Deck 6: The Economics of Political Action
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/208
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: The Economics of Political Action
1
Which one of the following was a secondary effect of the stock market crash of 1929?
A) An increase in the money supply in the early 1930s.
B) A decline in consumption expenditures because of the reduction in the wealth of stockholders.
C) An increase in the supply of loanable funds as people transferred funds from the stock market into savings accounts.
D) An increase in tax revenues as the sellers of stocks paid the capital gains tax on stocks that had appreciated during the 1920s.
A) An increase in the money supply in the early 1930s.
B) A decline in consumption expenditures because of the reduction in the wealth of stockholders.
C) An increase in the supply of loanable funds as people transferred funds from the stock market into savings accounts.
D) An increase in tax revenues as the sellers of stocks paid the capital gains tax on stocks that had appreciated during the 1920s.
A decline in consumption expenditures because of the reduction in the wealth of stockholders.
2
Fiscal policy analysis indicates that large tax increases during a severe recession will result in
A) an increase in the incentive to earn and the maintenance of a balanced federal budget.
B) higher tax revenues and an expansion in government spending.
C) smaller budget deficits, which will speed an economic recovery.
D) a reduction in aggregate demand and a worsening of the recession.
A) an increase in the incentive to earn and the maintenance of a balanced federal budget.
B) higher tax revenues and an expansion in government spending.
C) smaller budget deficits, which will speed an economic recovery.
D) a reduction in aggregate demand and a worsening of the recession.
a reduction in aggregate demand and a worsening of the recession.
3
Which of the following was a result of the many programs introduced as part of the New Deal?
A) A business environment of uncertainty that reduced output and investment.
B) A speeding up of the economic recovery process once these programs were enacted.
C) An increase in trade, investment, and output within the business sector.
D) A steady decline in the unemployment rate.
A) A business environment of uncertainty that reduced output and investment.
B) A speeding up of the economic recovery process once these programs were enacted.
C) An increase in trade, investment, and output within the business sector.
D) A steady decline in the unemployment rate.
A business environment of uncertainty that reduced output and investment.
4
Which of the following resulted from the Smoot-Hawley trade bill of 1930?
A) The stock market began a steady recovery from the crash of October 1929.
B) Many countries responded by imposing higher tariffs on American products, and the volume of international trade fell sharply.
C) Imports decreased, while exports increased, resulting in an overall increase in GDP and tariff revenues.
D) The unemployment rate, which had been rising, began to steadily decline as jobs were protected by the trade restrictions.
A) The stock market began a steady recovery from the crash of October 1929.
B) Many countries responded by imposing higher tariffs on American products, and the volume of international trade fell sharply.
C) Imports decreased, while exports increased, resulting in an overall increase in GDP and tariff revenues.
D) The unemployment rate, which had been rising, began to steadily decline as jobs were protected by the trade restrictions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When the money supply declined by approximately 30 percent during the 1929 through 1933 period,
A) real output increased.
B) the general level of prices increased.
C) the velocity of money increased by a proportional amount.
D) unemployment increased.
A) real output increased.
B) the general level of prices increased.
C) the velocity of money increased by a proportional amount.
D) unemployment increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Based on the experience of the Great Depression and the New Deal, which one of the following strategies would be most likely to stimulate recovery from a serious economic recession?
A) Increase trade restrictions and tariffs to save jobs and enhance tax revenue.
B) A reduction in the money supply in order to strengthen the dollar and combat inflation.
C) Keep taxes low in order to stimulate production and minimize the decline in personal and business income.
D) Institute frequent policy changes in order to search for and find the policy combination that would be most effective.
A) Increase trade restrictions and tariffs to save jobs and enhance tax revenue.
B) A reduction in the money supply in order to strengthen the dollar and combat inflation.
C) Keep taxes low in order to stimulate production and minimize the decline in personal and business income.
D) Institute frequent policy changes in order to search for and find the policy combination that would be most effective.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
During the Great Depression of 1929-1933,
A) the Fed allowed the money supply to contract substantially.
B) the Fed increased the money supply sharply.
C) Congress cut tax rates sharply.
D) Congress cut tariffs substantially.
A) the Fed allowed the money supply to contract substantially.
B) the Fed increased the money supply sharply.
C) Congress cut tax rates sharply.
D) Congress cut tariffs substantially.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Economic analysis indicates that the monetary policy of the 1930s, which shifted back and forth between restrictive monetary policy and expansionary monetary policy, would likely result in
A) economic stability and growth in real levels of output.
B) keeping the general level of prices relatively stable because the periods of restrictive policy would just offset the periods of expansion.
C) an environment of uncertainty, which would lead to economic instability.
D) economic stability, because changes in monetary policy can be counted on to exert a predictable impact on the economy quickly.
A) economic stability and growth in real levels of output.
B) keeping the general level of prices relatively stable because the periods of restrictive policy would just offset the periods of expansion.
C) an environment of uncertainty, which would lead to economic instability.
D) economic stability, because changes in monetary policy can be counted on to exert a predictable impact on the economy quickly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
According to the data, was the stock-market crash of 1929 the primary cause of the Great Depression?
A) No, the Great Depression actually began two years before the stock market crash of 1929.
B) Yes, after the stock market crash of October 1929 the market never recovered until the depression came to an end a decade later.
C) Yes, sharp reductions in stock prices like that of 1929 always result in prolonged depressions.
D) No, the stock market actually recovered to the level of October 1929 during the five months following the crash.
A) No, the Great Depression actually began two years before the stock market crash of 1929.
B) Yes, after the stock market crash of October 1929 the market never recovered until the depression came to an end a decade later.
C) Yes, sharp reductions in stock prices like that of 1929 always result in prolonged depressions.
D) No, the stock market actually recovered to the level of October 1929 during the five months following the crash.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
"The Great Depression was caused by the 1929 stock market crash." Which of the following is an indication that this statement is false?
A) The stock market had regained most of its losses from the October 1929 crash by April 1930.
B) The recessionary conditions actually began in the mid-1920s before the stock market crash.
C) The Great Depression was a result of government failure to intervene in market activity.
D) Economic theory indicates that a reduction in stock prices would reduce the consumer price index and thereby stimulate output and employment.
A) The stock market had regained most of its losses from the October 1929 crash by April 1930.
B) The recessionary conditions actually began in the mid-1920s before the stock market crash.
C) The Great Depression was a result of government failure to intervene in market activity.
D) Economic theory indicates that a reduction in stock prices would reduce the consumer price index and thereby stimulate output and employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
During 1929-1933, monetary policy was
A) highly expansionary and this led to an increase in the general level of prices.
B) characterized by steady monetary growth, which resulted in price stability.
C) characterized by a sharp reduction in the supply of money, which led to downward pressure on prices and a decline in output.
D) highly expansionary and this led to a reduction in the general level of prices.
A) highly expansionary and this led to an increase in the general level of prices.
B) characterized by steady monetary growth, which resulted in price stability.
C) characterized by a sharp reduction in the supply of money, which led to downward pressure on prices and a decline in output.
D) highly expansionary and this led to a reduction in the general level of prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The Great Depression was an era marked by
A) steady growth in GDP and a decline in the rate of unemployment.
B) a prolonged period of high unemployment and output substantially below its potential.
C) a large decline in the stock market followed by a steady recovery.
D) a failure of expansionary monetary policy to stimulate output and employment.
A) steady growth in GDP and a decline in the rate of unemployment.
B) a prolonged period of high unemployment and output substantially below its potential.
C) a large decline in the stock market followed by a steady recovery.
D) a failure of expansionary monetary policy to stimulate output and employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
An analysis of large declines in the stock market since the Great Depression indicates that
A) the stock market crash in October 1929 was more severe than subsequent crashes.
B) a prolonged recession will always follow a large decline in the stock market.
C) almost all stock market crashes since the Great Depression were followed by short recessions of 12 to 18 months, and in some cases, no recession at all.
D) the only way to recover from a stock market crash is through government spending, increased regulation, and tax-increases.
A) the stock market crash in October 1929 was more severe than subsequent crashes.
B) a prolonged recession will always follow a large decline in the stock market.
C) almost all stock market crashes since the Great Depression were followed by short recessions of 12 to 18 months, and in some cases, no recession at all.
D) the only way to recover from a stock market crash is through government spending, increased regulation, and tax-increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The rapid growth in stock prices during the 1920s was due in large part to
A) the expansionary monetary policy of the Federal Reserve.
B) the wartime demand for military equipment and supplies.
C) the artificially high value of the dollar, which eventually led to the stock market crash of 1929.
D) the technological innovations of the decade, which spurred economic growth.
A) the expansionary monetary policy of the Federal Reserve.
B) the wartime demand for military equipment and supplies.
C) the artificially high value of the dollar, which eventually led to the stock market crash of 1929.
D) the technological innovations of the decade, which spurred economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The Smoot-Hawley trade bill of 1930, designed to save jobs and increase revenue for the federal government, resulted in
A) an increase in both employment and federal tax revenue.
B) a sharp reduction in trade and a decline in federal tax revenue.
C) the protection of jobs while maintaining the level of trade, but it did not increase federal tax revenue.
D) a decline in the volume of trade, but an increase in revenue from tariffs, which made it possible for the federal government to balance its budget.
A) an increase in both employment and federal tax revenue.
B) a sharp reduction in trade and a decline in federal tax revenue.
C) the protection of jobs while maintaining the level of trade, but it did not increase federal tax revenue.
D) a decline in the volume of trade, but an increase in revenue from tariffs, which made it possible for the federal government to balance its budget.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following contributed to the severity of the Great Depression in the 1930s?
A) Constant structural changes that created uncertainty and undermined markets.
B) The Fed's policy of rapid monetary expansion during the early 1930s.
C) A reduction in tariffs protecting many U.S. industries.
D) A substantial tax rate reduction, which led to large deficits and high interest rates during the early 1930s.
A) Constant structural changes that created uncertainty and undermined markets.
B) The Fed's policy of rapid monetary expansion during the early 1930s.
C) A reduction in tariffs protecting many U.S. industries.
D) A substantial tax rate reduction, which led to large deficits and high interest rates during the early 1930s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
High marginal tax rates, such as those instituted during the Great Depression, will
A) increase the incentive of people to earn.
B) lead to a proportional increase in tax revenue and a reduction in the size of the budget deficit.
C) cause people to work, earn, and invest less than would be the case if marginal tax rates were lower.
D) attract workers from other countries where tax rates are lower.
A) increase the incentive of people to earn.
B) lead to a proportional increase in tax revenue and a reduction in the size of the budget deficit.
C) cause people to work, earn, and invest less than would be the case if marginal tax rates were lower.
D) attract workers from other countries where tax rates are lower.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Most economists believe the severity and duration of the Great Depression was primarily the result of
A) the large budget deficits of the federal government.
B) the reduction in tariffs and the influx of foreign imports during the early 1930s.
C) the excessive use of credit cards.
D) a sharp contraction in the money supply.
A) the large budget deficits of the federal government.
B) the reduction in tariffs and the influx of foreign imports during the early 1930s.
C) the excessive use of credit cards.
D) a sharp contraction in the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If higher tariffs, such as those enacted by the Smoot-Hawley trade bill, reduce the imports of the United States, which of the following will be most likely to occur?
A) U.S. employment will increase.
B) The unemployment rate of the United States will decline.
C) U.S. exports will increase because foreigners will want to buy more from U.S. producers.
D) U.S. exports will decline because foreigners will be earning fewer of the dollars needed to purchase goods and services from Americans.
A) U.S. employment will increase.
B) The unemployment rate of the United States will decline.
C) U.S. exports will increase because foreigners will want to buy more from U.S. producers.
D) U.S. exports will decline because foreigners will be earning fewer of the dollars needed to purchase goods and services from Americans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which one of the following factors contributed to the decline in real output during the Great Depression?
A) Deflation, which changed the terms of long-term contracts and discouraged long-term exchange.
B) Inflation, which reduced the value of the dollar and eroded the savings of the elderly.
C) Stable monetary policy, which caused business decision makers to lose confidence in the Fed's ability to fine-tune the economy.
D) Establishment of the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation.
A) Deflation, which changed the terms of long-term contracts and discouraged long-term exchange.
B) Inflation, which reduced the value of the dollar and eroded the savings of the elderly.
C) Stable monetary policy, which caused business decision makers to lose confidence in the Fed's ability to fine-tune the economy.
D) Establishment of the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following conditions during 2008-2009 most closely paralleled the economic conditions of the Great Depression?
A) Record-high unemployment rates for a period of many years.
B) A sharp and prolonged contraction in the money supply.
C) Significant increases in taxes and trade restrictions in order to counter budget deficits.
D) Frequent policy changes that generated an unstable and unpredictable economic climate.
A) Record-high unemployment rates for a period of many years.
B) A sharp and prolonged contraction in the money supply.
C) Significant increases in taxes and trade restrictions in order to counter budget deficits.
D) Frequent policy changes that generated an unstable and unpredictable economic climate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The Agricultural Adjustment Act, passed in 1933, was an effort to
A) keep agricultural prices high by increasing supply.
B) keep agricultural prices low by increasing supply.
C) keep agricultural prices high by decreasing supply.
D) keep agricultural prices low by decreasing supply.
A) keep agricultural prices high by increasing supply.
B) keep agricultural prices low by increasing supply.
C) keep agricultural prices high by decreasing supply.
D) keep agricultural prices low by decreasing supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Did the fiscal policy of the 1930s bring an end to the Great Depression?
A) No, government spending and budget deficits as a share of GDP were relatively small during the 1930s, and there is little evidence that fiscal policy did much to stimulate output.
B) No, even though budget deficits steadily rose from 2 percent of GDP in the early 1930s to more than 10 percent of GDP in 1939, this expansionary fiscal policy had little effect on output.
C) Yes, even though the spending programs of the New Deal led to budget deficits, they also led to a steady reduction in the rate of unemployment during the latter half of the 1930s.
D) Yes, the fiscal policy that kept the federal budget balanced throughout the 1930s created a stable business climate and eventually stimulated investment.
A) No, government spending and budget deficits as a share of GDP were relatively small during the 1930s, and there is little evidence that fiscal policy did much to stimulate output.
B) No, even though budget deficits steadily rose from 2 percent of GDP in the early 1930s to more than 10 percent of GDP in 1939, this expansionary fiscal policy had little effect on output.
C) Yes, even though the spending programs of the New Deal led to budget deficits, they also led to a steady reduction in the rate of unemployment during the latter half of the 1930s.
D) Yes, the fiscal policy that kept the federal budget balanced throughout the 1930s created a stable business climate and eventually stimulated investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following was most responsible for bringing the Great Depression to an end?
A) The increase in industrial demand due to the military build-up prior to World War II.
B) The expansionary monetary policy of the Fed during the 1930s.
C) The New Deal policies that expanded government spending, stimulated demand, and increased output.
D) The increase in import tariffs that saved jobs and expanded total employment.
A) The increase in industrial demand due to the military build-up prior to World War II.
B) The expansionary monetary policy of the Fed during the 1930s.
C) The New Deal policies that expanded government spending, stimulated demand, and increased output.
D) The increase in import tariffs that saved jobs and expanded total employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Analysis of the Great Depression indicates that
A) even though monetary and fiscal policies were highly expansionary, they were unable to offset the economic plunge.
B) even though monetary policy was expansionary, restrictive fiscal policy dominated during the 1930s.
C) a reduction in tax rates could not prevent the economic downturn from spiraling into a depression.
D) the severity of the economic decline, if not its onset, was the result of perverse monetary, fiscal and regulatory policies.
A) even though monetary and fiscal policies were highly expansionary, they were unable to offset the economic plunge.
B) even though monetary policy was expansionary, restrictive fiscal policy dominated during the 1930s.
C) a reduction in tax rates could not prevent the economic downturn from spiraling into a depression.
D) the severity of the economic decline, if not its onset, was the result of perverse monetary, fiscal and regulatory policies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
During the Great Depression fiscal and monetary policy was characterized by
A) an increase in tax rates and a contraction in the money supply.
B) a decrease in tax rates and a contraction in the money supply.
C) a decrease in tax rates and an expansion in the money supply.
D) an increase in tax rates and an expansion in the money supply.
A) an increase in tax rates and a contraction in the money supply.
B) a decrease in tax rates and a contraction in the money supply.
C) a decrease in tax rates and an expansion in the money supply.
D) an increase in tax rates and an expansion in the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
As unemployment rose during 1930 through 1932 and the economy plunged into the Great Depression, policy makers
A) reduced tax rates and increased the money supply.
B) increased tax rates and reduced the money supply.
C) increased both tax rates and the money supply.
D) reduced both the tax rates and the money supply.
A) reduced tax rates and increased the money supply.
B) increased tax rates and reduced the money supply.
C) increased both tax rates and the money supply.
D) reduced both the tax rates and the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is a lesson that can be learned from monetary policy during the Great Depression?
A) Monetary policy should be changed frequently in response to economic fluctuations.
B) Prolonged periods of monetary contraction will retard economic growth.
C) Low interest rates will direct an economy toward recovery.
D) Monetary policy should focus on variables such as output and employment.
A) Monetary policy should be changed frequently in response to economic fluctuations.
B) Prolonged periods of monetary contraction will retard economic growth.
C) Low interest rates will direct an economy toward recovery.
D) Monetary policy should focus on variables such as output and employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following perspectives exerted the most impact on fiscal policy during the Great Depression?
A) The Keynesian view.
B) The supply-side view.
C) The view that the federal government should maintain a balanced budget.
D) The new classical view that fiscal policy exerts little impact on demand and output.
A) The Keynesian view.
B) The supply-side view.
C) The view that the federal government should maintain a balanced budget.
D) The new classical view that fiscal policy exerts little impact on demand and output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following best describes the impact of fiscal policy during the Great Depression?
A) Despite the large increases in government spending as a share of GDP when the New Deal policies were initiated, the expansionary fiscal policy failed to stimulate demand.
B) Fiscal policy was focused on monetary expansion, when it should have focused on maintaining a balanced budget.
C) It is difficult to link expansionary fiscal policy with economic recovery because government spending and budget deficits were a relatively small portion of GDP prior to the beginning of World War II.
D) There is a direct correlation between increases in government spending as a share of GDP and increases in output and employment.
A) Despite the large increases in government spending as a share of GDP when the New Deal policies were initiated, the expansionary fiscal policy failed to stimulate demand.
B) Fiscal policy was focused on monetary expansion, when it should have focused on maintaining a balanced budget.
C) It is difficult to link expansionary fiscal policy with economic recovery because government spending and budget deficits were a relatively small portion of GDP prior to the beginning of World War II.
D) There is a direct correlation between increases in government spending as a share of GDP and increases in output and employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following did not contribute to the severity of the Great Depression?
A) A sharp reduction in the money supply during the early 1930s.
B) A large tax increase (to balance the budget) in the early 1930s.
C) Substantial increases in the tariff rates on imported goods.
D) A reduction in government expenditures and a substantial cut in personal income tax rates during 1932 and again in 1936.
A) A sharp reduction in the money supply during the early 1930s.
B) A large tax increase (to balance the budget) in the early 1930s.
C) Substantial increases in the tariff rates on imported goods.
D) A reduction in government expenditures and a substantial cut in personal income tax rates during 1932 and again in 1936.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Analysis of the Great Depression indicates that
A) even though monetary and fiscal policies were highly expansionary, they were unable to offset the economic downturn.
B) even though monetary policy was expansionary, restrictive fiscal policy dominated during the 1930s.
C) a reduction in tax rates could not prevent the economic downturn from spiraling into a depression.
D) the depth of the economic plunge, if not its onset, was the result of monetary, fiscal, and regulatory policies.
A) even though monetary and fiscal policies were highly expansionary, they were unable to offset the economic downturn.
B) even though monetary policy was expansionary, restrictive fiscal policy dominated during the 1930s.
C) a reduction in tax rates could not prevent the economic downturn from spiraling into a depression.
D) the depth of the economic plunge, if not its onset, was the result of monetary, fiscal, and regulatory policies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The Agriculture Adjustment Act of the Roosevelt Administration attempted to boost prices of agriculture products by
A) increasing the money supply from year to year at a constant rate.
B) decreasing the money supply through a policy of monetary contraction.
C) increasing demand through lower taxes and budget deficits.
D) reducing supply through the planned destruction of agricultural crops and livestock.
A) increasing the money supply from year to year at a constant rate.
B) decreasing the money supply through a policy of monetary contraction.
C) increasing demand through lower taxes and budget deficits.
D) reducing supply through the planned destruction of agricultural crops and livestock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The National Industrial Recovery Act essentially legalized
A) labor unions.
B) business cartels.
C) minimum wage laws.
D) import tariffs.
A) labor unions.
B) business cartels.
C) minimum wage laws.
D) import tariffs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What prompted the large increase in tax rates in 1932 in the midst of an economic recession?
A) Concern that inflation would rise due to increases in real output and aggregate demand.
B) Expansionary fiscal policy designed to stimulate aggregate demand.
C) The Keynesian view that taxes should be increased during a recession.
D) The view that the federal government should maintain a balanced budget.
A) Concern that inflation would rise due to increases in real output and aggregate demand.
B) Expansionary fiscal policy designed to stimulate aggregate demand.
C) The Keynesian view that taxes should be increased during a recession.
D) The view that the federal government should maintain a balanced budget.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If fiscal policy were able to exert a significant impact on the economy during the Great Depression, we would expect
A) an increase in government expenditures and a reduction in budget deficits.
B) an increase in government expenditures and an increase in budget deficits.
C) a decrease in government expenditures and a reduction in budget deficits.
D) a decrease in government expenditures and an increase in budget deficits.
A) an increase in government expenditures and a reduction in budget deficits.
B) an increase in government expenditures and an increase in budget deficits.
C) a decrease in government expenditures and a reduction in budget deficits.
D) a decrease in government expenditures and an increase in budget deficits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following contributed to the severity of the Great Depression?
A) The substantial budget surpluses run during the Hoover administration.
B) A sharp increase in tariff rates in 1930.
C) The large reduction in tax rates under the Hoover administration.
D) A highly expansionary monetary policy followed by the Fed in the late 1920s and early 1930s.
A) The substantial budget surpluses run during the Hoover administration.
B) A sharp increase in tariff rates in 1930.
C) The large reduction in tax rates under the Hoover administration.
D) A highly expansionary monetary policy followed by the Fed in the late 1920s and early 1930s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The National Industrial Recovery Act, passed in 1933,
A) broke up monopolies and cartels, and introduce competition into several different industries.
B) fixed prices, wages, and quotas for several industries in an effort to keep prices high.
C) lowered corporate taxes and removed collusive behavior in an effort to keep U.S. firms competitive with foreign manufacturers.
D) created a stable economic environment that encouraged investment and expansion in the industrial sector of the economy.
A) broke up monopolies and cartels, and introduce competition into several different industries.
B) fixed prices, wages, and quotas for several industries in an effort to keep prices high.
C) lowered corporate taxes and removed collusive behavior in an effort to keep U.S. firms competitive with foreign manufacturers.
D) created a stable economic environment that encouraged investment and expansion in the industrial sector of the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When overall production is taken into account, trade restrictions, such as those enacted by the Smoot-Hawley trade bill,
A) save good paying jobs.
B) neither create nor destroy jobs; they reallocate them.
C) increase employment in the domestic industries that are most productive.
D) reduce imports, without affecting the volume of exports.
A) save good paying jobs.
B) neither create nor destroy jobs; they reallocate them.
C) increase employment in the domestic industries that are most productive.
D) reduce imports, without affecting the volume of exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What impact did the National Industrial Recovery Act (NIRA) of 1933 have on industrial output?
A) Industrial output had been declining, but it stabilized during the months following passage of the NIRA.
B) Industrial output increased sharply after the passage of the NIRA.
C) Industrial output had begun to increase, but it fell sharply following the passage of the NIRA.
D) Industrial output and employment declined during the months prior to passage of the NIRA, and the legislation was unable to stop the decline.
A) Industrial output had been declining, but it stabilized during the months following passage of the NIRA.
B) Industrial output increased sharply after the passage of the NIRA.
C) Industrial output had begun to increase, but it fell sharply following the passage of the NIRA.
D) Industrial output and employment declined during the months prior to passage of the NIRA, and the legislation was unable to stop the decline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
During a recession, the political incentive structure will encourage politicians to
A) undertake sound economic policies that are consistent with stability and growth.
B) adopt any policies, even bad ones, that give the appearance of taking action.
C) undertake policies that promote long-term economic growth rather than short-term benefits.
D) do nothing and let the recession run its course.
A) undertake sound economic policies that are consistent with stability and growth.
B) adopt any policies, even bad ones, that give the appearance of taking action.
C) undertake policies that promote long-term economic growth rather than short-term benefits.
D) do nothing and let the recession run its course.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following was true with regard to the Great Depression?
A) The policies of the New Deal brought the Great Depression to an end well before World War II.
B) Sound economic policy was followed during this era, which makes the length and severity of the Great Depression puzzling to economists.
C) The length and severity of the Great Depression was the result of unsound economic policies followed by both the Hoover and Roosevelt Administrations.
D) The Great Depression was largely the result of the highly expansionary monetary policy of the Fed during the 1930s.
A) The policies of the New Deal brought the Great Depression to an end well before World War II.
B) Sound economic policy was followed during this era, which makes the length and severity of the Great Depression puzzling to economists.
C) The length and severity of the Great Depression was the result of unsound economic policies followed by both the Hoover and Roosevelt Administrations.
D) The Great Depression was largely the result of the highly expansionary monetary policy of the Fed during the 1930s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following is an important lesson that can be drawn from the experience of the Great Depression?
A) Frequent shifts in monetary policy can help smooth out unstable economic conditions during a recession.
B) Trade restrictions can "save jobs" and expand total employment during an economic downturn.
C) The good intentions of political decision-makers are no substitute for sound policy.
D) The federal government should always balance its budget during a recession.
A) Frequent shifts in monetary policy can help smooth out unstable economic conditions during a recession.
B) Trade restrictions can "save jobs" and expand total employment during an economic downturn.
C) The good intentions of political decision-makers are no substitute for sound policy.
D) The federal government should always balance its budget during a recession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The rational-ignorance effect is a result of
A) externalities that lead to an excess supply of information.
B) the limited incentive of the news media to cover political campaigns.
C) the expectation of individual voters that their vote will not be decisive.
D) the lack of a college education on the part of most voters in the United States.
A) externalities that lead to an excess supply of information.
B) the limited incentive of the news media to cover political campaigns.
C) the expectation of individual voters that their vote will not be decisive.
D) the lack of a college education on the part of most voters in the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
When voters pay taxes in proportion to the benefits they receive from government projects,
A) efficient projects will tend to be opposed by a majority of voters.
B) inefficient projects will often be favored by a majority of voters.
C) projects that are efficient will tend to be favored by an overwhelming majority of voters.
D) democratic political decision making can be expected to work poorly.
A) efficient projects will tend to be opposed by a majority of voters.
B) inefficient projects will often be favored by a majority of voters.
C) projects that are efficient will tend to be favored by an overwhelming majority of voters.
D) democratic political decision making can be expected to work poorly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In 2012, the combined expenditures of federal, state, and local governments in the United States were approximately
A) 9 percent of GDP.
B) 24 percent of GDP.
C) 38 percent of GDP.
D) 45 percent of GDP.
A) 9 percent of GDP.
B) 24 percent of GDP.
C) 38 percent of GDP.
D) 45 percent of GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Current tax rates are insufficient to finance the benefits promised by both the Social Security and Medicare programs. Are these unfunded promises surprising according to economic theory?
A) Yes, political representatives have a strong incentive to levy taxes that are sufficient to cover the cost of all programs they favor.
B) No, the unfunded promises reflect the shortsighted nature of the political process.
C) Yes, political representatives generally favor balancing the government budget because this is best for the economy.
D) No, even though debt financing often makes sense, politicians are reluctant to use it because it will damage their chances of being reelected.
A) Yes, political representatives have a strong incentive to levy taxes that are sufficient to cover the cost of all programs they favor.
B) No, the unfunded promises reflect the shortsighted nature of the political process.
C) Yes, political representatives generally favor balancing the government budget because this is best for the economy.
D) No, even though debt financing often makes sense, politicians are reluctant to use it because it will damage their chances of being reelected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Use the figure below to answer the following question(s).
Figure 6-1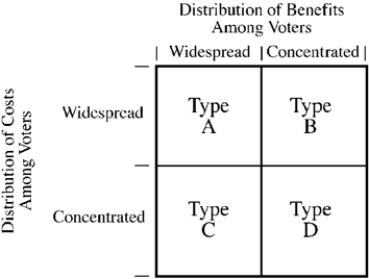
Figure 6-1 illustrates the four possibilities of the distribution of costs and benefits among voters for a government project. For which type would the government most likely undertake many projects that would be considered inefficient or counterproductive (in other words, do too many of them relative to economic efficiency)?
A) type A
B) type B
C) type C
D) type D
Figure 6-1

Figure 6-1 illustrates the four possibilities of the distribution of costs and benefits among voters for a government project. For which type would the government most likely undertake many projects that would be considered inefficient or counterproductive (in other words, do too many of them relative to economic efficiency)?
A) type A
B) type B
C) type C
D) type D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Use the figure below to answer the following question(s).
Figure 6-1
Figure 6-1 illustrates the four possibilities of the distribution of costs and benefits among voters for a government project. Programs that give subsidies to a small group of producers at general taxpayer expense would be considered
A) type A projects, and the government would be likely to undertake these projects if they were efficient and to reject them if they were inefficient.
B) type B projects, and the government would be likely to undertake many of these projects even when they were counterproductive (inefficient).
C) type C projects, and the government would be likely to fail to undertake many of these projects even when they were productive (efficient).
D) type D projects, and the government would be likely to undertake these projects if they were efficient and to reject them if they were inefficient.
Figure 6-1

Figure 6-1 illustrates the four possibilities of the distribution of costs and benefits among voters for a government project. Programs that give subsidies to a small group of producers at general taxpayer expense would be considered
A) type A projects, and the government would be likely to undertake these projects if they were efficient and to reject them if they were inefficient.
B) type B projects, and the government would be likely to undertake many of these projects even when they were counterproductive (inefficient).
C) type C projects, and the government would be likely to fail to undertake many of these projects even when they were productive (efficient).
D) type D projects, and the government would be likely to undertake these projects if they were efficient and to reject them if they were inefficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Most voters will likely be concerned with
A) most issues since most issues have some impact, however slight, on each citizen.
B) only a few special issues (those that exert the most impact on the voters' personal welfare).
C) most issues since information on most issues can be obtained at a low cost.
D) the views of a particular political candidate on all issues.
A) most issues since most issues have some impact, however slight, on each citizen.
B) only a few special issues (those that exert the most impact on the voters' personal welfare).
C) most issues since information on most issues can be obtained at a low cost.
D) the views of a particular political candidate on all issues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Prolonged periods of monetary contraction, as was the case during the Great Depression, will likely result in
A) an increase in real output and employment.
B) an increase in loanable funds and upward pressure on the rate of inflation.
C) a decrease in output and downward pressure on prices.
D) a decrease in unemployment and upward pressure on prices.
A) an increase in real output and employment.
B) an increase in loanable funds and upward pressure on the rate of inflation.
C) a decrease in output and downward pressure on prices.
D) a decrease in unemployment and upward pressure on prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following explains why managers of government agencies have little incentive to achieve operational efficiency?
A) Public-sector managers need not fear bankruptcy when operational efficiency is not achieved.
B) Public-sector managers seldom receive personal benefits if they find ways to improve the efficiency of their operations.
C) Public-sector agencies typically do not face competition.
D) All of the above explain why government agencies have little incentive to be efficient.
A) Public-sector managers need not fear bankruptcy when operational efficiency is not achieved.
B) Public-sector managers seldom receive personal benefits if they find ways to improve the efficiency of their operations.
C) Public-sector agencies typically do not face competition.
D) All of the above explain why government agencies have little incentive to be efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following is true about the Great Depression?
A) The Great Depression re-enforces the view that raising taxes in the midst of a severe recession is a bad idea.
B) The Great Depression clearly indicates that a prolonged period of monetary contraction will keep inflation low and promote monetary stability.
C) The Great Depression illustrates that trade restrictions will protect domestic industry and save jobs.
D) The Great Depression demonstrates that the political incentive structure during a severe downturn will encourage politicians to avoid frequent policy changes.
A) The Great Depression re-enforces the view that raising taxes in the midst of a severe recession is a bad idea.
B) The Great Depression clearly indicates that a prolonged period of monetary contraction will keep inflation low and promote monetary stability.
C) The Great Depression illustrates that trade restrictions will protect domestic industry and save jobs.
D) The Great Depression demonstrates that the political incentive structure during a severe downturn will encourage politicians to avoid frequent policy changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Use the figure below to answer the following question(s).
Figure 6-1
Figure 6-1 illustrates the four possibilities of the distribution of costs and benefits among voters for a government project. A tariff on imported steel to protect jobs in the domestic steel industry that raises the cost of many products for consumers would be considered which type of project?
A) type A
B) type B
C) type C
D) type D
Figure 6-1

Figure 6-1 illustrates the four possibilities of the distribution of costs and benefits among voters for a government project. A tariff on imported steel to protect jobs in the domestic steel industry that raises the cost of many products for consumers would be considered which type of project?
A) type A
B) type B
C) type C
D) type D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following provides the best summary of the basic idea of public choice analysis?
A) Public choice analysis applies the principles of economics to political science topics.
B) Public choice analysis takes the principles of political science and applies them to the traditional topics of economics.
C) Public choice analysis uses the principle of majority rule to determine the efficiency of an action.
D) Public choice analysis indicates there is a sharp distinction between economic and political topics.
A) Public choice analysis applies the principles of economics to political science topics.
B) Public choice analysis takes the principles of political science and applies them to the traditional topics of economics.
C) Public choice analysis uses the principle of majority rule to determine the efficiency of an action.
D) Public choice analysis indicates there is a sharp distinction between economic and political topics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Public choice theory suggests politicians will be most likely to favor redistribution of income from
A) the rich to the poor.
B) unorganized taxpayers to well-organized interest groups.
C) middle-income taxpayers to both the rich and the poor.
D) well-organized businesses and labor groups to consumers.
A) the rich to the poor.
B) unorganized taxpayers to well-organized interest groups.
C) middle-income taxpayers to both the rich and the poor.
D) well-organized businesses and labor groups to consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Why do nations impose trade barriers, such as those instituted during the Great Depression, that make it difficult for their own citizens to trade with people in other countries?
A) Trade restrictions are a good way for a country to increase the total employment and income level of its citizens.
B) As the experience during the 1930s illustrates, trade restrictions are an effective way to increase exports and tax revenues.
C) Trade restrictions provide gains to domestic residents at the expense of foreigners.
D) Trade restrictions often provide benefits to highly visible special interest groups while imposing a less visible cost on the general populace.
A) Trade restrictions are a good way for a country to increase the total employment and income level of its citizens.
B) As the experience during the 1930s illustrates, trade restrictions are an effective way to increase exports and tax revenues.
C) Trade restrictions provide gains to domestic residents at the expense of foreigners.
D) Trade restrictions often provide benefits to highly visible special interest groups while imposing a less visible cost on the general populace.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Special-interest programs are highly attractive to vote-seeking politicians because
A) these programs are highly efficient, and therefore, they tend to enhance the general welfare of the populace.
B) members of special interest groups favoring these programs are less likely to vote than the taxpayers who pay for them.
C) low-income recipients are the primary beneficiaries of special-interest programs.
D) members of special interest groups favoring these programs feel strongly about them while most other voters are rationally uninformed about them.
A) these programs are highly efficient, and therefore, they tend to enhance the general welfare of the populace.
B) members of special interest groups favoring these programs are less likely to vote than the taxpayers who pay for them.
C) low-income recipients are the primary beneficiaries of special-interest programs.
D) members of special interest groups favoring these programs feel strongly about them while most other voters are rationally uninformed about them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
When goods are produced privately, but the cost of their purchase is paid for by the taxpayer or some other third party,
A) consumers have a strong incentive to search out those firms offering them the best deal.
B) private producers of such goods will have little incentive to control costs and provide them at low prices.
C) goods and services will only be supplied if consumers are willing to pay an amount sufficient to cover their production costs.
D) the invisible hand will direct consumers and producers toward an efficient level of output.
A) consumers have a strong incentive to search out those firms offering them the best deal.
B) private producers of such goods will have little incentive to control costs and provide them at low prices.
C) goods and services will only be supplied if consumers are willing to pay an amount sufficient to cover their production costs.
D) the invisible hand will direct consumers and producers toward an efficient level of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Sound economic policy is policy that is consistent with
A) good intentions.
B) quick action and frequent policy changes until positive results are achieved.
C) monetary stability, free trade, and low tax rates.
D) saving jobs, protecting domestic industry, and increasing tax revenue.
A) good intentions.
B) quick action and frequent policy changes until positive results are achieved.
C) monetary stability, free trade, and low tax rates.
D) saving jobs, protecting domestic industry, and increasing tax revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following factors weakens the case for government provision of goods and services relative to private-sector provision?
A) monopoly
B) externalities
C) public goods
D) the special-interest effect
A) monopoly
B) externalities
C) public goods
D) the special-interest effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following factors weakens the case for private-sector provision of goods and services relative to public-sector provision?
A) externalities
B) the rational-ignorance effect
C) the shortsightedness effect
D) well-informed consumers
A) externalities
B) the rational-ignorance effect
C) the shortsightedness effect
D) well-informed consumers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Is calling a voter rationally ignorant the same as calling her irrational? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The park in Hammerhead, Florida, built to honor the city's founding father, General Hammerhead, is starting to deteriorate. It would take about $5,000 to restore the General's statue, repair the benches, and repair the fountain, but the city budget is tight. Also, the deterioration is not that noticeable. Mayor Grouper suggests delaying the repair until after the election, three years away. City Councilwoman Halibut notes that by then the park will be dilapidated, and repairs will cost $25,000. From a public choice perspective, what is the likely outcome of this debate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Suppose we coupled the pay of Congress with the federal budget, so that for every billion dollars of deficit spending, a lawmaker's pay would be reduced $1,000. How would this affect fiscal policy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Young John recently took a job with the U.S. Department of Agriculture. His supervisor gave him an assignment and a two-week deadline. He finished the job in three days and turned it in. Now his coworkers are mad at John. Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Suppose domestic automobiles were allocated in the United States the way public education is allocated. Describe how this system might work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In the case of a private good, which of the following forms of economic organization will result in the strongest incentive for consumers and producers to economize?
A) The good is produced privately and taxes are used to provide it to consumers free of charge.
B) The good is produced privately and consumers purchase it with their own money.
C) The good is produced by government enterprises and the cost of its production is covered by taxes.
D) The good is produced by government enterprises and consumers purchase it with their own money.
A) The good is produced privately and taxes are used to provide it to consumers free of charge.
B) The good is produced privately and consumers purchase it with their own money.
C) The good is produced by government enterprises and the cost of its production is covered by taxes.
D) The good is produced by government enterprises and consumers purchase it with their own money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Use the figure below to answer the following question(s).
Figure 6-1
Figure 6-1 illustrates the four possibilities of the distribution of costs and benefits among voters for a government project. For which type would the government most likely fail to undertake many projects that would be considered efficient or productive (in other words, do too few of them relative to economic efficiency)?
A) type A
B) type B
C) type C
D) type D
Figure 6-1

Figure 6-1 illustrates the four possibilities of the distribution of costs and benefits among voters for a government project. For which type would the government most likely fail to undertake many projects that would be considered efficient or productive (in other words, do too few of them relative to economic efficiency)?
A) type A
B) type B
C) type C
D) type D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Use the figure below to answer the following question(s).
Figure 6-1
Figure 6-1 illustrates the four possibilities of the distribution of costs and benefits among voters for a government project. For which types of projects would government action most likely work well, undertaking only efficient projects and rejecting inefficient ones?
A) types A and B
B) types B and D
C) types B and C
D) types A and D
Figure 6-1

Figure 6-1 illustrates the four possibilities of the distribution of costs and benefits among voters for a government project. For which types of projects would government action most likely work well, undertaking only efficient projects and rejecting inefficient ones?
A) types A and B
B) types B and D
C) types B and C
D) types A and D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Public choice analysis indicates
A) politicians under representative democracy are led as if by an invisible hand to adopt legislation that enhances the wealth of a nation.
B) political structures consistent with economic efficiency tend to emerge naturally from the ordinary political process.
C) constitutional rules establishing procedures and limiting the ability of the political process to engage in redistributive activities can improve the economic efficiency of government.
D) all of the above are correct.
A) politicians under representative democracy are led as if by an invisible hand to adopt legislation that enhances the wealth of a nation.
B) political structures consistent with economic efficiency tend to emerge naturally from the ordinary political process.
C) constitutional rules establishing procedures and limiting the ability of the political process to engage in redistributive activities can improve the economic efficiency of government.
D) all of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Congressman Localstuff always votes for a balanced budget amendment to the U.S. Constitution. He also always votes for spending bills supported by the leadership of his political party. Is this rational?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following factors weakens the case for private-sector provision of goods and services relative to public-sector provision?
A) constitutional rules
B) the shortsightedness effect
C) the special-interest effect
D) public goods
A) constitutional rules
B) the shortsightedness effect
C) the special-interest effect
D) public goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
With a strong and active federal government, why do we need state and local governments?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Use the figure below to answer the following question(s).
Figure 6-2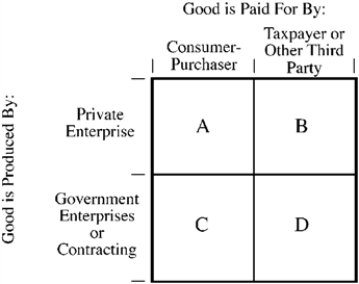
Figure 6-2 illustrates the four possibilities of the structure of production and consumption for a good or service. When the structure of production and consumption for a good places it in quadrant B,
A) consumers have little incentive to search out and patronize low-cost suppliers.
B) private producers of such goods will have little incentive to operate efficiently and to keep prices low.
C) goods and services will only be supplied if consumers are willing to pay an amount sufficient to cover their production costs.
D) both a and b, but not c, will be true.
Figure 6-2

Figure 6-2 illustrates the four possibilities of the structure of production and consumption for a good or service. When the structure of production and consumption for a good places it in quadrant B,
A) consumers have little incentive to search out and patronize low-cost suppliers.
B) private producers of such goods will have little incentive to operate efficiently and to keep prices low.
C) goods and services will only be supplied if consumers are willing to pay an amount sufficient to cover their production costs.
D) both a and b, but not c, will be true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A survey of income by county revealed that four of the five wealthiest counties were located in the suburbs surrounding Washington,
D.C. Why?
D.C. Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Use the figure below to answer the following question(s).
Figure 6-2
Figure 6-2 illustrates the four possibilities of the structure of production and consumption for a good or service. In which case is the incentive of producers to be efficient and the incentive for consumers to economize the weakest?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
Figure 6-2

Figure 6-2 illustrates the four possibilities of the structure of production and consumption for a good or service. In which case is the incentive of producers to be efficient and the incentive for consumers to economize the weakest?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
How does a voting structure that relies on unanimity for an action guarantee that no one will be adversely affected? Why isn't this type of decision making used more frequently?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
An analysis of market failure and government failure indicates
A) government decision making is always preferable to using markets.
B) market decision making is always preferable to public-sector action.
C) government action is necessary whenever market failure occurs.
D) both the market and the government may fail to meet conditions of economic efficiency; in each individual case, the choice of market or public-sector action requires careful evaluation.
A) government decision making is always preferable to using markets.
B) market decision making is always preferable to public-sector action.
C) government action is necessary whenever market failure occurs.
D) both the market and the government may fail to meet conditions of economic efficiency; in each individual case, the choice of market or public-sector action requires careful evaluation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Use the figure below to answer the following question(s).
Figure 6-2
Figure 6-2 illustrates the four possibilities of the structure of production and consumption for a good or service. In which case is the incentive of producers and consumers to economize the strongest?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
Figure 6-2

Figure 6-2 illustrates the four possibilities of the structure of production and consumption for a good or service. In which case is the incentive of producers and consumers to economize the strongest?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 208 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



