Deck 32: Maxwells Equations; Magnetism of Matter
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/81
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 32: Maxwells Equations; Magnetism of Matter
1
Four closed surfaces are shown, each with circular top and bottom faces and curved sides.The areas Atop and Abot of the top and bottom faces and the magnitudes Btop and Bbot of the uniform magnetic fields through the top and bottom faces are given.The fields are perpendicular to the faces and are either inward or outward.Rank the surfaces according to the magnitude of the magnetic flux through the curved sides, least to greatest. 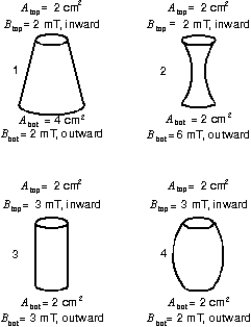
A)1, 2, 3, 4
B)3, 4, 1, 2
C)1, 2, 4, 3
D)4, 3, 2, 1
E)2, 1, 4, 3

A)1, 2, 3, 4
B)3, 4, 1, 2
C)1, 2, 4, 3
D)4, 3, 2, 1
E)2, 1, 4, 3
3, 4, 1, 2
2
A 1-A current is used to charge a parallel plate capacitor.A large square piece of paper is placed between the plates and parallel to them so it sticks out on all sides.The value of the integral around the perimeter of the paper is:
A)2 T.m
B)4 *10-7 T.m
C)8.85 *10-12 T.m
D)10-7 T.m
E)not determined from the given quantities
A)2 T.m
B)4 *10-7 T.m
C)8.85 *10-12 T.m
D)10-7 T.m
E)not determined from the given quantities
4 *10-7 T.m
3
An electric field exists in the cylindrical region shown and is parallel to the cylinder axis.The magnitude of the field might vary with time according to any of the four graphs shown.Rank the four variations according to the magnitudes of the magnetic field induced at the edge of the region, least to greatest. 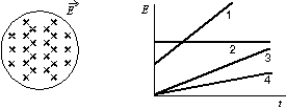
A)2, 4, 3, 1
B)1, 3, 4, 2
C)4, 3, 2, 1
D)4, 3, 1, 2
E)2, 1, 3, 4

A)2, 4, 3, 1
B)1, 3, 4, 2
C)4, 3, 2, 1
D)4, 3, 1, 2
E)2, 1, 3, 4
2, 4, 3, 1
4
Suppose you are looking into one end of a long cylindrical tube in which there is a uniform electric field, pointing away from you.If the magnitude of the field is decreasing with time the field lines of the induced magnetic field are:
A)circles
B)ellipses
C)straight lines parallel to the electric field
D)straight lines perpendicular to the electric field
E)none of the above
A)circles
B)ellipses
C)straight lines parallel to the electric field
D)straight lines perpendicular to the electric field
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
One of the Maxwell equations begins with ....The symbol means:
A)an infinitesimal displacement of a charge
B)an infinitesimal displacement of a magnetic pole
C)an infinitesimal inductance
D)an infinitesimal surface area
E)none of the above
A)an infinitesimal displacement of a charge
B)an infinitesimal displacement of a magnetic pole
C)an infinitesimal inductance
D)an infinitesimal surface area
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A cylindrical region contains a uniform electric field that is along the cylinder axis and is changing with time.If r is the distance from the cylinder axis the magnitude of the magnetic field within the region is:
A)uniform
B)proportional to 1/r
C)proportional to r2
D)proportional to 1/r2
E)proportional to r
A)uniform
B)proportional to 1/r
C)proportional to r2
D)proportional to 1/r2
E)proportional to r

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A 0.70-m radius cylindrical region contains a uniform electric field that is parallel to the axis and is increasing at the rate 5.0 *1012 V/m.s.The magnetic field at a point 0.25 m from the axis has a magnitude of:
A)0 T
B)7.0 * 10-6 T
C)2.8 * 10-5 T
D)5.4 * 10-5 T
E)7.0 * 10-5 T
A)0 T
B)7.0 * 10-6 T
C)2.8 * 10-5 T
D)5.4 * 10-5 T
E)7.0 * 10-5 T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
One of the Maxwell equations begins with ....The o symbol in the integral sign means:
A)the same as the subscript in 0
B)integrate clockwise around the path
C)integrate counterclockwise around the path
D)integrate around a closed path
E)integrate over a closed surface
A)the same as the subscript in 0
B)integrate clockwise around the path
C)integrate counterclockwise around the path
D)integrate around a closed path
E)integrate over a closed surface

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A magnetic field exists between the plates of a capacitor:
A)always
B)never
C)when the capacitor is fully charged
D)while the capacitor is being charged
E)only when the capacitor is starting to be charged
A)always
B)never
C)when the capacitor is fully charged
D)while the capacitor is being charged
E)only when the capacitor is starting to be charged

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Gauss' law for magnetism, , tells us:
A)the net charge in any given volume
B)that the line integral of a magnetic field around any closed loop must vanish
C)the magnetic field of a current element
D)that magnetic monopoles do not exist
E)charges must be moving to produce magnetic fields
A)the net charge in any given volume
B)that the line integral of a magnetic field around any closed loop must vanish
C)the magnetic field of a current element
D)that magnetic monopoles do not exist
E)charges must be moving to produce magnetic fields

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A sinusoidal emf is connected to a parallel plate capacitor.The magnetic field between the plates is:
A)zero
B)constant
C)sinusoidal and its amplitude does not depend on the frequency of the source
D)sinusoidal and its amplitude is proportional to the frequency of the source
E)sinusoidal and its amplitude is inversely proportional to the frequency of the source
A)zero
B)constant
C)sinusoidal and its amplitude does not depend on the frequency of the source
D)sinusoidal and its amplitude is proportional to the frequency of the source
E)sinusoidal and its amplitude is inversely proportional to the frequency of the source

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
According to Gauss' law for magnetism, magnetic field lines:
A)form closed loops
B)start at south poles and end at north poles
C)start at north poles and end at south poles
D)start at both north and south poles and end at infinity
E)do not exist
A)form closed loops
B)start at south poles and end at north poles
C)start at north poles and end at south poles
D)start at both north and south poles and end at infinity
E)do not exist

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
An electron is on the z axis moving toward the xy plane but it has not reached that plane yet.At that instant:
A)there is only a true current through the xy plane
B)there is only a displacement current through the xy plane
C)there are both true and displacement currents through the xy plane
D)there is neither a true nor a displacement current through the xy plane
E)none of the above are true
A)there is only a true current through the xy plane
B)there is only a displacement current through the xy plane
C)there are both true and displacement currents through the xy plane
D)there is neither a true nor a displacement current through the xy plane
E)none of the above are true

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The statement that magnetic field lines form closed loops is a direct consequence of:
A)Faraday's law
B)Ampere's law
C)Gauss' law for electricity
D)Gauss' law for magnetism
E)the Lorentz force
A)Faraday's law
B)Ampere's law
C)Gauss' law for electricity
D)Gauss' law for magnetism
E)the Lorentz force

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A 0.70-m radius cylindrical region contains a uniform electric field that is parallel to the axis and is increasing at the rate 5.0 *1012 V/m.s.The magnetic field at a point 1.2 m from the axis has a magnitude of:
A)0 T
B)7.0 *10-6 T
C)1.1 * 10-5 T
D)2.3 *10-5 T
E)2.8 * 10-5 T
A)0 T
B)7.0 *10-6 T
C)1.1 * 10-5 T
D)2.3 *10-5 T
E)2.8 * 10-5 T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The diagram shows one plate of a parallel-plate capacitor from within the capacitor.The plate is circular and has radius R.The dashed circles are four integration paths have radii of r1 = R/4, r2 = R/2, r3 =3 R/2, and r4 = 2R.Rank the paths according to the magnitude of around the paths during the discharging of the capacitor, least to greatest. 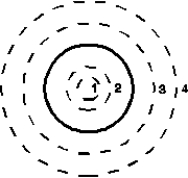
A)1, 2 and 3 tie, then 4
B)1, 2, 3, 4
C)1, then 2 and 4 tie, then 3
D)4, 3, 1, 2
E)3, then 2 and 4 tie, then 1

A)1, 2 and 3 tie, then 4
B)1, 2, 3, 4
C)1, then 2 and 4 tie, then 3
D)4, 3, 1, 2
E)3, then 2 and 4 tie, then 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A cylindrical region contains a uniform electric field that is parallel to the axis and is changing with time.If r is the distance from the cylinder axis the magnitude of the magnetic field outside the region is:
A)zero
B)proportional to 1/r
C)proportional to r2
D)proportional to 1/r2
E)proportional to r
A)zero
B)proportional to 1/r
C)proportional to r2
D)proportional to 1/r2
E)proportional to r

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A magnetic field parallel to the x axis with a magnitude that decreases with increasing x but does not change with y and z is impossible according to:
A)Faraday's law
B)Ampere's law
C)Gauss' law for electricity
D)Gauss' law for magnetism
E)Newton's second law
A)Faraday's law
B)Ampere's law
C)Gauss' law for electricity
D)Gauss' law for magnetism
E)Newton's second law

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Suppose you are looking into one end of a long cylindrical tube in which there is a uniform electric field, pointing away from you.If the magnitude of the field is decreasing with time the direction of the induced magnetic field is:
A)toward you
B)away from you
C)clockwise
D)counterclockwise
E)to your right
A)toward you
B)away from you
C)clockwise
D)counterclockwise
E)to your right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Gauss' law for magnetism:
A)can be used to find due to given currents provided there is enough symmetry
B)is false because there are no magnetic poles
C)can be used with open surfaces because there are no magnetic poles
D)contradicts Faraday's law because one says B = 0 and the other says = -d B/dt
E)none of the above
A)can be used to find due to given currents provided there is enough symmetry
B)is false because there are no magnetic poles
C)can be used with open surfaces because there are no magnetic poles
D)contradicts Faraday's law because one says B = 0 and the other says = -d B/dt
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Displacement current exists in the region between the plates of a parallel plate capacitor if:
A)the capacitor leaks charge across the plates
B)the capacitor is being discharged
C)the capacitor is fully charged
D)the capacitor is fully discharged
E)none of the above are true
A)the capacitor leaks charge across the plates
B)the capacitor is being discharged
C)the capacitor is fully charged
D)the capacitor is fully discharged
E)none of the above are true

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A circular parallel-plate capacitor whose plates have a radius of 25 cm is being charged with a current of 1.3 A.What is the magnetic field 11 cm from the center of the plates?
A)4.6 x 10-7 T
B)1.0 x 10-6 T
C)2.4 x 10-6 T
D)3.1 x 10-6 T
E)6.2 x 10-6 T
A)4.6 x 10-7 T
B)1.0 x 10-6 T
C)2.4 x 10-6 T
D)3.1 x 10-6 T
E)6.2 x 10-6 T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A 1.2-m radius cylindrical region contains a uniform electric field along the cylinder axis.It is increasing uniformly with time.To obtain a total displacement current of 2.0* 10 - 9 A through a cross section of the region, the magnitude of the electric field should change at a rate of:
A)5.0 V/m·s
B)12 V/m·s
C)37 V/m·s
D)50 V/m·s
E)4.0 * 107 V/m·s
A)5.0 V/m·s
B)12 V/m·s
C)37 V/m·s
D)50 V/m·s
E)4.0 * 107 V/m·s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A positively charged ion, due to a cosmic ray, is headed through Earth's atmosphere toward the center of Earth.Due to Earth's magnetic field, the ion will be deflected:
A)south
B)north
C)west
D)east
E)not at all since it is a charge and not a pole
A)south
B)north
C)west
D)east
E)not at all since it is a charge and not a pole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The magnetic field of Earth is roughly the same as that of a magnetic dipole with a dipole moment of about:
A)1017 J/T
B)1019 J/T
C)1021 J/T
D)1023 J/T
E)1025 J/T
A)1017 J/T
B)1019 J/T
C)1021 J/T
D)1023 J/T
E)1025 J/T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Maxwell's equations, along with an appropriate symmetry argument, can be used to calculate:
A)the electric force on a given charge
B)the magnetic force on a given moving charge
C)the flux of a given electric field
D)the flux of a given magnetic field
E)none of these
A)the electric force on a given charge
B)the magnetic force on a given moving charge
C)the flux of a given electric field
D)the flux of a given magnetic field
E)none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Two of Maxwell's equations contain a path integral on the left side and an area integral on the right.The directions of the infinitesimal path element and infinitesimal area element are:
A)always in the same direction
B)always in opposite directions
C)always perpendicular to each other
D)never perpendicular to each other
E)none of the above
A)always in the same direction
B)always in opposite directions
C)always perpendicular to each other
D)never perpendicular to each other
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A current of 1 A is used to charge a parallel plate capacitor with square plates.If the area of each plate is 0.6 m2 the displacement current through a 0.3 m2 area wholly between the capacitor plates and parallel to them is:
A)2 A
B)1 A
C)0.7 A
D)0.5 A
E)0.25 A
A)2 A
B)1 A
C)0.7 A
D)0.5 A
E)0.25 A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Displacement current is:
A)"d E/dt"
B)" 0d E/dt"
C)" 0d E/dt"
D)" 0 0d E/dt"
E)"-d B/dt"
A)"d E/dt"
B)" 0d E/dt"
C)" 0d E/dt"
D)" 0 0d E/dt"
E)"-d B/dt"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A bar magnet is placed vertically with its S pole up and its N pole down.The field at its center is:
A)zero
B)down
C)up
D)horizontal
E)slightly below the horizontal
A)zero
B)down
C)up
D)horizontal
E)slightly below the horizontal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Consider the four Maxwell equations: 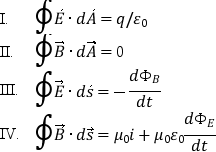 Which of these must be modified if magnetic poles are discovered?
Which of these must be modified if magnetic poles are discovered?
A)only I
B)only II
C)only II and III
D)only III and IV
E)only II, III, IV
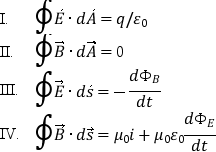 Which of these must be modified if magnetic poles are discovered?
Which of these must be modified if magnetic poles are discovered?A)only I
B)only II
C)only II and III
D)only III and IV
E)only II, III, IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Two of Maxwell's equations contain an integral over a closed surface.For them the infinitesimal vector area is always:
A)tangent to the surface
B)perpendicular to the surface and pointing outward
C)perpendicular to the surface and pointing inward
D)tangent to a field line
E)perpendicular to a field line
A)tangent to the surface
B)perpendicular to the surface and pointing outward
C)perpendicular to the surface and pointing inward
D)tangent to a field line
E)perpendicular to a field line

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Displacement current exists wherever there is:
A)moving charge
B)a magnetic field
C)a changing magnetic field
D)an electric field
E)a changing electric field
A)moving charge
B)a magnetic field
C)a changing magnetic field
D)an electric field
E)a changing electric field

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Two of Maxwell's equations contain a path integral on the left side and an area integral on the right.Suppose the area is the surface of a piece of paper at which you are looking and is chosen to point toward you.Then, the path integral is:
A)clockwise around the circumference of the paper
B)counterclockwise around the circumference of the paper
C)from left to right
D)from right to left
E)from top to bottom
A)clockwise around the circumference of the paper
B)counterclockwise around the circumference of the paper
C)from left to right
D)from right to left
E)from top to bottom

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Two of Maxwell's equations contain a path integral on the left side and an area integral on the right.For them:
A)the path must pierce the area
B)the path must be well-separated from the area
C)the path must be along a field line and the area must be perpendicular to the field line
D)the path must be the boundary of the area
E)the path must lie in the area, away from its boundary
A)the path must pierce the area
B)the path must be well-separated from the area
C)the path must be along a field line and the area must be perpendicular to the field line
D)the path must be the boundary of the area
E)the path must lie in the area, away from its boundary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The polarity of an unmarked magnet can be determined using:
A)a charged glass rod
B)a compass
C)an electroscope
D)another unmarked magnet
E)iron filings
A)a charged glass rod
B)a compass
C)an electroscope
D)another unmarked magnet
E)iron filings

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
One of the Maxwell equations begins with ....The o symbol in the integral sign means:
A)the same as the subscript in 0
B)integrate clockwise around the path
C)integrate counterclockwise around the path
D)integrate around a closed path
E)integrate over a closed surface
A)the same as the subscript in 0
B)integrate clockwise around the path
C)integrate counterclockwise around the path
D)integrate around a closed path
E)integrate over a closed surface

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
One of the crucial facts upon which the Maxwell equations are based is:
A)the numerical value of the electron charge
B)charge is quantized
C)the numerical value of the charge/mass ratio of the electron
D)there are three types of magnetic materials
E)none of the above
A)the numerical value of the electron charge
B)charge is quantized
C)the numerical value of the charge/mass ratio of the electron
D)there are three types of magnetic materials
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A 1- F capacitor is connected to an emf that is increasing uniformly with time at a rate of 100 V/s.The displacement current between the plates is:
A)0 A
B)1 * 10-8 A
C)1 *10-6 A
D)1 * 10-4 A
E)100 A
A)0 A
B)1 * 10-8 A
C)1 *10-6 A
D)1 * 10-4 A
E)100 A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Of the following places one would expect that the horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field to be largest in:
A)Maine
B)Florida
C)Maryland
D)New York
E)Iowa
A)Maine
B)Florida
C)Maryland
D)New York
E)Iowa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The magnetic dipole moment of an atomic electron is typically:
A)much less than a Bohr magneton
B)a few Bohr magnetons
C)much greater than a Bohr magneton
D)much greater or much less than a Bohr magneton, depending on the atom
E)not related to the value of the Bohr magneton
A)much less than a Bohr magneton
B)a few Bohr magnetons
C)much greater than a Bohr magneton
D)much greater or much less than a Bohr magneton, depending on the atom
E)not related to the value of the Bohr magneton

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The potential energy of a magnetic dipole in an external magnetic field is least when:
A)the dipole moment is parallel to the field
B)the dipole moment is antiparallel to the field
C)the dipole moment is perpendicular to the field
D)none of the above (the same energy is associated with all orientations)
E)none of the above (no energy is associated with the dipole-field interaction)
A)the dipole moment is parallel to the field
B)the dipole moment is antiparallel to the field
C)the dipole moment is perpendicular to the field
D)none of the above (the same energy is associated with all orientations)
E)none of the above (no energy is associated with the dipole-field interaction)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The magnetic field lines due to an ordinary bar magnet:
A)form closed curves
B)cross one another near the poles
C)are more numerous near the N pole than near the S pole
D)leave the S pole, loop around the outside of the magnet, and enter the N pole
E)none of the above
A)form closed curves
B)cross one another near the poles
C)are more numerous near the N pole than near the S pole
D)leave the S pole, loop around the outside of the magnet, and enter the N pole
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An electron traveling with speed v around a circle of radius r is equivalent to a current of:
A)evr/2
B)ev/r
C)ev/2 r
D)2 er/v
E)2 ev/r
A)evr/2
B)ev/r
C)ev/2 r
D)2 er/v
E)2 ev/r

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The diagram shows the spin angular momentum vectors of two electrons and two protons in the same external magnetic field.The field points upward in the diagram.Rank the situations according to the potential energy, least to greatest. 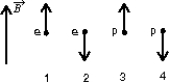
A)1 and 3 tie, then 2 and 4 tie
B)2 and 3 tie, then 1 and 4 tie
C)1 and 2 tie, then 3 and 4 tie
D)3 and 4 tie, then 1 and 2 tie
E)all tie

A)1 and 3 tie, then 2 and 4 tie
B)2 and 3 tie, then 1 and 4 tie
C)1 and 2 tie, then 3 and 4 tie
D)3 and 4 tie, then 1 and 2 tie
E)all tie

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The spin magnetic dipole moment of an electron:
A)is in the same direction as the spin angular momentum
B)is zero
C)has a magnitude that depends on the orbital angular momentum
D)has a magnitude that depends on the applied magnetic field
E)none of the above
A)is in the same direction as the spin angular momentum
B)is zero
C)has a magnitude that depends on the orbital angular momentum
D)has a magnitude that depends on the applied magnetic field
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A bar magnet is broken in half.Each half is broken in half again, etc.The observation is that each piece has both a north and south pole.This is usually explained by:
A)Ampere's theory that all magnetic phenomena result from electric currents
B)our inability to divide the magnet into small enough pieces
C)Coulomb's law
D)Lenz' law
E)conservation of charge
A)Ampere's theory that all magnetic phenomena result from electric currents
B)our inability to divide the magnet into small enough pieces
C)Coulomb's law
D)Lenz' law
E)conservation of charge

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following statements is correct?
A)The declination of the Earth's magnetic field is the angle between a horizontal plane and the direction of the field.
B)The declination of the Earth's magnetic field is the angle between a vertical plane and the direction of the field.
C)The inclination of the Earth's magnetic field is the angle between a horizontal plane and the direction of the field.
D)The inclination of the Earth's magnetic field is the angle between the horizontal component of the field direction and the direction to geographic north.
E)Inclination and declination mean the same thing.
A)The declination of the Earth's magnetic field is the angle between a horizontal plane and the direction of the field.
B)The declination of the Earth's magnetic field is the angle between a vertical plane and the direction of the field.
C)The inclination of the Earth's magnetic field is the angle between a horizontal plane and the direction of the field.
D)The inclination of the Earth's magnetic field is the angle between the horizontal component of the field direction and the direction to geographic north.
E)Inclination and declination mean the same thing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The molecular theory of magnetism can explain each of the following EXCEPT:
A)a N pole attracts a S pole
B)stroking an iron bar with a magnet will magnetize the bar
C)when a bar magnet is broken in two, each piece is a bar magnet
D)heating tends to destroy magnetization
E)hammering tends to destroy magnetization
A)a N pole attracts a S pole
B)stroking an iron bar with a magnet will magnetize the bar
C)when a bar magnet is broken in two, each piece is a bar magnet
D)heating tends to destroy magnetization
E)hammering tends to destroy magnetization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A small bar magnet is suspended horizontally by a string.When placed in a uniform horizontal magnetic field, it will:
A)translate in the direction of
B)translate in the opposite direction of
C)rotate so as to be at right angles to
D)rotate so as to be vertical
E)none of the above
A)translate in the direction of
B)translate in the opposite direction of
C)rotate so as to be at right angles to
D)rotate so as to be vertical
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Magnetic dipole X is fixed.Dipole Y is placed in the position indicated and is free to move.The first thing dipole Y will do is: 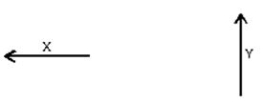
A)move toward X but not rotate
B)move away from X but not rotate
C)move toward X and rotate
D)move away from X and rotate
E)rotate but not move toward or away from X
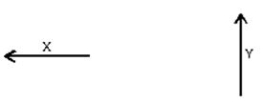
A)move toward X but not rotate
B)move away from X but not rotate
C)move toward X and rotate
D)move away from X and rotate
E)rotate but not move toward or away from X

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following statements is correct?
A)The spin angular momentum of the electron can be directly observed, but the spin magnetic dipole moment cannot be.
B)The spin angular momentum of the electron cannot be directly observed, but the spin magnetic dipole moment can be.
C)Both the spin angular momentum and the spin magnetic dipole moment of the electron can be directly observed.
D)Neither the spin angular momentum nor the spin magnetic dipole moment of the electron can be directly observed.
E)Although both the spin angular momentum and the spin magnetic dipole moment can be defined theoretically, neither has any physical meaning at all.
A)The spin angular momentum of the electron can be directly observed, but the spin magnetic dipole moment cannot be.
B)The spin angular momentum of the electron cannot be directly observed, but the spin magnetic dipole moment can be.
C)Both the spin angular momentum and the spin magnetic dipole moment of the electron can be directly observed.
D)Neither the spin angular momentum nor the spin magnetic dipole moment of the electron can be directly observed.
E)Although both the spin angular momentum and the spin magnetic dipole moment can be defined theoretically, neither has any physical meaning at all.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If is the orbital angular momentum of an electron, the magnetic dipole moment associated with its orbital motion:
A)is in the direction of and has magnitude proportional to L
B)is opposite to the direction of and has magnitude proportional to L
C)is in the direction of and has magnitude proportional to L2
D)is opposite to the direction of and has magnitude proportional to L2
E)does not depend on
A)is in the direction of and has magnitude proportional to L
B)is opposite to the direction of and has magnitude proportional to L
C)is in the direction of and has magnitude proportional to L2
D)is opposite to the direction of and has magnitude proportional to L2
E)does not depend on

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following statements about the Earth's magnetic field is correct?
A)The Earth's magnetic field is approximately that of a dipole, and the north magnetic pole is in the northern hemisphere.
B)The Earth's magnetic field is approximately that of a dipole, and the north magnetic pole is in the southern hemisphere.
C)The Earth's magnetic field is approximately that of a monopole, and the north magnetic pole is in the northern hemisphere.
D)The Earth's magnetic field is approximately that of a monopole, and the north magnetic pole is in the southern hemisphere.
E)The Earth's magnetic field is approximately that of a quadrupole, and the north magnetic pole is in the eastern hemisphere.
A)The Earth's magnetic field is approximately that of a dipole, and the north magnetic pole is in the northern hemisphere.
B)The Earth's magnetic field is approximately that of a dipole, and the north magnetic pole is in the southern hemisphere.
C)The Earth's magnetic field is approximately that of a monopole, and the north magnetic pole is in the northern hemisphere.
D)The Earth's magnetic field is approximately that of a monopole, and the north magnetic pole is in the southern hemisphere.
E)The Earth's magnetic field is approximately that of a quadrupole, and the north magnetic pole is in the eastern hemisphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If an electron has zero orbital angular momentum, the magnitude of its magnetic dipole moment equals:
A)zero
B)half the Bohr magneton
C)a Bohr magneton
D)twice a Bohr magneton
E)none of these
A)zero
B)half the Bohr magneton
C)a Bohr magneton
D)twice a Bohr magneton
E)none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The magnitude of the Bohr magneton is about:
A)10-15 J/T
B)10-19 J/T
C)10-23 J/T
D)10-27 J/T
E)10-31 J/T
A)10-15 J/T
B)10-19 J/T
C)10-23 J/T
D)10-27 J/T
E)10-31 J/T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What are the possible allowed values of the spin magnetic quantum number ms of the electron?
A)+1/2 only
B)±1/2
C)any half-odd integer
D)any integer
E)It depends on the external magnetic field.
A)+1/2 only
B)±1/2
C)any half-odd integer
D)any integer
E)It depends on the external magnetic field.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
If an electron has an orbital angular momentum with magnitude L the magnitude of the orbital contribution to its magnetic dipole moment is given by:
A)eL/m
B)eL/2m
C)2eL/m
D)mL/e
E)mL/2
A)eL/m
B)eL/2m
C)2eL/m
D)mL/e
E)mL/2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Magnetic dipole X is fixed and dipole Y is free to move.Dipole Y will initially: 
A)move toward X but not rotate
B)move away from X but not rotate
C)move toward X and rotate
D)move away from X and rotate
E)rotate but not translate

A)move toward X but not rotate
B)move away from X but not rotate
C)move toward X and rotate
D)move away from X and rotate
E)rotate but not translate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The magnetic properties of materials stem chiefly from:
A)particles with north poles
B)particles with south poles
C)motions of protons within nuclei
D)proton spin angular momentum
E)electron magnetic dipole moments
A)particles with north poles
B)particles with south poles
C)motions of protons within nuclei
D)proton spin angular momentum
E)electron magnetic dipole moments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
An unmagnetized steel bar is placed inside a solenoid.As the current in the solenoid is slowly increased from zero to some large value, the magnetization of the bar:
A)increases proportionally with the current
B)remains zero for a while and then increases linearly with any further increase in current
C)increases with increasing current at first but later is much less affected by it
D)is unaffected by the current
E)increases quadratically with the current
A)increases proportionally with the current
B)remains zero for a while and then increases linearly with any further increase in current
C)increases with increasing current at first but later is much less affected by it
D)is unaffected by the current
E)increases quadratically with the current

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A paramagnetic substance, in an external magnetic field, is thermally isolated.The field is then removed.As a result:
A)the magnetic energy of the magnetic dipoles decreases
B)the temperature of the substance increases
C)the magnetization decreases, but only slightly
D)the magnetization reverses direction
E)none of the above
A)the magnetic energy of the magnetic dipoles decreases
B)the temperature of the substance increases
C)the magnetization decreases, but only slightly
D)the magnetization reverses direction
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A paramagnetic substance is placed in a weak magnetic field and its absolute temperature T is increased.As a result, its magnetization:
A)increases in proportion to T
B)increases in proportion to T2
C)remains the same
D)decreases in proportion to 1/T
E)decreases in proportion to 1/T2
A)increases in proportion to T
B)increases in proportion to T2
C)remains the same
D)decreases in proportion to 1/T
E)decreases in proportion to 1/T2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Magnetization is:
A)the current density in an object
B)the charge density of moving charges in an object
C)the magnetic dipole moment of an object
D)the magnetic dipole moment per unit volume of an object
E)the magnetic field per unit volume produced by an object
A)the current density in an object
B)the charge density of moving charges in an object
C)the magnetic dipole moment of an object
D)the magnetic dipole moment per unit volume of an object
E)the magnetic field per unit volume produced by an object

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The soft iron core in the solenoid shown is removable.Then: 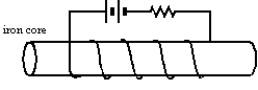
A)the current will be larger without the core
B)the current will be larger with the core
C)one must do work to remove the core
D)the circuit will do work in expelling the core
E)the stored energy is the same with or without the core

A)the current will be larger without the core
B)the current will be larger with the core
C)one must do work to remove the core
D)the circuit will do work in expelling the core
E)the stored energy is the same with or without the core

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
When a permanent magnet is strongly heated:
A)nothing happens
B)it becomes an induced magnet
C)it loses its magnetism
D)its magnetism increases
E)its polarity reverses
A)nothing happens
B)it becomes an induced magnet
C)it loses its magnetism
D)its magnetism increases
E)its polarity reverses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Paramagnetism is closely associated with:
A)the tendency of electron dipole moments to align with an applied magnetic field
B)the tendency of electron dipole moments to align opposite to an applied magnetic field
C)the exchange force between electrons
D)the force exerted by electron dipole moments on each other
E)the torque exerted by electron dipole moments on each other
A)the tendency of electron dipole moments to align with an applied magnetic field
B)the tendency of electron dipole moments to align opposite to an applied magnetic field
C)the exchange force between electrons
D)the force exerted by electron dipole moments on each other
E)the torque exerted by electron dipole moments on each other

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Because ferromagnets exhibit hysteresis, the magnetization:
A)can never be in the same direction as an applied field
B)may not vanish when an applied field is reduced to zero
C)can never vanish
D)is proportional to any applied magnetic field
E)is always opposite to the direction of any applied magnetic field
A)can never be in the same direction as an applied field
B)may not vanish when an applied field is reduced to zero
C)can never vanish
D)is proportional to any applied magnetic field
E)is always opposite to the direction of any applied magnetic field

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The units of magnetization are:
A)ampere
B)ampere.meter
C)ampere.meter2
D)ampere/meter
E)ampere/meter2
A)ampere
B)ampere.meter
C)ampere.meter2
D)ampere/meter
E)ampere/meter2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What are the possible allowed values of the orbital magnetic quantum number mℓ of the electron?
A)0 only
B)0, ±1 only
C)any half-odd integer
D)0, ±1, ±2, …, up to the maximum value for that orbit
E)It depends on the external magnetic field.
A)0 only
B)0, ±1 only
C)any half-odd integer
D)0, ±1, ±2, …, up to the maximum value for that orbit
E)It depends on the external magnetic field.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
An electron in a hydrogen atom moves in a circle of radius 1.1 x 10-10 m at a speed of about 1.6 x 106 m/s.What is the magnetic dipole moment of this electron due to its orbital motion?
A)9.3 x 10-24 J/T
B)1.4 x 10-23 J/T
C)1.9 x 10-23 J/T
D)2.8 x 10-23 J/T
E)3.5 x 10-23 J/T
A)9.3 x 10-24 J/T
B)1.4 x 10-23 J/T
C)1.9 x 10-23 J/T
D)2.8 x 10-23 J/T
E)3.5 x 10-23 J/T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A magnetic field is applied to a diamagnetic substance.In the interior the magnetic field produced by the magnetic dipoles of the substance is:
A)greater than and in the opposite direction
B)less than and in the opposite direction
C)greater than and in the same direction
D)less than and in the same direction
E)the same as
A)greater than and in the opposite direction
B)less than and in the opposite direction
C)greater than and in the same direction
D)less than and in the same direction
E)the same as

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A magnetic field is applied to a paramagnetic substance.In the interior the magnetic field produced by the magnetic dipoles of the substance is:
A)greater than and in the opposite direction
B)less than and in the opposite direction
C)greater than and in the same direction
D)less than and in the same direction
E)the same as
A)greater than and in the opposite direction
B)less than and in the opposite direction
C)greater than and in the same direction
D)less than and in the same direction
E)the same as

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Magnetization vectors in neighboring ferromagnetic domains are:
A)always in opposite directions
B)always in the same direction
C)always in different directions
D)sometimes in different directions and sometimes in the same direction
E)sometimes in opposite directions and sometimes in the same direction
A)always in opposite directions
B)always in the same direction
C)always in different directions
D)sometimes in different directions and sometimes in the same direction
E)sometimes in opposite directions and sometimes in the same direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Lenz' law can explain:
A)paramagnetism only
B)diamagnetism only
C)ferromagnetism only
D)only two of the three types of magnetism
E)all three of the types of magnetism
A)paramagnetism only
B)diamagnetism only
C)ferromagnetism only
D)only two of the three types of magnetism
E)all three of the types of magnetism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The diagram shows two small paramagnetic spheres, one near each end of a bar magnet.Which of the following statements is true? 
A)The force on 1 is toward the magnet and the force on 2 is away from the magnet
B)The force on 1 is away from the magnet and the force on 2 is away from the magnet
C)The forces on 1 and 2 are both toward the magnet
D)The forces on 1 and 2 are both away from the magnet
E)The magnet does not exert a force on either sphere

A)The force on 1 is toward the magnet and the force on 2 is away from the magnet
B)The force on 1 is away from the magnet and the force on 2 is away from the magnet
C)The forces on 1 and 2 are both toward the magnet
D)The forces on 1 and 2 are both away from the magnet
E)The magnet does not exert a force on either sphere

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Ferromagnetism is closely associated with:
A)the tendency of electron dipole moments to align with an applied magnetic field
B)the tendency of electron dipole moments to align opposite to an applied magnetic field
C)the tendency of electron dipole moments to change magnitude in an applied magnetic field
D)the tendency of electron dipole moments to align with each other
E)the force exerted by electron dipole moments on each other
A)the tendency of electron dipole moments to align with an applied magnetic field
B)the tendency of electron dipole moments to align opposite to an applied magnetic field
C)the tendency of electron dipole moments to change magnitude in an applied magnetic field
D)the tendency of electron dipole moments to align with each other
E)the force exerted by electron dipole moments on each other

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The intrinsic magnetic dipole moments of protons and neutrons are much less than that of an electron because:
A)their masses are greater
B)their angular momenta are much less
C)their angular momenta are much greater
D)their charges are much less
E)their radii are much less
A)their masses are greater
B)their angular momenta are much less
C)their angular momenta are much greater
D)their charges are much less
E)their radii are much less

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The behavior of ferromagnetic domains in an applied magnetic field gives rise to:
A)hysteresis
B)ferromagnetism
C)the Curie law
D)a lowering of the Curie temperature
E)Gauss' law for magnetism
A)hysteresis
B)ferromagnetism
C)the Curie law
D)a lowering of the Curie temperature
E)Gauss' law for magnetism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The diagram shows two small diamagnetic spheres, one near each end of a bar magnet.Which of the following statements is true? 
A)The force on 1 is toward the magnet and the force on 2 is away from the magnet
B)The force on 1 is away from the magnet and the force on 2 is away from the magnet
C)The forces on 1 and 2 are both toward the magnet
D)The forces on 1 and 2 are both away from the magnet
E)The magnet does not exert a force on either sphere

A)The force on 1 is toward the magnet and the force on 2 is away from the magnet
B)The force on 1 is away from the magnet and the force on 2 is away from the magnet
C)The forces on 1 and 2 are both toward the magnet
D)The forces on 1 and 2 are both away from the magnet
E)The magnet does not exert a force on either sphere

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



