in the sales factor numerator?
A) $0 in A and $0 in B.
B) $100,000 in A.
C) $100,000 in B.
D) In both A and B, according to the apportionment formulas of each.
A) $0 in A and $0 in B.
B) $100,000 in A.
C) $100,000 in B.
D) In both A and B, according to the apportionment formulas of each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
General Corporation is taxable in a number of states. This year, General made a $100,000 sale from its A headquarters to the State B office of the FBI, the Federal Bureau of Investigation. In which state(s) will the sale be included in the sales factor numerator?
A) $0 in A and $0 in B.
B) $50,000 in A, with the balance exempted from other states' sales factors under the Colgate doctrine.
C) $100,000 in A.
D) $100,000 in B.
A) $0 in A and $0 in B.
B) $50,000 in A, with the balance exempted from other states' sales factors under the Colgate doctrine.
C) $100,000 in A.
D) $100,000 in B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The most commonly used state income tax apportionment formula is:
A) Sales factor only.
B) Sales factor double-weighted.
C) Sales factor equally weighted with property and payroll.
D) Payroll factor only.
A) Sales factor only.
B) Sales factor double-weighted.
C) Sales factor equally weighted with property and payroll.
D) Payroll factor only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Typically, state taxable income includes:
A) Apportionable income only.
B) Different terms are used in the computation.
C) Both a. and b.
D) Neither a. nor b. Different terms are used in the computation.
A) Apportionable income only.
B) Different terms are used in the computation.
C) Both a. and b.
D) Neither a. nor b. Different terms are used in the computation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Generally, a taxpayer's business income is:
A) Apportioned.
B) Allocated.
C) Both a. and b.
D) Neither a. nor b.
A) Apportioned.
B) Allocated.
C) Both a. and b.
D) Neither a. nor b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Simpkin Corporation owns manufacturing facilities in States A, B, and C. A uses a three-factor apportionment formula under which the sales, property and payroll factors are equally weighted. B uses a three-factor apportionment formula under which sales are double-weighted. C employs a single-factor apportionment factor, based solely on sales. Simpkin's operations generated $1,000,000 of apportionable income, and its sales and payroll activity and average property owned in each of the three states is as follows.
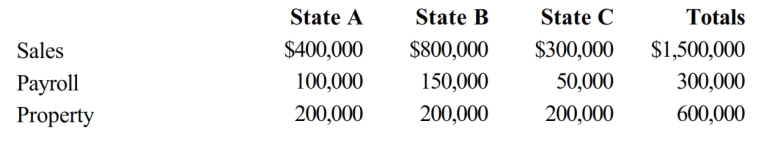
Simpkin's apportionable income assigned to B is:
A) $1,000,000.
B) $533,333.
C) $475,000.
D) $0.

Simpkin's apportionable income assigned to B is:
A) $1,000,000.
B) $533,333.
C) $475,000.
D) $0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Chipper Corporation realized $1,000,000 taxable income from the sales of its products in States X and Z. Chipper's activities establish nexus for income tax purposes only in Z, the state of its incorporation. Chipper's sales, payroll, and property among the states include the following. 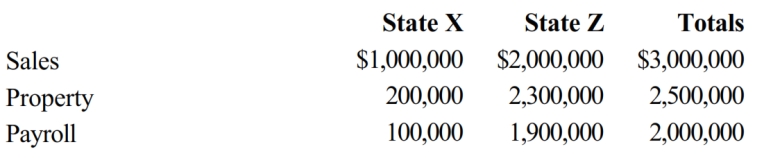
X utilizes a sales-only factor in its three-factor apportionment formula. How much of Chipper's taxable income is apportioned to X?
A) $0
B) $333,333
C) $500,000
D) $1,000,000

X utilizes a sales-only factor in its three-factor apportionment formula. How much of Chipper's taxable income is apportioned to X?
A) $0
B) $333,333
C) $500,000
D) $1,000,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
General Corporation is taxable in a number of states. This year, General made a $100,000 sale from its A headquarters to a customer in B. General has not established nexus with B. State A does not apply a throwback rule. In which state(s) will the sale be included in the sales factor numerator?
A) In all of the states, according to the apportionment formulas of each, as the U.S. government is present in all states.
B) $100,000 in A.
C) $100,000 in B.
D) $0 in A and $0 in B.
A) In all of the states, according to the apportionment formulas of each, as the U.S. government is present in all states.
B) $100,000 in A.
C) $100,000 in B.
D) $0 in A and $0 in B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
José Corporation realized $900,000 taxable income from the sales of its products in States X and Z. José's activities in both states establish nexus for income tax purposes. José's sales, payroll, and property among the states include the following. 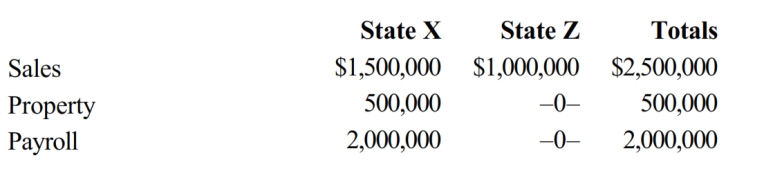
Z utilizes a double-weighted sales factor in its three-factor apportionment formula. How much of José's taxable income is apportioned to Z?
A) $1,000,000
B) $900,000
C) $180,000
D) $0

Z utilizes a double-weighted sales factor in its three-factor apportionment formula. How much of José's taxable income is apportioned to Z?
A) $1,000,000
B) $900,000
C) $180,000
D) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Generally, nonapportionable income includes:
A) Sales of products manufactured by the taxpayer.
B) License fees for intangible assets collected by the taxpayer.
C) Both a. and b.
D) Neither a. nor b.
A) Sales of products manufactured by the taxpayer.
B) License fees for intangible assets collected by the taxpayer.
C) Both a. and b.
D) Neither a. nor b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Marquardt Corporation realized $900,000 taxable income from the sales of its products in States X and Z. Marquardt's activities establish nexus for income tax purposes in both states. Marquardt's sales, payroll, and property among the states include the following.
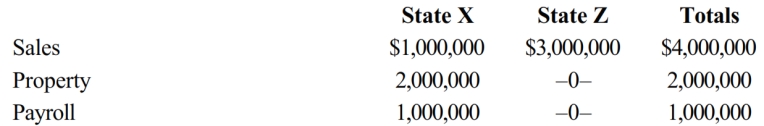
Z utilizes an equally weighted three-factor apportionment formula. Marquardt is incorporated in X. How much of Marquardt's taxable income is apportioned to Z?
A) $0
B) $225,000
C) $675,000
D) $3,000,000

Z utilizes an equally weighted three-factor apportionment formula. Marquardt is incorporated in X. How much of Marquardt's taxable income is apportioned to Z?
A) $0
B) $225,000
C) $675,000
D) $3,000,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Britta Corporation's entire operations are located in State a. Eighty percent ($800,000) of Britta's sales are made in A and the remaining sales ($200,000) are made in State B. B has not adopted a corporate income tax. If A has adopted a throwback rule, the numerator of Britta's A sales factor is:
A) $0.
B) $200,000.
C) $800,000.
D) $1,000,000.
A) $0.
B) $200,000.
C) $800,000.
D) $1,000,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
José Corporation realized $900,000 taxable income from the sales of its products in States X and Z. José's activities in both states establish nexus for income tax purposes. José's sales, payroll, and property among the states include the following. 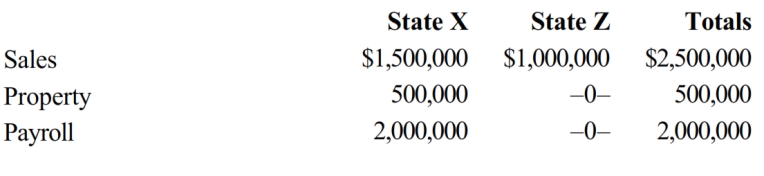
X utilizes an equally weighted three-factor apportionment formula. How much of José's taxable income is apportioned to X?
A) $120,000
B) $450,000
C) $780,000
D) $900,000

X utilizes an equally weighted three-factor apportionment formula. How much of José's taxable income is apportioned to X?
A) $120,000
B) $450,000
C) $780,000
D) $900,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In applying the typical apportionment formula:
A) The aggregate of state taxable incomes equals Federal taxable income.
B) The aggregate of state taxable incomes may not equal Federal taxable income.
C) When Federal taxable income is negative, all states' taxable incomes are negative.
D) When Federal taxable income is negative, aggregate state taxable incomes total to zero.
A) The aggregate of state taxable incomes equals Federal taxable income.
B) The aggregate of state taxable incomes may not equal Federal taxable income.
C) When Federal taxable income is negative, all states' taxable incomes are negative.
D) When Federal taxable income is negative, aggregate state taxable incomes total to zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Public Law 86-272:
A) Was written by the Multistate Tax Commission.
B) Provides nexus definitions for sales of stocks and bonds.
C) Provides nexus definitions for the sale of medical and legal services.
D) Was adopted by Congress.
A) Was written by the Multistate Tax Commission.
B) Provides nexus definitions for sales of stocks and bonds.
C) Provides nexus definitions for the sale of medical and legal services.
D) Was adopted by Congress.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Helene Corporation owns manufacturing facilities in States A, B, and C. A uses a three-factor apportionment formula under which the sales, property and payroll factors are equally weighted. B uses a three-factor apportionment formula under which sales are double-weighted. C employs a single-factor apportionment factor, based solely on sales. Helene's operations generated $1,000,000 of apportionable income, and its sales and payroll activity and average property owned in each of the three states is as follows.
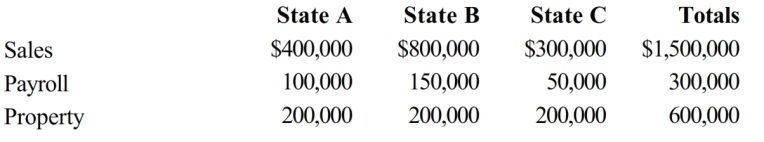
Helene's apportionable income assigned to A is:
A) $0.
B) $266,667.
C) $311,100.
D) $1,000,000.

Helene's apportionable income assigned to A is:
A) $0.
B) $266,667.
C) $311,100.
D) $1,000,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
General Corporation is taxable in a number of states. This year, General made a $100,000 sale from its A headquarters to a customer in B. This activity is not sufficient for General to create nexus with B. State A applies a throwback rule, but State B does not. In which state(s) will the sale be included in the sales factor numerator?
A) $0 in both A and B.
B) $100,000 in A.
C) $100,000 in B.
D) In both A and B, according to the apportionment formulas of each.
A) $0 in both A and B.
B) $100,000 in A.
C) $100,000 in B.
D) In both A and B, according to the apportionment formulas of each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Cruz Corporation owns manufacturing facilities in States A, B, and C. A uses a three-factor apportionment formula under which the sales, property and payroll factors are equally weighted. B uses a three-factor apportionment formula under which sales are double-weighted. C employs a single-factor apportionment factor, based solely on sales. Cruz's operations generated $1,000,000 of apportionable income, and its sales and payroll activity and average property owned in each of the three states is as follows.
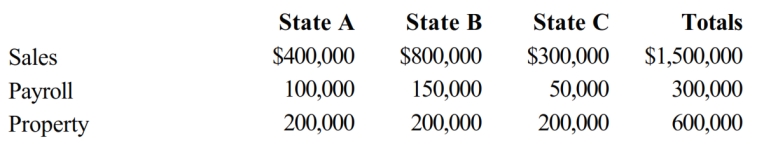
Cruz's apportionable income assigned to C is:
A) $1,000,000.
B) $273,333.
C) $200,000.
D) $0.

Cruz's apportionable income assigned to C is:
A) $1,000,000.
B) $273,333.
C) $200,000.
D) $0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 204 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



