Deck 11: Factorial Designs
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/67
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Factorial Designs
1
A researcher who is examining the effects of temperature and humidity on the eating behavior of rats uses a factorial experiment comparing three different temperatures (70?,80?,and 90?)and two humidity conditions (low and high).How many factors are in the experiment?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)6
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)6
B
2
How many separate groups of participants would be needed for a between-subjects,two-factor study with 3 levels of factor A and 4 levels of factor B?
A)3
B)4
C)7
D)12
A)3
B)4
C)7
D)12
D
3
In a factorial experiment,the number of factors is the number of ___________ variables.
A)independent
B)dependent
C)extraneous
D)confounding
A)independent
B)dependent
C)extraneous
D)confounding
A
4
The following data represent the means for each treatment condition in a two-factor experiment.What pattern of results is shown in the data? A1 A2
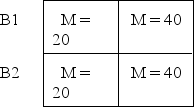
A)Main effects for both factors and an interaction.
B)Main effects for both factors and no interaction.
C)A main effect for factor A,no main effect for factor B,and no interaction.
D)A main effect for factor A and an interaction but no main effect for factor B.

A)Main effects for both factors and an interaction.
B)Main effects for both factors and no interaction.
C)A main effect for factor A,no main effect for factor B,and no interaction.
D)A main effect for factor A and an interaction but no main effect for factor B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In order to determine whether factors influence or interact with each other,a researcher must use
A)two experiments.
B)a factorial design.
C)a between-subjects design.
D)a mixed design.
A)two experiments.
B)a factorial design.
C)a between-subjects design.
D)a mixed design.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
How many independent variables are there in an experimental two-factor design?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The following data represent the means for each treatment condition in a two-factor experiment.What pattern of results is shown in the data? A1 A2
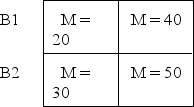
A)Main effects for both factors and an interaction.
B)Main effects for both factors and no interaction.
C)A main effect for factor A,no main effect for factor B,and no interaction.
D)A main effect for factor A and an interaction but no main effect for factor B.

A)Main effects for both factors and an interaction.
B)Main effects for both factors and no interaction.
C)A main effect for factor A,no main effect for factor B,and no interaction.
D)A main effect for factor A and an interaction but no main effect for factor B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is the correct description for a research study comparing problem solving scores obtained under three different levels of temperature?
A)single-factor design
B)two-factor design
C)three-factor design
D)factorial design
A)single-factor design
B)two-factor design
C)three-factor design
D)factorial design

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is the correct description for a research study comparing problem solving ability for girls versus boys under three different levels of temperature?
A)2 x 2 design
B)2 x 3 design
C)2 x 2 x 3 design
D)none of the other options is an accurate description.
A)2 x 2 design
B)2 x 3 design
C)2 x 2 x 3 design
D)none of the other options is an accurate description.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The following data show the means for four treatment conditions as well as the overall means for the columns and the rows.For these data,what numbers are compared to assess the main effect of factor A? A1 A2
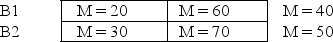
M = 25 M = 65
A)30; 70
B)20; 30
C)40; 50
D)25; 65

M = 25 M = 65
A)30; 70
B)20; 30
C)40; 50
D)25; 65

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In a 2 x 2 between-subjects factorial experiment,there are a total of _______ treatment conditions in the experiment,and each participant serves in _______ condition(s).
A)2,1
B)4,1
C)2,2
D)4,2
A)2,1
B)4,1
C)2,2
D)4,2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In an experiment examining the effects of task difficulty (easy/hard)for men and women,the factors are
A)male and female.
B)easy and hard.
C) male,female,easy,and hard.
D) difficulty and gender.
A)male and female.
B)easy and hard.
C) male,female,easy,and hard.
D) difficulty and gender.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In a 3*4 factorial design there are ________ main effect(s)and ________interaction(s)possible.
A)3; 4
B)2; 3
C)2; 1
D)1; 2
A)3; 4
B)2; 3
C)2; 1
D)1; 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
How many main effects are there in a 2*3 factorial design?
A)2
B)3
C)6
D)9
A)2
B)3
C)6
D)9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In a matrix representing the structure of a factorial design,the differences between the overall column means define
A)the main effect for one factor.
B)the interaction between the factors.
C)the main effect and the interaction between the factors.
D)nothing.
A)the main effect for one factor.
B)the interaction between the factors.
C)the main effect and the interaction between the factors.
D)nothing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
How many independent variables are there in a 2*2*2 factorial design?
A)2
B)3
C)4
D)8
A)2
B)3
C)4
D)8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A researcher who is examining the effects of temperature and humidity on the eating behavior of rats uses a factorial experiment comparing three different temperatures (70?,80?,and 90?)and two humidity conditions (low and high).The experiment has ______ level(s)for the temperature factor and a total of ______ treatment conditions.
A)1,3
B)3,6
C)6,6
D)3,2
A)1,3
B)3,6
C)6,6
D)3,2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The following data represent the means for each treatment condition in a two-factor experiment.What pattern of results is shown in the data? A1 A2
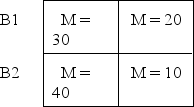
A)Main effects for both factors and an interaction.
B)Main effects for both factors and no interaction.
C)A main effect for factor A,no main effect for factor B,and no interaction.
D)A main effect for factor A and an interaction but no main effect for factor B.

A)Main effects for both factors and an interaction.
B)Main effects for both factors and no interaction.
C)A main effect for factor A,no main effect for factor B,and no interaction.
D)A main effect for factor A and an interaction but no main effect for factor B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In a 2 x 3 between-subjects factorial experiment,there are _____ groups of participants.
A)2
B)3
C)6
D)8
A)2
B)3
C)6
D)8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The advantage of a two-factor design compared to two single-factor designs is the ability to
A)save time.
B)evaluate the interaction between the independent variables.
C)evaluate the main effects.
D)check the manipulation.
A)save time.
B)evaluate the interaction between the independent variables.
C)evaluate the main effects.
D)check the manipulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Order effects can be measured and evaluated with a
A)counterbalanced single-factor within-subjects design.
B)factorial design using a participant variable (such as age)as a second factor.
C)factorial design using the order of treatments as a second factor.
D)the other three choices can each be used to assess order effects.
A)counterbalanced single-factor within-subjects design.
B)factorial design using a participant variable (such as age)as a second factor.
C)factorial design using the order of treatments as a second factor.
D)the other three choices can each be used to assess order effects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In a two-factor experiment with 2 levels of factor A and 2 levels of factor B,three of the treatment means are essentially identical and one is substantially different from the others.What result(s)would be produced by this pattern of treatment means?
A)a main effect for factor A
B)a main effect for factor B
C)an interaction between A and B
D)The pattern would produce main effects for both A and B,and an interaction.
A)a main effect for factor A
B)a main effect for factor B
C)an interaction between A and B
D)The pattern would produce main effects for both A and B,and an interaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A researcher is trying to determine the best time of day for patients to take a cholesterol medication.A sample of men who have high cholesterol is divided into six groups.One group takes the medication every morning,a second group takes the medication at mid-day,and a third group takes the medication each night.There are also three control groups that receive a placebo instead of the real medication,one in the morning,one at mid-day,and one at night.If the results of the study show a 50-point main effect for the medication (men taking the medicine average 50 points lower cholesterol than men taking the placebo)and also show a significant interaction between medication and time of day,then what can the researcher conclude about the effect of the medication?
A)The medication lowers cholesterol by around 50 points and it does not matter what time of day it is taken.
B)Although the average effect of the medication is to lower cholesterol by 50 points,the exact effect depends on what time of day it is taken.
C)Because there is an interaction,you cannot conclude that the medication has any effect on cholesterol.
D)None of the other options is an appropriate conclusion.
A)The medication lowers cholesterol by around 50 points and it does not matter what time of day it is taken.
B)Although the average effect of the medication is to lower cholesterol by 50 points,the exact effect depends on what time of day it is taken.
C)Because there is an interaction,you cannot conclude that the medication has any effect on cholesterol.
D)None of the other options is an appropriate conclusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In a factorial design,an interaction between the factors occurs whenever
A)the mean differences between the cells are not explained by the main effects.
B)the mean differences between the cells are explained by the main effects.
C)there are differences between the overall column means.
D)there are differences between the overall row means.
A)the mean differences between the cells are not explained by the main effects.
B)the mean differences between the cells are explained by the main effects.
C)there are differences between the overall column means.
D)there are differences between the overall row means.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
How many participants would be needed for a two-factor experiment with two levels of Factor A and three levels of Factor B if both factors are within subjects and there are five scores in each treatment condition?
A)5
B)10
C)15
D)30
A)5
B)10
C)15
D)30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The following data represent the means for each treatment condition in a two-factor experiment.What pattern of results is shown in the data? A1 A2
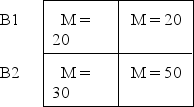
A)Main effects for both factors and an interaction.
B)Main effects for both factors and no interaction.
C)A main effect for factor A,no main effect for factor B,and no interaction.
D)A main effect for factor A and an interaction but no main effect for factor B.

A)Main effects for both factors and an interaction.
B)Main effects for both factors and no interaction.
C)A main effect for factor A,no main effect for factor B,and no interaction.
D)A main effect for factor A and an interaction but no main effect for factor B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The pretest-posttest control group design is an example of a
A)between-subjects design.
B)within-subjects design.
C)repeated measures design.
D)mixed design.
A)between-subjects design.
B)within-subjects design.
C)repeated measures design.
D)mixed design.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is not a possible outcome from a 2*2 factorial design?
A)two main effects and an interaction
B)two main effects and no interaction
C)no main effect for either factor but an interaction
D)The other three choices are all possible outcomes.
A)two main effects and an interaction
B)two main effects and no interaction
C)no main effect for either factor but an interaction
D)The other three choices are all possible outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is a possible outcome from a 2*2 factorial design?
A)two main effects and two interactions
B)a main effect for one factor,no main effect for the other factor,and two interactions
C)no main effect for either factor and one interaction
D)the other three choices are all possible to occur
A)two main effects and two interactions
B)a main effect for one factor,no main effect for the other factor,and two interactions
C)no main effect for either factor and one interaction
D)the other three choices are all possible to occur

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The following data represent the means for each treatment condition in a two-factor experiment.Note that one mean is not given.Which of the following values would result in no interaction between factors? B1 B2
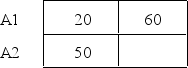
A)60
B)70
C)80
D)90

A)60
B)70
C)80
D)90

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The following data represent the means for each treatment condition in a two factor experiment.Note that one mean is not given.What value for the missing mean would result in no main effect for factor B? B1 B2
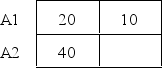
A)20
B)30
C)40
D)50

A)20
B)30
C)40
D)50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A clinician claims that the effectiveness of a new treatment varies depending on the gender of the client.Specifically,the new treatment has been shown to be very effective for females,but the treatment has little or no effect for males.In this example,
A)there is an interaction between the treatment and client's gender.
B)there is no interaction between the treatment and client's gender.
C)there is no main effect of treatment.
D)there is no main effect of gender.
A)there is an interaction between the treatment and client's gender.
B)there is no interaction between the treatment and client's gender.
C)there is no main effect of treatment.
D)there is no main effect of gender.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The following data represent the means for each treatment condition in a two factor experiment.Note that one mean is not given.What value for the missing mean would result in no A*B interaction? B1 B2
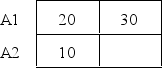
A)10
B)20
C)30
D)40

A)10
B)20
C)30
D)40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
An interaction between factors cannot occur unless
A)there is a main effect for at least one of the two factors.
B)there is a main effect for both of the two factors.
C)there is no main effect for either of the two factors.
D)The existence of an interaction is independent of the main effects.
A)there is a main effect for at least one of the two factors.
B)there is a main effect for both of the two factors.
C)there is no main effect for either of the two factors.
D)The existence of an interaction is independent of the main effects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A graph of a two-factor study indicates an interaction when the lines on the graph
A)are parallel.
B)cross or converge.
C)are steep in slope.
D)none of the other three choices demonstrate an interaction.
A)are parallel.
B)cross or converge.
C)are steep in slope.
D)none of the other three choices demonstrate an interaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If the means for a two-factor study are displayed in a graph and the lines in the graph are perfectly parallel,then what can you conclude about the main effects and interaction?
A)There is no main effect for either of the two factors.
B)There is a main effect for both of the two factors.
C)There is no interaction between factors.
D)There are no main effects and no interaction between factors.
A)There is no main effect for either of the two factors.
B)There is a main effect for both of the two factors.
C)There is no interaction between factors.
D)There are no main effects and no interaction between factors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is a possible outcome from a 2*2 factorial design?
A)one main effect
B)no main effects
C)one interaction
D)the other three choices are all possible to occur.
A)one main effect
B)no main effects
C)one interaction
D)the other three choices are all possible to occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In a two-factor ANOVA,what is the implication of a significant A*B interaction?
A)At least one of the main effects must also be significant.
B)Both of the main effects must also be significant.
C)Neither of the two main effects can be significant.
D) The significance of the interaction has no implications for the main effects.
A)At least one of the main effects must also be significant.
B)Both of the main effects must also be significant.
C)Neither of the two main effects can be significant.
D) The significance of the interaction has no implications for the main effects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A factorial study that measures depression before and after treatment for a treatment group and a control group is an example of a _______.
A)between-subjects design
B)within-subjects design
C)repeated measures design
D)mixed design
A)between-subjects design
B)within-subjects design
C)repeated measures design
D)mixed design

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A two-factor study with two levels of factor A and three levels of factor B uses a separate group of n = 5 participants in each treatment condition.How many participants are needed for the entire study?
A) 5
B) 10
C) 25
D) 30
A) 5
B) 10
C) 25
D) 30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A two-factor experimental design evaluates two main effects and one interaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In a two-factor study,it is possible to have one experimental factor and one nonexperimental factor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
There are four levels of the second factor in a 3*4*4 factorial design.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A two-factor study compares two different treatment conditions (factor 1)for males and females (factor 2).In this study,the males have an average score of 20 in the first treatment and an average of 25 in the second.The females average 35 in the first treatment and 45 in the second.For this study,there is no interaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In a two-factor design,there are two separate main effects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If the A x B interaction is significant,then at least one of the two main effects also must be significant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In a matrix representing the structure of a factorial design,the differences between the overall row means define the interaction between the factors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A doctor suspects that the effectiveness of a new cholesterol medication depends on the age of the patient.If the doctor is correct,the results from a two-factor study comparing medication versus no-medication for young versus old patients should produce an interaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
There are three treatment conditions in a 2*2*2 factorial design.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A two-factor experimental design must involve at least four different treatment conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In a two-factor experiment,an interaction can distort the main effects of either or both factors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In a two-factor design,there are two separate interactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In a two-factor study,it is possible to have one between-subjects factor and one within-subjects factor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
It is possible for the results of a two-factor study to show an interaction even though there is no main effect for either factor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A two-factor study comparing task performance for males versus females (factor 1)for three different levels of task difficulty (factor 2)would be described as a 2*3 design.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A two-factor study compares 2 levels of factor A and 3 levels of factor B with a separate sample of 5 participants in each treatment condition.This study will use a total of 25 participants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In a factorial experimental design,independent variables are commonly called factors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A two-factor study compares three different treatment conditions (factor 1)for males and females (factor 2).In this study,the main effect for gender is determined by comparing the overall mean score for the males (averaged over the three treatments)and the corresponding overall mean score for the females (averaged over the three treatments).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
It is often possible to reduce the variance in a between-subjects design by using a participant variable such as age or gender as a second factor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In a two-factor design,an interaction means that the effect of one factor depends on the levels of the second factor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
For a two-factor design,describe what is meant by a "main effect" and an "interaction."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Describe what it means to say that order effects are "symmetrical" or "asymmetrical?"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Explain why the existence of an interaction limits the interpretation of the main effects in a two-factor study.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Explain what it means to say that main effects and interactions are all independent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Describe two situations in which factorial designs are commonly used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Describe how a second factor can be used to reduce the variance in a between-subjects experiment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If the means from a two-factor study are displayed in a graph,how can you determine whether there is an interaction between factors?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



