Deck 17: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/47
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
1
Under what condition would phenylalanine exist as follows? 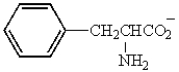
A) at a low pH
B) at a high pH
C) at the pI
D) when pH = pKa
E) none of these

A) at a low pH
B) at a high pH
C) at the pI
D) when pH = pKa
E) none of these
at a high pH
2
In the dipeptide shown the following segment of the molecule is likely to lie in a single plane: 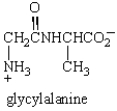
A)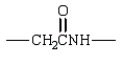
B)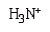
C)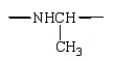
D)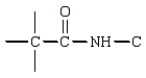
E)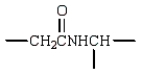

A)
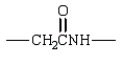
B)
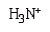
C)

D)

E)


3
What is the only -amino acid that does not have a stereogenic carbon?
A) glycine
B) alanine
C) phenylalanine
D) valine
E) leucine
A) glycine
B) alanine
C) phenylalanine
D) valine
E) leucine
glycine
4
Hydrogen bonds, -helices, and pleated sheets are structural properties of proteins.
A) primary
B) secondary
C) tertiary
D) quaternary
E) sole
A) primary
B) secondary
C) tertiary
D) quaternary
E) sole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following -amino acids contains a hydroxyl group?
A) asparagine
B) threonine
C) cysteine
D) isoleucine
E) phenylalanine
A) asparagine
B) threonine
C) cysteine
D) isoleucine
E) phenylalanine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following molecules is -aminopropanoic acid?
A)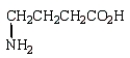
B)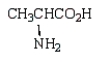
C)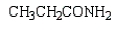
D)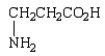
E)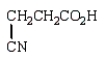
A)
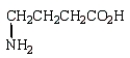
B)
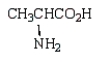
C)
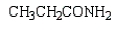
D)
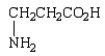
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the correct relationship between valylalanine and alanylvaline?
A) enantiomeric pair
B) meso compounds
C) structural isomers
D) geometric isomers
E) racemic mixture
A) enantiomeric pair
B) meso compounds
C) structural isomers
D) geometric isomers
E) racemic mixture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is the name of the following molecule? 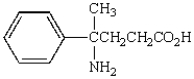
A) 3-amino-3-phenylvaleric acid
B) 4-amino-4-methyl-4-phenylbutanoic acid
C) 4-amino-4-phenylpentanoic acid
D) 4-amino-4-phenyl-4-methylbutanoic acid
E) 2-amino-2-phenylbutanoic acid

A) 3-amino-3-phenylvaleric acid
B) 4-amino-4-methyl-4-phenylbutanoic acid
C) 4-amino-4-phenylpentanoic acid
D) 4-amino-4-phenyl-4-methylbutanoic acid
E) 2-amino-2-phenylbutanoic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The dipeptides 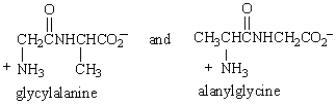 are
are
A) constitutional isomers.
B) stereoisomers.
C) diastereoisomers.
D) enantiomers.
E) identical.
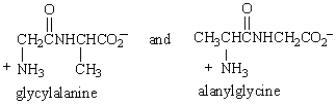 are
areA) constitutional isomers.
B) stereoisomers.
C) diastereoisomers.
D) enantiomers.
E) identical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is the name of the amide bond linking two amino acids?
A) ionic
B) hydrogen
C) glycosidic
D) nonpolar
E) peptide
A) ionic
B) hydrogen
C) glycosidic
D) nonpolar
E) peptide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
How many different combinations are possible for a tripeptide containing one of each of the following amino acids: Phe, Val, Asp?
A) 2
B) 6
C) 8
D) 10
E) greater than 10
A) 2
B) 6
C) 8
D) 10
E) greater than 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which one of the following represents a tetrapeptide?
A) Val-Ile-Asp-Asp
B) Ala-Ala-Ala-Ala-Val-Val
C) Ala-Ser-Val-Val-Ile
D) Ser-Ser-Ala-Ala-Gly-Gly-Glu-Glu
E) Ser-Ala-Thr-Pro-Leu
A) Val-Ile-Asp-Asp
B) Ala-Ala-Ala-Ala-Val-Val
C) Ala-Ser-Val-Val-Ile
D) Ser-Ser-Ala-Ala-Gly-Gly-Glu-Glu
E) Ser-Ala-Thr-Pro-Leu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which molecule is an -amino acid?
A)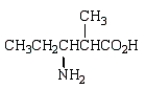
B)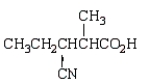
C)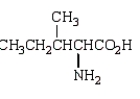
D)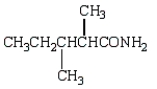
E)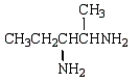
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following -amino acids contains an imidazole?
A) arginine
B) asparagine
C) aspartic acid
D) histidine
E) tyrosine
A) arginine
B) asparagine
C) aspartic acid
D) histidine
E) tyrosine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is the net charge of isoleucine at its isoelectric point?
A) 0
B) +1
C) +2
D) -1
E) -2
A) 0
B) +1
C) +2
D) -1
E) -2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In the octapeptide, Cys-Ile-Ser-Asp-Gly-His-Gly-Gly, which is the N-terminal amino acid?
A) Ser
B) Ile
C) Asp
D) Cys
E) Gly
A) Ser
B) Ile
C) Asp
D) Cys
E) Gly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
To what family of polymers do proteins belong?
A) polyesters
B) polyacids
C) polyamines
D) polyurethanes
E) polyamides
A) polyesters
B) polyacids
C) polyamines
D) polyurethanes
E) polyamides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
How many different combinations are possible for a tetrapeptide containing two glycines (Gly,) one alanine (Ala,) and one phenylalanine (Phe)?
A) 3
B) 6
C) 12
D) 24
E) 36
A) 3
B) 6
C) 12
D) 24
E) 36

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In the octapeptide, Phe-Ile-Ser-Asp-Gly-His-Gly-Tyr, which is the C-terminal amino acid?
A) Ser
B) Phe
C) Tyr
D) His
E) Gly
A) Ser
B) Phe
C) Tyr
D) His
E) Gly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following amino acids can form disulfide bonds?
A) Gly
B) His
C) Cys
D) Asp
E) Glu
A) Gly
B) His
C) Cys
D) Asp
E) Glu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following is Sanger's reagent?
A)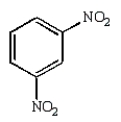
B)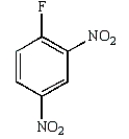
C)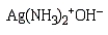
D)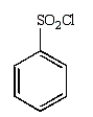
E)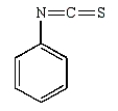
A)

B)

C)
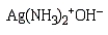
D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The structure of 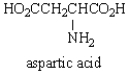 at the isoelectric point is:
at the isoelectric point is:
A)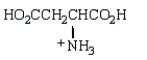
B)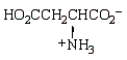
C)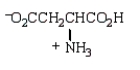
D)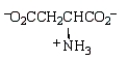
E)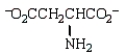
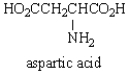 at the isoelectric point is:
at the isoelectric point is:A)
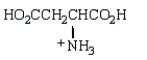
B)
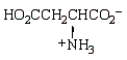
C)
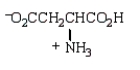
D)
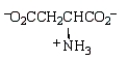
E)
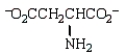

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Based on the pKa's of aspartic acid shown below, what is its approximate isoelectric point? 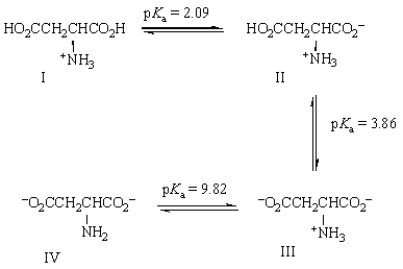
A) 2
B) 3
C) 5
D) 7
E) 10

A) 2
B) 3
C) 5
D) 7
E) 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A useful reagent for detecting amino acids is
A) hydrogen peroxide.
B) Tollens' reagent.
C) ninhydrin.
D) Benedict's reagent.
E) Merrifield's reagent.
A) hydrogen peroxide.
B) Tollens' reagent.
C) ninhydrin.
D) Benedict's reagent.
E) Merrifield's reagent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Bradykinin is a nonapeptide, Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg.In addition to one mole of Arg, what peptides are present after hydrolysis of bradykinin with chymotrypsin?
A) Arg-Pro-Pro and Gly-Phe and Ser-Pro-Phe
B) Pro-Pro-Gly and Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg
C) Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe and Ser-Pro-Phe
D) Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser and Pro-Phe
A) Arg-Pro-Pro and Gly-Phe and Ser-Pro-Phe
B) Pro-Pro-Gly and Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg
C) Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe and Ser-Pro-Phe
D) Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser and Pro-Phe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
At the isoelectric point, the structure of methionine (2-amino-4-methylthiobutanoic acid) is:
A)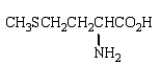
B)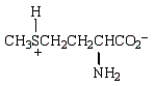
C)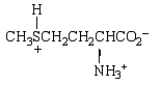
D)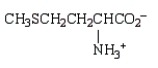
E)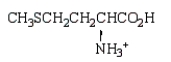
A)
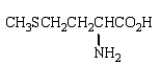
B)
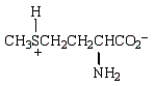
C)
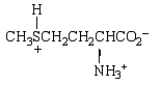
D)
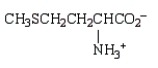
E)
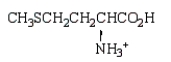

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What class of compound is produced when leucine reacts with acetyl chloride?
A) ester
B) amide
C) ether
D) phenol
E) alcohol
A) ester
B) amide
C) ether
D) phenol
E) alcohol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which reagent is used to determine the N-terminal amino acid of a peptide?
A) Jones'
B) Fehling's
C) Ninhydrin
D) Sanger's
E) Tollens'
A) Jones'
B) Fehling's
C) Ninhydrin
D) Sanger's
E) Tollens'

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What fragments will be obtained by a trypsin hydrolysis of the following octapeptide? Ala-Val-Trp-Lys-Phe-Gly-Arg-Met
A) Ala-Val-Trp-Lys-Phe and Gly-Arg-Met
B) Ala-Val-Trp-Lys-Phe -Gly and Arg-Met
C) Ala-Val-Trp-Lys and Phe-Gly-Arg and Met
D) Ala-Val-Trp-Lys and Phe and Gly-Arg and Met
E) Ala-Val-Trp and Lys-Phe-Gly and Arg-Met
A) Ala-Val-Trp-Lys-Phe and Gly-Arg-Met
B) Ala-Val-Trp-Lys-Phe -Gly and Arg-Met
C) Ala-Val-Trp-Lys and Phe-Gly-Arg and Met
D) Ala-Val-Trp-Lys and Phe and Gly-Arg and Met
E) Ala-Val-Trp and Lys-Phe-Gly and Arg-Met

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following will migrate toward the positive electrode in an electrophoresis experiment? 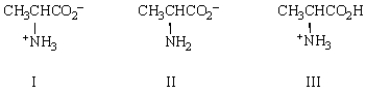
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) I and III
E) none will migrate

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) I and III
E) none will migrate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If an amino acid has one carboxyl group and one amino group, and the pKa's are 2.4 and 9.8 respectively, what is its isoelectric point?
A) 3.7
B) 6.1
C) 7.0
D) 7.9
E) 12.2
A) 3.7
B) 6.1
C) 7.0
D) 7.9
E) 12.2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Sanger's reagent is used
A) to determine the amino acid sequence of a peptide.
B) to determine the C-terminal amino acid of a peptide.
C) to determine the isoelectric point of a peptide.
D) to determine the number of amino acids in a peptide.
E) to determine the N-terminal amino acid of a peptide.
A) to determine the amino acid sequence of a peptide.
B) to determine the C-terminal amino acid of a peptide.
C) to determine the isoelectric point of a peptide.
D) to determine the number of amino acids in a peptide.
E) to determine the N-terminal amino acid of a peptide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Based on the equilibria shown below, what is the net charge on structure IV? 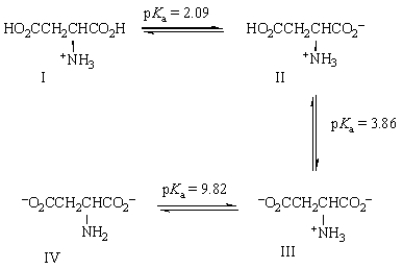
A) -2
B) -1
C) 0
D) +1
E) +2

A) -2
B) -1
C) 0
D) +1
E) +2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which reagent is used specifically to cleave the C-terminal amino acid of a peptide?
A) trypsin
B) carboxypeptidase
C) cyanogen bromide
D) chymotrypsin
E) HCl/H2O
A) trypsin
B) carboxypeptidase
C) cyanogen bromide
D) chymotrypsin
E) HCl/H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The Edman degradation is used
A) to identify the C-terminal amino acid of a peptide.
B) to determine the tertiary structure of peptides.
C) to synthesize peptides.
D) to cleave polypeptides on the carboxyl side of Phe, Tyr, and Trp residues.
E) to identify the N-terminal amino acid of a peptide.
A) to identify the C-terminal amino acid of a peptide.
B) to determine the tertiary structure of peptides.
C) to synthesize peptides.
D) to cleave polypeptides on the carboxyl side of Phe, Tyr, and Trp residues.
E) to identify the N-terminal amino acid of a peptide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Ninhydrin is used
A) to determine the N-terminal amino acid of a peptide.
B) to sequence amino acids in a peptide.
C) to detect amino acids derived from hydrolysis of a peptide.
D) to couple amino acids during solid-phase peptide synthesis.
E) to hydrolyze peptides on the carboxyl side of aromatic amino acid residues.
A) to determine the N-terminal amino acid of a peptide.
B) to sequence amino acids in a peptide.
C) to detect amino acids derived from hydrolysis of a peptide.
D) to couple amino acids during solid-phase peptide synthesis.
E) to hydrolyze peptides on the carboxyl side of aromatic amino acid residues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The isoelectric pH (pI) of  is likely to be at a pH that is
is likely to be at a pH that is
A) below pK1.
B) at pK1.
C) between pK1 and pK2.
D) at pK2.
E) above pK2.
 is likely to be at a pH that is
is likely to be at a pH that isA) below pK1.
B) at pK1.
C) between pK1 and pK2.
D) at pK2.
E) above pK2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What is the structure of the phenylhydantoin derived from the first cycle of the Edman degradation of Phe-Ala-Ser?
A)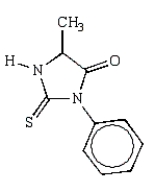
B)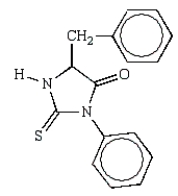
C)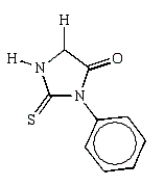
D)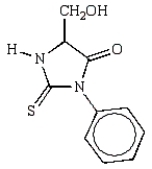
E)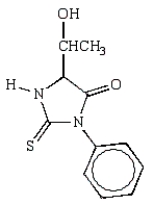
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A tetrapeptide contains the amino acids Phe, Ala, Gly, and Leu.Partial hydrolysis affords the dipeptides Phe-Ala, Ala-Gly, and Leu-Phe.The structure of the tetrapeptide is
A) Ala-Gly-Leu-Phe.
B) Leu-Phe-Ala-Gly.
C) Gly-Ala-Phe-Leu.
D) Leu-Phe-Gly-Ala.
E) Phe-Leu-Gly-Ala.
A) Ala-Gly-Leu-Phe.
B) Leu-Phe-Ala-Gly.
C) Gly-Ala-Phe-Leu.
D) Leu-Phe-Gly-Ala.
E) Phe-Leu-Gly-Ala.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The mechanism by which Sanger's reagent reacts with an amine is
A) nucleophilic aromatic substitution.
B) electrophilic aromatic substitution.
C) hydrolysis.
D) nucleophilic acyl substitution.
E) electrophilic addition.
A) nucleophilic aromatic substitution.
B) electrophilic aromatic substitution.
C) hydrolysis.
D) nucleophilic acyl substitution.
E) electrophilic addition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The reaction of 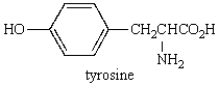 with bromine water is likely to give:
with bromine water is likely to give:
A)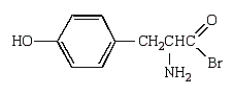
B)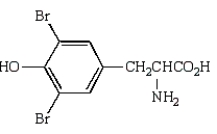
C)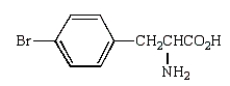
D)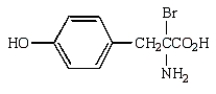
E)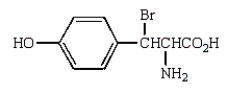
 with bromine water is likely to give:
with bromine water is likely to give:A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Sanger's reagent (2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene) reacts with the following to give, after complete hydrolysis, 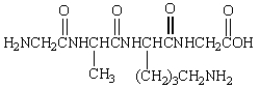
A) no labeled amino acids.
B) one labeled and two unlabeled amino acids.
C) one labeled and three unlabeled amino acids.
D) two labeled and one unlabeled amino acids.
E) two labeled and two unlabeled amino acids.

A) no labeled amino acids.
B) one labeled and two unlabeled amino acids.
C) one labeled and three unlabeled amino acids.
D) two labeled and one unlabeled amino acids.
E) two labeled and two unlabeled amino acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The product from the following is: 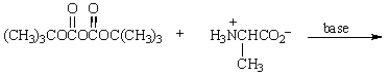
A)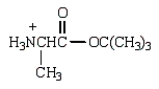
B)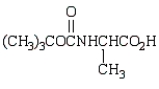
C)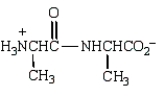
D)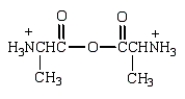
E)
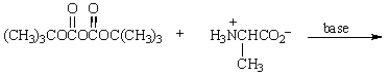
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Treatment of 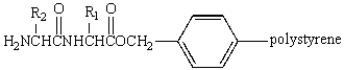 with HF (Merrifield method) gives:
with HF (Merrifield method) gives:
A)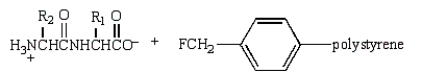
B)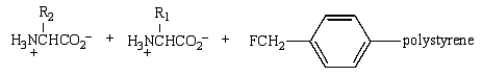
C)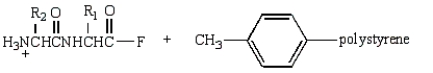
D)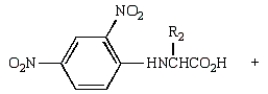
E)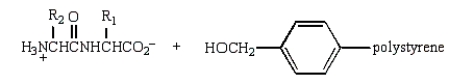
 with HF (Merrifield method) gives:
with HF (Merrifield method) gives:A)

B)

C)

D)

E)
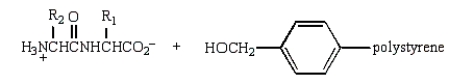

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following reagents is used to protect the N-terminal amino acid in a solid phase peptide synthesis?
A)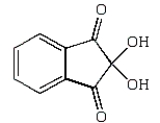
B)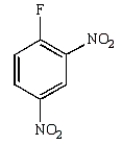
C)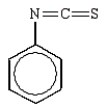
D)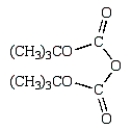
E)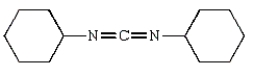
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)
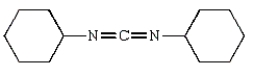

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) is used
A) to determine the N-terminal amino acid of a peptide.
B) to sequence amino acids in a peptide.
C) to detect amino acids derived from hydrolysis of a peptide.
D) to couple amino acids during solid-phase peptide synthesis.
E) to hydrolyze peptides on the carboxyl side of aromatic amino acid residues.
A) to determine the N-terminal amino acid of a peptide.
B) to sequence amino acids in a peptide.
C) to detect amino acids derived from hydrolysis of a peptide.
D) to couple amino acids during solid-phase peptide synthesis.
E) to hydrolyze peptides on the carboxyl side of aromatic amino acid residues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
An aniline derivative that is suitable for use in the Merrifield peptide synthesis is: 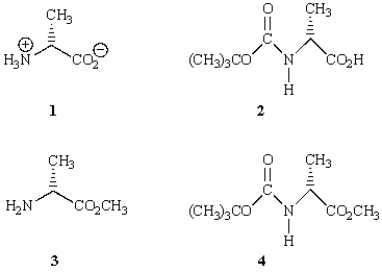
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) none of the above

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



