Deck 1: Introduction to Sectional Anatomy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/34
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: Introduction to Sectional Anatomy
1
The directional term proximal refers to which of the following?
A) On the same side
B) On the opposite side
C) Away from a reference point
D) Toward a reference point
A) On the same side
B) On the opposite side
C) Away from a reference point
D) Toward a reference point
D
2
The term flank refers to the area of the:
A) Upper chest or breast
B) Lower back between the ribs and hips
C) Side of the trunk adjoining the lumbar region
D) Abdomen
A) Upper chest or breast
B) Lower back between the ribs and hips
C) Side of the trunk adjoining the lumbar region
D) Abdomen
C
3
The term antebrachial refers to the area of the:
A) Armpit
B) Ribs
C) Forearm
D) Upper arm
A) Armpit
B) Ribs
C) Forearm
D) Upper arm
C
4
The directional term rostral refers to which of the following?
A) The front or palm of the hand
B) The sole of the foot
C) Toward the feet
D) Toward the nose
A) The front or palm of the hand
B) The sole of the foot
C) Toward the feet
D) Toward the nose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The term inguinal refers to the area of the:
A) Spine
B) Naval
C) Sternum
D) Groin
A) Spine
B) Naval
C) Sternum
D) Groin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Most of the small intestine is located in which of the abdominal quadrants?
A) Right upper quadrant (RUQ)
B) Right lower quadrant (RLQ)
C) Left upper quadrant (LUQ)
D) Left lower quadrant (LLQ)
A) Right upper quadrant (RUQ)
B) Right lower quadrant (RLQ)
C) Left upper quadrant (LUQ)
D) Left lower quadrant (LLQ)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The term cubital refers to the area of the:
A) Lower posterior portion of the leg
B) Posterior surface of elbow area of the arm
C) Lower back between the ribs and hips
D) Upper portion of the leg
A) Lower posterior portion of the leg
B) Posterior surface of elbow area of the arm
C) Lower back between the ribs and hips
D) Upper portion of the leg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The plane that passes diagonally between the axes of two other planes is the _____ plane.
A) Sagittal
B) Coronal
C) Axial
D) Oblique
A) Sagittal
B) Coronal
C) Axial
D) Oblique

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The directional term caudal refers to which of the following?
A) On the same side
B) On the opposite side
C) Toward the feet
D) Toward the head
A) On the same side
B) On the opposite side
C) Toward the feet
D) Toward the head

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The stomach and tail of the pancreas are located in which of the following abdominal quadrants?
A) Right upper
B) Left upper
C) Right lower
D) Left lower
A) Right upper
B) Left upper
C) Right lower
D) Left lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The inferior mesenteric artery is located:
A) 2 cm above the transpyloric plane
B) 4 cm above the transpyloric plane
C) 2.5 cm below the jugular notch
D) 4 cm above the bifurcation of the abdominal aorta
A) 2 cm above the transpyloric plane
B) 4 cm above the transpyloric plane
C) 2.5 cm below the jugular notch
D) 4 cm above the bifurcation of the abdominal aorta

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the body cavities is the largest?
A) Dorsal
B) Ventral
C) Abdominal
D) Pelvic
A) Dorsal
B) Ventral
C) Abdominal
D) Pelvic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The aortic arch is located:
A) 2.5 cm below the jugular notch
B) At T4-T5, sternal angle
C) 4 cm above the transpyloric plane
D) 2 cm above the transpyloric plane
A) 2.5 cm below the jugular notch
B) At T4-T5, sternal angle
C) 4 cm above the transpyloric plane
D) 2 cm above the transpyloric plane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The dorsal cavity can be further subdivided into which of the following cavities?
A) Cranial and spinal
B) Thoracic and abdominopelvic
C) Two lateral pleural
D) Abdominal and pelvic
A) Cranial and spinal
B) Thoracic and abdominopelvic
C) Two lateral pleural
D) Abdominal and pelvic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The directional term contralateral refers to which of the following?
A) On the same side
B) On the opposite side
C) Toward the midsagittal plane
D) Away from the midsagittal plane
A) On the same side
B) On the opposite side
C) Toward the midsagittal plane
D) Away from the midsagittal plane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A vertical plane that passes through the body, dividing it into anterior and posterior portions, is the _____ plane.
A) Sagittal
B) Coronal
C) Axial
D) Oblique
A) Sagittal
B) Coronal
C) Axial
D) Oblique

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The carotid bifurcation is located:
A) 4 cm above the pyloric plane
B) 4 cm above bifurcation of the abdominal aorta
C) At the upper border of the thyroid cartilage
D) At the upper margin of the sacroiliac joint
A) 4 cm above the pyloric plane
B) 4 cm above bifurcation of the abdominal aorta
C) At the upper border of the thyroid cartilage
D) At the upper margin of the sacroiliac joint

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The term popliteal refers to the area of the:
A) Upper portion of the leg
B) Back of the knee
C) Lower portion of the leg
D) Sole of the foot
A) Upper portion of the leg
B) Back of the knee
C) Lower portion of the leg
D) Sole of the foot

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The term axillary refers to the area of the:
A) Armpit
B) Forearm
C) Front of elbow
D) Upper arm
A) Armpit
B) Forearm
C) Front of elbow
D) Upper arm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The carina is located at:
A) L4 to L5.
B) T4 to T5, sternal angle.
C) L1 to L2.
D) T1 to T2, sternal angle.
A) L4 to L5.
B) T4 to T5, sternal angle.
C) L1 to L2.
D) T1 to T2, sternal angle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The figure below illustrates which of the following imaging planes? 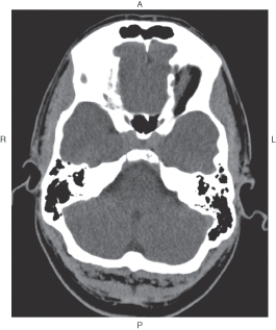
A) Axial
B) Coronal
C) Sagittal
D) Oblique

A) Axial
B) Coronal
C) Sagittal
D) Oblique

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The figure below is an example of which of the following? 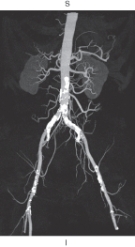
A) Multiplanar reformation
B) Shaded surface display
C) Maximum intensity projection
D) Volume rendering

A) Multiplanar reformation
B) Shaded surface display
C) Maximum intensity projection
D) Volume rendering

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Water is used as a reference tissue and is given the CT number of:
A) -1000
B) -500
C) 0
D) +1000
A) -1000
B) -500
C) 0
D) +1000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Images reconstructed from data obtained along any projection through the cube that result in a sagittal, coronal, transverse, or oblique image are termed:
A) Multiplanar reformation
B) Shaded surface display
C) Maximum intensity projection
D) Volume rendering
A) Multiplanar reformation
B) Shaded surface display
C) Maximum intensity projection
D) Volume rendering

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is a midline point at the anterior nasal spine where the upper lip and nasal septum meet?
A) Nasion
B) Gonion
C) Mastoid tip
D) Acanthion
A) Nasion
B) Gonion
C) Mastoid tip
D) Acanthion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The crest of the ilium is located at what vertebral level?
A) L2
B) L3
C) L4
D) L5
A) L2
B) L3
C) L4
D) L5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The figure below is an example of which of the following? 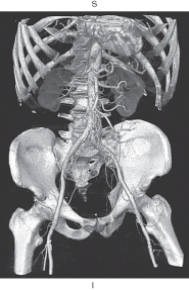
A) Multiplanar reformation
B) Shaded surface display
C) Maximum intensity projection
D) Volume rendering

A) Multiplanar reformation
B) Shaded surface display
C) Maximum intensity projection
D) Volume rendering

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is a parameter that allows for the adjustment of the gray scale?
A) CT number
B) Hounsfield unit
C) Window width
D) Window level
A) CT number
B) Hounsfield unit
C) Window width
D) Window level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following techniques can be described as a ray from the camera's view point that is directed to stop at a particular user-defined threshold value?
A) Multiplanar reformation
B) Shaded surface display
C) Maximum intensity projection
D) Volume rendering
A) Multiplanar reformation
B) Shaded surface display
C) Maximum intensity projection
D) Volume rendering

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The transpyloric plane is found midway between the:
A) Xiphosternal joint and the pubic symphysis
B) Xiphosternal joint and umbilicus
C) Tubercles of the iliac crests
D) Tubercles of the iliac crests and L3
A) Xiphosternal joint and the pubic symphysis
B) Xiphosternal joint and umbilicus
C) Tubercles of the iliac crests
D) Tubercles of the iliac crests and L3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
All of the following image algorithms use the principle of ray-tracing, except:
A) Shaded surface display (SSD)
B) Maximum intensity projection (MIP)
C) 2D imaging
D) Volume rendering (VR)
A) Shaded surface display (SSD)
B) Maximum intensity projection (MIP)
C) 2D imaging
D) Volume rendering (VR)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The figure below illustrates which of the following imaging planes? 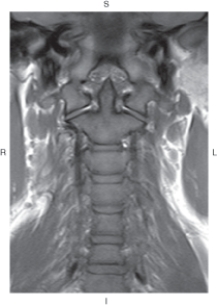
A) Axial
B) Coronal
C) Sagittal
D) Oblique

A) Axial
B) Coronal
C) Sagittal
D) Oblique

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The figure below illustrates which of the following imaging planes? 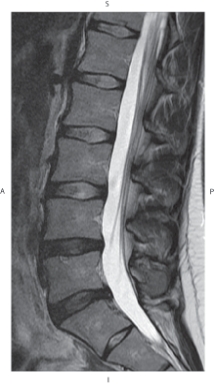
A) Axial
B) Coronal
C) Sagittal
D) Oblique

A) Axial
B) Coronal
C) Sagittal
D) Oblique

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The figure below illustrates which of the following imaging planes? 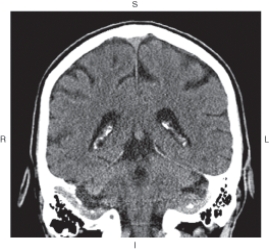
A) Axial
B) Coronal
C) Sagittal
D) Oblique

A) Axial
B) Coronal
C) Sagittal
D) Oblique

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



