Deck 33: America in World War II
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/101
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 33: America in World War II
1
Identify and state the historical significance of George S. Patton.
American general who successfully liberated large portions of France with armored vehicles.
2
Identify and state the historical significance of Joseph Stalin.
Totalitarian communist leader of the USSR.
3
Identify and state the historical significance of Thomas E. Dewey.
1944 Republican presidential nominee from New York.
4
Identify and state the historical significance of J. Robert Oppenheimer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Identify and state the historical significance of Executive Order No. 9066.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Identify and state the historical significance of the ABC-1 agreement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Identify and state the historical significance of Jiang Jieshi (Chiang Kai-shek).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Identify and state the historical significance of Henry A. Wallace.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Identify and state the historical significance of Harry S Truman.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Identify and state the historical significance of Albert Einstein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Identify and state the historical significance of Dwight D. Eisenhower.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Identify and state the historical significance of Winston Churchill.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Identify and state the historical significance of "Issei" and "Nissei".

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Identify and state the historical significance of Henry Stimson.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Identify and state the historical significance of the War Production Board.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Identify and state the historical significance of Douglas MacArthur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Identify and state the historical significance of Korematsu v. United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Identify and state the historical significance of Chester W. Nimitz.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Identify and state the historical significance of Erwin Rommel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Identify and state the historical significance of A. Philip Randolph.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Identify and state the historical significance of SPARs (U.S. Coast Guard Women's Reserve).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Identify and state the historical significance of Guadalcanal Island.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Identify and state the historical significance of the Casablanca Conference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Identify and state the historical significance of the Fair Employment Practices Commission (FEPC).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Identify and state the historical significance of D-Day.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Identify and state the historical significance of the Battle of Midway.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Identify and state the historical significance of the Bataan Death March.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Identify and state the historical significance of WAVES (Women Accepted for Volunteer Emergency Service).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Identify and state the historical significance of braceros.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Identify and state the historical significance of the Congress of Racial Equality (CORE).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Identify and state the historical significance of the Office of Price Administration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Identify and state the historical significance of the Tehran Conference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Identify and state the historical significance of the island-hopping strategy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
flying "over the hump"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Identify and state the historical significance of the WACs (Women's Army Corps).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Identify and state the historical significance of the National War Labor Board.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Identify and state the historical significance of the Navajo "code talkers".

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Identify and state the historical significance of "Rosie the Riveter".

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Identify and state the historical significance of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Identify and state the historical significance of the second front.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In sharp contrast to World War I, during World War II, Americans were
A) ready to use conscription if necessary to raise an army.
B) forced to sacrifice civilian economic well-being for the military effort.
C) weakened by constant isolationist criticism of the war effort.
D) nearly unanimous in support of the war.
E) actually invaded by enemy forces.
A) ready to use conscription if necessary to raise an army.
B) forced to sacrifice civilian economic well-being for the military effort.
C) weakened by constant isolationist criticism of the war effort.
D) nearly unanimous in support of the war.
E) actually invaded by enemy forces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Despite the demands of the wartime economy, inflation was kept well in check during the war by
A) directing production to whatever goods were in most demand.
B) prosecuting war profiteers and black marketers who tried to earn windfall profits.
C) voluntary wage and price controls agreed to by business and organized labor.
D) sharply constricting the flow of credit from the Federal Reserve Board.
E) federally imposed mandatory wage and price controls.
A) directing production to whatever goods were in most demand.
B) prosecuting war profiteers and black marketers who tried to earn windfall profits.
C) voluntary wage and price controls agreed to by business and organized labor.
D) sharply constricting the flow of credit from the Federal Reserve Board.
E) federally imposed mandatory wage and price controls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
About half of the women war workers said that the main reason they left the labor force at the end of World War II was
A) union demands.
B) employer demands that they quit because of inferior work efficiency and output.
C) male discrimination on the job.
D) government requirements to hire veterans under the GI Bill of Rights.
E) family obligations.
A) union demands.
B) employer demands that they quit because of inferior work efficiency and output.
C) male discrimination on the job.
D) government requirements to hire veterans under the GI Bill of Rights.
E) family obligations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Overall, most ethnic groups in the United States during World War II
A) experienced a speeding up of their assimilation into American society.
B) were not allowed to serve in the military.
C) had their patriotism questioned as in World War I.
D) cast their vote for Republican candidates opposed to the war.
E) served in ethnically distinct military units.
A) experienced a speeding up of their assimilation into American society.
B) were not allowed to serve in the military.
C) had their patriotism questioned as in World War I.
D) cast their vote for Republican candidates opposed to the war.
E) served in ethnically distinct military units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Match each of the wartime agencies below with its correct function:
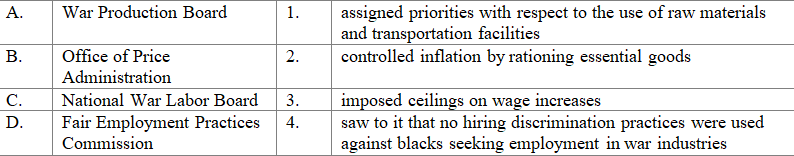
A) A-2, B-3, C-4, D-1
B) A-1, B-2, C-3, D-4
C) A-2, B-4, C-3, D-1
D) A-3, B-2, C-1, D-4
E) A-4, B-1, C-2, D-3

A) A-2, B-3, C-4, D-1
B) A-1, B-2, C-3, D-4
C) A-2, B-4, C-3, D-1
D) A-3, B-2, C-1, D-4
E) A-4, B-1, C-2, D-3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
After the United States entered World War II in 1941, the term "alien 4-C" referred to
A) Japanese living in the U.S.
B) Italians living in the U.S.
C) Germans living in the U.S.
D) All of these choices are correct.
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) Japanese living in the U.S.
B) Italians living in the U.S.
C) Germans living in the U.S.
D) All of these choices are correct.
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Japanese Americans were placed in concentration camps during World War II
A) due to numerous acts of sabotage.
B) in retaliation for the placement of Americans in concentration camps by the Japanese.
C) as a result of anti-Japanese prejudice and fear.
D) because many were loyal to Japan.
E) All of these choices are correct.
A) due to numerous acts of sabotage.
B) in retaliation for the placement of Americans in concentration camps by the Japanese.
C) as a result of anti-Japanese prejudice and fear.
D) because many were loyal to Japan.
E) All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
While most American workers were strongly committed to the war effort, wartime production was disrupted by strikes led by the
A) Teamsters.
B) United Steel Workers.
C) Longshoremen's International Union.
D) United Mine Workers.
E) United Auto Workers.
A) Teamsters.
B) United Steel Workers.
C) Longshoremen's International Union.
D) United Mine Workers.
E) United Auto Workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Historians look to the fact that many women wanted to keep work and did after the war as
A) foreshadowing the eventual revolution in women's roles in America.
B) helping to expand the nation's economy.
C) fueling the rise of home-buying across America.
D) facilitating the increasing divorce rate.
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) foreshadowing the eventual revolution in women's roles in America.
B) helping to expand the nation's economy.
C) fueling the rise of home-buying across America.
D) facilitating the increasing divorce rate.
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Once at war, America's first great challenge was to
A) pass a conscription law.
B) maintain public support and patriotism for the war effort.
C) extend aid to the Soviet Union.
D) develop atomic weapons.
E) retool its industry for all-out war production.
A) pass a conscription law.
B) maintain public support and patriotism for the war effort.
C) extend aid to the Soviet Union.
D) develop atomic weapons.
E) retool its industry for all-out war production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The impact of World War II on many of the New Deal programs launched during the Great Depression was that they
A) were expanded to gear up for wartime production.
B) were discontinued due to wartime production needs.
C) provided much-needed jobs for the poor.
D) became an established fixture of U.S. government programs.
E) None of these choices are correct.
A) were expanded to gear up for wartime production.
B) were discontinued due to wartime production needs.
C) provided much-needed jobs for the poor.
D) became an established fixture of U.S. government programs.
E) None of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Identify and state the historical significance of V-E (Victory in Europe) Day.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
During World War II, the United States government commissioned the production of synthetic ____ in order to offset the loss of access to prewar supplies in East Asia.
A) textiles
B) rubber
C) tin
D) fuels
E) bauxite
A) textiles
B) rubber
C) tin
D) fuels
E) bauxite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When the United States entered World War II in December 1941
A) it took nearly two years for the country to unite.
B) the conflict soon became an idealistic crusade for democracy.
C) the government repudiated the Atlantic Charter.
D) a majority of Americans had no clear idea of what the war was about.
E) the idea of allying with the Communist Soviet Union against Nazi Germany was repugnant and unacceptable
To most Americans.
A) it took nearly two years for the country to unite.
B) the conflict soon became an idealistic crusade for democracy.
C) the government repudiated the Atlantic Charter.
D) a majority of Americans had no clear idea of what the war was about.
E) the idea of allying with the Communist Soviet Union against Nazi Germany was repugnant and unacceptable
To most Americans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
African Americans did all of the following during World War II EXCEPT
A) fight in integrated combat units.
B) rally behind the slogan "Double V" (victory over dictators abroad and racism at home).
C) move north and west in large numbers.
D) form a militant organization called the Congress of Racial Equality.
E) serve in the Army Air Corps.
A) fight in integrated combat units.
B) rally behind the slogan "Double V" (victory over dictators abroad and racism at home).
C) move north and west in large numbers.
D) form a militant organization called the Congress of Racial Equality.
E) serve in the Army Air Corps.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The minority group most adversely affected by Washington's wartime policies was
A) German Americans.
B) blacks.
C) Japanese Americans.
D) American communists.
E) Italian Americans.
A) German Americans.
B) blacks.
C) Japanese Americans.
D) American communists.
E) Italian Americans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The fundamental strategic decision of World War II made by President Roosevelt and the British at the very beginning of the war was to
A) plan for a second front in Western Europe as soon as possible.
B) force Italy out of the war first by attacking the soft underbelly of Europe.
C) arouse the American people to an idealistic crusade of the same sort that Woodrow Wilson had so effectively used in World War I.
D) concentrate first on the war in Europe and to place the Pacific war against Japan on the back burner.
E) fight an equally vigorous naval war against Japan and a land war against Germany and Italy.
A) plan for a second front in Western Europe as soon as possible.
B) force Italy out of the war first by attacking the soft underbelly of Europe.
C) arouse the American people to an idealistic crusade of the same sort that Woodrow Wilson had so effectively used in World War I.
D) concentrate first on the war in Europe and to place the Pacific war against Japan on the back burner.
E) fight an equally vigorous naval war against Japan and a land war against Germany and Italy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The employment of more than six million women in American industry during World War II led to
A) equal pay for men and women.
B) a greater percentage of American women in war industries than anywhere else in the world.
C) the establishment of day-care centers by the government.
D) a reduction in employment for black males.
E) a strong desire of most women to work for wages.
A) equal pay for men and women.
B) a greater percentage of American women in war industries than anywhere else in the world.
C) the establishment of day-care centers by the government.
D) a reduction in employment for black males.
E) a strong desire of most women to work for wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
All of the following are true statements about the effect of Executive Order No. 9066 on Japanese living in the U.S. EXCEPT
A) they were put in internment camps.
B) they were victims of anti-Japanese prejudice.
C) they lost hundreds of millions of dollars in property and lost wages.
D) The U.S. Supreme Court declared the Japanese relocation unconstitutional.
E) The U.S. government officially apologized four decades later and gave each camp survivor $20,000.
A) they were put in internment camps.
B) they were victims of anti-Japanese prejudice.
C) they lost hundreds of millions of dollars in property and lost wages.
D) The U.S. Supreme Court declared the Japanese relocation unconstitutional.
E) The U.S. government officially apologized four decades later and gave each camp survivor $20,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Identify and state the historical significance of the Battle of the Bulge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Hitler's advance in the European theater of war crested in late 1942 at the Battle of ____, after which his fortunes gradually declined.
A) the Bulge
B) Stalingrad
C) Monte Cassino
D) Britain
E) El Alamein
A) the Bulge
B) Stalingrad
C) Monte Cassino
D) Britain
E) El Alamein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
By the end of World War II, the heart of the United States' African American community had shifted to
A) Florida and the Carolinas.
B) southern cities.
C) Texas and New Mexico.
D) Midwestern small towns.
E) northern and western cities.
A) Florida and the Carolinas.
B) southern cities.
C) Texas and New Mexico.
D) Midwestern small towns.
E) northern and western cities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
During World War II, American Indians
A) demanded that President Roosevelt end discrimination in defense industries.
B) rarely enlisted in the armed forces.
C) moved south to replace African American laborers.
D) moved off reservations in large numbers.
E) promoted recovery of tribal languages.
A) demanded that President Roosevelt end discrimination in defense industries.
B) rarely enlisted in the armed forces.
C) moved south to replace African American laborers.
D) moved off reservations in large numbers.
E) promoted recovery of tribal languages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The northward migration of African Americans accelerated after World War II because
A) the southern system of sharecropping was declared illegal.
B) Latinos had replaced blacks in the workforce.
C) mechanical cotton pickers came into use.
D) northern cities repealed segregation laws.
E) All of these choices are correct.
A) the southern system of sharecropping was declared illegal.
B) Latinos had replaced blacks in the workforce.
C) mechanical cotton pickers came into use.
D) northern cities repealed segregation laws.
E) All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Most of the money raised to finance World War II came through
A) tariff collections.
B) excise taxes on luxury goods.
C) raising income taxes.
D) voluntary contributions.
E) borrowing.
A) tariff collections.
B) excise taxes on luxury goods.
C) raising income taxes.
D) voluntary contributions.
E) borrowing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The Allies postponed opening a second front in Europe until 1944 because
A) they wanted to wait until Germany and the Soviet Union had badly bloodied each other.
B) the Soviet Union seemed poised to finish off Nazi Germany after its counteroffensive following the Battle of Stalingrad.
C) the Soviet Union requested a delay until they could coordinate attacks on the eastern and western fronts.
D) they believed that North Africa was more strategically vital.
E) the British were fearful of becoming bogged down in a ground war in France.
A) they wanted to wait until Germany and the Soviet Union had badly bloodied each other.
B) the Soviet Union seemed poised to finish off Nazi Germany after its counteroffensive following the Battle of Stalingrad.
C) the Soviet Union requested a delay until they could coordinate attacks on the eastern and western fronts.
D) they believed that North Africa was more strategically vital.
E) the British were fearful of becoming bogged down in a ground war in France.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Arrange these events in chronological order: (A) V-J Day, (B) V-E Day, (C) D-Day, and (D) Invasion of Italy.
A) D, C, B, A
B) A, C, B, D
C) B, D, A, C
D) C, A, D, B
E) A, D, B, C
A) D, C, B, A
B) A, C, B, D
C) B, D, A, C
D) C, A, D, B
E) A, D, B, C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
After the Italian surrender in August 1943
A) the Allies found it easy to conquer Rome and the rest of Italy.
B) there was a major upsurge in German domestic political opposition to Hitler and dissent against the war effort by Nazi Germany.
C) the British demanded the restoration of the monarchy in Italy.
D) the Americans withdrew from Italy to prepare for D-Day.
E) the German army poured into Italy and stalled the Allied advance.
A) the Allies found it easy to conquer Rome and the rest of Italy.
B) there was a major upsurge in German domestic political opposition to Hitler and dissent against the war effort by Nazi Germany.
C) the British demanded the restoration of the monarchy in Italy.
D) the Americans withdrew from Italy to prepare for D-Day.
E) the German army poured into Italy and stalled the Allied advance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In waging war against Japan, the United States relied mainly on a strategy of
A) heavy bombing from Chinese air bases.
B) invading Japanese strongholds in Southeast Asia.
C) fortifying China by transporting supplies from India over the Himalayan hump.
D) island hopping across the South Pacific while bypassing Japanese strongholds.
E) turning the Japanese flanks in New Guinea and Alaska.
A) heavy bombing from Chinese air bases.
B) invading Japanese strongholds in Southeast Asia.
C) fortifying China by transporting supplies from India over the Himalayan hump.
D) island hopping across the South Pacific while bypassing Japanese strongholds.
E) turning the Japanese flanks in New Guinea and Alaska.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
One of the significant contributions of Native Americans to the war effort was
A) as industrial factory workers producing war materials.
B) as code talkers who transmitted war messages into their native languages.
C) as arms experts who consulted with generals and military planners.
D) as farmers who helped expand crop output for soldiers on the front.
E) as espionage agents based in California spying on Japanese Americans.
A) as industrial factory workers producing war materials.
B) as code talkers who transmitted war messages into their native languages.
C) as arms experts who consulted with generals and military planners.
D) as farmers who helped expand crop output for soldiers on the front.
E) as espionage agents based in California spying on Japanese Americans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The first naval battle in history in which all the fighting was done by carrier-based aircraft was the Battle of
A) Leyte Gulf.
B) the Java Sea.
C) the Coral Sea.
D) Midway.
E) Guadalcanal.
A) Leyte Gulf.
B) the Java Sea.
C) the Coral Sea.
D) Midway.
E) Guadalcanal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The greatest consequence of World War II for American race relations was
A) the tensions in wartime factories between blacks and whites.
B) the wartime integration of the armed forces.
C) African Americans' experience of more positive European racial attitudes.
D) the massive migration of African Americans from the rural South to northern and western cities.
E) the Atlantic Charter declaring that the war was being fought for democracy and freedom.
A) the tensions in wartime factories between blacks and whites.
B) the wartime integration of the armed forces.
C) African Americans' experience of more positive European racial attitudes.
D) the massive migration of African Americans from the rural South to northern and western cities.
E) the Atlantic Charter declaring that the war was being fought for democracy and freedom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The major consequence of the Allied conquest of Sicily in August 1943 was
A) a modification of the demand for unconditional surrender of Italy.
B) the overthrow of Mussolini and Italy's unconditional surrender.
C) the swift Allied conquest of the Italian peninsula.
D) a conflict between Churchill and General Eisenhower over the invasion of the Italian mainland.
E) the threat of a Communist takeover of the Italian government.
A) a modification of the demand for unconditional surrender of Italy.
B) the overthrow of Mussolini and Italy's unconditional surrender.
C) the swift Allied conquest of the Italian peninsula.
D) a conflict between Churchill and General Eisenhower over the invasion of the Italian mainland.
E) the threat of a Communist takeover of the Italian government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Until spring 1943, perhaps Hitler's greatest opportunities of defeating Britain and winning the war was
A) the possibility of a successful invasion across the English Channel.
B) that German U-boat would destroy Allied shipping.
C) the German V-2 rockets fired into Britain that would cause their terrified civilian population to demand Prime Minister Churchill to surrender to Nazi Germany.
D) that General Rommel would conquer Egypt and the Suez Canal.
E) that the American-British-Soviet alliance would collapse.
A) the possibility of a successful invasion across the English Channel.
B) that German U-boat would destroy Allied shipping.
C) the German V-2 rockets fired into Britain that would cause their terrified civilian population to demand Prime Minister Churchill to surrender to Nazi Germany.
D) that General Rommel would conquer Egypt and the Suez Canal.
E) that the American-British-Soviet alliance would collapse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The national debt increased most during
A) Franklin Roosevelt's New Deal.
B) Herbert Hoover's administration.
C) World War II.
D) World War I.
E) the 1920s.
A) Franklin Roosevelt's New Deal.
B) Herbert Hoover's administration.
C) World War II.
D) World War I.
E) the 1920s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Arrange these wartime conferences in chronological order: (A) Potsdam, (B) Casablanca, and (C) Teheran.
A) A, B, C
B) C, B, A
C) B, C, A
D) B, A, C
E) A, C, B
A) A, B, C
B) C, B, A
C) B, C, A
D) B, A, C
E) A, C, B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The American conquest of ____ in 1944 was especially critical, because from there, U.S. aircraft could conduct round-trip bombing raids on the Japanese home islands.
A) Saipan
B) Wake Island
C) New Guinea
D) Okinawa
E) Marianas including Guam
A) Saipan
B) Wake Island
C) New Guinea
D) Okinawa
E) Marianas including Guam

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Roosevelt's and Churchill's insistence on the absolute and "unconditional surrender" of Germany
A) guaranteed that Germany would have to be totally reconstructed after the war.
B) had no effect on the strategic calculations made in the war planning efforts of the Allies.
C) was largely unacceptable to the Soviets, who hoped to encourage a communist revolution inside Germany.
D) may have prevented a "separate peace" between Hitler and Stalin.
E) encouraged anti-Hitler resisters in Germany to try to overthrow the Nazis.
A) guaranteed that Germany would have to be totally reconstructed after the war.
B) had no effect on the strategic calculations made in the war planning efforts of the Allies.
C) was largely unacceptable to the Soviets, who hoped to encourage a communist revolution inside Germany.
D) may have prevented a "separate peace" between Hitler and Stalin.
E) encouraged anti-Hitler resisters in Germany to try to overthrow the Nazis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
During World War II, most Americans economically experienced
A) serious hardships due to rationing of essential goods.
B) prosperity and a doubling of personal income.
C) a continuing struggle to find employment.
D) growing class conflict between the wealthy and the working class.
E) prosperity in the cities but disastrous conditions on farms and in small towns.
A) serious hardships due to rationing of essential goods.
B) prosperity and a doubling of personal income.
C) a continuing struggle to find employment.
D) growing class conflict between the wealthy and the working class.
E) prosperity in the cities but disastrous conditions on farms and in small towns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
President Roosevelt's promise to the Soviets to open a second front in Western Europe by the end of 1942
A) was fulfilled by the invasion of North Africa.
B) was made to deceive Stalin and encourage him to slow his army's movement into Eastern Europe.
C) was strongly supported by Churchill and British military leaders.
D) proved utterly impossible to keep.
E) represented the key goal to which all early American military efforts were directed.
A) was fulfilled by the invasion of North Africa.
B) was made to deceive Stalin and encourage him to slow his army's movement into Eastern Europe.
C) was strongly supported by Churchill and British military leaders.
D) proved utterly impossible to keep.
E) represented the key goal to which all early American military efforts were directed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



