Deck 17: Tree Structures
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/110
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Tree Structures
1
Consider the following tree diagram: 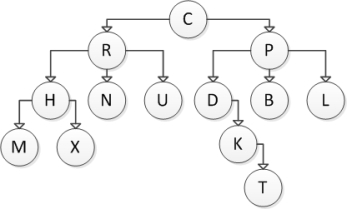 What is the size of the subtree with root R?
What is the size of the subtree with root R?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 6
 What is the size of the subtree with root R?
What is the size of the subtree with root R?A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 6
D
2
Consider the following tree diagram: 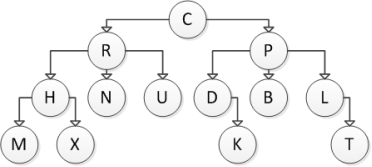 Which of the following nodes are siblings?
Which of the following nodes are siblings?
A) D and U
B) H and M
C) D and B
D) L and T
 Which of the following nodes are siblings?
Which of the following nodes are siblings?A) D and U
B) H and M
C) D and B
D) L and T
C
3
Consider the following tree diagram: 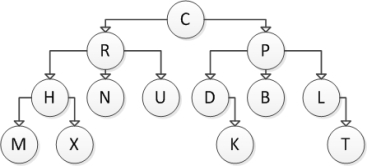 Which of the following nodes are parent nodes?
Which of the following nodes are parent nodes?
A) C
B) C and R
C) R and D
D) C, R, and D
 Which of the following nodes are parent nodes?
Which of the following nodes are parent nodes?A) C
B) C and R
C) R and D
D) C, R, and D
D
4
Consider the following tree diagram: 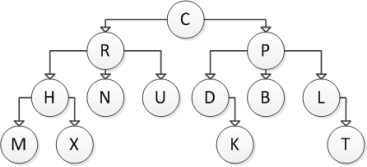 Which of the following nodes are child nodes?
Which of the following nodes are child nodes?
A) C
B) C and R
C) R and D
D) C, R, and D
 Which of the following nodes are child nodes?
Which of the following nodes are child nodes?A) C
B) C and R
C) R and D
D) C, R, and D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Consider the following tree diagram: 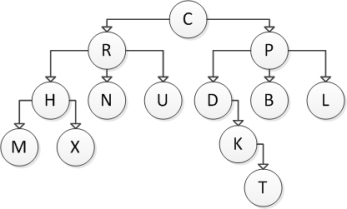 What is the size of this tree?
What is the size of this tree?
A) 4
B) 5
C) 6
D) 13
 What is the size of this tree?
What is the size of this tree?A) 4
B) 5
C) 6
D) 13

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Consider the following tree diagram: 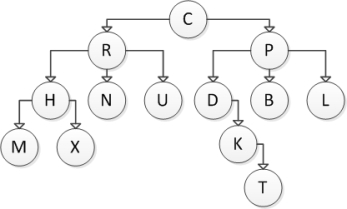 What is the height of the subtree with root R?
What is the height of the subtree with root R?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 6
 What is the height of the subtree with root R?
What is the height of the subtree with root R?A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
As implemented in the textbook, a tree class contains which of the following?
I Node class
II Root node
III List of child nodes
A) I
B) I and II
C) II and III
D) I and III
I Node class
II Root node
III List of child nodes
A) I
B) I and II
C) II and III
D) I and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Consider the following tree diagram: 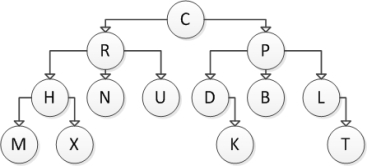 Which of the following nodes are child nodes?
Which of the following nodes are child nodes?
A) C
B) C and X
C) P and X
D) C and P
 Which of the following nodes are child nodes?
Which of the following nodes are child nodes?A) C
B) C and X
C) P and X
D) C and P

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Consider the following tree diagram: 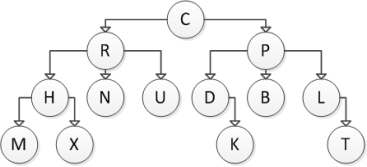 Which of the following nodes are leaf nodes?
Which of the following nodes are leaf nodes?
A) C
B) B
C) H
D) B and H
 Which of the following nodes are leaf nodes?
Which of the following nodes are leaf nodes?A) C
B) B
C) H
D) B and H

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Given the Node class discussed in section 17.1 (partially shown below), select an expression to complete the isLeaf method, which is designed to return true if the node is a leaf, false otherwise. class Node
{
Public Object data;
Public List children;
) . .
Public boolean isLeaf()
{
Return _______________;
}
}
A) data == null
B) children.get(0) == null
C) children.size() == 0
D) root == null
{
Public Object data;
Public List
) . .
Public boolean isLeaf()
{
Return _______________;
}
}
A) data == null
B) children.get(0) == null
C) children.size() == 0
D) root == null

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Consider the following tree diagram: 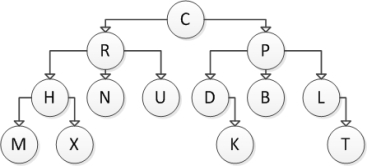 What is the height of this tree?
What is the height of this tree?
A) 3
B) 4
C) 6
D) 7
 What is the height of this tree?
What is the height of this tree?A) 3
B) 4
C) 6
D) 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Consider the following tree diagram: 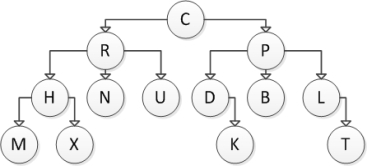 Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
A) N is a descendant of R
B) N is a descendant of C
C) L is a descendant of C
D) H is a descendant of M
 Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?A) N is a descendant of R
B) N is a descendant of C
C) L is a descendant of C
D) H is a descendant of M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Consider the following tree diagram: 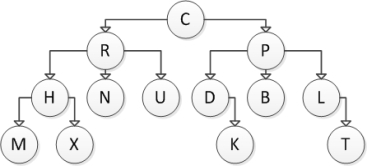 Which of the following nodes are leaf nodes?
Which of the following nodes are leaf nodes?
A) H
B) N
C) H and P
D) H, N, and P
 Which of the following nodes are leaf nodes?
Which of the following nodes are leaf nodes?A) H
B) N
C) H and P
D) H, N, and P

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Consider the following tree diagram: 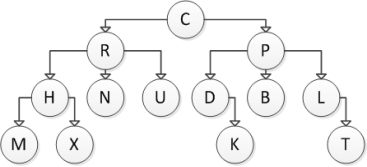 Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
A) R is an ancestor of N
B) C is an ancestor of N
C) D is an ancestor of P
D) H is an ancestor of M
 Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?A) R is an ancestor of N
B) C is an ancestor of N
C) D is an ancestor of P
D) H is an ancestor of M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Consider the following tree diagram: 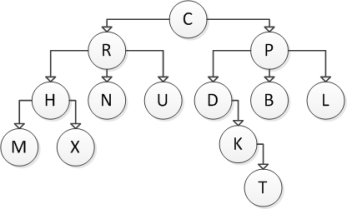 What is the height of the subtree with root P?
What is the height of the subtree with root P?
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
 What is the height of the subtree with root P?
What is the height of the subtree with root P?A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Consider the following tree diagram: 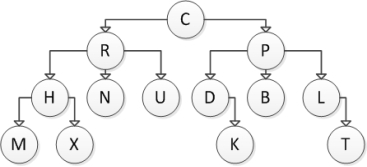 Which of the following nodes are root nodes?
Which of the following nodes are root nodes?
A) C
B) R
C) P
D) R and P
 Which of the following nodes are root nodes?
Which of the following nodes are root nodes?A) C
B) R
C) P
D) R and P

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Consider the following tree diagram: 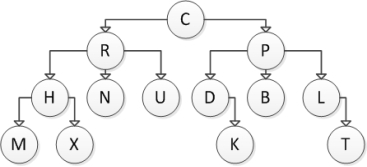 Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
A) Nodes D and K form a subtree
B) Nodes H, M, and X form a subtree
C) Nodes R and N form a subtree
D) Nodes L and T form a subtree
 Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?A) Nodes D and K form a subtree
B) Nodes H, M, and X form a subtree
C) Nodes R and N form a subtree
D) Nodes L and T form a subtree

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Consider the following tree diagram: 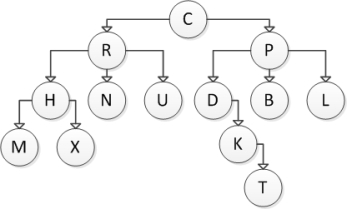 What is the height of this tree?
What is the height of this tree?
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 7
 What is the height of this tree?
What is the height of this tree?A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Consider the following tree diagram: 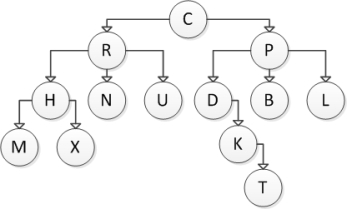 What is the size of the subtree with root P?
What is the size of the subtree with root P?
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
 What is the size of the subtree with root P?
What is the size of the subtree with root P?A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Consider the following tree diagram: 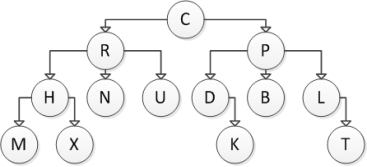 Which of the following nodes are interior nodes?
Which of the following nodes are interior nodes?
A) C
B) N
C) C and P
D) C, N, and P
 Which of the following nodes are interior nodes?
Which of the following nodes are interior nodes?A) C
B) N
C) C and P
D) C, N, and P

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The height of a tree can be obtained by recursively computing the heights of its subtrees, while keeping track of the height of the deepest subtree. Given the Node class discussed in section 17.1 (partially shown below), select an expression to complete the recursive method height, which is designed to return the height of the tree rooted at a node. class Node
{
Public Object data;
Public List children;
) . .
Public int height()
{
Int maxChildHeight = 0;
For (Node child : children)
{
Int childHeight = child.height();
If (childHeight > maxChildHeight)
MaxChildHeight = childHeight;
}
Return _________________;
}
}
A) maxChildHeight
B) maxChildHeight + 1
C) maxChildHeight + 2
D) maxChildHeight + height()
{
Public Object data;
Public List
) . .
Public int height()
{
Int maxChildHeight = 0;
For (Node child : children)
{
Int childHeight = child.height();
If (childHeight > maxChildHeight)
MaxChildHeight = childHeight;
}
Return _________________;
}
}
A) maxChildHeight
B) maxChildHeight + 1
C) maxChildHeight + 2
D) maxChildHeight + height()

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
You are using a tree to show the evaluation order of arithmetic expressions. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
A) Leaves contain numbers.
B) Interior nodes contain numbers.
C) The root contains an operator.
D) Every level of the tree must contain an operator.
A) Leaves contain numbers.
B) Interior nodes contain numbers.
C) The root contains an operator.
D) Every level of the tree must contain an operator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Consider the following tree diagrams: 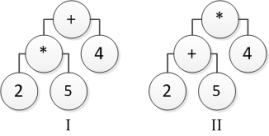 Which tree represents the arithmetic expression 2 + 5 *4?
Which tree represents the arithmetic expression 2 + 5 *4?
A) I
B) II
C) Both I and II
D) Neither I nor II
 Which tree represents the arithmetic expression 2 + 5 *4?
Which tree represents the arithmetic expression 2 + 5 *4?A) I
B) II
C) Both I and II
D) Neither I nor II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Consider the following tree diagrams: 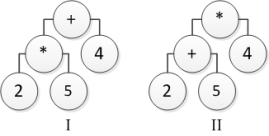 Which tree represents the arithmetic expression 2 *5 + 4?
Which tree represents the arithmetic expression 2 *5 + 4?
A) I
B) II
C) Both I and II
D) Neither I nor II
 Which tree represents the arithmetic expression 2 *5 + 4?
Which tree represents the arithmetic expression 2 *5 + 4?A) I
B) II
C) Both I and II
D) Neither I nor II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A completely filled binary tree with a height of 3 has ____ nodes.
A) 6
B) 7
C) 8
D) 12
A) 6
B) 7
C) 8
D) 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Consider the following tree diagrams: 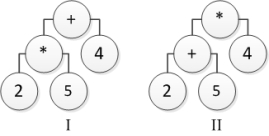 Which tree represents the arithmetic expression (2 + 5) *4?
Which tree represents the arithmetic expression (2 + 5) *4?
A) I
B) II
C) Both I and II
D) Neither I nor II
 Which tree represents the arithmetic expression (2 + 5) *4?
Which tree represents the arithmetic expression (2 + 5) *4?A) I
B) II
C) Both I and II
D) Neither I nor II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The height h of a completely filled binary tree with n nodes is ____.
A) h = log2(n) - 1
B) h = log2(n) + 1
C) h = log2(n - 1)
D) h = log2(n + 1)
A) h = log2(n) - 1
B) h = log2(n) + 1
C) h = log2(n - 1)
D) h = log2(n + 1)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Given the Node class discussed in section 17.1 (partially shown below), select a statement to complete the recursive method descendants, which is designed to return the number of descendants of a node. class Node
{
Public Object data;
Public List children;
) . .
Public int descendants()
{
Int num = 0;
For (Node child : children)
{
_____________________________
}
Return num;
}
}
A) num = child.descendants();
B) num = num + child.descendants();
C) num = num + child.children.size();
D) num = num + child.descendants() + 1;
{
Public Object data;
Public List
) . .
Public int descendants()
{
Int num = 0;
For (Node child : children)
{
_____________________________
}
Return num;
}
}
A) num = child.descendants();
B) num = num + child.descendants();
C) num = num + child.children.size();
D) num = num + child.descendants() + 1;

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Consider the following tree diagrams: 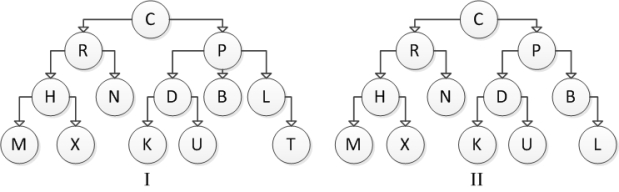 Which of the above are binary trees?
Which of the above are binary trees?
A) I
B) II
C) I and II
D) Neither I nor II
 Which of the above are binary trees?
Which of the above are binary trees?A) I
B) II
C) I and II
D) Neither I nor II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A binary tree with 260 nodes has a height of approximately ____.
A) 8
B) 10
C) 12
D) 13
A) 8
B) 10
C) 12
D) 13

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A binary tree of height h can have up to ____ nodes.
A) 2h - 1
B) 2h + 1
C) 2h - 1
D) 2h + 1
A) 2h - 1
B) 2h + 1
C) 2h - 1
D) 2h + 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Consider the following Huffman encoding tree: 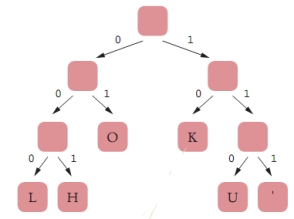 The letter H will be encoded as ____.
The letter H will be encoded as ____.
A) 000
B) 011
C) 001
D) 010
 The letter H will be encoded as ____.
The letter H will be encoded as ____.A) 000
B) 011
C) 001
D) 010

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Consider the following tree diagram: ![<strong>Consider the following tree diagram: Which arithmetic expression is represented by this tree?</strong> A) 2 * 3 + 5 + 4 * 6 - 1 B) 2 * 3 + 5 + 4 - 6 - 1 C) 2 * (3 + 5 + 4) * (6 - 1) D) [(2 * 3) + 5 + 4] * (6 - 1)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7390/11eadbc7_3ec6_4f5b_a3bf_7fe359995295_TB7390_00.jpg) Which arithmetic expression is represented by this tree?
Which arithmetic expression is represented by this tree?
A) 2 * 3 + 5 + 4 * 6 - 1
B) 2 * 3 + 5 + 4 - 6 - 1
C) 2 * (3 + 5 + 4) * (6 - 1)
D) [(2 * 3) + 5 + 4] * (6 - 1)
![<strong>Consider the following tree diagram: Which arithmetic expression is represented by this tree?</strong> A) 2 * 3 + 5 + 4 * 6 - 1 B) 2 * 3 + 5 + 4 - 6 - 1 C) 2 * (3 + 5 + 4) * (6 - 1) D) [(2 * 3) + 5 + 4] * (6 - 1)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7390/11eadbc7_3ec6_4f5b_a3bf_7fe359995295_TB7390_00.jpg) Which arithmetic expression is represented by this tree?
Which arithmetic expression is represented by this tree?A) 2 * 3 + 5 + 4 * 6 - 1
B) 2 * 3 + 5 + 4 - 6 - 1
C) 2 * (3 + 5 + 4) * (6 - 1)
D) [(2 * 3) + 5 + 4] * (6 - 1)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Consider a balanced binary tree with 520 nodes. The average length of all paths from the root to the leaves is approximately ____.
A) 9
B) 10
C) 12
D) 13
A) 9
B) 10
C) 12
D) 13

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Consider the following Huffman encoding tree: 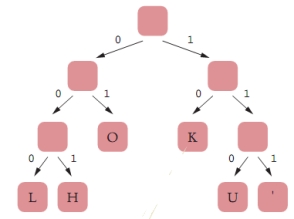 The letter K will be encoded as ____.
The letter K will be encoded as ____.
A) 10
B) 010
C) 001
D) 100
 The letter K will be encoded as ____.
The letter K will be encoded as ____.A) 10
B) 010
C) 001
D) 100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following statements about binary trees is correct?
A) Each node in a binary tree has at least two child nodes.
B) Each node in a binary tree has at most two child nodes.
C) The number of child nodes for each node in a binary tree is any power of two.
D) If divided down the middle from top to bottom, a binary tree must be symmetrical.
A) Each node in a binary tree has at least two child nodes.
B) Each node in a binary tree has at most two child nodes.
C) The number of child nodes for each node in a binary tree is any power of two.
D) If divided down the middle from top to bottom, a binary tree must be symmetrical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Consider the following tree diagram: ![<strong>Consider the following tree diagram: Which arithmetic expression is represented by this tree?</strong> A) (2 + 3) + (5* 4) * 6 * (- 1) B) 2 + 3 + 5 * 4 - 6 - 1 C) (2 + 3) *(5 * 4) * (6 - 1) D) [(2 + 3) + (5 *4)] * (6 - 1)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7390/11eadbc7_3ec6_766c_a3bf_19888b61a69f_TB7390_00.jpg) Which arithmetic expression is represented by this tree?
Which arithmetic expression is represented by this tree?
A) (2 + 3) + (5* 4) * 6 * (- 1)
B) 2 + 3 + 5 * 4 - 6 - 1
C) (2 + 3) *(5 * 4) * (6 - 1)
D) [(2 + 3) + (5 *4)] * (6 - 1)
![<strong>Consider the following tree diagram: Which arithmetic expression is represented by this tree?</strong> A) (2 + 3) + (5* 4) * 6 * (- 1) B) 2 + 3 + 5 * 4 - 6 - 1 C) (2 + 3) *(5 * 4) * (6 - 1) D) [(2 + 3) + (5 *4)] * (6 - 1)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7390/11eadbc7_3ec6_766c_a3bf_19888b61a69f_TB7390_00.jpg) Which arithmetic expression is represented by this tree?
Which arithmetic expression is represented by this tree?A) (2 + 3) + (5* 4) * 6 * (- 1)
B) 2 + 3 + 5 * 4 - 6 - 1
C) (2 + 3) *(5 * 4) * (6 - 1)
D) [(2 + 3) + (5 *4)] * (6 - 1)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Given the BinaryTree class discussed in section 17.2 (partially shown below), select an expression to complete the static recursive helper method countLeaves, which returns the number of leaf nodes in the binary tree rooted at node n. public class BinaryTree
{
Private Node root;
Public BinaryTree()
{
Root = null;
}
Public BinaryTree(Object rootData, BinaryTree left, BinaryTree right)
{
Root = new Node();
Root.data = rootData;
Root.left = left.root;
Root.right = right.root;
}
Class Node
{
Public Object data;
Public Node left;
Public Node right;
}
Public int countLeaves()
{
Return countLeaves(root);
}
Public static int countLeaves (Node n)
{
If (n == null)
{
Return 0;
}
Else if (_____________________)
{
Return 1;
}
Else
{
Return countLeaves(n.left) + countLeaves(n.right);
}
}
}
A) n.left == null
B) n.right == null
C) n.left == null && n.right == null
D) n.left == null || n.right == null
{
Private Node root;
Public BinaryTree()
{
Root = null;
}
Public BinaryTree(Object rootData, BinaryTree left, BinaryTree right)
{
Root = new Node();
Root.data = rootData;
Root.left = left.root;
Root.right = right.root;
}
Class Node
{
Public Object data;
Public Node left;
Public Node right;
}
Public int countLeaves()
{
Return countLeaves(root);
}
Public static int countLeaves (Node n)
{
If (n == null)
{
Return 0;
}
Else if (_____________________)
{
Return 1;
}
Else
{
Return countLeaves(n.left) + countLeaves(n.right);
}
}
}
A) n.left == null
B) n.right == null
C) n.left == null && n.right == null
D) n.left == null || n.right == null

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Given the BinaryTree class discussed in section 17.2 (partially shown below), select an expression to complete the static recursive helper method rightMostValue, which is designed to return the data value in the rightmost node of the tree rooted at node n. public class BinaryTree
{
Private Node root;
Public BinaryTree()
{
Root = null;
}
Public BinaryTree(Object rootData, BinaryTree left, BinaryTree right)
{
Root = new Node();
Root.data = rootData;
Root.left = left.root;
Root.right = right.root;
}
Class Node
{
Public Object data;
Public Node left;
Public Node right;
}
Public Object rightMostValue()
{
If (root == null)
{
Return null;
}
Else
{
Return rightMostValue(root);
}
}
Public static Object rightMostValue(Node n)
{
If (n.right == null)
{
Return n.data;
}
Else
{
Return ______________________;
}
}
}
A) rightMostValue(n.right)
B) rightMostValue(n.left)
C) rightMostValue(n)
D) rightMostValue(root.right)
{
Private Node root;
Public BinaryTree()
{
Root = null;
}
Public BinaryTree(Object rootData, BinaryTree left, BinaryTree right)
{
Root = new Node();
Root.data = rootData;
Root.left = left.root;
Root.right = right.root;
}
Class Node
{
Public Object data;
Public Node left;
Public Node right;
}
Public Object rightMostValue()
{
If (root == null)
{
Return null;
}
Else
{
Return rightMostValue(root);
}
}
Public static Object rightMostValue(Node n)
{
If (n.right == null)
{
Return n.data;
}
Else
{
Return ______________________;
}
}
}
A) rightMostValue(n.right)
B) rightMostValue(n.left)
C) rightMostValue(n)
D) rightMostValue(root.right)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A completely filled binary tree with a height of 4 has ____ nodes.
A) 8
B) 12
C) 15
D) 16
A) 8
B) 12
C) 15
D) 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What does the left node reference of a newly inserted binary search tree node get set to?
A) depends where the node is inserted
B) it gets set to the left child of the new node, if one exists
C) always null
D) it gets set to the left child of the root, if it exists
A) depends where the node is inserted
B) it gets set to the left child of the new node, if one exists
C) always null
D) it gets set to the left child of the root, if it exists

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Consider the following binary search tree diagram: 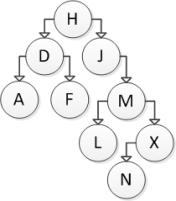 If node M is to be removed, which action should be taken?
If node M is to be removed, which action should be taken?
A) Replace M with the smallest value in its left subtree.
B) Replace M with the smallest value in its right subtree.
C) Replace M with the largest value in its left subtree.
D) Replace M with the largest value in its right subtree.
 If node M is to be removed, which action should be taken?
If node M is to be removed, which action should be taken?A) Replace M with the smallest value in its left subtree.
B) Replace M with the smallest value in its right subtree.
C) Replace M with the largest value in its left subtree.
D) Replace M with the largest value in its right subtree.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The nodes in our binary search tree implement the Comparable interface. Which tree operations benefit from this design decision?
I add
II search
III delete
A) I
B) II
C) I and III
D) I, II and III
I add
II search
III delete
A) I
B) II
C) I and III
D) I, II and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following may occur as a result of an add operation, on a non-empty binary search tree?
I a new root is created
II the new node becomes the left child of the root
III the new node has a right child upon insertion
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) II and III
I a new root is created
II the new node becomes the left child of the root
III the new node has a right child upon insertion
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) II and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following sequences of insertions will result in a balanced tree?
I 12 , 7, 25, 6, 9, 13, 44
II 12 , 7, 25, 44, 13, 6, 9
III 12, 25, 44, 13, 6, 9, 7
A) I
B) II
C) I and II
D) I and III
I 12 , 7, 25, 6, 9, 13, 44
II 12 , 7, 25, 44, 13, 6, 9
III 12, 25, 44, 13, 6, 9, 7
A) I
B) II
C) I and II
D) I and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If the child references of a binary tree node are both null, the node is ____.
A) a root node
B) a leaf node
C) a parent node
D) an interior node
A) a root node
B) a leaf node
C) a parent node
D) an interior node

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Consider the following binary search tree diagram: 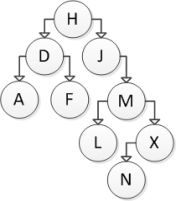 If node J is to be removed, which node should be copied into its location?
If node J is to be removed, which node should be copied into its location?
A) M
B) L
C) X
D) N
 If node J is to be removed, which node should be copied into its location?
If node J is to be removed, which node should be copied into its location?A) M
B) L
C) X
D) N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If both of the child references of a binary tree node are non-null, it follows that the node must be ____.
A) a root node
B) a leaf node
C) a child node
D) an interior node
A) a root node
B) a leaf node
C) a child node
D) an interior node

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Consider the following binary search tree diagram: 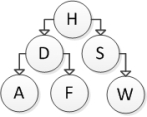 Which of the following trees represents the correct result after inserting element B?
Which of the following trees represents the correct result after inserting element B? 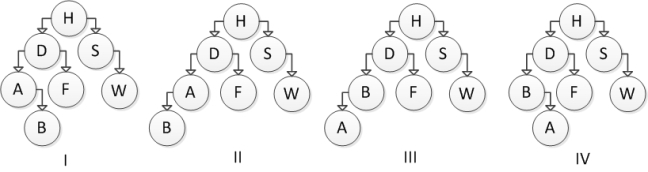
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
 Which of the following trees represents the correct result after inserting element B?
Which of the following trees represents the correct result after inserting element B? 
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Consider the following binary search tree diagram: 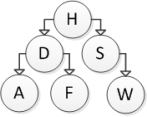 Which nodes will be visited in order to insert the letter E into this tree?
Which nodes will be visited in order to insert the letter E into this tree?
A) H
B) H and D
C) H, D, and F
D) H, D, and A
 Which nodes will be visited in order to insert the letter E into this tree?
Which nodes will be visited in order to insert the letter E into this tree?A) H
B) H and D
C) H, D, and F
D) H, D, and A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In a binary search tree, where the root node data value = 45, what do we know about the values of all the descendants in the right subtree of the root?
A) the root's right child value > 45, but the left child of the root's right child key is < 45
B) some values will be > 45, but there may be a few values < 45
C) approximately half the values are < 45, the other half are > 45
D) all will be > 45
A) the root's right child value > 45, but the left child of the root's right child key is < 45
B) some values will be > 45, but there may be a few values < 45
C) approximately half the values are < 45, the other half are > 45
D) all will be > 45

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Consider the following tree diagrams: 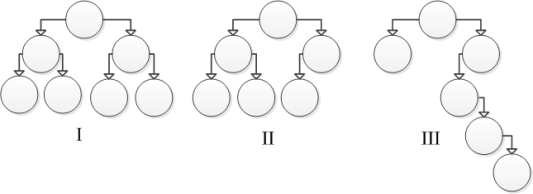 Which of these trees is considered to be balanced?
Which of these trees is considered to be balanced?
A) I
B) I and II
C) II and III
D) I and III
 Which of these trees is considered to be balanced?
Which of these trees is considered to be balanced?A) I
B) I and II
C) II and III
D) I and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Consider the following binary search tree diagram: 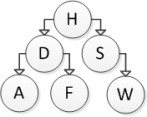 Which of the following trees represents the correct result after inserting element T?
Which of the following trees represents the correct result after inserting element T? 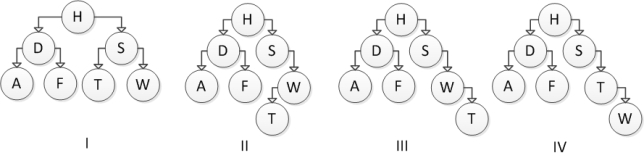
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
 Which of the following trees represents the correct result after inserting element T?
Which of the following trees represents the correct result after inserting element T? 
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Consider the following tree diagrams: 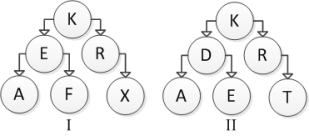 Which of the above are binary search trees?
Which of the above are binary search trees?
A) I
B) II
C) I and II
D) Neither I nor II
 Which of the above are binary search trees?
Which of the above are binary search trees?A) I
B) II
C) I and II
D) Neither I nor II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A binary search tree is made up of a collection of nodes organized with smaller data values on the left and greater values on the right relative to any node. Which of the following Node references must be instance variables of any implementation of a Node class?
I root
II left
III right
A) I
B) II and III
C) I and II
D) I, II and III
I root
II left
III right
A) I
B) II and III
C) I and II
D) I, II and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Consider the following tree diagrams: 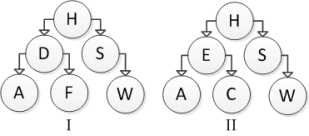 Which are binary search trees?
Which are binary search trees?
A) I
B) II
C) I and II
D) Neither I nor II
 Which are binary search trees?
Which are binary search trees?A) I
B) II
C) I and II
D) Neither I nor II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A binary search tree is made up of a collection of nodes organized with smaller data values on the left and greater values on the right, relative to any node. Which of the following Node references must be instance variables of any implementation of a BinarySearchTree class?
I root
II left
III right
A) I
B) II and III
C) I and II
D) I, II and III
I root
II left
III right
A) I
B) II and III
C) I and II
D) I, II and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Consider the following binary search tree diagram: 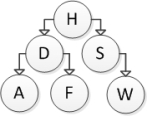 Which nodes will be visited in order to insert the letter B into this tree?
Which nodes will be visited in order to insert the letter B into this tree?
A) H
B) H and D
C) H, D, and F
D) H, D, and A
 Which nodes will be visited in order to insert the letter B into this tree?
Which nodes will be visited in order to insert the letter B into this tree?A) H
B) H and D
C) H, D, and F
D) H, D, and A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Consider the following tree diagrams: 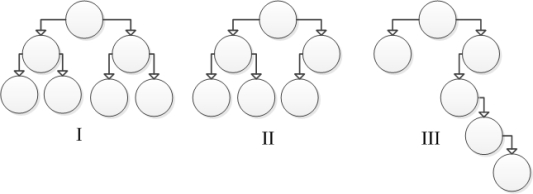 Which of these trees is considered to be unbalanced?
Which of these trees is considered to be unbalanced?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) II and III
 Which of these trees is considered to be unbalanced?
Which of these trees is considered to be unbalanced?A) I
B) II
C) III
D) II and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In a binary search tree, where the root node data value = 45, what do we know about the data values of all the descendants in the left subtree of the root?
A) the root's left child value < 45, but the right child of the root's left child value is > 45
B) some values will be < 45, but there may be a few values > 45
C) approximately half the values are < 45, the other half are > 45
D) all will be < 45
A) the root's left child value < 45, but the right child of the root's left child value is > 45
B) some values will be < 45, but there may be a few values > 45
C) approximately half the values are < 45, the other half are > 45
D) all will be < 45

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Adding an element to an unbalanced binary search tree takes ____ time.
A) O(n)
B) O(log (n))
C) O(1)
D) O(n2)
A) O(n)
B) O(log (n))
C) O(1)
D) O(n2)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Consider the following binary search tree diagram: 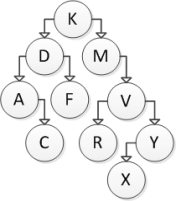 If node Y is to be removed, which action should be taken? Use the technique presented in the textbook.
If node Y is to be removed, which action should be taken? Use the technique presented in the textbook.
A) Modify the V's left reference to point to X.
B) Modify the V's right reference to point to X.
C) Swap the values in V and X, and modify X's right reference to point to V.
D) Modify V to have a null right pointer.
 If node Y is to be removed, which action should be taken? Use the technique presented in the textbook.
If node Y is to be removed, which action should be taken? Use the technique presented in the textbook.A) Modify the V's left reference to point to X.
B) Modify the V's right reference to point to X.
C) Swap the values in V and X, and modify X's right reference to point to V.
D) Modify V to have a null right pointer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
You wish to traverse a binary search tree in sorted order. Which of the following schemes will accomplish this?
I inorder traversal
II preorder traversal
III postorder traversal
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) II and III
I inorder traversal
II preorder traversal
III postorder traversal
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) II and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Consider the following binary search tree diagram: 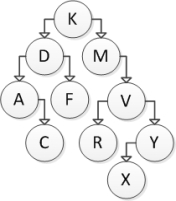 If node D is to be removed, which action should be taken? Use the technique presented in the textbook.
If node D is to be removed, which action should be taken? Use the technique presented in the textbook.
A) Modify K to point to A as its left child, and modify A to point to F as its right child.
B) Modify K to make its left child null.
C) Swap the values in C and D so that C has A as its left child, then remove the new D node.
D) Modify K to point to F as its left child and modify F to point to A as its left child.
 If node D is to be removed, which action should be taken? Use the technique presented in the textbook.
If node D is to be removed, which action should be taken? Use the technique presented in the textbook.A) Modify K to point to A as its left child, and modify A to point to F as its right child.
B) Modify K to make its left child null.
C) Swap the values in C and D so that C has A as its left child, then remove the new D node.
D) Modify K to point to F as its left child and modify F to point to A as its left child.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
You wish to traverse a binary search tree using postorder traversal. Arrange the following actions in the correct order to accomplish this.
I Print the right subtree recursively
II Print the root
III Print the left subtree recursively
A) I, II, III
B) III, II, I
C) II, III, I
D) III, I, II
I Print the right subtree recursively
II Print the root
III Print the left subtree recursively
A) I, II, III
B) III, II, I
C) II, III, I
D) III, I, II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Locating an element in an unbalanced binary search tree takes ____ time.
A) O(n)
B) O(log (n))
C) O(1)
D) O(n2)
A) O(n)
B) O(log (n))
C) O(1)
D) O(n2)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Given the Visitor interface discussed in section 17.4 (shown below), select a statement to complete the class CodeFinder. The class is to be used when traversing a binary tree while displaying every data value that contains the code "007". public interface Visitor
{
Void visit(Object data);
}
Class CodeFinder implements Visitor
{
Public void visit(Object data)
{
If (______________________________)
{
System.out.println(data);
}
}
}
A) data.toString().indexOf("007") >= 0
B) data.toString().indexOf("007") > 0
C) data.equals("007")
D) data.toString().contains("007")
{
Void visit(Object data);
}
Class CodeFinder implements Visitor
{
Public void visit(Object data)
{
If (______________________________)
{
System.out.println(data);
}
}
}
A) data.toString().indexOf("007") >= 0
B) data.toString().indexOf("007") > 0
C) data.equals("007")
D) data.toString().contains("007")

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
You wish to traverse a binary search tree in sorted order using inorder traversal. Arrange the following actions in the correct order to accomplish this.
I Print the right subtree recursively
II Print the root
III Print the left subtree recursively
A) I, II, III
B) III, II, I
C) II, III, I
D) III, I, II
I Print the right subtree recursively
II Print the root
III Print the left subtree recursively
A) I, II, III
B) III, II, I
C) II, III, I
D) III, I, II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following statements about the three tree traversal schemes studied, is correct?
A) Preorder traversal is used for evaluating arithmetic expression trees on a stack-based calculator.
B) Postorder traversal is used for evaluating arithmetic expression trees on a stack-based calculator.
C) Postorder traversal is used for copying file directories.
D) Preorder traversal is used for removing file directories by removing subdirectories first.
A) Preorder traversal is used for evaluating arithmetic expression trees on a stack-based calculator.
B) Postorder traversal is used for evaluating arithmetic expression trees on a stack-based calculator.
C) Postorder traversal is used for copying file directories.
D) Preorder traversal is used for removing file directories by removing subdirectories first.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following statements about the three tree traversal schemes studied is correct?
A) Inorder traversal is used for evaluating arithmetic expression trees on a stack-based calculator.
B) Postorder traversal is used for copying file directories.
C) Inorder traversal is used for copying file directories.
D) Postorder traversal is used for removing file directories by removing subdirectories first.
A) Inorder traversal is used for evaluating arithmetic expression trees on a stack-based calculator.
B) Postorder traversal is used for copying file directories.
C) Inorder traversal is used for copying file directories.
D) Postorder traversal is used for removing file directories by removing subdirectories first.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
You wish to traverse a binary search tree in sorted order using preorder traversal. Arrange the following actions in the correct order to accomplish this.
I Print the right subtree recursively
II Print the root
III Print the left subtree recursively
A) I, II, III
B) III, II, I
C) II, III, I
D) III, I, II
I Print the right subtree recursively
II Print the root
III Print the left subtree recursively
A) I, II, III
B) III, II, I
C) II, III, I
D) III, I, II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Removing an element from a balanced binary search tree takes ____ time.
A) O(n)
B) O(log (n))
C) O(1)
D) O(n2)
A) O(n)
B) O(log (n))
C) O(1)
D) O(n2)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Locating an element in a balanced binary search tree takes ____ time.
A) O(n)
B) O(log(n))
C) O(1)
D) O(n2)
A) O(n)
B) O(log(n))
C) O(1)
D) O(n2)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Removing an element from an unbalanced binary search tree takes ____ time.
A) O(n)
B) O(log (n))
C) O(1)
D) O(n2)
A) O(n)
B) O(log (n))
C) O(1)
D) O(n2)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Adding an element to a balanced binary search tree takes ____ time.
A) O(n)
B) O(log (n))
C) O(1)
D) O(n2)
A) O(n)
B) O(log (n))
C) O(1)
D) O(n2)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Given the BinarySearchTree class discussed in section 17.3 (partially shown below), select a sequence of statements to complete the recursive postorder method. The method performs a postorder traversal of the binary search tree rooted at node n. public class BinarySearchTree
{
Private Node root;
Public BinarySearchTree() {...}
Public void postorderTraversal()
{
Postorder(root);
}
Private static void postorder(Node n)
{
If (n != null)
{
____________________
____________________
____________________
}
}
) . .
}
A) postorder(n.right);
Postorder(n.left);
System.out.print(n.data + " ");
B) postorder(n.left);
Postorder(n.right);
System.out.print(n.data + " ");
C) postorder(n.left);
System.out.print(n.data + " ");
Postorder(n.right);
D) postorder(n.right);
System.out.print(n.data + " ");
Postorder(n.left);
{
Private Node root;
Public BinarySearchTree() {...}
Public void postorderTraversal()
{
Postorder(root);
}
Private static void postorder(Node n)
{
If (n != null)
{
____________________
____________________
____________________
}
}
) . .
}
A) postorder(n.right);
Postorder(n.left);
System.out.print(n.data + " ");
B) postorder(n.left);
Postorder(n.right);
System.out.print(n.data + " ");
C) postorder(n.left);
System.out.print(n.data + " ");
Postorder(n.right);
D) postorder(n.right);
System.out.print(n.data + " ");
Postorder(n.left);

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Given the BinarySearchTree and Node classes discussed in section 17.3 (partially shown below), select an expression to complete the recursive method smallest in the Node class. The method returns the smallest data value in the binary search tree rooted at a node. public class BinarySearchTree
{
Private Node root;
Public BinarySearchTree() {...}
Public void add(Comparable obj) {...}
Public Comparable smallest()
{
If (root == null)
Throw new NoSuchElementException();
Else
Return root.smallest();
}
Class Node
{
Public Comparable data;
Public Node left;
Public Node right;
Public Comparable smallest()
{
If (left == null)
Return data;
Else
Return _______________;
}
}
}
A) left.smallest()
B) right.smallest()
C) data.smallest()
D) Math.min(left.smallest(), right.smallest())
{
Private Node root;
Public BinarySearchTree() {...}
Public void add(Comparable obj) {...}
Public Comparable smallest()
{
If (root == null)
Throw new NoSuchElementException();
Else
Return root.smallest();
}
Class Node
{
Public Comparable data;
Public Node left;
Public Node right;
Public Comparable smallest()
{
If (left == null)
Return data;
Else
Return _______________;
}
}
}
A) left.smallest()
B) right.smallest()
C) data.smallest()
D) Math.min(left.smallest(), right.smallest())

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following statements about a binary search tree is correct?
A) Adding elements that are already sorted will result in a balanced binary search tree.
B) Nodes must be moved when a node is removed from the middle of a subtree.
C) The speed of inserting or removing a node is dependent on the shape of the tree.
D) The speed of inserting or removing a node is dependent on the number of subtrees.
A) Adding elements that are already sorted will result in a balanced binary search tree.
B) Nodes must be moved when a node is removed from the middle of a subtree.
C) The speed of inserting or removing a node is dependent on the shape of the tree.
D) The speed of inserting or removing a node is dependent on the number of subtrees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Consider the following binary search tree diagram: 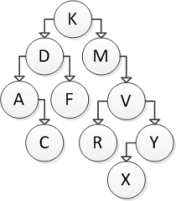 If node F is to be removed, which action should be taken? Use the technique presented in the textbook.
If node F is to be removed, which action should be taken? Use the technique presented in the textbook.
A) Move C into the right subtree of D.
B) Move C into the left subtree of A.
C) Replace F with D's value and replace D with C's value.
D) Modify D to have a null right reference.
 If node F is to be removed, which action should be taken? Use the technique presented in the textbook.
If node F is to be removed, which action should be taken? Use the technique presented in the textbook.A) Move C into the right subtree of D.
B) Move C into the left subtree of A.
C) Replace F with D's value and replace D with C's value.
D) Modify D to have a null right reference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Given the BinarySearchTree class discussed in section 17.3, select a statement to complete the following code segment, so that the resulting binary search tree has a height of 4. BinarySearchTree t = new BinarySearchTree();
T)add("a");
T)add("day");
T)add("in");
__________________
T)add("life");
A) t.add("my");
B) t.add("his");
C) t.add("the");
D) t.add("your");
T)add("a");
T)add("day");
T)add("in");
__________________
T)add("life");
A) t.add("my");
B) t.add("his");
C) t.add("the");
D) t.add("your");

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



